Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
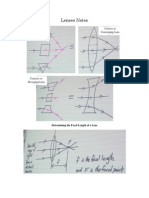
Microbiology Notes
Enviado por
Athena HuynhDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Microbiology Notes
Enviado por
Athena HuynhDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Microbiology Notes
Viruses Viruses are non-cellular structures that are capable of reproduction, but only when they use a cells machinery. Common viruses cause the flu, mumps, measles, smallpox, Hepatitis, and HIV. Some are believed to cause cancer. They are 5-200 nm long and electron microscopes are needed to see them. Head Prokaryotic Cells: 1000 - 10 000 nm in size Eukaryotic Cells: 10 000 - 1 000 000 nm in size Viruses are made of at least 2 parts: 1. *an outer coat of protein - capsid 2. *an inner core of nucleic acid - RNA and DNA 3. sometimes they have a disguise, an outer envelope made of membrane Viruses are known for their ability to attack and kill cells. They are able to kill or hurt plants, animals, fungi, or even bacteria. Viruses can attack only 1 type of cell; they are very specific. The head of the virus holds the information. The tail of the virus is for attachment. All viruses can do the lytic cycle. Overview of the Lytic Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. the virus enters the cell it makes millions of copies of itself and lyses the cell Attachment (and injection of viral DNA) Synthesis (Replication) of Viral Parts Combining of Viral Parts Lysis/Exocytosis + Tail = Capsid
What is lysis? the cell wall or membrane bursts and releases new viruses
What is exocytosis? exo = exit cyt = cell osis = process
some viruses (eg. HIV) trick the cell into exocytosing it this will allow the virus to be coated in membrane see diagram below
Lysogenic Cycle Some viruses can do the lysogenic cycle: 1. Instead of killing the cell, it joins the cells nucleus. 2. When joined to the cells nucleus, it is called a prophage. 3. Both daughter cells have the virus. When unfavourable environmental conditions occur (like sudden changes in temperature and availability of nutrients), the prophage goes into the lytic cycle. For example, you get cold sores when stressed. The prophage may block other viruses from coming into the cell, or it could add useful DNA to the host cell. For example, the lambda virus allows E. Coli (a bacteria) to make important amino acids. Immune System how your body fights off diseases and infection two main types of defenses: 1. Non-specific defenses are defenses that work on all types of bacteria: skin (best defense) - physical barrier that prevents bacteria from getting into blood earwax - gooey stuff that traps bacteria nose hair
lysozymes - specialized enzymes in tears stomach acid - kills a lot of bacteria normal flora - good bacteria that block bad bacteria from getting into your body Inside your body you have many different types of white blood cells. Phagocytes, macrophage, and monocytes are non-specific. They eat pathogens (bad things in your body that make you sick) in a process called phagocytosis. 2. There are 3 main types of cells involved in the specific defenses: Killer T-Cells kill your own cells that have been infected. This prevents millions of viruses from being released. B-Cells make proteins called antibodies. Antibodies will surround the virus and make it unable to attach to cells. They respond to certain antigens (anything foreign in your body) on the surface of the virus.
Helper T-Cells warn other cells that the body is under attack. HIV kills helper T-cells so that the immune system never fully activates. HIV is also tricky because it changes its shape and has a membrane disguise.
Why can you not get chickenpox or another disease twice? After you have a successful primary response to an antigen, your body makes memory cells. Memory cells make antibodies right away and do not need confirmation by helper T-cells. This means the virus will be caught before you get sick. A primary response needs 5-6 days to kick in and make antibodies, and you might be sick for about 3 days while your body fights the pathogens. A secondary response will activate in about 2 days, and you will not get sick. How do vaccinations work? you give someone dead or weakened virus (or bacteria) to help them make a primary response and memory cells this will protect you for 10-15 years first vaccination was for smallpox using a similar antigen in cowpox
Allergies are when the body overreacts to a non-harmful antigen (eg. dust, cat hair). Your body releases histamines which cause swelling and excess fluid to come to the area.
Você também pode gostar
- DR - Gold Immunology NotesDocumento11 páginasDR - Gold Immunology NotesAaron PhuaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Lecture NotesDocumento95 páginasMicrobiology Lecture NotesRabia Haider67% (3)
- Birth of The Limitless Ancient EgyptDocumento24 páginasBirth of The Limitless Ancient EgyptAnonymous lsnDTjv100% (2)
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocumento34 páginasAntimicrobial Agentssuchi_mohan08Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento14 páginasCardiovascular SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- BMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationDocumento6 páginasBMI1014: Chapter 2 - Bacteria-Morphology and ClassificationAkmal Adib FadzilAinda não há avaliações
- Basic MicrobiologyDocumento35 páginasBasic MicrobiologyOsama Bakheet100% (2)
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocumento12 páginasThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- 1-Bacterial MorphologyDocumento20 páginas1-Bacterial MorphologyMuzammil NawazAinda não há avaliações
- MicrobiologyDocumento45 páginasMicrobiologyStephen Niroshan Xavier67% (3)
- All BacteriaDocumento15 páginasAll Bacteriae100% (1)
- Microb Summary 3314Documento28 páginasMicrob Summary 3314KPAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology NotesDocumento3 páginasMicrobiology NotesAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Microbiology ReviewerDocumento8 páginasMicrobiology ReviewerSteph Vee100% (6)
- MicrobiologyDocumento44 páginasMicrobiologyBonnie Hardy100% (1)
- PathologyDocumento184 páginasPathologymaximazarov100% (1)
- Lecture Notes BacteriologyDocumento138 páginasLecture Notes BacteriologyJunalyn Banawe Ocden100% (2)
- Fundamental of Microbiology Notes FinalDocumento111 páginasFundamental of Microbiology Notes Finalshi vaniAinda não há avaliações
- Complete MicroBiology NOTESDocumento55 páginasComplete MicroBiology NOTESrida100% (4)
- Microbiology Lecture NotesDocumento116 páginasMicrobiology Lecture NotesDodge StuffAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Boards Lecture 1Documento48 páginasMicrobiology Boards Lecture 1Fait Hee100% (3)
- Microbiology SummaryDocumento9 páginasMicrobiology SummaryMargaretha IreneAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in MicrobiologyDocumento25 páginasReviewer in MicrobiologyMicole Manahan100% (1)
- Digestive System and NutritionDocumento6 páginasDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Chpater 1 MicrobiologyDocumento7 páginasChpater 1 MicrobiologyRoma Blaise G FloresAinda não há avaliações
- The Immune SystemDocumento15 páginasThe Immune SystemAslak Torgersen100% (1)
- S. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusDocumento14 páginasS. Aureus, Cons: S.Epidermidis, Cons: S.SaprophyticusMugiAinda não há avaliações
- Instant Notes On Microbiology For Cerficate Level StudentDocumento33 páginasInstant Notes On Microbiology For Cerficate Level StudentYogendra ShahAinda não há avaliações
- FAQ in MicrobiologyDocumento117 páginasFAQ in MicrobiologyVenkatesh Arumugam100% (1)
- Parasitology Notes AlishyaDocumento100 páginasParasitology Notes AlishyaSarah Zwany Goodman100% (1)
- Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisNo EverandPathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisMukesh SamantAinda não há avaliações
- Immunology NotesDocumento27 páginasImmunology Notescomputerlois88% (8)
- Microbial Culture MediaDocumento9 páginasMicrobial Culture Mediaማላያላም ማላያላም100% (2)
- Microbiology: Higher Secondary-First YearDocumento140 páginasMicrobiology: Higher Secondary-First Yearwiranchana-na3014100% (3)
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocumento14 páginasMicrobiology and Parasitologymadam joyAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Micro ChartDocumento6 páginasDetailed Micro Chartmatt100% (1)
- LP Bacteria ChartDocumento21 páginasLP Bacteria ChartTaman HoangAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Microbial Physiology and GeneticsDocumento47 páginasChapter 7 Microbial Physiology and GeneticsJhane Kimberly A. RustiaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology and Parasitology NotesDocumento13 páginasMicrobiology and Parasitology NotesJomar Tibig100% (1)
- BacteriophagesDocumento35 páginasBacteriophagestummalapalli venkateswara raoAinda não há avaliações
- The Human Immune System: VideoDocumento31 páginasThe Human Immune System: VideoCrystal Joy RebelloAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Final Exam MaterialDocumento37 páginasMicrobiology Final Exam MaterialEdgar Mandeng100% (1)
- Microbiology NotesDocumento83 páginasMicrobiology NotesPauline Añes100% (1)
- MicrobiologyDocumento17 páginasMicrobiologyMompati Letsweletse100% (3)
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocumento79 páginasIntroduction To ParasitologyLeeShauran100% (7)
- CHAPTER 1.ppt-2Documento49 páginasCHAPTER 1.ppt-2Gemechis MergaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 11 - Antimicrobial ChemotherapyDocumento24 páginasLecture 11 - Antimicrobial Chemotherapyapi-3703352100% (2)
- BacteriologyDocumento75 páginasBacteriologyHoward BarlomentoAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Lecture - 05 Bacterial GeneticsDocumento37 páginasMicrobiology Lecture - 05 Bacterial GeneticsChris Queiklin50% (2)
- Microbiology Quiz: Answer All Questions in Two Minutes To Win A Lollypop!Documento13 páginasMicrobiology Quiz: Answer All Questions in Two Minutes To Win A Lollypop!SwaraAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandMedical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology NotesDocumento177 páginasMicrobiology NotesMarichu Rogas91% (11)
- Microbiology Study GuideDocumento9 páginasMicrobiology Study GuideMonica E. AgogoAinda não há avaliações
- Free Ebook - Microbiology Review Notes by MedpgnotesDocumento103 páginasFree Ebook - Microbiology Review Notes by Medpgnotesdr dixit100% (1)
- ParasitologyDocumento15 páginasParasitologyamelia_ericaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of MicrobiologyDocumento9 páginasIntroduction of MicrobiologyRahul PalsAinda não há avaliações
- Morphology of Bacteria & Its CharacteristicsDocumento13 páginasMorphology of Bacteria & Its CharacteristicsMonika Kshetri100% (2)
- Microbiology Antibiotics AntimicrobialDocumento12 páginasMicrobiology Antibiotics AntimicrobialSandeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Quiz QuestionsDocumento19 páginasMicrobiology Quiz QuestionsAkram NiaziAinda não há avaliações
- Staphylococci: Streptococcus PyogenesDocumento20 páginasStaphylococci: Streptococcus PyogenesPharmacy2015100% (2)
- Acid Fast StainingDocumento4 páginasAcid Fast Stainingchaudhary TahiraliAinda não há avaliações
- The Human Immune SystemDocumento24 páginasThe Human Immune Systemmilka berhaneAinda não há avaliações
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious Disease: PathogensDocumento5 páginas6.3 Defence Against Infectious Disease: PathogensantonioolufAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum PhysicsDocumento3 páginasQuantum PhysicsAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocumento14 páginasKingdom AnimaliaAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion: Q: in Which Direction Is TheDocumento6 páginasCircular Motion: Q: in Which Direction Is TheAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics: Some DefinitionsDocumento6 páginasThermodynamics: Some DefinitionsAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowDocumento13 páginasKingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Heat, Temperature, and Thermal Energy NotesDocumento4 páginasHeat, Temperature, and Thermal Energy NotesAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Government of Canada: Structure and FunctionDocumento7 páginasGovernment of Canada: Structure and FunctionAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Kingdom MoneraDocumento3 páginasKingdom MoneraAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Lenses Notes: Convex or Converging LensDocumento9 páginasLenses Notes: Convex or Converging LensAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Arguments For and Against Quebec SeparationDocumento2 páginasArguments For and Against Quebec SeparationAthena Huynh25% (4)
- Trudeau and Canada - Defecit and DeceitDocumento4 páginasTrudeau and Canada - Defecit and DeceitAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Bagh College of Arts and Modern Sciences: 1 GST Test ObjectiveDocumento2 páginasBagh College of Arts and Modern Sciences: 1 GST Test ObjectiveAbdul Waheed KhawajaAinda não há avaliações
- I. Observation of Virus On Bacteria With Plaque MethodDocumento9 páginasI. Observation of Virus On Bacteria With Plaque MethodDevina AlifahAinda não há avaliações
- Bi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsDocumento39 páginasBi 341 Chapter 7 Bacterial GeneticsMATHIXAinda não há avaliações
- Jipmer 2015 Solved QPDocumento67 páginasJipmer 2015 Solved QPS Balagopal Sivaprakasam67% (3)
- Virology NotesDocumento46 páginasVirology NotesJoseph ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 19 VirusesDocumento8 páginasChapter 19 Virusesjpayne655Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocumento211 páginasIntroduction To MicrobiologyGaurav JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Group 4 Poster Template bl100 Spring 2018-3Documento1 páginaGroup 4 Poster Template bl100 Spring 2018-3api-528179516Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12-13 HomeworkDocumento7 páginasChapter 12-13 HomeworkKvn4N6Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 9 - 13.01.2023Documento33 páginasLecture 9 - 13.01.2023Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatAinda não há avaliações
- CH 15-Microbial Mechanisms of PathogenicityDocumento64 páginasCH 15-Microbial Mechanisms of PathogenicitySisi Zhang100% (1)
- Biology 10 Chapter 6 (Checked) PDFDocumento64 páginasBiology 10 Chapter 6 (Checked) PDFJames SoeAinda não há avaliações
- Viral Latency and Immune EvasionDocumento11 páginasViral Latency and Immune Evasionማላያላም ማላያላም100% (1)
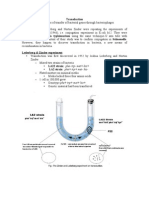
- Topic 6 TransductionDocumento17 páginasTopic 6 TransductionnsjunnarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Microbiology The Human Experience First Edition First EditionDocumento14 páginasTest Bank For Microbiology The Human Experience First Edition First Editionkimberlyjensen19071984omn100% (29)
- BacteriophagesDocumento25 páginasBacteriophagesHamza KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Investigating The Efficacy of Nisin When Combined With First Line Antibiotics in The Treatment of MRSA 252Documento47 páginasInvestigating The Efficacy of Nisin When Combined With First Line Antibiotics in The Treatment of MRSA 252Joe CloAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteriophage Research: Early History: William C. SummersDocumento24 páginasBacteriophage Research: Early History: William C. Summersjoaojoaomendes6846Ainda não há avaliações
- VKM Draft Trans Duct IonDocumento12 páginasVKM Draft Trans Duct IonvinodkumarmishraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 21 Model OrganismDocumento100 páginasChapter 21 Model OrganismA.F. ShuvoAinda não há avaliações
- Lytic CycleDocumento3 páginasLytic CycleOPSAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryDocumento90 páginas3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryMajd HallakAinda não há avaliações
- Viral Symbiosis in The Origins and Evolution of Life With A Particular Focus On The Placental MammalsDocumento22 páginasViral Symbiosis in The Origins and Evolution of Life With A Particular Focus On The Placental MammalsFernandoAinda não há avaliações
- Lect Notes - Bacterial Genetics 2012-2013Documento10 páginasLect Notes - Bacterial Genetics 2012-2013CristinaConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- BIO CH21 Foundations PDFDocumento15 páginasBIO CH21 Foundations PDFKristina CatomerisAinda não há avaliações