Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Delphi Technique: Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Analysis
Enviado por
ggggiiiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Delphi Technique: Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Analysis
Enviado por
ggggiiiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Risk Management Risk response should be a balance between risk taking and risk tolerance The Delphi Technique
is based on the Hegelian Principle of achieving Oneness of Mind through a three step process of thesis, antithesis, and synthesis. In thesis and antithesis, all present their opinion or views on a given subject, establishing views and opposing views. In synthesis, opposites are brought together to form the new thesis. All participants are then to accept ownership of the new thesis and support it, changing their own views to align with the new thesis. Through a continual process of evolution, Oneness of Mind will supposedly occur. The Delphi Technique was originally conceived as a way to obtain the opinion of experts without necessarily bringing them together face to face The Delphi technique is a group process used to survey and collect the opinions of experts on a particular subject. Assumptions analysis (to check the validity of the assumptions, their accuracy, instability, inconsistency or incompleteness of them) Diagramming techniques Cause and effect diagrams (or Ishikawa/fishbone diagrams) System/process flowcharts (showing how various elements of a system interrelate, and the mechanism of causation) Influence diagrams (graphical representations of situation showing casual influences, time ordering of events, and other relationships among variables and outcomes Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Analysis EMV is:
a method of calculating the average outcome when the future is uncertain (i.e.
Opportunities will have positive values and risks will have negative values).
found by mulitplying the monetary value of a possible outcome by the probability it will
occur.
used in decision tree analysis. A sensitivity analysis determines which risks have the most potential impact on the project.
Sensitivity charts are used to visualize impacts (best and worst outcome values) of different uncertain variables over their individual ranges.
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Expected monetary value (EMV) analysis is a statistical concept that calculates the average outcome when the future includes scenarios that may or may not happen. An EMV analysis is usually mapped out using a decision tree to represent the different options or scenarios.
Decision Makers' Toolkit Decision-making is the cognitive process of selecting a course of action from among multiple alternatives. Every decision-making process produces a final choice. Thats what Wikipedia says anyway. What it doesnt say is that some decisions must be made for outcomes that will occur in the future. However, there are a couple of tools that can be put to use in helping make complex decisions, namely, Expected Monetary Value and Decision Tree Analysis.
The development of a decision tree is a multi step process. The first step is to structure the problem using a method called decomposition, similar to the method used in the development of a work breakdown structure. This step enables the decision-maker to break a complex problem down into a series of simpler, more individually manageable problems, graphically displayed in a type of flow diagram called a decision tree. These are the symbols commonly used:
In simple terms, Monte Carlo analysis combines distributions, and thereby propagating more than just summary statistics. Rather than analytic calculations, Monte Carlo analysis uses intensive random number generation. Let us use a simple equation to illustrate the Monte Carlo analysis: Risk = Probably x Consequence Instead of just solving the equation using simple arithmetic, Monte Carlo analysis draws 2 random numbers from pre-defined distributions, multiples the 2 numbers and stores the result. This process is then iterated several thousands of times, and the results are displayed as a new combined distribution. 2 main types of distribution can be used for Monte Carlo simulation analysis. Empirical distributions rely on larger sets of real world, historical data and sample sizes are used the most often. When data sets and sample sizes are small, theoretical distributions in the form of binomial distributions and lognormal distributions, for instance, may also be appropriate when there is some mechanical or probabilistic basis. All distributions used for Monte Carlo analysis are normally correlated significantly (i.e. with a probability factor of more than 0.75). What is Monte Carlo simulation? Monte Carlo simulation is a computerized mathematical technique that allows people to account for risk in quantitative analysis and decision making. The technique is used by professionals in such widely disparate fields as finance, project management, energy, manufacturing, engineering, research and development, insurance, oil & gas, transportation, and the environment. Monte Carlo simulation furnishes the decision-maker with a range of possible outcomes and the probabilities they will occur for any choice of action.. It shows the extreme possibilitiesthe outcomes of going for broke and for the most conservative decisionalong with all possible consequences for middle-of-the-road decisions.
The technique was first used by scientists working on the atom bomb; it was named for Monte Carlo, the Monaco resort town renowned for its casinos. Since its introduction in World War II, Monte Carlo simulation has been used to model a variety of physical and conceptual systems.
How Monte Carlo simulation works Monte Carlo simulation performs risk analysis by building models of possible results by substituting a range of valuesaprobability distributionfor any factor that has inherent uncertainty. It then calculates results over and over, each time using a different set of random values from the probability functions. Depending upon the number of uncertainties and the ranges specified for them, a Monte Carlo simulation could involve thousands or tens of thousands of recalculations before it is complete. Monte Carlo simulation produces distributions of possible outcome values. By using probability distributions, variables can have different probabilities of different outcomes occurring. Probability distributions are a much more realistic way of describing uncertainty in variables of a risk analysis. Common probability distributions include: Normal Or bell curve. The user simply defines the mean or expected value and a standard deviation to describe the variation about the mean. Values in the middle near the mean are most likely to occur. It is symmetric and describes many natural phenomena such as peoples heights. Examples of variables described by normal distributions include inflation rates and energy prices. Lognormal Values are positively skewed, not symmetric like a normal distribution. It is used to represent values that dont go below zero but have unlimited positive potential. Examples of variables described by lognormal distributions include real estate property values, stock prices, and oil reserves. Uniform All values have an equal chance of occurring, and the user simply defines the minimum and maximum. Examples of variables that could be uniformly distributed include manufacturing costs or future sales revenues for a new product.
Triangular The user defines the minimum, most likely, and maximum values. Values around the most likely are more likely to occur. Variables that could be described by a triangular distribution include past sales history per unit of time and inventory levels. PERT- The user defines the minimum, most likely, and maximum values, just like the triangular distribution. Values around the most likely are more likely to occur. However values between the most likely and extremes are more likely to occur than the triangular; that is, the extremes are not as emphasized. An example of the use of a PERT distribution is to describe the duration of a task in a project management model. Discrete The user defines specific values that may occur and the likelihood of each. An example might be the results of a lawsuit: 20% chance of positive verdict, 30% change of negative verdict, 40% chance of settlement, and 10% chance of mistrial. During a Monte Carlo simulation, values are sampled at random from the input probability distributions. Each set of samples is called an iteration, and the resulting outcome from that sample is recorded. Monte Carlo simulation does this hundreds or thousands of times, and the result is a probability distribution of possible outcomes. In this way, Monte Carlo simulation provides a much more comprehensive view of what may happen. It tells you not only what could happen, but how likely it is to happen. Monte Carlo simulation provides a number of advantages over deterministic, or single-point estimate analysis:
Probabilistic Results. Results show not only what could happen, but how likely each outcome is.
Graphical Results. Because of the data a Monte Carlo simulation generates, its easy to create graphs of different outcomes and their chances of occurrence. This is important for communicating findings to other stakeholders.
Sensitivity Analysis. With just a few cases, deterministic analysis makes it difficult to see which variables impact the outcome the most. In Monte Carlo simulation, its easy to see which inputs had the biggest effect on bottom-line results.
Scenario Analysis: In deterministic models, its very difficult to model different combinations of values for different inputs to see the effects of truly different scenarios. Using Monte Carlo simulation, analysts can see exactly which inputs had which values together when certain outcomes occurred. This is invaluable for pursuing further analysis.
Correlation of Inputs. In Monte Carlo simulation, its possible to model interdependent relationships between input variables. Its important for accuracy to represent how, in reality, when some factors goes up, others go up or down accordingly. An enhancement to Monte Carlo simulation is the use of Latin Hypercube sampling, which samples more accurately from the entire range of distribution functions.
very project will be based on many assumptions. These will apply to all departments and at all stages of the project. For example, if you plan to purchase equipment in 6 months time for a large sum it may be based upon a particular exchange rate.
Você também pode gostar
- Top 20 MS Excel VBA Simulations, VBA to Model Risk, Investments, Growth, Gambling, and Monte Carlo AnalysisNo EverandTop 20 MS Excel VBA Simulations, VBA to Model Risk, Investments, Growth, Gambling, and Monte Carlo AnalysisNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- Assessing and Improving Prediction and Classification: Theory and Algorithms in C++No EverandAssessing and Improving Prediction and Classification: Theory and Algorithms in C++Ainda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Watch TestimonialsDocumento4 páginasMonte Carlo Simulation: Watch TestimonialsJennelyn MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Deterministic Risk Analysis - "Best Case, Worst Case, Most Likely"Documento25 páginasDeterministic Risk Analysis - "Best Case, Worst Case, Most Likely"Başchir CameliaAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation TechniqueDocumento2 páginasSimulation TechniqueMs. Anitharaj M. SAinda não há avaliações
- Risk AnalysisDocumento3 páginasRisk AnalysisAtul KhatriAinda não há avaliações
- Deterministic Risk AnalysisDocumento25 páginasDeterministic Risk Analysisanon_98105004Ainda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento3 páginasMonte Carlo SimulationHema SiyagAinda não há avaliações
- Adeel SCM AssignmentDocumento4 páginasAdeel SCM AssignmentSo'hail TariqAinda não há avaliações
- How Monte Carlo Simulation WorksDocumento3 páginasHow Monte Carlo Simulation WorkspragyaAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Simulation ExplainedDocumento3 páginasMonte Carlo Simulation ExplainedNihar DeyAinda não há avaliações
- Week-4 Supply Chain Optimization - UOCDocumento6 páginasWeek-4 Supply Chain Optimization - UOCMK KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation NotesDocumento6 páginasSimulation NotesGeeAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment DST 2 OriginalDocumento5 páginasAssignment DST 2 OriginalGm KanharAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Simulation OCRDocumento19 páginasMonte Carlo Simulation OCRspiridisAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento3 páginasMonte Carlo SimulationLuna YeshaAinda não há avaliações
- Alido, Kevin F - Research WorkDocumento4 páginasAlido, Kevin F - Research Workkevin alidoAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Programming, Decision Theory, Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento4 páginasLinear Programming, Decision Theory, Monte Carlo SimulationApurva JawadeAinda não há avaliações
- Project Risk Management and The Application of Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento5 páginasProject Risk Management and The Application of Monte Carlo SimulationTeófanes de Oliveira Jr.100% (1)
- ACFrOgAurKcMWZgiCHpgudL IDmdYF0hdPpNTMQ8toRY4CVfXRhQbPVb0tsmc86iZwLQ1rYDPiXdzPf4scv1vJExr1K4C9S PtcARbg9hF9zs9wfJ2hSlHTh-dZKG49GKtiaG VFixdn6CK-NG6jDocumento31 páginasACFrOgAurKcMWZgiCHpgudL IDmdYF0hdPpNTMQ8toRY4CVfXRhQbPVb0tsmc86iZwLQ1rYDPiXdzPf4scv1vJExr1K4C9S PtcARbg9hF9zs9wfJ2hSlHTh-dZKG49GKtiaG VFixdn6CK-NG6jAjey MendiolaAinda não há avaliações
- Use of MCS in Valuation NeilDocumento5 páginasUse of MCS in Valuation Neilay shaukatAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Simulation ExplainedDocumento15 páginasMonte Carlo Simulation ExplainedVijay SagarAinda não há avaliações
- Using Monte Carlo Analysis To Estimate RiskDocumento8 páginasUsing Monte Carlo Analysis To Estimate RiskMegersa RaseAinda não há avaliações
- Finsearch ReportDocumento3 páginasFinsearch ReportTushaar JhamtaniAinda não há avaliações
- Quant SRCDocumento7 páginasQuant SRCYangshu HuAinda não há avaliações
- Q1Documento6 páginasQ1kacaAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento8 páginasMonte Carlo SimulationnthabisengAinda não há avaliações
- Sensitivity AnalysisDocumento17 páginasSensitivity AnalysisBOBBY212Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorial SimulaciónDocumento25 páginasTutorial SimulaciónVannelly PortocarreroAinda não há avaliações
- Absolute Var From Risk Free Rate (Which Takes Into Account The Max Loss Including The Risk Free Rate and TimeDocumento7 páginasAbsolute Var From Risk Free Rate (Which Takes Into Account The Max Loss Including The Risk Free Rate and TimeGeorgian Viorel IonAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Civil Engineering: Risk Analysis TechniquesDocumento39 páginasDepartment of Civil Engineering: Risk Analysis Techniquesอพัชชา บํารุงไทยAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 8Documento4 páginasTopic 8mmmd.krmv.00Ainda não há avaliações
- UNIT 4 SeminarDocumento10 páginasUNIT 4 SeminarPradeep Chaudhari50% (2)
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento2 páginasMonte Carlo SimulationThanh XuânAinda não há avaliações
- Describe How To Use A ProbabilityDocumento2 páginasDescribe How To Use A ProbabilityVikram KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Analysis (DA)Documento18 páginasDecision Analysis (DA)K. Lee B.Ainda não há avaliações
- Cf-Unit - IvDocumento17 páginasCf-Unit - IvSabha PathyAinda não há avaliações
- The Monte Carlo Simulation: Rustom D. Sutaria - Avia Intelligence 2016, DubaiDocumento4 páginasThe Monte Carlo Simulation: Rustom D. Sutaria - Avia Intelligence 2016, DubaiNajmul HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Regression Analysis GuideDocumento31 páginasRegression Analysis Guidegalaxy123Ainda não há avaliações
- Statistics and Probability For Simulation-2Documento43 páginasStatistics and Probability For Simulation-2Carl Edgar Ambid AyatonAinda não há avaliações
- Risk AMPDocumento4 páginasRisk AMPEl Ehsan Abinya FatihAinda não há avaliações
- Deliberate Sampling Any Method of Selecting Individuals To Participate in Research On The Basis of A Specific Plan, Rather Than Randomly. ThisDocumento5 páginasDeliberate Sampling Any Method of Selecting Individuals To Participate in Research On The Basis of A Specific Plan, Rather Than Randomly. ThisIshrat NadiaAinda não há avaliações
- A VAR Model As Risk Management ToolDocumento15 páginasA VAR Model As Risk Management Toolnamnh0307Ainda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Simulation ModelingDocumento8 páginasAn Introduction To Simulation ModelingNaga BalajiAinda não há avaliações
- Sensitivity AnalysisDocumento4 páginasSensitivity AnalysisjhllkjlghkjlAinda não há avaliações
- 12 SimulationDocumento9 páginas12 SimulationUmesh Poudel JoJo100% (1)
- Eers 1014Documento10 páginasEers 1014Mutahar_HezamAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento38 páginasChapter 2ThitinaAinda não há avaliações
- Sensitivity AnalysisDocumento5 páginasSensitivity AnalysisMohsin QayyumAinda não há avaliações
- Monte Carlo Methods ExplainedDocumento22 páginasMonte Carlo Methods Explainedgajendra2010Ainda não há avaliações
- The Monte Carlo MethodDocumento22 páginasThe Monte Carlo MethodRajesh RathodAinda não há avaliações
- Bet Smarter With The Monte Carlo SimulationDocumento7 páginasBet Smarter With The Monte Carlo SimulationOladipupo Mayowa PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of VaR Approaches on Stock PortfolioDocumento10 páginasComparison of VaR Approaches on Stock Portfolioraj_gargiAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative TechniquesDocumento9 páginasQuantitative Techniquessatishvarma142100% (1)
- DECISION TREE AND INFLUENCE DIAGRAM ANALYSISDocumento26 páginasDECISION TREE AND INFLUENCE DIAGRAM ANALYSISParizie0% (1)
- 611 MbaDocumento10 páginas611 MbaTECH CENTRALAinda não há avaliações
- ProbabilityDocumento5 páginasProbabilityfakharulAinda não há avaliações
- Process Performance Models: Statistical, Probabilistic & SimulationNo EverandProcess Performance Models: Statistical, Probabilistic & SimulationAinda não há avaliações
- Fast Sequential Monte Carlo Methods for Counting and OptimizationNo EverandFast Sequential Monte Carlo Methods for Counting and OptimizationAinda não há avaliações
- Uncertainty Quantification and Stochastic Modeling with MatlabNo EverandUncertainty Quantification and Stochastic Modeling with MatlabAinda não há avaliações
- Deep ShoringDocumento4 páginasDeep ShoringggggiiiAinda não há avaliações
- Seetharam P GDocumento2 páginasSeetharam P GggggiiiAinda não há avaliações
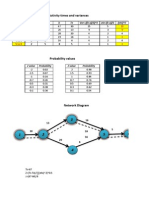
- Activity times and variances analysisDocumento4 páginasActivity times and variances analysisggggiiiAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Normal Distribution Table ActivityDocumento2 páginasStandard Normal Distribution Table ActivityggggiiiAinda não há avaliações
- DS2006 Compaction of Concrete PDFDocumento7 páginasDS2006 Compaction of Concrete PDFparamarthasom1974Ainda não há avaliações
- Financial Management KangraDocumento12 páginasFinancial Management Kangramanik_chand_patnaikAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Claims DelaysDocumento23 páginasConstruction Claims Delaysgerx11xregAinda não há avaliações
- PLM SyllabusDocumento1 páginaPLM SyllabusGobivel KathirvelAinda não há avaliações
- Checklist For Selecting A CMMS Solution PDFDocumento4 páginasChecklist For Selecting A CMMS Solution PDFambuenaflorAinda não há avaliações
- CAPdoDocumento5 páginasCAPdoPauloanDiasAinda não há avaliações
- Hexagon Head Screw ISO 4017 - M8 X 20 - 5.6Documento1 páginaHexagon Head Screw ISO 4017 - M8 X 20 - 5.6Cbh FastenersAinda não há avaliações
- Faurecia Automotive Maneser NSF Project Time Plan PS Trails (6152)Documento2 páginasFaurecia Automotive Maneser NSF Project Time Plan PS Trails (6152)Tushar KohinkarAinda não há avaliações
- Cabletrunking - MultipleDocumento13 páginasCabletrunking - MultipleHassan FarazAinda não há avaliações
- BigFix User GuideDocumento29 páginasBigFix User GuidepriteshjAinda não há avaliações
- LINCOLN Lubrication Centro - MaticDocumento53 páginasLINCOLN Lubrication Centro - Maticrmartinf2527Ainda não há avaliações
- FLUID LEAKAGE-What To Do?: John C. Cox, Business Development Manager Swagelok Company, Solon, OhioDocumento6 páginasFLUID LEAKAGE-What To Do?: John C. Cox, Business Development Manager Swagelok Company, Solon, OhiotakemetovikasAinda não há avaliações
- Ose 5-91 2066-9001-200-Im PDFDocumento210 páginasOse 5-91 2066-9001-200-Im PDFironite100% (1)
- Investigation and Analysis of Cold Shut Casting Defect ReductionDocumento3 páginasInvestigation and Analysis of Cold Shut Casting Defect Reductionvivek1312Ainda não há avaliações
- Application of Response Surface Methodology and Central Composite RotatableDocumento7 páginasApplication of Response Surface Methodology and Central Composite RotatableManishankar PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Engineering SpecificationDocumento2 páginasMaterials Engineering SpecificationRonald AraujoAinda não há avaliações
- Metro RailDocumento59 páginasMetro Railகீர்த்திவாசன் தமிழன்50% (2)
- Human Factors EngineeringDocumento54 páginasHuman Factors Engineeringganeshrams88Ainda não há avaliações
- AP Electrical Safety SWPDocumento12 páginasAP Electrical Safety SWPjvigforuAinda não há avaliações
- Application Erc Case No. 2012-013 RC Iselco IIDocumento78 páginasApplication Erc Case No. 2012-013 RC Iselco IIKathlene Lacosta LastimosaAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Theme Presentation For 30th Ala MayarDocumento12 páginasSample Theme Presentation For 30th Ala Mayarhermain khanAinda não há avaliações
- Process Validation ProtocolDocumento10 páginasProcess Validation ProtocolDivya SekarAinda não há avaliações
- Kristen's Cookie Case AnalysisDocumento7 páginasKristen's Cookie Case Analysisjulianpaulo23Ainda não há avaliações
- Fall and Rise of Valjoux 7750Documento12 páginasFall and Rise of Valjoux 7750john100% (1)
- Iso 9001:2008 Pre-TestDocumento2 páginasIso 9001:2008 Pre-TestMau TauAinda não há avaliações
- Reservoir Simulation Basics 1Documento5 páginasReservoir Simulation Basics 1Vladimir PriescuAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersDocumento16 páginasSample Interview Questions For Planning EngineersPooja PawarAinda não há avaliações
- 20160316162112020Documento2 páginas20160316162112020ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA) AND RISK ASSESSMENT FORMDocumento6 páginasJOB SAFETY ANALYSIS (JSA) AND RISK ASSESSMENT FORMBeriandi HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure Ec380d Ec480d t2 t3 en 30 20030338 DDocumento32 páginasBrochure Ec380d Ec480d t2 t3 en 30 20030338 DJose Martin Rodriguez YarlequeAinda não há avaliações
- SAS Institute A00-250Documento21 páginasSAS Institute A00-250rajeshmsitAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical and Tribological Performance of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesDocumento27 páginasMechanical and Tribological Performance of Aluminium Metal Matrix CompositesPradeepkumar SamanthulaAinda não há avaliações