Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
An Introduction To Railway Signalling and Equipment
Enviado por
Nitesh JadhavTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
An Introduction To Railway Signalling and Equipment
Enviado por
Nitesh JadhavDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The History of Railway Signalling
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
Andy Lawrence
18th August 2011
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
What will this talk be about???
Aim: I aim to provide a general overview of the concepts and terminology used in railway signalling. Overview:
1 2 3
The history of railway signalling The key components of a signalling system Trackwork: Rails, sleepers ballast etc
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
In the Beginning....
Police men would provide signals to trains. Coloured ags were used during the day. Lights were used at night.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
And how did they know where the trains were?
There was no system to track train location. Once the train went out of sight there was no way to tell its location. Clocks timed a delay in-between trains.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
The Original Fixed Signal
The rst major advance in railway signalling was the introduction of Fixed Signals. These essentially were wooden boards mounted on rotating posts Board visible Stop!, Do not proceed Board not visible Track ahead is clear, Proceed
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
More Fixed Signals
One improvement on the basic xed signal is the disc and crossbar. Either the disc or the crossbar is visible at any given time. Disc visible Proceed Aspect Crossbar visible Stop Aspect The term aspect refers to the dierent modes or visible state of a signal.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Disc and Crossbar
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
The Semaphore Signal
A new signal called the semaphore was introduced in 1841. Used a signal arm with could be positioned at dierent angles. With a oil lamp for night operation.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
A Bright Idea!
Up to this point one policeman controlled one signal Then someone had an amazing idea! Connect signals to a central point called a signal box with cables A signaller set the signals using levers.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
The Introduction of Interlockings
This allowed for the development of the interlocking: Prevents the signalling system entering an unsafe state. Physically locks levers in the signal box. Levers can only be moved if it is safe to do so. By 1890 an interlocking was a legal requirement for every train station in the UK.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
An Old Interlocking
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Futher Advances
Communications between railway stations was enabled around the same time. Originally this was using Morse code transmitted along telegraph lines. Another major advance was the introduction of the absolute block system. A piece of track between two signal boxes was called a block. This track could be in one of 3 states: Line blocked (Default/ Failsafe state) Line clear Train on line A simple device was used to communicate the state of the track between the two signal boxes
Andy Lawrence An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Human Error
The interlocking an the absolute block system created a much safer railway. However it was still susceptible to human error. For instance a signaller may forget that a train has been waiting at a signal for a long period of time. This resulted in the infamous Rule 55: If a train is stopped at a signal for more than 3 minutes then either the reman or the guard must walk to the signal box and formally remind the signaller of the presence of the train
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Track Circuits
This problem with human error was solved at the end of the 19th century. Electric track circuits enabled the detection of trains automatically. Track circuits were installed along whole segments of track.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Automatic Signals
This in turn made automatic signalling possible. A signal would automatically display a stop aspect if the track it controlled was occupied This type of signalling was called track circuit block signalling.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Electric Point Machines
Following the general trend of electrication in the railways points were electried. Electric point machines enabled points to be controlled remotely A point could be moved at the ick of a switch
A modern electric point
Andy Lawrence An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Electromechanical interlockings
This electrication called for the introduction of electromechanical interlockings These made use of relays Old style mechanical interlockings could take up a 2 storey building. These interlockings were much smaller.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Coloured Light Signals
In 1923 the rst coloured light signals were introduced. These gave the same indications day and night. Brighter than oil lamps Red Stop aspect. Yellow Proceed with caution. (Not called Amber!!!) Green Proceed aspect.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Coloured Light Signals
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Electrifying the Signal Box
Now that both the points and the lights were electried the big levers of the early railways became redundant. Electric switches could now control both points and lights. Power Frames: Contain some mechanical locking Control Panels: Fully electric
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Illuminated Diagrams
An illuminated diagram used lamps to indicate the position of trains
A panel with coloured lamps was introduced to display the descriptor of a train.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Routes
The introduction of switches over levers allowed for the introduction of Routes. Instead of setting all points and signals, an entrance and exit signal are selected. The control system automatically sets all points and signals in-between.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Remote Control Systems
Up to this point railway signalling was very cable intensive. 2 pairs of cable for every point and signal. Remote controlled systems could control a remote junction with just two pairs of cable. A signalling centre was connected to an on-site interlocking. Signalling centres controlled a large numbers of trains. Train numbers consisting of 4 characters were introduced e.g. 2P22.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Solid State Interlocking
Up until the 1980s the use of electronics for any safety critical system was forbidden. The behaviour of relays was well understood by engineers at the time. The behaviour of electronics was not. The advent of microprocessors caused a review of this situation. A new generation of solid state interlockings was designed. These were as least as safe or safer than their relay counterparts. Allowed for automatic route setting.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Automatic Safety Systems
More recently it has been possible to pass signalling information from the track to a train. This has led to the developement of: Automatic Warning System Provides a warning if the train approaches a non-proceed aspect. Applies the breaks if the warning is not acknowledged Automatic Train Protection System constantly calculates the maximum safe speed of the train Applies the breaks if the train exceeds the safe speed.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Where is the interlocking?
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Signalling Centre
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Trackside Equipment
Cables are housed in a cable route alongside the railway This is typically a concrete trough with a loose lid. If the cable route has to cross the railway then an undertrack crossing is used. These consist of two man hole covers and a small tunnel. The nal interface to any track side equipment is stored in an Apparatus Case also called a Location Case.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Trackside Equipment
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Rail Types
There are currently two dierent types of rail used in the UK. Bullhead Older design, placed in chairs. Flat-Bottom Modern design, easier to install, attached with clips.
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Bullhead Rail
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Bullhead Rail
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
The History of Railway Signalling
Flat Bottom Rail
Andy Lawrence
An Introduction to Railway Signalling and Equipment
Você também pode gostar
- Basic Concepts of SignallingDocumento285 páginasBasic Concepts of Signallingj320f samsungAinda não há avaliações
- Railroad Signal Specialist: Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandRailroad Signal Specialist: Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Signalling and InterlockingDocumento23 páginasSignalling and InterlockingRatheesh gv100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of SignallingDocumento92 páginasBasic Concepts of SignallingGopipavanAinda não há avaliações
- IRSE ARTICLE Signalling RelaysDocumento23 páginasIRSE ARTICLE Signalling Relaysmaxxand100% (1)
- The Development and Principles of UK SignallingDocumento62 páginasThe Development and Principles of UK SignallingesataydinAinda não há avaliações
- ERTMS ETCS Signalling System Revf PDFDocumento58 páginasERTMS ETCS Signalling System Revf PDFVikasAroraAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Computer Based InterlockingDocumento23 páginasAnalysis of Computer Based InterlockingSandeep Patalay80% (5)
- Signalling PrinciplesDocumento36 páginasSignalling PrincipleswranghelAinda não há avaliações
- S1Documento118 páginasS1Pratik_Ranjan_7382100% (4)
- IRSE Signalling Philosophy Review 2001Documento192 páginasIRSE Signalling Philosophy Review 2001atif_aman123Ainda não há avaliações
- Interlocking in Railway Signalling CirciutDocumento88 páginasInterlocking in Railway Signalling Circiutmanpreet singh100% (6)
- Railways Signalling Design Practices & Scope For StandardisationDocumento16 páginasRailways Signalling Design Practices & Scope For Standardisationgkdwivedy100% (1)
- Ertms EtcsDocumento32 páginasErtms EtcsAbdulhmeed MutalatAinda não há avaliações
- Railway SignallingDocumento46 páginasRailway Signallingtharun0% (1)
- BSPAC Book 1 The Basics of Railway SignallingDocumento51 páginasBSPAC Book 1 The Basics of Railway SignallingVuppala Srinivas0% (1)
- Railway SignallingDocumento27 páginasRailway SignallingSubin GeevargheseAinda não há avaliações
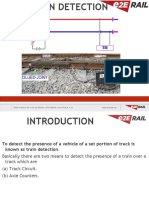
- Train Detection SystemDocumento26 páginasTrain Detection SystemrajunagaAinda não há avaliações
- EtoE Rail Training SoftDocumento278 páginasEtoE Rail Training Softvoru89Ainda não há avaliações
- Honkong Signalling - IRSE 2016 PDFDocumento36 páginasHonkong Signalling - IRSE 2016 PDFdidGivAinda não há avaliações
- LED SignalDocumento32 páginasLED SignalJatin ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- RATP Safety Approach For Railway Signalling Systems PDFDocumento25 páginasRATP Safety Approach For Railway Signalling Systems PDFpoketupi100% (4)
- Unit-IV Railway EngineeringDocumento177 páginasUnit-IV Railway Engineeringmshanraj100% (1)
- Rail TerminologyDocumento6 páginasRail Terminologyaleksandra_delo6374Ainda não há avaliações
- Microprocessors in Railway SignalingDocumento9 páginasMicroprocessors in Railway SignalingNECDET ÇİLİNGİRAinda não há avaliações
- ERTMS ETCS Signalling System RevFDocumento58 páginasERTMS ETCS Signalling System RevFzara100% (1)
- Railway SignallingDocumento118 páginasRailway Signallingjonathan30100% (1)
- Railway Signalling Railway SignallingDocumento14 páginasRailway Signalling Railway SignallingShahnawaz Haque100% (1)
- Technical Standards OCSDocumento76 páginasTechnical Standards OCStaarak143Ainda não há avaliações
- Track CircuitDocumento20 páginasTrack CircuitTanay P100% (1)
- Ansaldo ERTMSDocumento7 páginasAnsaldo ERTMSpassworldgerezAinda não há avaliações
- 1 S5J1 Route Relay InterlockingDocumento63 páginas1 S5J1 Route Relay InterlockingSantosh Dharphal100% (2)
- Sample Assessment QuestionsDocumento31 páginasSample Assessment QuestionsVidya SagarAinda não há avaliações
- Aftc - AbbDocumento48 páginasAftc - AbbFaizan Nazir100% (3)
- Digital Axle Counter Hand BookDocumento79 páginasDigital Axle Counter Hand BookrnvvprasadAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Railway Signals Points & Crossings (Turnouts)Documento43 páginasIndian Railway Signals Points & Crossings (Turnouts)ipsbassiAinda não há avaliações
- Track Design HandbookDocumento0 páginaTrack Design HandbookTilahun Sarka100% (2)
- Moving Block SignalDocumento6 páginasMoving Block SignalErlyn AlagonAinda não há avaliações
- Under The Guidance Of: Prof. Ajoya Ku Pradhan HOD Dept. of Electrical EngineeringDocumento27 páginasUnder The Guidance Of: Prof. Ajoya Ku Pradhan HOD Dept. of Electrical Engineeringishfaq222100% (1)
- Basics of Railway Principles (Signalling/Interlocking)Documento20 páginasBasics of Railway Principles (Signalling/Interlocking)Vishwanath S GargAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank S & T-02Documento29 páginasQuestion Bank S & T-02Nagesh GaliAinda não há avaliações
- Railway SignallingDocumento25 páginasRailway SignallingMuhammad Asim Raza100% (3)
- Lecture 23: Interlocking and Construction of Track: Dr. Ankit Gupta, Assistant ProfessorDocumento51 páginasLecture 23: Interlocking and Construction of Track: Dr. Ankit Gupta, Assistant ProfessorAastha Soni100% (1)
- Indian RailwaysDocumento22 páginasIndian RailwayssuyogAinda não há avaliações
- Communications Based Train Control (CBTC)Documento29 páginasCommunications Based Train Control (CBTC)v2brother63% (8)
- Advanced Train Operations PTC and CBTCDocumento35 páginasAdvanced Train Operations PTC and CBTCpoketupiAinda não há avaliações
- Axel Counter Summer Training ReportDocumento81 páginasAxel Counter Summer Training ReportMitil VarshneyAinda não há avaliações
- Railway Signalling Systems PDFDocumento103 páginasRailway Signalling Systems PDFAdetunji Taiwo67% (3)
- 7 - RB Etcs AcademyDocumento25 páginas7 - RB Etcs Academyhay902100% (1)
- Signalling Design Hand BookDocumento102 páginasSignalling Design Hand Bookmallikarjuna100% (2)
- Principles and Concepts of InterlockingDocumento31 páginasPrinciples and Concepts of InterlockingMohd. ShafeequeAinda não há avaliações
- In The Beginning .: Railway Signal and Automatic Track ChangeDocumento14 páginasIn The Beginning .: Railway Signal and Automatic Track ChangenikhithaAinda não há avaliações
- CDC-Booklet On S&TDocumento136 páginasCDC-Booklet On S&TAbhijitAinda não há avaliações
- Sig Telcom PDFDocumento82 páginasSig Telcom PDFFALAN TONAinda não há avaliações
- A History of Railway SignallingDocumento18 páginasA History of Railway SignallingWindow SeatAinda não há avaliações
- AWS Edited 23 JuneDocumento6 páginasAWS Edited 23 JuneVishwanath PujariAinda não há avaliações
- Positive Train Control: Wireless PTC Technology Outline White PaperDocumento28 páginasPositive Train Control: Wireless PTC Technology Outline White Papersudhirdash7311Ainda não há avaliações
- A History of Railway Signalling From The Bobby To The Balise (Stephen Clark)Documento20 páginasA History of Railway Signalling From The Bobby To The Balise (Stephen Clark)r_berthetAinda não há avaliações
- Virtual Tutor: Page 1 of 1Documento1 páginaVirtual Tutor: Page 1 of 1Nitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- UART Interfacing With 8051 PrimerDocumento10 páginasUART Interfacing With 8051 PrimerNitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Sandeepalani Course of 16 WeeksDocumento3 páginasSandeepalani Course of 16 WeeksNitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Festo PLC Basic Level TP301-218Documento218 páginasFesto PLC Basic Level TP301-218Marcos Aldana Villalda0% (1)
- 331 Ning B Ed Advanced Train Control SystemsDocumento167 páginas331 Ning B Ed Advanced Train Control SystemsNitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- 10d FormDocumento7 páginas10d FormNitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Customer SatisfactionDocumento21 páginasCustomer SatisfactionNitesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Audio Speech DeliveryDocumento2 páginasRubric For Audio Speech DeliveryMarie Sol PanganAinda não há avaliações
- 1013CCJ - T3 2019 - Assessment 2 - CompleteDocumento5 páginas1013CCJ - T3 2019 - Assessment 2 - CompleteGeorgie FriedrichsAinda não há avaliações
- Feb-May SBI StatementDocumento2 páginasFeb-May SBI StatementAshutosh PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Bhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingDocumento14 páginasBhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingJai MenDparaAinda não há avaliações
- Neural Computing and ApplicationsDocumento49 páginasNeural Computing and ApplicationsLine PhamAinda não há avaliações
- RTD IncotestDocumento2 páginasRTD IncotestJabari KaneAinda não há avaliações
- Nielsen Report - The New Trend Among Indonesia's NetizensDocumento20 páginasNielsen Report - The New Trend Among Indonesia's NetizensMarsha ImaniaraAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Risk Opportunity RegisterDocumento4 páginas3 - Risk Opportunity RegisterArmando CorboAinda não há avaliações
- Milestone BillingDocumento3 páginasMilestone BillingJagadeesh Kumar RayuduAinda não há avaliações
- All Siae Skus: SF Product Name SIAE Product Code Descrip:on Availability Product Family Unit LIST Price ($)Documento7 páginasAll Siae Skus: SF Product Name SIAE Product Code Descrip:on Availability Product Family Unit LIST Price ($)Emerson Mayon SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Smart Cockpit System Questions - FlattenedDocumento85 páginasSmart Cockpit System Questions - FlattenedBarut Brkk100% (4)
- Master Thesis On Smart GridDocumento6 páginasMaster Thesis On Smart Gridsandraandersondesmoines100% (2)
- Max9924 Max9927Documento23 páginasMax9924 Max9927someone elseAinda não há avaliações
- Topfast BRAND Catalogue Ingco 2021 MayDocumento116 páginasTopfast BRAND Catalogue Ingco 2021 MayMoh AwadAinda não há avaliações
- General Introduction: 1.1 What Is Manufacturing (MFG) ?Documento19 páginasGeneral Introduction: 1.1 What Is Manufacturing (MFG) ?Mohammed AbushammalaAinda não há avaliações
- Contract 1 ProjectDocumento21 páginasContract 1 ProjectAditi BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Comsol - Guidelines For Modeling Rotating Machines in 3DDocumento30 páginasComsol - Guidelines For Modeling Rotating Machines in 3DtiberiupazaraAinda não há avaliações
- Consequences of Self-Handicapping: Effects On Coping, Academic Performance, and AdjustmentDocumento11 páginasConsequences of Self-Handicapping: Effects On Coping, Academic Performance, and AdjustmentAlliah Kate SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- IMS - Integrated Management System Implementation Steps-Sterling - Rev00-240914 PDFDocumento28 páginasIMS - Integrated Management System Implementation Steps-Sterling - Rev00-240914 PDFNorman AinomugishaAinda não há avaliações
- Research Design: An Overview: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento28 páginasResearch Design: An Overview: Multiple Choice QuestionsBashayerhmmAinda não há avaliações
- Reclaimer PDFDocumento8 páginasReclaimer PDFSiti NurhidayatiAinda não há avaliações
- Vacon NX, Non-Regenerative Front End FI9 UD01217B PDFDocumento48 páginasVacon NX, Non-Regenerative Front End FI9 UD01217B PDFSilvian IonescuAinda não há avaliações
- Read The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDocumento5 páginasRead The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDavid GainesAinda não há avaliações
- 103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Documento11 páginas103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Elok KurniaAinda não há avaliações
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT (What Is Personal Development?)Documento37 páginasPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT (What Is Personal Development?)Ronafe Roncal GibaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Templates in C++Documento16 páginasIntroduction To Templates in C++hammarbytpAinda não há avaliações
- Nc4 Student BookDocumento128 páginasNc4 Student Book178798156Ainda não há avaliações
- Building g5Documento45 páginasBuilding g5ammarsteel68Ainda não há avaliações
- Prof Ed 3 Module 1Documento9 páginasProf Ed 3 Module 1alexa dawatAinda não há avaliações
- Cot Observation ToolDocumento14 páginasCot Observation ToolArnoldBaladjayAinda não há avaliações
- University of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesNo EverandUniversity of Chicago Press Fall 2009 Distributed TitlesNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)