Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
SA SmallBore SepticTank
Enviado por
Raaeess SaaeedDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SA SmallBore SepticTank
Enviado por
Raaeess SaaeedDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
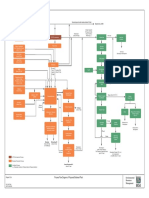
Septic tank and soakaway or small bore solid-free sewer
Wastewater treatment works To river Tertiary treatment
Secondary treatment
Primary treatment
Inlet works
Full flush toilet Water trap Access cover
To option A or B
Scum Liquid Sludge Septic tank
Small bore sewer to main sewer in road
A
(soakpit or drainage trench)
Soakaway
Septic tank and soakaway: An in-house full flush-toilet connected via pipe and plumbing fixtures to an underground watertight settling chamber (the digester) with a liquids outlet to a subsoil drainage/soakaway system. Small bore solid-free sewer: An in-house toilet discharging to a septic tank (or on-site digester) with liquids disposal via a small diameter sewer to a central collection sump or existing sewer system.
Principles of operation
Septic tank and soakaway Waste from the toilet, and generally domestic wastewater, is flushed into the settling chamber where it is retained for at least 24hrs to allow settlement and biological digestion. Partially treated liquids then pass out of the tank and into the subsoil drainage/soakaway system. Digested sludge gradually builds up in the tank and requires eventual removal by tanker. Small bore solid-free sewer As for the septic tank and soakaway except that the liquid effluent is conveyed by a system of small-diameter pipes to a communal treatment point (which may be off-site treatment works reached either via existing sewerage or by tanker).
Operational and institutional requirements
Requires a reliable household water connection. Specific design criteria must be applied to the settlement tank and soakaway system. This option is applicable only in areas of low settlement density and where soils have a high ability to drain effluent away. Ensure access for emptying of tanks by vacuum tanker, as well as availability of sludge treatment and disposal. Although its water requirements may be less than those of a septic tank and soakaway, a household connection is needed. Ensure access for emptying of septic tank, as well as availability of sludge treatment and disposal. Routine maintenance of pipe network essential.
Costs
Experience and comment
Widely used by formal rural households and farming areas, where reliable water supply is available. Provides a high level of service and user convenience. Failures due to poor design and construction, and use of inappropriate anal cleansing material. Soakaway system is particularly prone to failure in the long-term if detailed soil testing is not carried out. Not widely used in South Africa, except where existing septic tank and soakaway systems have been converted for convenience and/or environmental reasons. Failures as for septic tanks above, and due to lack of maintenance of the pipe network.
Capital: R7 000-R8 500. Operating: R200-R450 per emptying, depending on emptying frequency.
Within the septic tank and soakaway range detailed above if septic tank systems already in place, otherwise capital cost much higher.
Você também pode gostar
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- 200 Questions and Answers On Practical Civil Engineering Works 2008Documento84 páginas200 Questions and Answers On Practical Civil Engineering Works 2008ramdj100% (4)
- Standard Operating Procedure of Tank Cleaning - Fixed / Floating RoofDocumento3 páginasStandard Operating Procedure of Tank Cleaning - Fixed / Floating RoofZulhilmi Zalizan50% (2)
- Speaking PteDocumento3 páginasSpeaking PteHansen Gunawan0% (2)
- ASEAN Public Toilet StandardDocumento104 páginasASEAN Public Toilet StandardNabila Febitsukarizky Bunyamin100% (1)
- Sewage-ExtendedAeration - Design CalculationDocumento51 páginasSewage-ExtendedAeration - Design CalculationSayyid Syafiq Syed Mohamed100% (1)
- Bridge Inspection, Maintenance, and RepairDocumento186 páginasBridge Inspection, Maintenance, and Repairapi-3741340Ainda não há avaliações
- Steel StructuresDocumento133 páginasSteel Structuresabdikarim_omarAinda não há avaliações
- Concrete Barrier Distress in La Grande, Oregon Final Report: PROJECT SR 500-211Documento33 páginasConcrete Barrier Distress in La Grande, Oregon Final Report: PROJECT SR 500-211Raaeess SaaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Shinedfgsd Bright Like A DiamondDocumento18 páginasShinedfgsd Bright Like A DiamondRaaeess SaaeedAinda não há avaliações
- C 7Documento3 páginasC 7Raaeess SaaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Bridge Inspection, Maintenance, and RepairDocumento186 páginasBridge Inspection, Maintenance, and Repairapi-3741340Ainda não há avaliações
- BMP ManualDocumento144 páginasBMP ManualRaaeess SaaeedAinda não há avaliações
- 2182 ColorDocumento16 páginas2182 ColorRaaeess SaaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Power and CreationDocumento77 páginasPower and CreationAnwar SadeedAinda não há avaliações
- Fate and DestinyDocumento68 páginasFate and DestinyabuqudamahAinda não há avaliações
- General Concept Idea of Environmental ConservationDocumento43 páginasGeneral Concept Idea of Environmental ConservationSamAinda não há avaliações
- Method Statement of Open CutDocumento7 páginasMethod Statement of Open CutMuditha Indeewarie GunarathnaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulic Statement - SewerageDocumento1 páginaHydraulic Statement - SewerageMuhammad UmairAinda não há avaliações
- The Eden ProjectDocumento1 páginaThe Eden Project11ptangAinda não há avaliações
- Học tiếng anh với cô Trang Anh Khóa họcDocumento6 páginasHọc tiếng anh với cô Trang Anh Khóa họcNgọc Minh LêAinda não há avaliações
- A Systematic Approach To Reduce Power Plant Auxiliary PowerDocumento2 páginasA Systematic Approach To Reduce Power Plant Auxiliary PowerrajeshAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Decision TreeDocumento18 páginasSolar Decision TreeabovmabovAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear SitesDocumento3 páginasNuclear SitesThe GuardianAinda não há avaliações
- Deepak Spinners Guna Unit PresentationDocumento34 páginasDeepak Spinners Guna Unit PresentationViplove SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Puro Line ManualDocumento8 páginasPuro Line ManualAltif AboodAinda não há avaliações
- Namba Park Sub by - SoorajDocumento25 páginasNamba Park Sub by - SoorajsoorajAinda não há avaliações
- Sparrevohn: Proposed Plan For Seven ERP Sites atDocumento32 páginasSparrevohn: Proposed Plan For Seven ERP Sites atsinned1944100% (2)
- Green Supply Chain ManagementDocumento17 páginasGreen Supply Chain ManagementtazeenseemaAinda não há avaliações
- Raw Water Flow SchemeDocumento1 páginaRaw Water Flow SchemeAsifAinda não há avaliações
- Preventol MP 100 IPDocumento5 páginasPreventol MP 100 IPFadhli KusumaAinda não há avaliações
- Geological Engineers: Solving Earth Problems Through ScienceDocumento2 páginasGeological Engineers: Solving Earth Problems Through SciencebimoAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Management Case StudyDocumento6 páginasWaste Management Case StudySamuel Takeshi PanAinda não há avaliações
- Headpond 1Documento1 páginaHeadpond 1katoAinda não há avaliações
- Writing SATDocumento173 páginasWriting SATMustafa ElazazyAinda não há avaliações
- GTW and waste treatment process at biodiesel plantDocumento1 páginaGTW and waste treatment process at biodiesel plantAdriana StAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Your Carbon FootprintDocumento4 páginasCalculating Your Carbon FootprintJohn OoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Filtration SV - 4slidesDocumento20 páginasChapter 4 Filtration SV - 4slidesBắp BắpAinda não há avaliações
- 5-Sediment Traps and BasinsDocumento16 páginas5-Sediment Traps and BasinsAnonymous d6vkxJAinda não há avaliações
- POLYSEED Application Procedure 3.15Documento2 páginasPOLYSEED Application Procedure 3.15ALVARO ENRIQUE CANTILLO GUZMANAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Waste TreatmentDocumento24 páginasSolid Waste TreatmentalenocitoAinda não há avaliações
- Bioenzyme BrochureDocumento1 páginaBioenzyme BrochureDayday AbleAinda não há avaliações