Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
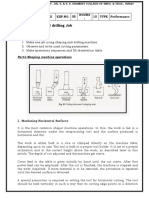
Marking Out Tools Information Sheets Mel02inf4436+v1.2
Enviado por
youngfpDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Marking Out Tools Information Sheets Mel02inf4436+v1.2
Enviado por
youngfpDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Page 1 of 3
Competenz - N Z Engineering Food & Manufacturing Industry Training Organisation Inc.
MARKING-OUT INFORMATION SHEETS MEL02INF4436 v1.2 HEALTH & SAFETY REQUIREMENTS RECORDING REQUIREMENTS: Record the results of your work on Task Worksheet MEL02TWS01 v1.3 REFERENCES: This document relates in part to the requirements of Unit Standard 4436 v5 MARKING OUT The purpose of marking-out is to; Define the shape of an article Indicate position of holes and other features Provide alignment and machining marks Minimize material wastage Marking-out techniques include the use of datum, pitch circle diameters (PCD) and templates. Marking-out is usually done on a firm, flat work surface or vertically using marking-out tools on a surface table. Marking-out Using Datums Effective marking-out requires clean edges and faces on the work piece, and uses a combination of at least two primary reference points such as Datum Points, Datum Lines and Datum Edges.
Odd-leg calipers Dividers
Tools Commonly Used for Marking-out Tasks
Steel Rule Scriber Engineers Square
Center and Dot-Punches Combination Set
Angle Plates
Scribing Block Height Gauge Vee Blocks
Surface Table
Marking-out using datums can be done using either;
Simple hand tools such as a ruler, scriber, square
and odd-leg calipers, or
Vertical marking-out tools such as an angle plate,
scribing block or vernier height gauge situated on a marking-out table
Parallels
IP! When finish ed, re the to turn ol to i ts sto box, t rage ool ca binet marke or the d plac e on t works he hop sh adow board .
SMAR TT
Marking Hole Positions Along a Centerline
Brush a thin layer of marking blue onto the surface of the metal bar to highlight the lines.
Use odd-leg calipers to find and scribe the centerline along the bar using one edge as the datum.
Use a rule, scriber and square to mark the hole positions along the centerline working from the datum at one end of the bar.
Use a rule to re-check the marked position. Center punch the location of each hole ready for drilling.
Marking Hole Positions on a Pitch Circle Diameter (PCD)
Use an engineers square and odd-leg calipers to mark the position of the PCD centerlines from the datum edges.
Center punch the PCD center-point and use a pair of dividers to scribe the pitch circle. Trammels are required for scribing larger PCDs.
Calculate the hole positions and use dividers to step-out and scribe the positions around the PCD.
Recheck the scribed positions. If OK, center punch the location of each hole ready for drilling.
s osition d by; Hole p lculate a c e b ence can cumfer r i c Marking Shapes and Hole Positions Using Templates e h er gt e numb dividin h t y b PCD Templates are commonly made of sheet metal, plastic and wood and shaped to of the s or, represent the finished article. Templates can be simple geometric shapes or of hole ing jig-bor g detailed profiles used for fabricating complex structures. in s u by les. ate tab Hole positions in the template are marked on the work-piece surface using transfer punches. coordin
HANDY HINT; to ensure clean marking out, check the caliper, divider and center punch tips are not worn or damaged.
TIP! SMART on a PCD
Use an a square, odd-leg calipers, a rule and a scriber to lay-out the template
Locate the template on the alignment marks. Clamp in place if necessary.
HANDY HINT; templates are a useful time-saver when marking-out repetitive fabrication work.
Use a scriber to mark-out the template profiles. Use transfer punches to mark the locations of the holes ready for drilling. Use a rule to recheck the profiles and hole positions.
Marking-out Using a Combination Set
A scriber and a combination set protractor can be used for marking-out virtually any angle from a datum face.
A scriber and a combination try-square can be used for marking-out at 90 and 45 to a datum face.
A combination set center-finder is used for scribing intersecting lines to establish the center of a round bar or circular shape.
Marking-out On a Table Work requiring accuracy to within 0.15 mm can be done using a scribing block.
Accuracy to within 0.02 mm can be achieved by using a vernier height gauge.
Vee blocks are used to support and clamp round work pieces during marking out with a vernier height gauge. The round bar should be supported on the angled faces of the vee block.
An angle plate can be used to hold larger work pieces while marking-out vertical distances using a vernier height gauge. Smaller, less accurate marking-out can be done using a scribing block.
Marking-out Using Spirit Levels and Plumb-bobs
Check for a true right-angle using an Engineers Square or a Rafter Square.
T TIP! Check t he tool for any damage or fault s such as worn, b roken o r missin parts, e g xpired calibrat or the t io n ool not zeroing Report . any pro blems t your su o pervisor .
SMAR
Use a scriber to mark the final position prior to riveting, bolting-up or welding. Use a spirit-level to check and adjust the position of a horizontal structural component. A protractor can be used to establish the correct angle of a horizontal beam in respect to a vertical component. Plumb-lines provide a datum when positioning vertical components in larger structures. When positioned vertically, the horizontal distance between the plumb-line and the vertical component will be the same at the top and the bottom. HANDY HINT; increasing the vertical distance between the measuring points on a vertical plumb-line will improve the accuracy of the setup. Steel beam
The glass or plastic vial on a spirit level is usually marked in 1-degree increments. A small air bubble sits central to the vial when the level is placed on a horizontally true surface.
Plumb-bob
Flat and true machined surface.
Você também pode gostar
- Sheet Metal Duct Layout BookDocumento40 páginasSheet Metal Duct Layout BookRyan Murray77% (13)
- The Home Handyman - May 2016 PDFDocumento68 páginasThe Home Handyman - May 2016 PDFzvezdelina100% (1)
- (Metalworking) Welding and MachiningDocumento1.767 páginas(Metalworking) Welding and MachiningEugeneAinda não há avaliações
- Ryo Yoshida BJD Making Guide English TranslationDocumento61 páginasRyo Yoshida BJD Making Guide English TranslationChe Jael Flaviano100% (4)
- Engineering Drawing NotesDocumento81 páginasEngineering Drawing NotesAnonymous OFP2ygPIdAinda não há avaliações
- Wood & Wood ProductsDocumento33 páginasWood & Wood ProductsPatricia Erika ArgusAinda não há avaliações
- Screw Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesDocumento17 páginasScrew Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesRay NjorogeAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft PowerPoint - G D & T 17.11Documento96 páginasMicrosoft PowerPoint - G D & T 17.11vijaykkhal100% (1)
- Lettering and DimensionsDocumento23 páginasLettering and DimensionsMujtaba AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- International ShippingDocumento17 páginasInternational ShippingyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Verification and Validation Guidelines For High Integrity SystemsDocumento198 páginasVerification and Validation Guidelines For High Integrity SystemsyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Roundness IDocumento13 páginasRoundness Ibalasubramani_srinivAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 Working DrawingDocumento63 páginasChapter 12 Working DrawingLhen Mediante AsuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Marine Offshore Safety Sign PDFDocumento9 páginasMarine Offshore Safety Sign PDFyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Your Source For GD&T Training and MaterialsDocumento6 páginasYour Source For GD&T Training and Materialskharsh23Ainda não há avaliações
- Cold Ironing and Onshore Generation For Airborne Emission ReductionsDocumento34 páginasCold Ironing and Onshore Generation For Airborne Emission ReductionsyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- 2-4 Basic Engineering Drawing and CAD I PDFDocumento233 páginas2-4 Basic Engineering Drawing and CAD I PDFsmendoza100% (2)
- Planer MachineDocumento46 páginasPlaner Machinepoohru puru100% (15)
- CE102-W5-Wood and Its PropertiesDocumento43 páginasCE102-W5-Wood and Its PropertiesRomel BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning StandardsDocumento100 páginasChapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning Standardsapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Drafting and Dimensioning StandardsDocumento30 páginasDrafting and Dimensioning StandardskrristinAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Report 2 - de LunaDocumento7 páginasLaboratory Report 2 - de LunaAgent PAinda não há avaliações
- Drill JigsDocumento195 páginasDrill JigsArun PeriyasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Setting OutDocumento8 páginasSetting OutSuranga Gayan100% (1)
- DJF - Model Question PaperDocumento6 páginasDJF - Model Question PaperMohammedRafficAinda não há avaliações
- Vernacular Terms in Philippine ContructionDocumento3 páginasVernacular Terms in Philippine ContructionClaro III TabuzoAinda não há avaliações
- JJ 103 Fitting ReportDocumento12 páginasJJ 103 Fitting ReportNasrul Haziq Murad55% (20)
- XH7126 CNC Milling MachineDocumento2 páginasXH7126 CNC Milling MachineMUHAMMAD NAUMANAinda não há avaliações
- ME 114 - Engineering Drawing II: SectioningDocumento31 páginasME 114 - Engineering Drawing II: SectioningTemmy Candra WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- MSP - Week 7 8Documento7 páginasMSP - Week 7 8John MarkAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - Dimensioning - EGE4Documento162 páginasChapter 2 - Dimensioning - EGE4bmyertekinAinda não há avaliações
- Jigs and FixturesDocumento85 páginasJigs and FixturesNithin Mathew Eyyalil100% (2)
- Sample Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) : Unit - IDocumento22 páginasSample Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) : Unit - IDaveed stark100% (1)
- Projection of Points and PlanesDocumento30 páginasProjection of Points and PlanesAnonymous p8bHAAxAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - Introduction To Tool DesignDocumento18 páginasLecture 2 - Introduction To Tool DesignPratik PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Engg Drawing Viva QuestionsDocumento8 páginasEngg Drawing Viva Questionsmahdzia0% (1)
- MarkingouttoolsDocumento24 páginasMarkingouttoolsOmar EzzatAinda não há avaliações
- 02 - Workshop-Machine Shop o GDocumento17 páginas02 - Workshop-Machine Shop o Gsakali aliAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 9 Tools For Basic Layout: StructureDocumento7 páginasUnit 9 Tools For Basic Layout: StructureAkash Kumar DevAinda não há avaliações
- Machining FixedDocumento512 páginasMachining FixedstephendixAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing Engineering 2Documento7 páginasManufacturing Engineering 2Study SuccessAinda não há avaliações
- Marking OutDocumento2 páginasMarking OutOladimeji TaiwoAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Workshop CH 2 & 3 and Projects ASTUDocumento14 páginasBasic Workshop CH 2 & 3 and Projects ASTUandu habshaAinda não há avaliações
- Benchwork and Fitting: Linear Measurements Angular Measurements Surface MeasurementDocumento8 páginasBenchwork and Fitting: Linear Measurements Angular Measurements Surface MeasurementJohn smithAinda não há avaliações
- Production Technology: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento17 páginasProduction Technology: Department of Mechanical Engineeringrahul bhattAinda não há avaliações
- Tecnolco Institute of Hvac Mep Nampally HYD.: Layout and Fabrication of Sheet-Metal and Fiber-Glass DuctDocumento40 páginasTecnolco Institute of Hvac Mep Nampally HYD.: Layout and Fabrication of Sheet-Metal and Fiber-Glass DuctAnkush NayarAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclatures of Single Point Cutting Tool Using Tool Makers MicroscopeDocumento7 páginasNomenclatures of Single Point Cutting Tool Using Tool Makers Microscopeविशाल पुडासैनीAinda não há avaliações
- Toolpaths: Ste P Toolpath CommentsDocumento11 páginasToolpaths: Ste P Toolpath CommentsuzeyirAinda não há avaliações
- 3) Marking Tools Used in FittingDocumento5 páginas3) Marking Tools Used in FittingKrako Tram100% (1)
- Basic Marking Out and Measuring InstrumentsDocumento70 páginasBasic Marking Out and Measuring Instrumentsbonganishiba594Ainda não há avaliações
- Gear CuttingDocumento3 páginasGear CuttingBarun DeAinda não há avaliações
- Marking ToolsDocumento14 páginasMarking ToolsFabian NdegeAinda não há avaliações
- Contouring and TurningDocumento9 páginasContouring and Turning123anthonyAinda não há avaliações
- Session 09Documento59 páginasSession 09etaAinda não há avaliações
- Dial Indicator: The Premier Source of Parts and Accessories For Mini Lathes and Mini MillsDocumento2 páginasDial Indicator: The Premier Source of Parts and Accessories For Mini Lathes and Mini MillsAmin UviantoAinda não há avaliações
- Metalwork Notes NEWDocumento49 páginasMetalwork Notes NEWJudeAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Machine Elements ProjectDocumento43 páginasDesign of Machine Elements ProjectGirish ChandankarAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Machine Processes: Identify The Basic Concepts of The Manufacturing ProcessesDocumento34 páginasBasic Machine Processes: Identify The Basic Concepts of The Manufacturing ProcessesDeepti KanadeAinda não há avaliações
- Kiran Universal CouplingDocumento10 páginasKiran Universal CouplingMurali SiddarthAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDocumento12 páginasDr. Richard E. Link U.S. Naval Academy Department of Mechanical Engineering 590 Holloway Road Annapolis, MD 21402-5042 All Rights ReservedDaveB2008Ainda não há avaliações
- SMEA1304Documento164 páginasSMEA1304y2k405 kaosAinda não há avaliações
- Line and Grade PresentationDocumento35 páginasLine and Grade PresentationRick Pongi100% (1)
- Common Terms and Definitions: Basic DimensionDocumento9 páginasCommon Terms and Definitions: Basic Dimensionswap dAinda não há avaliações
- Dimensioning ME DrawingsDocumento50 páginasDimensioning ME DrawingsLuis NunesAinda não há avaliações
- CAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022Documento46 páginasCAM-CIM Manual - M.tech - Jan 2022KUNAL SHIMPIAinda não há avaliações
- m2 U6 Recessing and RadiusingDocumento13 páginasm2 U6 Recessing and RadiusingViệt Đặng XuânAinda não há avaliações
- Bezel Bezel Lock: Rotate The Bezel To Zero The Needle. Tighten To Lock The Bezel in PlaceDocumento2 páginasBezel Bezel Lock: Rotate The Bezel To Zero The Needle. Tighten To Lock The Bezel in PlaceAmin UviantoAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report ME3Documento8 páginasLab Report ME3Hassan Iftekhar AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 5.EMM Lab ManualDocumento38 páginas5.EMM Lab ManualRakeshkumarcegAinda não há avaliações
- Different Measuring ToolsDocumento2 páginasDifferent Measuring Toolsanon_449620137Ainda não há avaliações
- Light Signal Alarm System LSAS BrochureDocumento5 páginasLight Signal Alarm System LSAS BrochureyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Light Signal Alarm System LSAS Brochure PDFDocumento6 páginasLight Signal Alarm System LSAS Brochure PDFyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Symbols For Triangular LightsDocumento1 páginaSymbols For Triangular LightsyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Selection Guide For Process InstrumentationDocumento3 páginasCable Selection Guide For Process InstrumentationyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- BNWAS Le Guardian 2025 English Brochure PDFDocumento6 páginasBNWAS Le Guardian 2025 English Brochure PDFyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- DNV GUIDANCE Emergency Stop SystemsDocumento13 páginasDNV GUIDANCE Emergency Stop SystemsyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- IACS Joint Safety StatementDocumento3 páginasIACS Joint Safety StatementyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Dead Man Alarm DMA English BrochureDocumento6 páginasDead Man Alarm DMA English BrochureyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Sulzer Zv40/48 Zgoda Crankshaft Replacement & In-Place MachiningDocumento2 páginasSulzer Zv40/48 Zgoda Crankshaft Replacement & In-Place MachiningyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Wartsila Seals Bearings Portable CBMDocumento2 páginasWartsila Seals Bearings Portable CBMyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Becker Intelligent Monitoring System BIMS PDFDocumento4 páginasBecker Intelligent Monitoring System BIMS PDFyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- Information On Detention and Action Taken Rev5Documento12 páginasInformation On Detention and Action Taken Rev5youngfpAinda não há avaliações
- Amendments To SOLAS PDFDocumento2 páginasAmendments To SOLAS PDFyoungfpAinda não há avaliações
- CNC TURNING MachineDocumento14 páginasCNC TURNING MachineFaiz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- GDS PQDocumento108 páginasGDS PQSaad AkramAinda não há avaliações
- Consumable Stock June 2021Documento497 páginasConsumable Stock June 2021isser150Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Cutting and Routing Techniques Using The Festool MFS Fence System ReducedDocumento57 páginasAdvanced Cutting and Routing Techniques Using The Festool MFS Fence System ReducedxanderAinda não há avaliações
- Victorian PlayhouseDocumento12 páginasVictorian Playhousepierre van wykAinda não há avaliações
- Bamboo-Based Biocomposite: Application For A Sustainable Naval ArchitectureDocumento11 páginasBamboo-Based Biocomposite: Application For A Sustainable Naval ArchitectureNimna ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- Veneer and LaminatesDocumento14 páginasVeneer and Laminates1DC20AT025 Ganesh AkshayAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 MM Mandible Trauma and Locking Reconstruction.J9499ADocumento3 páginas2.4 MM Mandible Trauma and Locking Reconstruction.J9499AprincaroAinda não há avaliações
- Following Is The 27 Page Instruction Manual For The Microlux 7 X 14 High-Precision Heavy-Duty LatheDocumento31 páginasFollowing Is The 27 Page Instruction Manual For The Microlux 7 X 14 High-Precision Heavy-Duty LatheRichard BedellAinda não há avaliações
- The WoodcutterDocumento1 páginaThe WoodcutterBaobab DramatherapyAinda não há avaliações
- WIPDocumento3 páginasWIPAris SusantoAinda não há avaliações
- Desert Daze Bed Desert Daze: Sunshine WristyDocumento10 páginasDesert Daze Bed Desert Daze: Sunshine WristycformnemAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 5 - Canned Cycle-TurningDocumento11 páginasLecture 5 - Canned Cycle-TurningAditya RatleyAinda não há avaliações
- Manuale 43631P000Documento20 páginasManuale 43631P000kinkywoodesignAinda não há avaliações
- Project For Mechanical DrawingDocumento19 páginasProject For Mechanical DrawingMoh AmmAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - First Rate CatalogueDocumento32 páginas2 - First Rate CatalogueMarcelo VisintinAinda não há avaliações
- Grinding Eqipment: Product CatalogueDocumento32 páginasGrinding Eqipment: Product CataloguePablo OlórtigaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Plywood IndustryDocumento9 páginasIntroduction To Plywood IndustryShakeel AhamedAinda não há avaliações
- MCF VTU Question BankDocumento6 páginasMCF VTU Question BankRAKSHITH MAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Types of Wood Framing To KnowDocumento19 páginas9 Types of Wood Framing To KnowMarion LauritoAinda não há avaliações
- Wood JointsDocumento22 páginasWood JointsRaju RoyAinda não há avaliações
- AA Revised Instructions Connectors 9-25-14 BC 7-15-16Documento3 páginasAA Revised Instructions Connectors 9-25-14 BC 7-15-16mohamed hamedAinda não há avaliações
- English FP4MEDocumento2 páginasEnglish FP4MEHossein TomariAinda não há avaliações
- Smaw 9 Summative Test Q1Documento2 páginasSmaw 9 Summative Test Q1Jose Intraboy Arais Tabugoc Jr.Ainda não há avaliações