Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Purines and Nitrogenous Bases
Enviado por
Ian FranciaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Purines and Nitrogenous Bases
Enviado por
Ian FranciaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
FOOD CHEMISTRY I PURINES AND NITROGENOUS BASES
REPORTER 1: Francia, B.N. -A ribose and nitrogenous base are covalently joined by a glycosidic bond to form a nucleoside molecule: -Nucleosides are named by adding the suffix "-idine" to the pyrimidine or "-osine" to the purine name. -Purine nucleosides include Adenosine and Guanosine
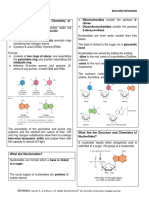
NITROGEN BASES The molecules of nitrogen bases comprise C, H, O and N. In these molecules 2 nitrogen atoms are directly linked to a carbon atom on its two sides. There are two types of nitrogen bases: Purines and Pyrimidines. Purines - The purine structure consists of two rings, having 5 carbon and 4 nitrogen atoms.Adenine and Guanine are purine bases.
-The above nucleosides are all ribonucleosides as is found in RNA. Deoxyribonucleosides would be found in DNA, and would include deoxyThymidine instead of Uridine -The common purines are Guanine (G) and Adenine (A). They are used in both DNA and RNA http://library.med.utah.edu/NetBiochem/pup yr/pp.htm http://www.mikeblaber.org/oldwine/BCH40 53/Lecture18/Lecture18.htm RNA (mono-Pi) AMP GMP DNA (mono-Pi) dAMP dGMP
Base Adenine Guanine
Nucleoside (deoxy-)Adenosine (deoxy-)Guanosine
Nucleotide (deoxy-)Adenylic acid (deoxy-)Guanylic acid
Code A G
REPORTER 2: Jarabejo, F.A. Properties of purines Adenine and guanine are found in both DNA and RNA The pyrimidine ring systems is planar, whereas the purine rings have some pucker The purine bases have a 9-membered double-ring system with four nitrogens and five carbons. The plain purine molecules have low solubility, but A base have higher solubility due to additional polar groups Purines can undergo a keto-enol tautomeric shift. The keto tautomer is called a lactam ring, wheres the enol tautomer is a lactim ring. The lactam (keto) tautomer is the predominant form at neutral pH.
Purines are metabolized into uric acid When cells die and get recycled, the purines in their genetic material also get broken down. Uric acid is the chemical formed when purines have been broken down completely. It's normal and healthy for uric acid to be formed in the body from breakdown of purines. In our blood, for example, uric acid serves as an antioxidant and helps prevent damage to our blood vessel linings, so a continual supply of uric acid is important for protecting our blood vessels. Uric acid levels in the blood and other parts of the body can become too high, however, under a variety of circumstances. Since our kidneys are responsible for helping keep blood levels of uric acid balanced, kidney problems can lead to excessive accumulation of uric acid in various parts of the body. Excessive breakdown of cells can also cause uric acid build-up. When uric acid accumulates, uric acid crystals (called monosodium urate crystals) can become deposited in our tendons, joints, kidneys, and other organs. This accumulation of uric acid crystals is called gouty arthritis, or simply "gout."
In the Lactam form, the ring nitrogens can serve as H-bond donors, and the keto oxygens serve as H-bond acceptors, when interacting with other molecules All of the pyrimidine and purine bases absorb U.V. light (a consequence of their aromatic ring structure). Therefore, the concentration of DNA or RNA in a sample can be determined by measuring the UV absorbance. The end product of purine catabolism in man is uric acid. Other mammals have the enzyme urate oxidase and excrete the more soluble allantoin as the end product. Man does not have this enzyme so urate is the end product for us. Uric acid is formed primarily in the liver and excreted by the kidney into the urine.
REPORTER 3: Lita, J What are purines and in which foods are they found? Introduction Purines are natural substances found in all of the body's cells, and in virtually all foods. The reason for their widespread occurrence is simple: purines provide part of the chemical structure of our genes and the genes of plants and animals. A relatively small number of foods, however, contain concentrated amounts of purines. For the most part, these high-purine foods are also high-protein foods, and they include organ meats like kidney, fish like mackerel, herring, sardines and mussels, and also yeast. Foods that contain purines Because uric acid is formed from the breakdown of purines, low-purine diets are often used to help treat conditions like gout in which excessive uric acid is deposited in the tissues of the body. The average daily diet for an adult in the U.S. contains approximately 600-1,000 milligrams of purines. Recent research by Choi and others has shown that the impact of plant purines on gout risk is very different from the impact of animal purines, and that within the animal food family, purines from meat and fish act very differently than purines from dairy. Choi's work has demonstrated that purines from meat and fish clearly increase our risk of gout, while purines from vegetables fail to change our risk. Dairy foods (which can contain purines) actually appear to lower our risk of gout. In summary, this epidemiological research (on tens of
thousands of men and women) makes it clear that all purine-containing foods are not the same, and that plant purines are far safer than meat and fish purines in terms of gout risk. In a case of severe or advanced gout, dietitians will often ask individuals to decrease their total daily purine intake to 100-150 milligrams. A 3.5 ounce serving of some foods, all by itself, can contain up to 1,000 milligrams of purines. These foods include anchovies, herring, kidney, liver, mackerel, meat extracts, mincemeat, mussels, sardines, and yeast. You'll notice that only of these foods - liver - is included amongst the World's Healthiest Foods. The table below lists other foods that contain higher-than-usual amounts of purines, though not nearly as much as the foods described above. Foods with very high purine levels(up to 1,000 mg per 3.5 ounce serving):
Anchovies, Brains, Gravies, Kidneys,Liver, Sardines, Sweetbreads Asparagus, Bacon, Beef, Bluefish, Bouillon, Calf tongue, Carp, Cauliflower, Chicken, Chicken soup, Codfish, Crab, Duck, Goose, Halibut, Ham, Kidney beans, Lamb, Lentils, Lima beans, Lobster, Mushrooms, Mutton, Navy beans, Oatmeal, Oysters, Peas, Perch, Pork, Rabbit, Salmon, Sheep, Shellfish,
Foods with high and moderately high purine levels(5-100 mg per 3.5 ounch serving):
Snapper, Spinach, Tripe, Trout, Tuna, Turkey, Veal, Venison Purines and health In general, we want purines in our diet. As mentioned previously, our bodies can break purines down into uric acid, a substance that can help protect our blood vessels from damage and that is a common recycled product when our cells die. There are rare conditions, however, in which metabolism of purines in the body gets disrupted. While research in this area is not conclusive, many health care practitioners suggest screening for purine metabolism problems whenever confronted with other problems, particularly in children and infants, which cannot readily be explained. These problems include anemia, failure to thrive, autism, cerebral palsy, deafness, epilepsy, susceptibility to recurrent infection, and the inability to walk or talk. You'll notice from Table 1 that most of the purine-containing foods included within the World's Healthiest Foods - asparagus, cauliflower, chicken, kidney beans, lima beans, mushrooms, navy beans, oatmeal, peas salmon, spinach, and tuna - contain about 5-50 milligrams of purines in a 3.5 ounce serving. If you are not at risk for gout or other health problems related to purine metabolism, you would be unlikely to consume greater than the U.S. average for purine intake even if you ate more than ten 3.5 ounce servings of the above foods. If you have been placed on a low purine diet that calls for no more than 150 milligrams of dietary purines, you should still be able to consume a 3.5 ounce serving of these foods per day without exceeding the 150 milligram limit for your overall diet. http://www.whfoods.com/genpage.php?tna me=george&dbid=51
Você também pode gostar
- Tofu TacosDocumento1 páginaTofu Tacosbookish33sAinda não há avaliações
- Low Oxalate DietDocumento5 páginasLow Oxalate DietBB Dahl100% (1)
- Gouty PowerpointDocumento14 páginasGouty PowerpointBSN4AAinda não há avaliações
- Bentgo Prep EbookDocumento23 páginasBentgo Prep EbookFernando CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- That Guy Who Ate All The Potatoes CookbookDocumento52 páginasThat Guy Who Ate All The Potatoes CookbookAstrid SabirinAinda não há avaliações
- 30 Day Diabetic Mealplan PDFDocumento1 página30 Day Diabetic Mealplan PDFMad-Max-1100% (1)
- Foods ranked by purine contentDocumento7 páginasFoods ranked by purine contentShamim RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Purine Table Provides Foods Highest and Moderately High in PurinesDocumento10 páginasPurine Table Provides Foods Highest and Moderately High in PurinesYohan Parulian SinagaAinda não há avaliações
- Soft Foods Guide for Easy Chewing and SwallowingDocumento12 páginasSoft Foods Guide for Easy Chewing and SwallowingTerence Shane AcodAinda não há avaliações
- 7-Day Meal Plan for Health & PerformanceDocumento9 páginas7-Day Meal Plan for Health & PerformanceJimmyAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Essential NutrientsDocumento133 páginas6 Essential NutrientsLouisa Marie MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Carnitine Deficiency: Structure, Function, Metabolism and DeficiencyDocumento58 páginasCarnitine Deficiency: Structure, Function, Metabolism and DeficiencyRafael Francisco Garcia Munoz100% (1)
- Ersonalized Diet Cha Ersonalized Diet Chart For Umar: Diabetes Management Diet Diabetes Management DietDocumento11 páginasErsonalized Diet Cha Ersonalized Diet Chart For Umar: Diabetes Management Diet Diabetes Management DietRamaiah KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Metabolic Diet - Strict Carb - 4,000 Calorie Week 1Documento5 páginasThe Metabolic Diet - Strict Carb - 4,000 Calorie Week 1andrea90bragaAinda não há avaliações
- For People With Diabetes and Their Families: March 2011Documento31 páginasFor People With Diabetes and Their Families: March 2011Milan RafaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Mediterranean Diet Cookbook for Beginners: Unlock the Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet with Easy and Delicious Recipes for Everyday Eating!No EverandMediterranean Diet Cookbook for Beginners: Unlock the Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet with Easy and Delicious Recipes for Everyday Eating!Ainda não há avaliações
- Diabetes Diet DelightsDocumento14 páginasDiabetes Diet DelightsYanoAinda não há avaliações
- Stocks, Soups, and Sauces: The Chef's Building BlocksDocumento36 páginasStocks, Soups, and Sauces: The Chef's Building Blocksfernandez ararAinda não há avaliações
- Pork RecipesDocumento2 páginasPork RecipesBob SmithAinda não há avaliações
- PPS Meal Plan for Marcus LeongDocumento5 páginasPPS Meal Plan for Marcus LeongMarcus LeongAinda não há avaliações
- Various Food Types and Their Purine ContentDocumento12 páginasVarious Food Types and Their Purine ContentelsadehoAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy Vegetarian Part 1Documento2 páginasHealthy Vegetarian Part 1Frank BradshawAinda não há avaliações
- Ifct2017 Github Io/readDocumento5 páginasIfct2017 Github Io/readSubhajit Sahu100% (1)
- 100 Healthy ThingsDocumento30 páginas100 Healthy Thingsuser.giuAinda não há avaliações
- Written Report NutriDocumento7 páginasWritten Report NutriMark James MelendresAinda não há avaliações
- Dialysis and DietDocumento2 páginasDialysis and DietgregcolletteAinda não há avaliações
- Review of Low-Carb Vs High-Carb DietsDocumento15 páginasReview of Low-Carb Vs High-Carb Dietswtbliss100% (8)
- Sciencehealthywell BalancedmealplanDocumento6 páginasSciencehealthywell Balancedmealplanapi-256103874Ainda não há avaliações
- India Diet Plans For Weight LossDocumento4 páginasIndia Diet Plans For Weight LossAkshay WahalAinda não há avaliações
- Therapeutic DietDocumento3 páginasTherapeutic DietWendy EscalanteAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Support CalculationsDocumento5 páginasNutrition Support Calculationsapi-333590706Ainda não há avaliações
- Balanced MealsDocumento20 páginasBalanced MealsPamela WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Food ExchangeDocumento19 páginasFood ExchangeJoycel CeñidozaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Habits That Add Years To Your LifeDocumento5 páginas4 Habits That Add Years To Your Lifejohntandra100% (1)
- Keto Diet ArticleDocumento11 páginasKeto Diet Articlethomas taglerAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Inflammatory DietDocumento6 páginasAnti Inflammatory DietHW GomarAinda não há avaliações
- Food Guidelines To Lower Your LDL (Bad) CholesterolDocumento4 páginasFood Guidelines To Lower Your LDL (Bad) Cholesterola3llamAinda não há avaliações
- Is Vegetarianism More Favorable Than An Omnivorous DietDocumento13 páginasIs Vegetarianism More Favorable Than An Omnivorous Dietapi-609404860Ainda não há avaliações
- Case Study: Hydrosalpinx, Adnexal Mass, Status Post AppendectomyDocumento19 páginasCase Study: Hydrosalpinx, Adnexal Mass, Status Post AppendectomyChedan B. Ceriaco100% (2)
- Diabetic Diet: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento6 páginasDiabetic Diet: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMeta BachtiarAinda não há avaliações
- Pros and Cons of FadDocumento12 páginasPros and Cons of FadLeilah CaitAinda não há avaliações
- Food Substitue ListsDocumento2 páginasFood Substitue ListsMiguel LeybaAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Menu With JustificationDocumento1 páginaSample Menu With JustificationAbigail Lonogan100% (1)
- Low-Recipes: 10g of Carbs or Less in Every RecipeDocumento43 páginasLow-Recipes: 10g of Carbs or Less in Every Recipesabam1993Ainda não há avaliações
- 7 Days High Protein Diet Plan For Weight Loss (Indian, Vegetarian Diet Chart) - DietburrpDocumento8 páginas7 Days High Protein Diet Plan For Weight Loss (Indian, Vegetarian Diet Chart) - DietburrpayushAinda não há avaliações
- Food GuideDocumento6 páginasFood Guideapi-228130677Ainda não há avaliações
- Dietetics Module: Therapeutic Diets and Chronic Disease ManagementDocumento24 páginasDietetics Module: Therapeutic Diets and Chronic Disease ManagementSara MagedAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case StudyDocumento5 páginasChronic Kidney Disease Case Studyhailey guzzoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Protein?Documento11 páginasWhat Is Protein?Muhammad Rizal ArdianaAinda não há avaliações
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocumento10 páginasCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloAinda não há avaliações
- Food Poisoning Final Print!Documento3 páginasFood Poisoning Final Print!Joeven HilarioAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Therapy For Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders Case QuestionsDocumento11 páginasNutrition Therapy For Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders Case QuestionspeytonAinda não há avaliações
- Micronutrients For HealthDocumento4 páginasMicronutrients For HealthIsaac GoldAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Nutrition Management Protocol 2015 PDFDocumento27 páginasRenal Nutrition Management Protocol 2015 PDFShefali RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Guideline Nutrition For Liver DiseaseDocumento75 páginasGuideline Nutrition For Liver Diseasedwi yuniari100% (1)
- Comprehensive Elimination Diet PDFDocumento20 páginasComprehensive Elimination Diet PDFJeffrey PeekoAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Cholesterol LevelsDocumento5 páginasUnderstanding Cholesterol LevelsKaren ManochaAinda não há avaliações
- The Diabetic NutriBullet Recipe Guide: 100+NutriBullet Diabetes Blasting Ultra Low Carb Delicious and Health Optimizing Nutritious Juice and Smoothie RecipesNo EverandThe Diabetic NutriBullet Recipe Guide: 100+NutriBullet Diabetes Blasting Ultra Low Carb Delicious and Health Optimizing Nutritious Juice and Smoothie RecipesAinda não há avaliações
- Easy Keto Chicken: Delicious low-carb, high-fat, Ketogentic CookbookNo EverandEasy Keto Chicken: Delicious low-carb, high-fat, Ketogentic CookbookAinda não há avaliações
- Questionpaper Unit1 (6BI01) June2012Documento24 páginasQuestionpaper Unit1 (6BI01) June2012Mahiat Miftah ShowkatAinda não há avaliações
- Sandra Central DogmaDocumento82 páginasSandra Central Dogmakaren milloAinda não há avaliações
- 2015chandra BasicConceptsofBiotechnology PDFDocumento518 páginas2015chandra BasicConceptsofBiotechnology PDFmayur borseAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDocumento4 páginasNucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDaine MarconAinda não há avaliações
- Wbi11 01 Que 2023101we30Documento28 páginasWbi11 01 Que 2023101we30Amal AbuelfotouhAinda não há avaliações
- BMAT BIOLOGY CELL STRUCTUREDocumento22 páginasBMAT BIOLOGY CELL STRUCTUREAngel SyAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Biology of the CellDocumento84 páginasMolecular Biology of the CellSisira NisyAinda não há avaliações
- Neuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocumento21 páginasNeuclic Acid and Protein SynthesisPradyut BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acid PDFDocumento32 páginasNucleic Acid PDFRachelle Anne LuisAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules - Year 9Documento19 páginasBiological Molecules - Year 9ArmanAinda não há avaliações
- Bicol Nursing Biochemistry ModuleDocumento11 páginasBicol Nursing Biochemistry ModuleValerie Heart GomezAinda não há avaliações
- What's in Breast Milk?Documento1 páginaWhat's in Breast Milk?Sunny SideAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Molecular Introduction To Molecular Biology BiologyDocumento18 páginasIntroduction To Molecular Introduction To Molecular Biology BiologyNur AdilahAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics in BiochemistryDocumento16 páginasThermodynamics in BiochemistrySurya DoleyAinda não há avaliações
- Chromosome structure and functionDocumento9 páginasChromosome structure and functionMatt Mc Henry HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)Documento3 páginasChapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)JayjayAinda não há avaliações
- Mycophenolate Mofetil and Its Mechanisms of Action: ReviewDocumento34 páginasMycophenolate Mofetil and Its Mechanisms of Action: ReviewAnna GozaliAinda não há avaliações
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocumento2 páginasDNA Replication Worksheetfabyunaaa100% (1)
- NucleotideDocumento56 páginasNucleotideDhara NPAinda não há avaliações
- Als ExamDocumento2 páginasAls ExamJannette JaneAinda não há avaliações
- Che 3111 Lecture Notes, Nitrogen Metabolism 2019 July 2020 PDFDocumento34 páginasChe 3111 Lecture Notes, Nitrogen Metabolism 2019 July 2020 PDFLucy ZuluAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism REVIEW - Linda Fall 09 PDFDocumento7 páginasNucleic Acid Metabolism REVIEW - Linda Fall 09 PDFPeachesOrangesApplesAinda não há avaliações
- RNA and Protein SynthesisDocumento14 páginasRNA and Protein SynthesisFelicia Landon-HicksAinda não há avaliações
- DNA - The Double Helix: Chromosomes Are Composed of Genes. A Gene Is A Segment of DNA ThatDocumento4 páginasDNA - The Double Helix: Chromosomes Are Composed of Genes. A Gene Is A Segment of DNA Thatapi-310760045Ainda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acid Structure and FunctionsDocumento19 páginasNucleic Acid Structure and FunctionsDaniel LohAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Molecules: Mrs. Mary Vienne M. PascualDocumento73 páginasBiological Molecules: Mrs. Mary Vienne M. PascualVienne Monroid100% (1)
- Dr. Romano's Dynamite Bio Review July 2019 PDFDocumento560 páginasDr. Romano's Dynamite Bio Review July 2019 PDFkatherineevo473100% (2)
- Biomedical Analysis Techniques and MethodsDocumento25 páginasBiomedical Analysis Techniques and MethodsKrisan Mallion LuisAinda não há avaliações
- Ahmad Hamoud: Ester BondDocumento22 páginasAhmad Hamoud: Ester BondAhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Documento16 páginasCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12shabanaAinda não há avaliações