Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Elca
Enviado por
arness22Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Elca
Enviado por
arness22Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
watt ohm coulomb volt In addition to Ohms law, solving multiple-load multiple circuits requires the use of:
Coulombs laws Amperes laws Kirchhoffs laws none of the above
The formula that can be used in any type of circuit is: IT = IR1 + IR2 + IR3 + etc. RT = RR1 + RR2 + RR3 + etc. PT = PR1 + PR2 + PR3 + etc. none of the above
For the circuit below:
RT PR2 = 533 mW PT = 1.6 W all of the above
Solving simultaneous equations requires: no more than two independent equations at least three independent equations
as many independent equations as there are unknown variables one fewer independent equations than unknown variables
The technique that cant be used on single single-source circuits is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above
The technique that cant be used on multiple-source circuits is: loop equations superposition theorem Thevenins theorem none of the above
The technique that uses only series-parallel rules and procedures is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above The technique that may not determine all current and voltage values is loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above ) The technique that may require the use of another technique before it can be applied is: loop equations superposition theorem Thevenins theorem all of the above
The technique that requires only one calculation to determine the new load current when the load resistance res is changed is:
loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above The technique that may yield a negative value of current is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem all of the above
201) The technique that cant be used on multiple-source circuits is: loop equations superposition theorem Thevenins theorem none of the above
202) The technique that uses only series-parallel rules and procedures is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above
203) The technique that may not determine all current and voltage values is loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above
204) The technique that may require the use of another technique before it can be applied is: loop equations superposition theorem
Thevenins theorem all of the above
205) The technique that requires only one calculation to determine the new load current when the load resistance is changed is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem none of the above
206) The technique that may yield a negative value of current is: loop equations superposition theorem Nortons theorem all of the above
Determine the value of IR2, IR3, and VR2 in the circuit below. IR2 = 1.25 mA, IR3 = 1.75 mA, VR2 = 3 V IR2 = 2.05 mA, IR3 = 1.99 mA, VR2 = 3 V IR2 = 3.98 mA, IR3 = 2.09 mA, VR2 = 4 V IR2 = 7.90 mA, IR3 = 3.00 mA, VR2 = 5 V
The direction of the flux around a conductor can be determined by: the left-hand rule and the polarity of the applied voltage the left-hand rule and the direction of the current flow either of the above neither of the above
When the currents in two parallel conductors are in the same direction:
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- lf356 DataDocumento45 páginaslf356 DataBhayu alfianAinda não há avaliações
- The Journey of A Signal - Inside Your OscilloscopeDocumento1 páginaThe Journey of A Signal - Inside Your Oscilloscopearness22Ainda não há avaliações
- ASEE2000 AmplifiersDocumento9 páginasASEE2000 Amplifiersarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Fcp190N60 / Fcpf190N60: N-Channel Superfet Ii MosfetDocumento10 páginasFcp190N60 / Fcpf190N60: N-Channel Superfet Ii Mosfetarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- 2sk3679 - 900V, 9ADocumento4 páginas2sk3679 - 900V, 9ARenatoMaiaAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- User ManualDocumento44 páginasUser Manualarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Remote Control System: Full Control of CP Propellers and ThrustersDocumento4 páginasRemote Control System: Full Control of CP Propellers and Thrustersarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Apc Smartups 1500 Smt1500 ManualDocumento21 páginasApc Smartups 1500 Smt1500 ManualskibcobsaivigneshAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- TEKTRONIX THS3024 DatasheetDocumento13 páginasTEKTRONIX THS3024 Datasheetarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- How To Calibrate Thermocouples - Common TechniquesDocumento1 páginaHow To Calibrate Thermocouples - Common Techniquesarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Training TC Theory SaafgDocumento6 páginasTraining TC Theory SaafgMuhammad Ikhsan HermasAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Tdi Turbdstart Two™: Tech Development IncDocumento1 páginaTdi Turbdstart Two™: Tech Development Incarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- SC92F7352 7351 7350v0.1enDocumento109 páginasSC92F7352 7351 7350v0.1enarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermalcouple GuideDocumento37 páginasThermalcouple GuideTrung Dũng100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Engin'e Air Starters: Tditurbostarttwd™Documento1 páginaEngin'e Air Starters: Tditurbostarttwd™arness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- 3W Ultra Low-EMI Anti-Clipping Stereo Class D Audio Power AmplifierDocumento17 páginas3W Ultra Low-EMI Anti-Clipping Stereo Class D Audio Power Amplifierarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- MY81SPK02M2: Bluetooth 3.0+EDR Stereo Audio ModuleDocumento5 páginasMY81SPK02M2: Bluetooth 3.0+EDR Stereo Audio Modulearness22Ainda não há avaliações
- 0302 - Test3 - Instruction ManualDocumento2 páginas0302 - Test3 - Instruction Manualarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- MT1898EDocumento1 páginaMT1898Earness22Ainda não há avaliações
- CXD9981TN Texas Instruments Product DetailsDocumento3 páginasCXD9981TN Texas Instruments Product Detailsarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Airst 4Documento1 páginaAirst 4arness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Turbdstart TWD"™: Tech DevelopmentDocumento1 páginaTurbdstart TWD"™: Tech Developmentarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Turbdstart Two™: WarningDocumento1 páginaTurbdstart Two™: Warningarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Designing For High Common-Mode Rejection in Balanced Audio InputsDocumento7 páginasDesigning For High Common-Mode Rejection in Balanced Audio Inputsarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- An 960Documento12 páginasAn 960Engr. AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
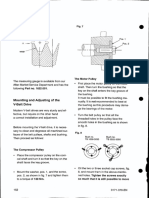
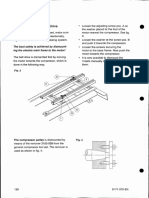
- Mounting of The V-Belt Drive: Kept Parallel With The Compres-Sor, Which Can Be Checked by Means ofDocumento1 páginaMounting of The V-Belt Drive: Kept Parallel With The Compres-Sor, Which Can Be Checked by Means ofarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- Fig. 6 - Wear On Belt Grooves Fig. 7: Mounting and Adjusting of The V-Belt DriveDocumento1 páginaFig. 6 - Wear On Belt Grooves Fig. 7: Mounting and Adjusting of The V-Belt Drivearness22Ainda não há avaliações
- # Boilers Settings PDFDocumento19 páginas# Boilers Settings PDFarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Belts PDFDocumento1 páginaBelts PDFarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- # IncinDocumento1 página# Incinarness22Ainda não há avaliações
- 7 2009 FinalDocumento12 páginas7 2009 FinalRic ManAinda não há avaliações
- EC3361 Lab ExptDocumento4 páginasEC3361 Lab ExptAMMU R100% (1)
- Envytools PDFDocumento701 páginasEnvytools PDFgo88Ainda não há avaliações
- EECTCH98Documento79 páginasEECTCH98Harry JacobsonAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For Electrical EngineeringDocumento4 páginasSyllabus For Electrical EngineeringNandgulabDeshmukhAinda não há avaliações
- 325 Final Design Lab ReportDocumento11 páginas325 Final Design Lab Reportapi-241454978Ainda não há avaliações
- Krone 4 Category 6Documento18 páginasKrone 4 Category 6jose carlosAinda não há avaliações
- USB - PD - R2 - 0 V1.2 - 20160325 - ECN Clean Markup 20160802Documento552 páginasUSB - PD - R2 - 0 V1.2 - 20160325 - ECN Clean Markup 20160802BDole1234Ainda não há avaliações
- Applicationnote, V1.1, December2011: Never Stop ThinkingDocumento12 páginasApplicationnote, V1.1, December2011: Never Stop ThinkingYudi ElektroAinda não há avaliações
- Nirvana and R Series 37kW-50HP To 250kW-300HP Modular Drive Troubleshooting Manual REV13 February 20121Documento75 páginasNirvana and R Series 37kW-50HP To 250kW-300HP Modular Drive Troubleshooting Manual REV13 February 20121Eriton Cavalcanti100% (1)
- XXX - Cyclone V Product TableDocumento2 páginasXXX - Cyclone V Product TableBru MAinda não há avaliações
- Biasing and Transfer Characteristic of Mach-Zehnder Modulator (MZM) 1Documento12 páginasBiasing and Transfer Characteristic of Mach-Zehnder Modulator (MZM) 1Ranjan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Datasheet Dub Cr100Documento2 páginasDatasheet Dub Cr100Christian BolivarAinda não há avaliações
- TV Plasma Panasonic TH 37 pwd7bx Ex pwd7 BK Ek Uy 42pw7ex BX pwd7bk Ek Es Uy Chassis GP 7dDocumento160 páginasTV Plasma Panasonic TH 37 pwd7bx Ex pwd7 BK Ek Uy 42pw7ex BX pwd7bk Ek Es Uy Chassis GP 7dvideosonAinda não há avaliações
- Si 7326 DNDocumento12 páginasSi 7326 DNyayayalAinda não há avaliações
- MicroKinetics MightyDrive SL PIN OUTS Reference Manual Official CNC DMicroriver Stepper Controller BoardDocumento2 páginasMicroKinetics MightyDrive SL PIN OUTS Reference Manual Official CNC DMicroriver Stepper Controller BoardAndreus GrotiusAinda não há avaliações
- Govt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabDocumento2 páginasGovt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabAnkit100% (1)
- Protection Relay StandardDocumento3 páginasProtection Relay StandardThirumalAinda não há avaliações
- PT 2256Documento4 páginasPT 2256zektorAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 220 Exam 2 Solutions Multiple Choice Section (5 Pts. Ea.) More Than One Version of Exam - Same Questions, Different Orders. 1)Documento4 páginasPhysics 220 Exam 2 Solutions Multiple Choice Section (5 Pts. Ea.) More Than One Version of Exam - Same Questions, Different Orders. 1)Nava ZabiAinda não há avaliações
- Transistor Radio DX 7500 Bfg235Documento7 páginasTransistor Radio DX 7500 Bfg235hurantiaAinda não há avaliações
- 90210-1083DEA E KLogic KLadder PDFDocumento154 páginas90210-1083DEA E KLogic KLadder PDFBobyAinda não há avaliações
- Siemens SRA/SRT: Transport Network ProductsDocumento3 páginasSiemens SRA/SRT: Transport Network ProductsEhsan RohaniAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture3. Parallel Circuits-Chapter 6Documento35 páginasLecture3. Parallel Circuits-Chapter 6Keshav GopaulAinda não há avaliações
- XT2051 eDocumento12 páginasXT2051 eale_dimmserviciosAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Totem Pole OutputDocumento3 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Totem Pole OutputSiva Guru50% (2)
- Interfacing DAC 0800 With 8051trainerDocumento9 páginasInterfacing DAC 0800 With 8051trainerNaveen Kumar SagantiAinda não há avaliações
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: Presented byDocumento12 páginasOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: Presented byTHIRUCHANOORU SREENATHAinda não há avaliações
- 2 SD 424Documento2 páginas2 SD 424Ruben David Ibañez RetamalAinda não há avaliações
- Reference Essay Computer)Documento4 páginasReference Essay Computer)Trane SamAinda não há avaliações