Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Sow For:: Pupil Track 1
Enviado por
Jonathan RichardsonTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sow For:: Pupil Track 1
Enviado por
Jonathan RichardsonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SoW FOR PUPIL TRACK 1:
PLANT BIOLOGY
~ SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 2012 ~ Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Plant Structure Gas Exchange in Plants Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis The Fate of the End Products of Photosynthesis Conditions for Plant Growth Plants for Food 1 Plants for Food 2
YEAR 8 BIOLOGY
Lesson 4
Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 7
Lesson 1: Plant Structure
Lesson Objectives: 1. That plants are comprised of cells, tissues and organs. 2. That plants make their own food by photosynthesis. Starter Remind pupils of structure of Cells, Tissues and Organs (brainstorm those in humans and plants). Main Body Activity 1: PowerPoint Presentation (PPP) show presentation (Lesson_1.ppt) and discuss with pupils as they fill in p1-3 in booklet Activity 2: Revision of a balanced diet for humans. Name the 7 requirements. The same requirements are needed by plants for much the same reasons. Food to respire and food to make new cells (remember plants dont need roughage as their cell walls are roughage.) Plants differ because they can make their own food by photosynthesis. Notes in books. Plenary Tie it all together. Plant structure is designed to obtain the requirements for photosynthesis and to reproduce. Different plant shapes are different methods of doing this and evolution has occurred by competition to give all the modern types of plant. Homework Word search (in booklet): students answer the questions on p4 and then find the words. Year 8 Biology Pupil Track 1 Sep-Oct 2011
TIMING
RESOURCES/ NOTES
0-5min
545min
Riley: Biology Now! textbook and/ or Coordinated Science: Biology textbook Worksheet in filing cabinet next to pigeon holes:
1. Plant Structure
45-50 min
PowerPoint presentations and videos in R:/Science/KS3/Y 8/ Biology/Lesson Resources.
Lesson 2: Gas Exchange in Plants
Lesson Objectives: 1. What is meant by photosynthesis and how it is used by plants to make food. 2. The word equation for photosynthesis. 3. That photosynthesis requires light and how this can be shown experimentally.
TIMING
Year 8 Biology Pupil Track 1 Sep-Oct 2011
010min 1045min
45-50 min
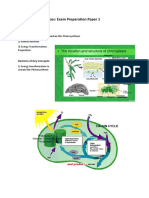
Starter Optional: go over homework (word search). Set up activity 1 while introducing the lesson (this experiment needs about 55mins to work). Introduce the idea that all living cells respire all the time (MRSGREN). Plant cells are no exception. Respiration requires oxygen and produces carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis is the way a plant obtains its nutrition and this requires carbon dioxide and produces oxygen. This reaction requires light energy. Main Body Activity 1: An experiment to show how carbon dioxide exchanges in the light and dark (see p5 in booklet). Activity 2: Notes in exercise books: General heading: PLANT NUTRITION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Brief introduction as the way the plant obtains nutrition. Give word equation: Carbon dioxide+Water+Light Energy Chlorophyll Glucose+Oxygen Respiration is the way the plant obtains the energy from the glucose made in photosynthesis. Give word equation: Glucose+Oxygen Carbon dioxide+Water+Energy Sub heading: Gas Exchange in a plant. Gas exchange is by diffusion. Gases pass through stomata in leaves and very small holes called lenticels in the woody parts of stems and roots Air must be present in the soil for the roots to respire. Over-watered pot plants die due to lack of air to the roots; animals such as earthworms aerate the soil. Touch on the mechanism by which stomata open and close due to osmosis in the guard cells if time Plenary Show and discuss results of experiment; pupils to answer questions on this experiment in their booklets (p6). Homework Revise the equations for photosynthesis and respiration for a mini-test at the start of next lesson/ finish questions as above.
LESSON_2: Practical Tips Method Set up at different distances from a single constant light source, a pair of clear glass airtight bottles as follows: o Bottle 1: control - red-orange equilibrated bicarbonate indicator. o Bottle 2: experiment - same volume of red-orange indicator with Elodea. All bottles have the same volume of equilibrated indicator/ the samples of Elodea are from the same plant and same mass/ temperature to remain constant at room temperature, 20C. Leave the set up for an hour. Passing fresh air through the indicator makes its carbon dioxide concentration equal to the atmosphere - it is said to be 'equilibrated' and has a red-orange colour. The colour will change if the pH changes. Loss or gain of CO2 changes the pH of the indicator because CO2 is reasonably soluble in water forming carbonic acid. Therefore bicarbonate indicator responds to changes in its carbon dioxide concentration. If equilibrated indicator gains CO2 (Elodea adds it to water during respiration) it becomes more acidic turning yellow. If equilibrated indicator loses CO2 (Elodea removes it from water during photosynthesis) it becomes more basic turning purple. Results Control Results: the indicator colour has not changed, all red-orange. The plant at compensation point is still red-orange - unchanged indicator. P = R: no loss or gain of CO2 by the indicator. The plants closer to the light will have turned the indicator purple. The light intensity is greater than compensation point. P > R. Indicator lost carbon dioxide to the plant so the indicator went more basic. The plants further from the light will have turned the indicator yellow. Light intensity is less than compensation point. P < R. Indicator gained carbon dioxide from the plant so the indicator went more acidic.
RESOURCES/ NOTES
Riley: Biology Now! textbook and/ or Coordinated Science: Biology textbook Worksheets (x10) in filing cabinet next to pigeon holes on the subject of Photosynthesis and one on the subject of Gas Exchange. PowerPoint presentations and videos in R:/Science/KS3/Y 8/ Biology/Lesson Resources.
Information for Technician
Equipment for teacher demonstration: Lamp
2 clear, airtight bottles Red-orange equilibrated bicarbonate indicator Elodea
AT THIS POINT IN THE TRACK IT WOULD BE AN APPROPRIATE TIME TO SET THE 20-MARK COMMON ASSESSMENT, Investigating the Effect of Light Intensity on Photosynthesis Rate. THE PUPIL GUIDANCE SHEET AND MARK SCHEMES ARE SHOWN BELOW; PLEASE ASK DAVID M FOR COPIES OF BOTH.
Lesson 3: Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis
Lesson Objectives: 1. Revise that photosynthesis requires light and how this can be shown experimentally. 2. That starch is the storage molecule used by plants as food and that this can be tested for using iodine 3. That chlorophyll, the green pigment, is used by plants to absorb light for photosynthesis. Starter TIMING 1. Quick test on the equations for photosynthesis and respiration; use this to remind 0-5min pupils of the processes. 2. Go over questions (p6) based on gas exchange experiment from last lesson: 1. The tube in the light should have turned a darker red. 2. The tube in the dark should have turned a lighter red (yellow). 3. There should be no change in the tubes without elodea 4. The plant took up carbon dioxide in the light. The plant gave out carbon dioxide in the dark. 5. Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide. Respiration produces carbon dioxide. 6. The two tubes are a control to make sure there are no colour changes without the plant. Main Body 51. Class practical of starch test 45min Discussion of starch as an energy store used by plants. Go through method on p6-7 and explain certain aspects (e.g. we need to boil the leaf such that the iodine can penetrate the waxy cuticle) Highlight safety (especially the requirement to turn off Bunsen burners before ethanol is used consider turning the gas key after water has boiled for all pupils and provide ethanol only when there are no naked flames!). Advise pupils that once finished they should pack away and answer questions on p8 in their booklet 2. Go over answers on p8 Plenary 45-50 Summary notes and discussion based on lesson: Chlorophyll is necessary for min photosynthesis. Include: The use of starch by plants to store energy Basic process of starch test How a starch test on variegated leaves shows that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis Homework Pupils to complete the exercises relating to variegated plants in the booklet (p9).
LESSON_3: Practical Tips Method Place a plant with variegated leaves in darkness for at least 24 hours - this de-starches the leaves. Place the plant into good light for six hours at room temperature (20C) to ensure a high rate of photosynthesis. Compare the iodine stain pattern to the original 'green/non-green' pattern. Place the leaf in boiling water - kills the leaf stopping all biochemical activity and breaks open the cells making easier the removal of chlorophyll and the entry of iodine stain. Place the leaf in boiling alcohol - this removes the green chlorophyll from the leaf and so the colour of the iodine stain, when added to the leaf, can be clearly seen. The alcohol is not to be heated by a Bunsen flame. Heat the alcohol in a water bath of very hot water. Place the leaf into boiling water - alcohol made the leaf brittle and unreceptive to the iodine stain, the alcohol is replaced with water softening the leaf. Apply iodine solution to the leaf - to check for the presence or absence of starch. A blue-black colour indicates starch is present (iodine enters the spiral starch molecule changing its colour). A yellow-brown, the colour of the iodine solution, indicates that starch is absent. The iodine stain is iodine dissolved in a solution of potassium iodide.
Year 8 Biology Pupil Track 1 Sep-Oct 2011
RESOURCES/ NOTES
Riley: Biology Now! textbook and/ or Coordinated Science: Biology textbook Worksheets (x10) in filing cabinet next to pigeon holes on the subject of Photosynthesis and one on the subject of Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis. PowerPoint presentations and videos in R:/Science/KS3/Y 8/ Biology/Lesson Resources.
Results Chlorophyll: green parts blue-black with iodine starch present photosynthesis occurred. No Chlorophyll: white parts yellow-brown with iodine starch absent photosynthesis did not take place. Therefore, chlorophyll is necessary, as photosynthesis only occurs when it is present.
Information for Technician
Equipment for class practical (x13):
Você também pode gostar
- Teacher Notes Energy (STD)Documento37 páginasTeacher Notes Energy (STD)Bernard ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Noah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodNo EverandNoah's Fascinating World of STEAM Experiments: Chemical Reactions: A Junior Scientist's Lab Notebook for Learning Scientific MethodAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis - The Practicals 16 APRIL 2014 Lesson DescriptionDocumento9 páginasPhotosynthesis - The Practicals 16 APRIL 2014 Lesson DescriptionKeneilweAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 13 PhotosynthesisDocumento9 páginasLab 13 PhotosynthesispreciousalabiteAinda não há avaliações
- Sci+TG Module 4 Acid&BasesDocumento10 páginasSci+TG Module 4 Acid&BasesRjvm Net Ca Fe100% (1)
- Science: Photosynthesis: Plant'S Food Making ProcessDocumento11 páginasScience: Photosynthesis: Plant'S Food Making ProcessMark Ivan Abriza100% (1)
- BTB PS CR LabDocumento7 páginasBTB PS CR LabKathy XiangAinda não há avaliações
- Factors That Affect The Rate of PhotosynthesisDocumento7 páginasFactors That Affect The Rate of PhotosynthesisSamantha Jesi Shania Estrada100% (1)
- GenBio Q2 M1Documento16 páginasGenBio Q2 M1Allaine BenitezAinda não há avaliações
- GMH SCI9Documento6 páginasGMH SCI9Siobhanie ZianAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthesisDocumento10 páginasPhotosynthesisRaazia Arbab - 91028/TCHR/BSSCAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainable Ecosystems and Human ActivityDocumento5 páginasSustainable Ecosystems and Human ActivityMarina XuAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis in ColorsDocumento3 páginasPhotosynthesis in ColorsLorence VillaminAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Handout-01: NSC 1110 - BiologyDocumento7 páginasLaboratory Handout-01: NSC 1110 - BiologyEmsy MukukaAinda não há avaliações
- Bamboo: Class: Class 7 - Section A Subject: Science Chapter: Nutrition in Plants TitleDocumento2 páginasBamboo: Class: Class 7 - Section A Subject: Science Chapter: Nutrition in Plants TitleArvind Murali100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - How CO2 is Released During RespirationDocumento7 páginasCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - How CO2 is Released During RespirationSumit BissuAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Edexcel (9-1) Biology Unit 3 Chapter 10 Plants and FoodDocumento24 páginasIGCSE Edexcel (9-1) Biology Unit 3 Chapter 10 Plants and FoodMostafa A MansiAinda não há avaliações
- Elodea and Photosynthesis Lab AnswersDocumento2 páginasElodea and Photosynthesis Lab AnswersLilOgLemon 1010% (1)
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Documento25 páginasStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Saraswati PAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Respiration BIOLOGY FORM 4Documento34 páginasPlant Respiration BIOLOGY FORM 4sitimarziahAinda não há avaliações
- 6.1a Experiments To Investigate PhotosynthesisDocumento21 páginas6.1a Experiments To Investigate PhotosynthesisDea TjahyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular RespirationDocumento33 páginasCellular Respirationapi-202349222100% (1)
- Biology Lab 5 FinalDocumento5 páginasBiology Lab 5 FinalAlice Lin75% (12)
- Carbon Dioxide and Living ThingsDocumento6 páginasCarbon Dioxide and Living ThingsDeepa RaniAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE 6 Plant Nutrition 2020Documento35 páginasIGCSE 6 Plant Nutrition 2020Harry is the coolestAinda não há avaliações
- Testing For Starch With IodineDocumento2 páginasTesting For Starch With IodineKharyle CharisseAinda não há avaliações
- Plant NutririonDocumento21 páginasPlant NutririonMuhammad Hassan TariqAinda não há avaliações
- Cot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Documento9 páginasCot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Marlon S. Baranggan100% (3)
- Sugar Makers: Energy Harnessed by Photosynthesis Powers Ecosystems, Machines, and Even Our Own BodiesDocumento8 páginasSugar Makers: Energy Harnessed by Photosynthesis Powers Ecosystems, Machines, and Even Our Own BodiesAurora ÇizmjaAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis TheoryDocumento6 páginasPhotosynthesis TheorySamia KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Alex DDocumento5 páginasAlex Dapi-612845363Ainda não há avaliações
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 8.v1Documento50 páginasScheme of Work Science Stage 8.v1Sue Adames de Velasco100% (2)
- The Role of Light and Carbon Dioxide in PhotosynthesisDocumento10 páginasThe Role of Light and Carbon Dioxide in PhotosynthesisEPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis and Food: The Process and EquationsDocumento73 páginasPhotosynthesis and Food: The Process and EquationsMadhavi KapadiaAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Task 1Documento7 páginasLearning Task 1Ron StephenAinda não há avaliações
- X_EM_LAB MANUALDocumento16 páginasX_EM_LAB MANUALrubeel.bcAinda não há avaliações
- Instructor's Copy Lab Worksheet - Let The Sun inDocumento2 páginasInstructor's Copy Lab Worksheet - Let The Sun injohnmccauleyAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Chem AppleDocumento5 páginasLab Chem AppleMaryrose CatubigAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Biology PracticalDocumento9 páginasGCSE Biology Practicalcoffee beanAinda não há avaliações
- Quarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 1: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesDocumento4 páginasQuarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 1: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesMonica SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- Life ProcessesDocumento36 páginasLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- Sec1 Photosynthesis 1 StudenthandoutDocumento5 páginasSec1 Photosynthesis 1 StudenthandoutqorestAinda não há avaliações
- Building Lava Lamps (STEAM ActivityDocumento2 páginasBuilding Lava Lamps (STEAM ActivityjoeyAinda não há avaliações
- PhotosynthicesDocumento7 páginasPhotosynthicesMoona NoorAinda não há avaliações
- 10th Biology NotesDocumento56 páginas10th Biology NotesJYOTHI D100% (1)
- K01582 - 20180302121452 - Lab ManualDocumento32 páginasK01582 - 20180302121452 - Lab ManualNur Hana SyamsulAinda não há avaliações
- Labbio - Tue - Lab Report 4 - Group 5 TuesdayDocumento6 páginasLabbio - Tue - Lab Report 4 - Group 5 TuesdayVân Anh Nguyễn NgọcAinda não há avaliações
- Matric Exam Paper 100187Documento10 páginasMatric Exam Paper 100187Charles OssuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Botany LabDocumento14 páginasBotany LabHorang HaeAinda não há avaliações
- Values: Cooperation, Industriousness: Science and Health VDocumento2 páginasValues: Cooperation, Industriousness: Science and Health VRichardDumlaoAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Nutrition FullDocumento20 páginasPlant Nutrition FullArif UllahAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Laboratory 1Documento7 páginasAP Biology Laboratory 1Ricardo PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration in YeastDocumento11 páginasCellular Respiration in YeastxshelyAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration Lab ResultsDocumento13 páginasCellular Respiration Lab ResultsAlyona Booth100% (1)
- Life Process - Megha Suneja 2Documento51 páginasLife Process - Megha Suneja 2nad.recordbookAinda não há avaliações
- Ssc-Biology Text Book Must StudyDocumento212 páginasSsc-Biology Text Book Must StudyShaik BajiAinda não há avaliações
- How Plants Obtain Food Materials Through PhotosynthesisDocumento212 páginasHow Plants Obtain Food Materials Through PhotosynthesisSridhar RaparthiAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis LabDocumento11 páginasCell Respiration & Photosynthesis LabSherida GibbsAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Instructional ModuleDocumento19 páginasSelf-Instructional ModuleMarlon S. BarangganAinda não há avaliações
- Biomaterials As A Pillar of ImplantsDocumento5 páginasBiomaterials As A Pillar of ImplantsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Contrac BloxDocumento4 páginasContrac Bloxwahyu99Ainda não há avaliações
- Booklet 2 Topic 1Documento61 páginasBooklet 2 Topic 1Sarah Al ObaidanAinda não há avaliações
- Problem #2b: Chromium Crystallizes With A Body-Centered Cubic Unit Cell. The Radius of ADocumento8 páginasProblem #2b: Chromium Crystallizes With A Body-Centered Cubic Unit Cell. The Radius of ARadica AyuAinda não há avaliações
- A Simplified Method For The Cultivation of Extreme Anaerobic Archaea Based SULFIDE 2000 !!!!Documento6 páginasA Simplified Method For The Cultivation of Extreme Anaerobic Archaea Based SULFIDE 2000 !!!!Vera Brok-VolchanskayaAinda não há avaliações
- Effectiveness of Liquid Oxygen BleachDocumento4 páginasEffectiveness of Liquid Oxygen BleachSingh GurleenAinda não há avaliações
- Combustion in SI & CI EnginesDocumento25 páginasCombustion in SI & CI EnginesVenkatesh KabraAinda não há avaliações
- Science - Form 4 - Chapter 5Documento12 páginasScience - Form 4 - Chapter 5Marcia PattersonAinda não há avaliações
- The Chemistry of The Morphine Alkaloids Bentley (Oxford 1954) PDFDocumento452 páginasThe Chemistry of The Morphine Alkaloids Bentley (Oxford 1954) PDFJim Leonard100% (2)
- Quantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Documento4 páginasQuantum-Mechanical Aspects of The L. Pauling's Resonance Theory.Bezverkhniy VolodymyrAinda não há avaliações
- Feasibility Study of Cumene ProductionDocumento4 páginasFeasibility Study of Cumene ProductionIntratec SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Jazeera Deco Primer-MsdsDocumento5 páginasJazeera Deco Primer-MsdsMahmoud FlefilAinda não há avaliações
- Welds CracksDocumento8 páginasWelds Cracksaltaf94Ainda não há avaliações
- CarbonicAnhydrases Manuscript withDOIDocumento11 páginasCarbonicAnhydrases Manuscript withDOIFadhil MiftahulAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of Core Sample Absolute Permeability Using Gas Permeameter and Liquid Fluid Practicum ReportDocumento17 páginasDetermination of Core Sample Absolute Permeability Using Gas Permeameter and Liquid Fluid Practicum ReportAqsal IlhamAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Balance and Thermo PresentationDocumento83 páginasEnergy Balance and Thermo Presentationca2n27Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics For EngineersDocumento620 páginasThermodynamics For Engineersgsuresh40100% (8)
- Concrete Soil Identification GuideDocumento3 páginasConcrete Soil Identification GuideKangAinda não há avaliações
- Summary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsDocumento4 páginasSummary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsAzman SamerAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Substituent On Benzene RingDocumento12 páginasEffects of Substituent On Benzene Ringyashfa khalidAinda não há avaliações
- p095 Re Struct 07 PCDocumento12 páginasp095 Re Struct 07 PCmidhungbabu88Ainda não há avaliações
- UOP Polybed PSA System For Gas Extraction PurificationDocumento2 páginasUOP Polybed PSA System For Gas Extraction PurificationchemiafAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Matter PresentationDocumento9 páginasProperties of Matter PresentationMica Ela MañoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Laser TechnologyDocumento31 páginasIntroduction To Laser TechnologyJames Sullivan100% (1)
- ANTHE 2021 (Engineering) Sample PaperDocumento17 páginasANTHE 2021 (Engineering) Sample PaperDida CowernAinda não há avaliações
- N52 Grade Neodymium Magnets DataDocumento1 páginaN52 Grade Neodymium Magnets DataSteve HsuAinda não há avaliações
- Fermi DistrbutionDocumento17 páginasFermi DistrbutionnazarAinda não há avaliações
- 1 SR Star Jee Main GTM 02 - 03 01 2024 KeyDocumento14 páginas1 SR Star Jee Main GTM 02 - 03 01 2024 Keyjahnavimogarala9Ainda não há avaliações
- KapilDocumento69 páginasKapilPraveen SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- DP Level Measurement BasicsDocumento2 páginasDP Level Measurement Basicsjsrplc7952Ainda não há avaliações