Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lesson Plan Trig Angles
Enviado por
Jonathan RobinsonDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lesson Plan Trig Angles
Enviado por
Jonathan RobinsonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
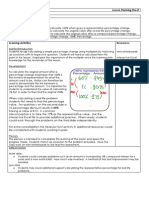
Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Trigonometry Angles Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson: All students should
d be able to use the Sine and Cosine function to calculate angles in right-angled triangles. Most students should be able to use the Sine, Cosine and Tangent function to calculate angles in right angled triangles. Some students should be able to calculate an angle in an isosceles triangle using Trigonometrical functions. Keywords: Trigonometry, Opposite, Adjacent, Hypotenuse, ArcTan, ArcCos, ArcSin Learning Activities Starter/Introduction Students develop their problem solving skills by using Pytha goras theorem and trigonometric functions to calculate the lengths in right-angled triangles. It is important for the class to sketch their diagrams and label the edges in respect to the angle, i.e., Opposite, Adjacent and Hypotenuse side. Development To calculate an angle in a triangle it is necessary to first identify which trigonometric function can be used. Use the angle to label the sides the opposite side is opposite the angle, the adjacent side runs adjacent to it and the hypotenuse is opposite the right angle. In the base of the diagram to the right both the Opposite and Adjacent are known to therefore the Tangent function is necessary since Sine and Cosine require the hypotenuse side. Explain that ArcTan, ArcSin and ArcCos are the opposite functions to Tan, Sin, and Cos respectively. In a similar way to that plus is the opposite function to subtract and divide is the opposite to multiply. Therefore, in the example above, by taking the ArcTan of both sides the Tan function on the left hand side is cancelled. When demonstrating this to the class it is important to provide a clear writing frame since multiple lines of working are needed. Continue to work through the remaining examples on the second slide for consolidation. The interactive Microsoft Excel file can be used to provide examples for the students to work from on mini-whiteboards in order to assess their progress. When ready students could progress through the problems on the third slide independently. Feedback solutions throughout to maintain pace and challenge. Plenary The plenary is intended to both consolidate and extend the learning by having the class consider an isosceles triangle rather than one that is right-angled. It may be necessary to guide the students to create a right angled triangle by bisecting and halving the vertical distance. Have the class attempt this on mini-whiteboards for assessment and feedback. Differentiation More able: Students could consider right angled triangles within 3D grids. Less Able Students may benefit from using only the sine and cosine function one lesson and move on to all three functions in the next. Resources: MiniWhiteboards Calculators Interactive Microsoft Excel file. YouTube Videos
Você também pode gostar
- Time Lesson PlanDocumento1 páginaTime Lesson PlanJonathan Robinson100% (4)
- Bar Model Math LessonDocumento7 páginasBar Model Math Lessonapi-301426684Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Conversion GraphsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Conversion GraphsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Trig IntroDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Trig IntroJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Planning Sheet BisectorsDocumento1 páginaLesson Planning Sheet BisectorsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Pythagorean Theorem Lesson Plan G8Documento19 páginasPythagorean Theorem Lesson Plan G8KENO MARTIN ADVIENTOAinda não há avaliações
- DAILY LESSON LOG in Math 9Documento9 páginasDAILY LESSON LOG in Math 9Jesryl Remerata OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- RectangleDocumento5 páginasRectangleRetchel ManguilimotanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan 3D TrigDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan 3D TrigJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento19 páginasLesson Planapi-549572509Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Planning Quadratic GraphDocumento1 páginaLesson Planning Quadratic GraphJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Scatter GraphsDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan Scatter GraphsJonathan Robinson100% (2)
- Lesson Plan CubicDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan CubicJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasLesson PlanHanna Grace HonradeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Plan 325 TlegrandDocumento14 páginasUnit Plan 325 Tlegrandapi-309177617Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 ProbabilityDocumento2 páginasUnit 5 Probabilityapi-328465459Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan - Pythagorean TheoremEric StottAinda não há avaliações
- 16.illustrate Systems of Linear EquationsDocumento3 páginas16.illustrate Systems of Linear EquationsMiriam Galicia100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Math 9Documento3 páginasLesson Plan Math 9Roy PizaAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometry 5Documento31 páginasTrigonometry 5Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoAinda não há avaliações
- Tandaay National High School Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 January 21, 2016 I. Learning ObjectivesDocumento8 páginasTandaay National High School Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 January 21, 2016 I. Learning ObjectivesOmixam OdagrebAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Year 8 Maths Cartesian CoordinatesDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan Year 8 Maths Cartesian Coordinatesapi-269319313Ainda não há avaliações
- Ubd Final MathDocumento6 páginasUbd Final Mathapi-296454132Ainda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasMathematics Lesson PlanLeilani Dela Cruz PelobelloAinda não há avaliações
- RATIONAL NUMBERS Lesson Plan PDFDocumento3 páginasRATIONAL NUMBERS Lesson Plan PDFHaribabu SunkaraAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan - May 3,2023-Trigonometric RatiosDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan - May 3,2023-Trigonometric RatiosKenneth AlboriaAinda não há avaliações
- Elective Mathematics Scheme of Work1Documento36 páginasElective Mathematics Scheme of Work1yaw197Ainda não há avaliações
- Time Allotment in Each Step) : Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityDocumento1 páginaTime Allotment in Each Step) : Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityJerson YhuwelAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in TrigonometryDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan in TrigonometryJeraldJayEngracialBalanayAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Trigonometric Functions (Soh-Cah-Toa) Grade 9 Mathematics - Section Molave Monday (8:40am-9:40am)Documento5 páginasLesson Plan Trigonometric Functions (Soh-Cah-Toa) Grade 9 Mathematics - Section Molave Monday (8:40am-9:40am)RICHMON ALLAN B. GRACIAAinda não há avaliações
- Module4 Complex Rational ExpressionsDocumento6 páginasModule4 Complex Rational ExpressionsAlbert BalingitAinda não há avaliações
- U9l3 - Transformations of Quadratic Functions Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasU9l3 - Transformations of Quadratic Functions Lesson Planapi-242122700Ainda não há avaliações
- Measure of Central Tendency (Ungrouped and Grouped Data)Documento40 páginasMeasure of Central Tendency (Ungrouped and Grouped Data)Ahlan Marciano Emmanuel De Silva100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability WHLP Q1 W1 2Documento6 páginasStatistics and Probability WHLP Q1 W1 2Dianne TelmoAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - Slope-Intercept Formal Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginas7 - Slope-Intercept Formal Lesson Planapi-304704633Ainda não há avaliações
- Solving Sle by Graphing MethodDocumento21 páginasSolving Sle by Graphing Methodapi-313517608Ainda não há avaliações
- Six TrigoDocumento19 páginasSix TrigoJLacissej 117Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics: IFL: Don't Forget To Have Your IFLLDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan in Mathematics: IFL: Don't Forget To Have Your IFLLKent MarianitoAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometry Project Information SheetDocumento7 páginasTrigonometry Project Information Sheetapi-261139685Ainda não há avaliações
- MaM LYN Pandemo TUNAYDocumento8 páginasMaM LYN Pandemo TUNAYROMMEL M. APOLINARAinda não há avaliações
- DLL 0-00 Math Curriculum Guide Grade 10Documento16 páginasDLL 0-00 Math Curriculum Guide Grade 10Rondex Corpuz PabloAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Trig RatiosDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan Trig RatiosNazimul GhanieAinda não há avaliações
- Similarity in The Real World - Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasSimilarity in The Real World - Lesson Planapi-215449942Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Triangle InequLITYDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan Triangle InequLITYachumbreAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 9 9-Perserverance First Day: I - ObjectiveDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan in Mathematics 9 9-Perserverance First Day: I - ObjectiveOmarkheign Bungso AlimuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8: Mathematics First Quarter Lesson 7: Rectangular Coordinate SystemDocumento1 páginaGrade 8: Mathematics First Quarter Lesson 7: Rectangular Coordinate SystemHaydee FelicenAinda não há avaliações
- Trigonometry Lesson Plan and ReflectionDocumento4 páginasTrigonometry Lesson Plan and Reflectionapi-278122461Ainda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 10Documento21 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 10Cathline AustriaAinda não há avaliações
- The Cartesian Coordinate SystemDocumento13 páginasThe Cartesian Coordinate SystemWinnie PoliAinda não há avaliações
- Module 7 Triangle CongruenceDocumento80 páginasModule 7 Triangle CongruenceMarlon Hernandez Jr100% (2)
- m201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1Documento4 páginasm201 Math Lesson Plan 4 1api-384966224Ainda não há avaliações
- Angle of ElevationDocumento6 páginasAngle of ElevationMary Ann RascoAinda não há avaliações
- Work ProblemsDocumento15 páginasWork ProblemsFauline CarlosAinda não há avaliações
- Using Distance Between Two Points and The Pythagorean TheoremDocumento2 páginasUsing Distance Between Two Points and The Pythagorean TheoremLauren EricksonAinda não há avaliações
- Common Core State StandardsDocumento7 páginasCommon Core State Standardsapi-343459926Ainda não há avaliações
- Generate and Describe Arithmetic SequencesDocumento4 páginasGenerate and Describe Arithmetic SequencesRECHEL BURGOSAinda não há avaliações
- Math7 Q3 DLL15Documento3 páginasMath7 Q3 DLL15JOEY COTACTEAinda não há avaliações
- Special AnglesDocumento38 páginasSpecial AnglesPrincess Clarina Catina JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Right Triangle Lesson PlanDocumento6 páginasRight Triangle Lesson PlanErra PeñafloridaAinda não há avaliações
- DLL LCDocumento5 páginasDLL LCSisa Vargas Mabuyao100% (1)
- Jigsaw - Kind of FunctionDocumento5 páginasJigsaw - Kind of FunctionZha YunaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Trig LengthsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Trig LengthsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Planning Sheet Title: Angles in Triangles Learning ObjectivesDocumento2 páginasLesson Planning Sheet Title: Angles in Triangles Learning ObjectivesJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Reverse PercentagesDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Reverse PercentagesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Ordering NegativesDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Ordering NegativesJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Similar VolumesDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan Similar VolumesJonathan Robinson100% (1)
- Tables of Functions Lesson PlanDocumento1 páginaTables of Functions Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Simlar LengthsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Simlar LengthsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan MetricDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan MetricJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Venn Diagrams StarterDocumento1 páginaVenn Diagrams StarterJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan SpeedDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan SpeedJonathan Robinson100% (8)
- Imperial Lesson PlanDocumento1 páginaImperial Lesson PlanJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Travel GraphsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Travel GraphsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Similar CalculationsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Similar CalculationsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Similar AreasDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Similar AreasJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Trig LengthsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Trig LengthsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- 3D Trig WorksheetDocumento4 páginas3D Trig WorksheetJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan HypotenuseDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan HypotenuseJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Excel TrigDocumento3 páginasExcel TrigJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Proof of Pythagoras' TheoremDocumento1 páginaProof of Pythagoras' TheoremJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet For Basic EnlargementDocumento3 páginasWorksheet For Basic EnlargementJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Pythagoras 3Documento1 páginaLesson Plan Pythagoras 3Jonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational Symmetry WorksheetDocumento4 páginasRotational Symmetry WorksheetJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Rotation WorksheetDocumento4 páginasBasic Rotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection Grid WorksheetDocumento4 páginasReflection Grid WorksheetJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Pythag IntroDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Pythag IntroJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Basic EnlargementsDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Basic EnlargementsJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Rotation WorksheetDocumento3 páginasRotation WorksheetJonathan RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Asian Paints Tile Grout Cement BasedDocumento2 páginasAsian Paints Tile Grout Cement Basedgirish sundarAinda não há avaliações
- Accomplishment Report Yes-O NDCMC 2013Documento9 páginasAccomplishment Report Yes-O NDCMC 2013Jerro Dumaya CatipayAinda não há avaliações
- 07.03.09 Chest Physiotherapy PDFDocumento9 páginas07.03.09 Chest Physiotherapy PDFRakesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- PDFViewer - JSP 3Documento46 páginasPDFViewer - JSP 3Kartik ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Flexibility Personal ProjectDocumento34 páginasFlexibility Personal Projectapi-267428952100% (1)
- EP - EngineDocumento4 páginasEP - EngineAkhmad HasimAinda não há avaliações
- CAT Ground Engaging ToolsDocumento35 páginasCAT Ground Engaging ToolsJimmy Nuñez VarasAinda não há avaliações
- Idioms & Phrases Till CGL T1 2016Documento25 páginasIdioms & Phrases Till CGL T1 2016mannar.mani.2000100% (1)
- Reflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Documento5 páginasReflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Trishika NamrataAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanDocumento7 páginasEffect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanJuniper PublishersAinda não há avaliações
- ML AiDocumento2 páginasML AiSUYASH SHARTHIAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Framing SystemDocumento56 páginasMetal Framing SystemNal MénAinda não há avaliações
- 47-Article Text-338-1-10-20220107Documento8 páginas47-Article Text-338-1-10-20220107Ime HartatiAinda não há avaliações
- Interpreting Piping and Instrumentation DiagramsDocumento41 páginasInterpreting Piping and Instrumentation DiagramsFredric Tun100% (2)
- O2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFDocumento20 páginasO2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFplayer osamaAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure Personal CareDocumento38 páginasBrochure Personal CarechayanunAinda não há avaliações
- Embankment PDFDocumento5 páginasEmbankment PDFTin Win HtutAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Pick UpsDocumento4 páginasMagnetic Pick UpslunikmirAinda não há avaliações
- F-16c.1 Ginkgo Ginkgolic AcidDocumento2 páginasF-16c.1 Ginkgo Ginkgolic AcidNarongchai PongpanAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Elements of Interior DesignDocumento4 páginas2 - Elements of Interior DesignYathaarth RastogiAinda não há avaliações
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDocumento12 páginasSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesAinda não há avaliações
- Maureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichDocumento20 páginasMaureen L. Walsh - Re-Imagining Redemption. Universal Salvation in The Theology of Julian of NorwichAni LupascuAinda não há avaliações
- Apollo TyresDocumento78 páginasApollo TyresADITYA33% (3)
- The Temple of ChaosDocumento43 páginasThe Temple of ChaosGauthier GohorryAinda não há avaliações
- Motor GraderDocumento24 páginasMotor GraderRafael OtuboguatiaAinda não há avaliações
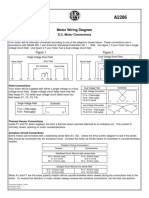
- Motor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor ConnectionsDocumento1 páginaMotor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor Connectionsczds6594Ainda não há avaliações
- Survey Report on Status of Chemical and Microbiological Laboratories in NepalDocumento38 páginasSurvey Report on Status of Chemical and Microbiological Laboratories in NepalGautam0% (1)
- Stability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelDocumento7 páginasStability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelSamwailAinda não há avaliações
- Math 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionDocumento2 páginasMath 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionNyannue FlomoAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal BurnsDocumento50 páginasThermal BurnsPooya WindyAinda não há avaliações