Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER ENGINEERING SERVICES
Enviado por
Arnulfo LavaresDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER ENGINEERING SERVICES
Enviado por
Arnulfo LavaresDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER PRODUCTS, INC.
Power Systems Engineering Services Department 530 Keystone Drive Warrendale, PA 15086-7538, USA Phone: (724) 778-5111 Fax: (724) 778-5149 Home Page: www.meppi.com
POWER SYSTEMS ENGINEERING SERVICES COMMERCIAL & INDUSTRIAL POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
Advanced Power Systems Engineering for Technical Analysis, Training, and Support Mitsubishi Electrics Power Systems Engineering Services Department provides technical analysis, training, and support for commercial and industrial power distribution systems rated 72.5 kV through 208 V. A wide range of technical study areas and support services are available to our customers. ENGINEERING STUDIES Short-Circuit All power systems are subjected to the potential damaging effects of high magnitude currents flowing from short-circuits occurring in system components. To ensure that circuit protective devices are capable of quickly isolating faults to minimize equipment damage and personal hazard, it is essential that a short-circuit study be performed on the electrical design of new and existing facilities. The purpose of a short-circuit study is: To calculate the system fault currents and compare these values to the first cycle (momentary) and interrupting short-circuit current ratings of circuit protective devices such as circuit breakers and fuses To compare the calculated system fault currents to shorttime, or withstand ratings of electrical components such as cables, transformers, and reactors To provide the system fault current data needed to perform a protective device coordination study for the power system
Protective Device Coordination There are three major aspects to consider when performing a protective device coordination study: safety, equipment protection, and protective device selectivity. Safety requirements are satisfied if the protective devices are rated to carry and interrupt maximum load currents and withstand and interrupt maximum fault currents. Protection goals are fulfilled if protective devices are set to operate above normal load conditions and below equipment damage curves. Selectivity objectives are satisfied if during a system fault or overload condition, a minimal amount of electrical equipment is removed from the system. The purpose of a protective device coordination study is: To specify the proper protective devices (relays, fuses, and circuit breakers) to protect distribution equipment To calculate the proper circuit breaker trip unit and protective relay settings to minimize damage to the faulted component and selectively remove the faulted device from the power system To ensure that protective devices do not operate under normal load conditions To generate the time-current curves (TCCs) needed to perform an arc-flash hazard study on the power system
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, Inc. Power Systems Engineering Services Dept.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER PRODUCTS, INC.
Arc-Flash Hazard An arcing fault is the flow of current through the air between phase conductors, or phase conductors and neutral or ground. An arcing fault can release tremendous amounts of concentrated radiant energy in a small fraction of a second resulting in extremely high temperatures, a significant pressure blast, shrapnel hurling at high velocities (in excess of 700 mph), and severe or fatal injuries to personnel. The purpose of an arcflash hazard study is: To determine and label the maximum incident energy available at every location along the distribution network likely to require examination, adjustment, service, or maintenance To specify the protective clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE) required for the application To determine the arc-flash boundary distance (safe working distance) that must be maintained by unprotected plant personnel
MEPPI Headquarters located in Warrendale, PA
Voltage Regulation In a power system, voltage drops (or rises) can greatly affect the operation of voltage sensitive equipment such as magnetic solenoids, lighting circuits, power electronic equipment, and computers. When line-starting a large induction motor, the voltage drop experienced for several seconds at the terminals of the motor reduces the available accelerating torque of the machine. As a result, the overall motor starting performance is compromised. A voltage regulation study should be performed for new power system designs as well as for changes to existing designs. The purpose of a voltage regulation study is: To determine the voltage decrease (or increase) due to the application of impact loads, line-starting large induction motors, or adding capacitors to the power system To determine necessary remedial actions if voltages are not within acceptable operating tolerances (increase cable cross-sectional area, adjust voltage taps of substation transformers, etc.) Power Factor Many benefits provided by power factor improvement result from the reduction of reactive power in a power system. These benefits include: lower purchased energy costs (if the utility company enforces a power factor clause and/or demand charge), increase of available system electrical capacity, voltage profile improvement, and lower system losses. Adding capacitors is generally the most economical and efficient means to improve overall plant power factor. The purpose of a power factor study is: To determine the proper sizing and placement of capacitors in a power system to improve overall plant power factor To ensure the addition of power factor correction capacitors will not create abnormal resonance problems with the existing power system configuration To minimize electrical utility service penalties (low power factor and demand charges)
Load Flow Load flow studies are performed for normal as well as emergency operating conditions of a facility. A load flow study will determine whether the distribution system will operate properly under various conditions. This type of study should be considered for the design of new power systems as well as for evaluating the impact of changes to an existing distribution system. The purpose of a load flow study is: To determine bus voltage levels and branch current levels for a given load condition To determine if bus voltage levels are within acceptable limits for both normal and emergency operating conditions To determine if the calculated power flows are within the ratings of all electrical equipment
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, Inc. Power Systems Engineering Services Dept.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER PRODUCTS, INC.
Harmonics and Power Quality Within all commercial and industrial facilities, there are many non-linear harmonic producing loads. Examples of these types of loads include: adjustable speed motor drives, static power converters, computers, UPS systems, and electronic ballasts for lighting. These types of loads cause distortion of the sinusoidal voltage and current waveforms in the power system. This could lead to improper operation and/or complete failure of the connected electrical equipment. The purpose of a harmonics and power quality study is: To evaluate the harmonic voltage and current distortion at the point of common coupling (PCC) with the electric utility service to ensure compliance with IEEE 519 To calculate system resonances in the existing power system or future power system design To select and locate capacitors and/or passive filters to mitigate the effect of harmonics and optimize system performance
To determine the system response during and after transient disturbances while including the dynamic responses of automatic voltage regulator and speed governor systems To evaluate protective device schemes and settings associated with the local generation and utility interface
Ground Mat A properly designed ground mat limits the neutral to ground voltages normally present during ground faults to levels that the human body can tolerate. Safe ground mat design is essential for all sizes of substations for proper protection of plant personnel. The purpose of a ground mat study is: To calculate the earth potential, touch potential, step potential, and perform a safety analysis of the substation grounding system per IEEE Standard 80 To identify unsafe areas within existing and proposed ground mat designs To optimize the ground mat design and verify that the design is safe throughout the area in question Transient Stability and Dynamic Performance Transient stability and dynamic performance studies are usually performed on commercial or industrial power systems with large amounts of local generation. This type of study is essential when adding or upgrading generators within a facility. Stability is defined as the ability of a power system to experience a sudden change in generation, load, or system characteristics without a loss of synchronism. The purpose of a transient stability and dynamic performance study is: To determine the system response during and after transient disturbances such as faults, load changes, switching, large motor starting, loss of a utility connection, and loss of a local generator
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, Inc. Power Systems Engineering Services Dept.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER PRODUCTS, INC.
ADDITIONAL SERVICES In addition to the aforementioned power distribution systems engineering and analysis capabilities, Mitsubishi Electrics Power System Engineering Services Department has other services to offer to the commercial and industrial power distribution systems market including: Power System Protection Specify and provide settings for electro-mechanical, digital, and microprocessor based protective relays Program microprocessor based protective relays including protection and control logic settings, monitoring and reporting settings, and communication settings Review/recommend protection schemes for generators, buses, transformers, capacitors, and motors using existing protective devices or new specified solid state protective equipment Specify lightning and surge protection for medium voltage equipment Review/recommend proper grounding techniques for electrical equipment and ground fault protection Equipment Specify emergency generation equipment and transfer switches Specify pad mounted oil-filled transformers for outdoor substation applications and dry-type transformers for indoor unit substation equipment Specify metal clad switchgear, switchboards, load break switches, bolted pressure switches, and motor control centers Specify electronic voltage regulation equipment Specify AC/DC adjustable speed drives and other solid state power conversion equipment Specify electronic power conditioning and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems Specify power monitoring equipment and power system data acquisition systems MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC POWER PRODUCTS, INC. Power Systems Engineering Services Dept. 530 Keystone Drive Warrendale, PA 15086-7538, USA Phone: (724) 778-5111 FAX: (724) 778-5149 Home Page: www.meppi.com Specify/program programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for power control related projects Documentation Review one-line and three-line power drawings and breaker control logic diagrams for completeness and correctness Review/recommend breaker control logic schemes including close/trip circuits and lock-out relay operation On-Site Field Work Perform measurements of all electrical quantities including voltage, current, real and reactive power, harmonics, and power factor Investigate and/or troubleshoot power distribution systems problems Gather necessary data required to perform engineering studies Other Support Provide training seminars, short courses, and tutorials related to power distribution systems Expert witness litigation services Mitsubishi Electric is dedicated to providing products and services to help bring our customers into the 21st century with technology that is proven and reliable. Whether its solving power quality related issues, analyzing power distribution operating procedures, or providing advanced instruction, we offer the dedication, expertise, and quality to better serve your needs now and into the future. Please contact us to discuss your organizations power system engineering service needs.
Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, Inc. Power Systems Engineering Services Dept.
Você também pode gostar
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityNo EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityAinda não há avaliações
- PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE INSPECTION SHEETDocumento2 páginasPREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE INSPECTION SHEETArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Hazards ZoneDocumento4 páginasHazards Zonedarsh2001patelAinda não há avaliações
- 3412C EMCP II For MUI Engines Electrical System: Tgc1-Up Djn1-Up 9EP1-2988 Tft1-Up BCW1-744 Lry1-Up Rty1-Up 4BZ1-6087Documento4 páginas3412C EMCP II For MUI Engines Electrical System: Tgc1-Up Djn1-Up 9EP1-2988 Tft1-Up BCW1-744 Lry1-Up Rty1-Up 4BZ1-6087luis alberto rodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Circuit Breaker SelectionDocumento16 páginasCircuit Breaker SelectionCinar Inal100% (3)
- BS 12464 Lighting Standard Design Examples in DIALuxDocumento17 páginasBS 12464 Lighting Standard Design Examples in DIALuxnhatvpAinda não há avaliações
- Nema Motor Data CalculatorDocumento19 páginasNema Motor Data Calculatorwado11100% (1)
- Dynamic Braking ResistorsDocumento2 páginasDynamic Braking Resistorsjsrplc7952Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecodial enDocumento3 páginasEcodial envijaydev75Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.panelboard Spec ChartDocumento2 páginas2.panelboard Spec ChartangelAinda não há avaliações
- Bosch/Electro-Voice Ceiling Speaker Placement CalculatorDocumento6 páginasBosch/Electro-Voice Ceiling Speaker Placement CalculatorKp SatishAinda não há avaliações
- Frequency of Maintenance Tests MatrixDocumento4 páginasFrequency of Maintenance Tests MatrixAhmed Hasan100% (4)
- Co Axial CableDocumento9 páginasCo Axial Cablemsiddique295Ainda não há avaliações
- Check List For Power DBsDocumento13 páginasCheck List For Power DBsjeetAinda não há avaliações
- 3 PhaseDocumento9 páginas3 PhaseArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- ANo116 Design Rules For PFC Systems - 090205Documento11 páginasANo116 Design Rules For PFC Systems - 090205Ricardo LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Cooling Systems PDFDocumento6 páginasLiquid Cooling Systems PDFPerdanio Nosal April JoyAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing Electrical and PLC Panel BoardsDocumento11 páginasManufacturing Electrical and PLC Panel BoardsVikram PhalakAinda não há avaliações
- Busbar DesignDocumento25 páginasBusbar DesigngusgifAinda não há avaliações
- Maintenance of Electrical SwitchgearDocumento186 páginasMaintenance of Electrical SwitchgearvthiseasAinda não há avaliações
- Intelligent Load SheddingDocumento22 páginasIntelligent Load SheddingNikhil Jagirdar50% (2)
- 245 KV GisDocumento9 páginas245 KV Gisanon_608771851Ainda não há avaliações
- Logix5000 Controllers FBD Programming ManualDocumento28 páginasLogix5000 Controllers FBD Programming ManualmorriseyAinda não há avaliações
- Panel Type (Dm1-A) 24Kv Switchgear Sm6: Scale: NTSDocumento19 páginasPanel Type (Dm1-A) 24Kv Switchgear Sm6: Scale: NTSFadly Fachrul RozyAinda não há avaliações
- Dowell's Price List 18.3.2022Documento26 páginasDowell's Price List 18.3.2022Sunil WadekarAinda não há avaliações
- Auto TransformerDocumento7 páginasAuto TransformerPrincess Diane GravidesAinda não há avaliações
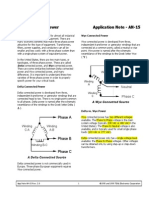
- Delta Wye Power Application AN-15Documento2 páginasDelta Wye Power Application AN-15gabematicAinda não há avaliações
- Siemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer's HandbookDocumento58 páginasSiemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer's Handbookkala2011100% (1)
- JACOB Online Catalogue 2018 en EU OPDocumento296 páginasJACOB Online Catalogue 2018 en EU OPVladan PetrovićAinda não há avaliações
- Chicken Industry Performance Report 2012Documento18 páginasChicken Industry Performance Report 2012Donald RemulaAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas Info SheetDocumento5 páginasBiogas Info SheetKopi BrisbaneAinda não há avaliações
- Current Electrical Electronics Engineering Project Topics For Nigerian StudentsDocumento1 páginaCurrent Electrical Electronics Engineering Project Topics For Nigerian StudentsGrace Opara100% (1)
- CP Testing EquipmentDocumento5 páginasCP Testing Equipmentadeoye_okunoyeAinda não há avaliações
- RFQDocumento4 páginasRFQPaul SigeiAinda não há avaliações
- RCCB - ID B TypeDocumento2 páginasRCCB - ID B TypeWahyu ArdiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- UL 508A Quadri NECDocumento2 páginasUL 508A Quadri NECmatteo2009Ainda não há avaliações
- Vertical Steel Shot Blasting Systems Ship HullDocumento3 páginasVertical Steel Shot Blasting Systems Ship Hullvran77Ainda não há avaliações
- National Workshop Lab Manual on ImmunoinformaticsDocumento2 páginasNational Workshop Lab Manual on ImmunoinformaticsSukanthan RAinda não há avaliações
- Unbalanced Three-Phase Distribution SystemDocumento5 páginasUnbalanced Three-Phase Distribution SystemIraj Az IraniAinda não há avaliações
- Profibus DP Master Protocol APIDocumento336 páginasProfibus DP Master Protocol APImail87523100% (2)
- Burndy Products: Quick Reference GuideDocumento6 páginasBurndy Products: Quick Reference Guidegrupo4mAinda não há avaliações
- Optimize Factory Assets with FactoryTalk AssetCentreDocumento28 páginasOptimize Factory Assets with FactoryTalk AssetCentrericardorobsonAinda não há avaliações
- Vaya Flood MP G2 RGB DataSheetDocumento4 páginasVaya Flood MP G2 RGB DataSheetBeni MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Reliable MV Switchgear with VR Vacuum Circuit BreakersDocumento16 páginasReliable MV Switchgear with VR Vacuum Circuit Breakerseshscribd123Ainda não há avaliações
- MME Group Anode BookletDocumento158 páginasMME Group Anode BookletYurizki LhzAinda não há avaliações
- PMPDocumento30 páginasPMPFeras Mohammed SiddigAinda não há avaliações
- EarthingDocumento3 páginasEarthingvinay nagvanshiAinda não há avaliações
- EmcDocumento161 páginasEmcPradeep MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Push and Pull StrategyDocumento41 páginasPush and Pull StrategyAbhishek NagarajAinda não há avaliações
- 9 DaysElectrical Design EngineeringDocumento7 páginas9 DaysElectrical Design EngineeringNissi Jimmy0% (1)
- 26 18 00 MV Circuit Protection Devices SicamDocumento21 páginas26 18 00 MV Circuit Protection Devices SicamRahul S.JagtapAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage Drop Calculations For Engineers - Beginners GuideDocumento6 páginasVoltage Drop Calculations For Engineers - Beginners GuideAbdul Rawoof ShaikAinda não há avaliações
- Transformer Sizing PDFDocumento2 páginasTransformer Sizing PDFSelva MaharajanAinda não há avaliações
- Selection ChartDocumento2 páginasSelection Chartultrasonic81Ainda não há avaliações
- Automatic Load Shedding Using GSMDocumento2 páginasAutomatic Load Shedding Using GSMPrayog TechAinda não há avaliações
- 716 - UniGear ZS2 With VD4 05Documento6 páginas716 - UniGear ZS2 With VD4 05srmohapatra5086Ainda não há avaliações
- SS Electrical - Electrical Price Bid ScheduleDocumento32 páginasSS Electrical - Electrical Price Bid Scheduledox4printAinda não há avaliações
- Rowan University Design Guide - PanelboardsDocumento1 páginaRowan University Design Guide - PanelboardszeliteAinda não há avaliações
- Gland Selection Chart PDFDocumento2 páginasGland Selection Chart PDFNazeeruddin MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- General Specifications For Soft StarterDocumento7 páginasGeneral Specifications For Soft StarterIsmael AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Amtech Quick Guide 2015Documento16 páginasAmtech Quick Guide 2015Mohammad SamourAinda não há avaliações
- 20130724+EN EC10+&+EX16+quick+start+guideDocumento2 páginas20130724+EN EC10+&+EX16+quick+start+guideRefaat RaslanAinda não há avaliações
- Data Communication Circuit Configurations and HardwareDocumento14 páginasData Communication Circuit Configurations and HardwareIndira KunduAinda não há avaliações
- Consulting Engineering SolutionsDocumento28 páginasConsulting Engineering SolutionsRamesh AnanthanarayananAinda não há avaliações
- Legrand MCCBDocumento183 páginasLegrand MCCBFernando LoteroAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical All PDFDocumento155 páginasElectrical All PDFTayyibAinda não há avaliações
- LVSG SpecificationsDocumento10 páginasLVSG SpecificationsperijoyAinda não há avaliações
- Why StudiesDocumento4 páginasWhy StudiesRavindra GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Resistance WorksheetDocumento2 páginasResistance WorksheetArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- MLM Harare 2012-11 Cold Chain ManagementDocumento38 páginasMLM Harare 2012-11 Cold Chain ManagementArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Drawing RubricDocumento1 páginaDrawing RubricArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- A B C D: What Base Ten Number Is Represented by The Above Binary Fingers?Documento1 páginaA B C D: What Base Ten Number Is Represented by The Above Binary Fingers?Arnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- When Good Grounds Go Bad PDFDocumento7 páginasWhen Good Grounds Go Bad PDFArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- B 807 A 85 A 6Documento8 páginasB 807 A 85 A 6Arnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDocumento75 páginasLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- The D.C. Power Supply: Experiment ADocumento6 páginasThe D.C. Power Supply: Experiment AArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Motor Starter MS132: Data SheetDocumento8 páginasManual Motor Starter MS132: Data SheetArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Circuits WorksheetDocumento1 páginaBasic Circuits WorksheetArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- AC MotorDocumento13 páginasAC MotorAjay DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ElectronicDocumento4 páginasBasic ElectronicArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Electrical Circuits: Basic Definitions, Current, Voltage, Resistance, PowerDocumento16 páginasIntroduction to Electrical Circuits: Basic Definitions, Current, Voltage, Resistance, PowerArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Checklist FNLDocumento5 páginasElectrical Checklist FNLArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- C092Documento16 páginasC092Arnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electricity (Exploratory)Documento85 páginasBasic Electricity (Exploratory)Arnulfo Lavares0% (1)
- Lecture 01 - IntroductionDocumento6 páginasLecture 01 - IntroductionArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Pcea: ": Electrical Preventive Maintenance - Spend A Little - Save A Lot"Documento30 páginasPcea: ": Electrical Preventive Maintenance - Spend A Little - Save A Lot"Arnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Preventative MaintenanceDocumento25 páginasPreventative MaintenanceArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- At 7Documento14 páginasAt 7Arnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment-1 2Documento6 páginasExperiment-1 2Manigandan212Ainda não há avaliações
- SyncronisationDocumento7 páginasSyncronisationmuvivekAinda não há avaliações
- Voltage Regulation of Three-Phase AlternatorDocumento10 páginasVoltage Regulation of Three-Phase AlternatorNAYEEM100% (1)
- Experiment No. 3: 1.0 TitleDocumento5 páginasExperiment No. 3: 1.0 TitleArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Resistor CktsDocumento5 páginas02 Resistor CktsArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- When Good Grounds Go Bad PDFDocumento7 páginasWhen Good Grounds Go Bad PDFArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- Crydom Panel Mount AC Output SSR InstallationDocumento2 páginasCrydom Panel Mount AC Output SSR InstallationArnulfo LavaresAinda não há avaliações
- SMD e Vls Number 176 1Documento1 páginaSMD e Vls Number 176 1blancaAinda não há avaliações
- Saes P 107Documento18 páginasSaes P 107bilal hussain qureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Haramaya UniversityDocumento30 páginasHaramaya UniversityDire Abdulaxif100% (1)
- Wesm Wesmmnm 64Documento64 páginasWesm Wesmmnm 64rudy.langeAinda não há avaliações
- HVDC Transmission Basic CircuitDocumento3 páginasHVDC Transmission Basic CircuitDEPARTMENT OF EEE SVEWAinda não há avaliações
- Beyerdynamic Accessories 1Documento6 páginasBeyerdynamic Accessories 1Mario HdezAinda não há avaliações
- ACB VCB OCB LT Panel ChecklistDocumento7 páginasACB VCB OCB LT Panel ChecklistAnonymous mNQq7oj100% (1)
- REB500 SingaporeDocumento2 páginasREB500 Singaporejaved shaikh chaandAinda não há avaliações
- IBA DOC - Concise for Recloser (Relai Penutup Balik) DocumentDocumento50 páginasIBA DOC - Concise for Recloser (Relai Penutup Balik) Documentsheila hariAinda não há avaliações
- 132kV GIS Substation RFP DetailsDocumento552 páginas132kV GIS Substation RFP DetailsMohanraj NidumoluAinda não há avaliações
- Open-phase Protection for MotorsDocumento5 páginasOpen-phase Protection for MotorsAnamarialuzAinda não há avaliações
- IJEDR1802085Documento6 páginasIJEDR1802085Rizky RamadhaniAinda não há avaliações
- JSA - Electrical ActivitiesDocumento3 páginasJSA - Electrical ActivitiesNisith SahooAinda não há avaliações
- MDGF Testing 80043-703-01Documento37 páginasMDGF Testing 80043-703-01AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Cenovnik PunjacaDocumento6 páginasCenovnik PunjacaDEJAN SRECKOVICAinda não há avaliações
- Eaton FERRUPS User GuideDocumento128 páginasEaton FERRUPS User GuideGordon WilkinsAinda não há avaliações
- Installation of Basic Final Circuits: Conduit or TrunkingDocumento37 páginasInstallation of Basic Final Circuits: Conduit or TrunkingbendeniAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Adil Salin GanayDocumento6 páginasRay Adil Salin GanayJevan CalaqueAinda não há avaliações
- Main Component of Kaplan TurbineDocumento3 páginasMain Component of Kaplan TurbineMahira AlyyAinda não há avaliações
- 12 KV Outdoor Type Ring Main UnitDocumento10 páginas12 KV Outdoor Type Ring Main Unitzeeshan SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ProjectDocumento8 páginasPhysics ProjectXigfon SqitroAinda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Relay: Wiring DiagramDocumento1 páginaIntermediate Relay: Wiring DiagramRamius HamdaniAinda não há avaliações
- Et214 2005Documento17 páginasEt214 2005syamdev3150Ainda não há avaliações