Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP - Difficulty of Breathing
Enviado por
Tarquin TomadaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP - Difficulty of Breathing
Enviado por
Tarquin TomadaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Care Plan
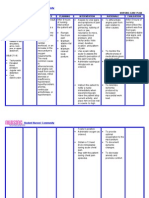
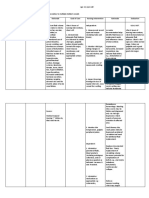
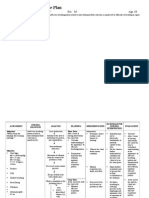
Problem Identified: Difficulty of breathing Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased lung expansion secondary to surgery as evidenced by decreased respiratory depth. Cause Analysis: Respiratory depression is the most serious adverse effect of opioid analgesics administered by IV, SubQ, or epidural routes. Specific notable changes are decreasing respiratory rate or shallow respirations. (Brunner & Suddarths Medical Surgical Nursing, Page 190) Cues Objective: Tachypnea: 26 breathes per minute Decreased respiratory depth Cyanotic STO: After 10 minutes of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to decrease breathes per minute from 26 to 1220. LTO: After 20 minutes of nursing intervention, the patient will establish normal breathing pattern as evidenced by the Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Independent actions: 1. Administer oxygen at lowest concentration indicated and prescribed respiratory medications. 2. Monitor pulse oximeter, as indicated. 3. Suction airway, as needed. 4. Elevate head of bed, as appropriate. 5. Provide/encourage use of adjuncts, such as incentive spirometer. Rationale Independent actions: 1. For management of underlying pulmonary condition, respiratory distress, or cyanosis. 2. To verify maintenance and improvement in oxygen saturation. 3. To clear secretions. 4. To promote physiological ease of maximal inspiration. 5. To facilitate deeper respiratory effort. Goal met, the patient established LTO: Evaluation STO: Goal met, the patient was able to decrease breathes per minute from 26 to 12-20.
absence of cyanosis.
normal breathing pattern as evidenced by the absence of cyanosis.
References: Nurses Pocket Guide Pages 151-155
Você também pode gostar
- Drug Study - HydrocodoneDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - HydrocodoneTarquin Tomada86% (7)
- Food StampsDocumento80 páginasFood StampsAnvitaRamachandranAinda não há avaliações
- FWA CMS Training (4346) PDFDocumento13 páginasFWA CMS Training (4346) PDFinfo3497Ainda não há avaliações
- Response To States 4.2 Motion in Limine Character of VictimDocumento10 páginasResponse To States 4.2 Motion in Limine Character of VictimLaw of Self DefenseAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - IbuprofenTarquin Tomada100% (1)
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPTracy Camille EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Acute Pain Related Decreased Myocardial Blood FlowDocumento2 páginasNCP - Acute Pain Related Decreased Myocardial Blood FlowKian HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Prioritization of Nursing ProblemsDocumento1 páginaPrioritization of Nursing ProblemsAbigail Lonogan100% (2)
- Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis - AddictionDocumento14 páginasInterpretative Phenomenological Analysis - AddictionAna MariaAinda não há avaliações
- Nebulization (Final Output)Documento5 páginasNebulization (Final Output)Tamil Villardo100% (2)
- Case Study (Aub)Documento16 páginasCase Study (Aub)Lucila Lugo0% (2)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocumento3 páginasNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPJhel NabosAinda não há avaliações
- Feeds and Feedings - Margie EranDocumento29 páginasFeeds and Feedings - Margie EranAlliah Dela RosaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824Ainda não há avaliações
- Nurses Progress NotesDocumento2 páginasNurses Progress Notesvan100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- Knowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionDocumento2 páginasKnowledge Deficit Related To HypertensionChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- 7 NCPDocumento7 páginas7 NCPVina EmpialesAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento2 páginasIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiAinda não há avaliações
- Outline The Role of The Health Care AssistantDocumento13 páginasOutline The Role of The Health Care AssistantTarquin Tomada67% (3)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento5 páginasNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP DobDocumento2 páginasNCP DobTata Wendz100% (1)
- Students Sleep During Classes: The Amount of Time VariesDocumento7 páginasStudents Sleep During Classes: The Amount of Time Variesjason_aaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Myocardial InfarctionDocumento1 páginaNCP Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- NCP Cushing's SyndromeDocumento2 páginasNCP Cushing's Syndromerngeneral50% (6)
- IMCI Chart Booklet PDFDocumento80 páginasIMCI Chart Booklet PDFmikay100% (1)
- Oregon SOS Audit On Child WelfareDocumento49 páginasOregon SOS Audit On Child WelfareSinclair Broadcast Group - Eugene100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyTarquin Tomada100% (2)
- Respiratory Failure NCPDocumento1 páginaRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- NCP AnginaDocumento3 páginasNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- Ventilator Care 1Documento11 páginasVentilator Care 1Friends ForeverAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento5 páginasIneffective Breathing PatternruguAinda não há avaliações
- Acupuncture LectureDocumento10 páginasAcupuncture Lectureapi-5481010020% (1)
- Liver NCPDocumento5 páginasLiver NCPMerrill HansAinda não há avaliações
- Care For Mechanical VentilationDocumento14 páginasCare For Mechanical Ventilationmaeya186135100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadAinda não há avaliações
- Mapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaDocumento2 páginasMapagod at Manghina" As: Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With AsthmaKian Herrera100% (1)
- NCP HemothoraxDocumento3 páginasNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocumento3 páginasNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Nclex Review Pneumonia COPD AsDocumento11 páginasNclex Review Pneumonia COPD Asmj078Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP For Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento3 páginasNCP For Acute Coronary Syndromesarahtot75% (4)
- NCP - CopdDocumento3 páginasNCP - CopdhystericoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Mi PainDocumento2 páginasNCP For Mi PainKahMallariAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocumento4 páginasNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP Chest PainDocumento2 páginasNCP Chest PainLinsae Troy50% (2)
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPDidith AbanAinda não há avaliações
- Diversity and IndividualityDocumento2 páginasDiversity and IndividualityTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - AnxietyDocumento1 páginaNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- NCP Difficulty in BreathingDocumento3 páginasNCP Difficulty in BreathingEllyza Grace Tejada75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Documento1 páginaNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaAinda não há avaliações
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaDocumento9 páginasLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocumento3 páginasNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Near DrowningDocumento1 páginaNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 páginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 páginasNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP Epidural HemDocumento32 páginasNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP MiDocumento4 páginasNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocumento1 páginaPleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraAinda não há avaliações
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocumento1 páginaTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocumento2 páginasProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawAinda não há avaliações
- MS Post TestDocumento8 páginasMS Post TestAliyah Jewel JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Final VentilatorDocumento62 páginasFinal VentilatorDrmirfat AlkashifAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Mechanical VentilationDocumento16 páginasManagement of Mechanical Ventilationyuliana muinAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Olga Alexeevna EfremovaDocumento56 páginasChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Olga Alexeevna Efremovaسيف الشمريAinda não há avaliações
- ICN Lec (Activities)Documento6 páginasICN Lec (Activities)Kimmy NgAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Documento1 páginaNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaAinda não há avaliações
- Transient Tachypnea of The NewbornDocumento6 páginasTransient Tachypnea of The NewbornTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- DMV 2016Documento116 páginasDMV 2016రణధీర్ గౌడ్Ainda não há avaliações
- Fluid Balance ChartDocumento1 páginaFluid Balance ChartTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Pain Management Nursing RoleDocumento13 páginasPain Management Nursing Rolebacky_pzAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary BankDocumento2 páginasVocabulary BankTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Health IssuesDocumento13 páginasHealth IssuesTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Herbal Medications (DOH)Documento2 páginasHerbal Medications (DOH)Tarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Therapy: Type of Therapy Objectives Materials Mechanics of TherapyDocumento3 páginasTypes of Therapy: Type of Therapy Objectives Materials Mechanics of TherapyTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Mindanao Sanitarium and Hospital College: School of NursingDocumento2 páginasMindanao Sanitarium and Hospital College: School of NursingTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - FolfoxDocumento3 páginasDrug Study - FolfoxTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Acls Aha 2010Documento67 páginasAcls Aha 2010heraaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - PanitumumabDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - PanitumumabTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Death and DyingDocumento4 páginasDeath and DyingTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Caring AidsDocumento9 páginasCaring AidsTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal ExercisesDocumento2 páginasAbdominal ExercisesTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Role and Responsibility of Director of NursingDocumento1 páginaRole and Responsibility of Director of NursingTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - IrinotecanDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - IrinotecanTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- 14 PrognosisDocumento1 página14 PrognosisTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - BevacizumabDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - BevacizumabTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - CetuximabDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - CetuximabTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrointestinal Tract AnatomyDocumento4 páginasGastrointestinal Tract AnatomyTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - AcetaminophenDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - AcetaminophenTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Care of The Elder Person: Evidence Based PracticeDocumento11 páginasCare of The Elder Person: Evidence Based PracticeTarquin TomadaAinda não há avaliações
- Benefit Manual Group Health Insurance - CMSDocumento35 páginasBenefit Manual Group Health Insurance - CMSUmang WarudkarAinda não há avaliações
- Group1-FINAL-Chapter-1-2-3 (G1)Documento46 páginasGroup1-FINAL-Chapter-1-2-3 (G1)Sydney BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project DescriptionDocumento6 páginasFinal Project DescriptionCahyani DamawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocumento4 páginasTypology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeLeah Abdul KabibAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Legal Dimensions of Nursing Chapter ReviewDocumento2 páginas7 Legal Dimensions of Nursing Chapter ReviewAmy AnonymousAinda não há avaliações
- Test AaDocumento55 páginasTest AaKaye PatanindagatAinda não há avaliações
- Vaccination BOON or BANEDocumento5 páginasVaccination BOON or BANERushil BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Sensus Harian TGL 05 Maret 2022........Documento104 páginasSensus Harian TGL 05 Maret 2022........Ruhut Putra SinuratAinda não há avaliações
- ComplaintDocumento28 páginasComplaintLia TabackmanAinda não há avaliações
- Profile of Osteopathic Practice in Spain Results FDocumento11 páginasProfile of Osteopathic Practice in Spain Results FBerenice LimarkAinda não há avaliações
- Covid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & Certification: Certificate IssuedDocumento1 páginaCovid-19 RT-PCR Test Report & Certification: Certificate IssuedJerome OliverosAinda não há avaliações
- Provide Advanced Nursing Care (HLT NUR4 01222) : For Regular Nursing (Level Iv - TVET) Students AAMBC, January 2022Documento56 páginasProvide Advanced Nursing Care (HLT NUR4 01222) : For Regular Nursing (Level Iv - TVET) Students AAMBC, January 2022Abel100% (1)
- History of Architecture and Town Planning-Course-BrochureDocumento42 páginasHistory of Architecture and Town Planning-Course-BrochureSabita AmaniAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical and Hortatory ExpositionDocumento3 páginasAnalytical and Hortatory ExpositionChie TjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Types of PovertyDocumento6 páginasTypes of PovertyJacobAinda não há avaliações
- Ecological Analysis of The Prevalence of PulmonaryDocumento10 páginasEcological Analysis of The Prevalence of PulmonaryLazy SlothAinda não há avaliações
- Discuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesDocumento5 páginasDiscuss Any Four Challenges Faced by Ovc and Their Intervention StrategiesJohn MugabeAinda não há avaliações
- Shisha: GNS By: Lingaiswaran S/O BalasupramaniamDocumento13 páginasShisha: GNS By: Lingaiswaran S/O BalasupramaniamLinga IngloriousAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 HivDocumento1 página2020 HivhenkAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Testing For DioxinsDocumento2 páginasBlood Testing For DioxinstedmozbiAinda não há avaliações