Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Explaining Features of Plosive Consonants
Enviado por
SyafqhDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Explaining Features of Plosive Consonants
Enviado por
SyafqhDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Short Essay: Explain in articulatory terms the features of plosives consonants Prepared by: Syafiqah binti Hasram Plosives
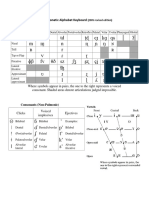
or stops are consonants in which the airstream is completely blocked in the oral cavity for a short period of time (Victoria Fromkin, 2011). The blockage or occlusion may be done with the tongue (front tip [ t ], [ d ], or middle/ body [ k ], [ g ], lips [ b ], [ p ], or glottis [ ]).
According to Peter Roach in 2009, there are four stages in which the plosives are produced. The first phase is the closing phase in which the articulator or articulators move to form the stricture for the plosive. The second phase is called the compression phase; in which the compressed air is stopped from escaping. The third phase is when the articulators used to form the stricture are moved as to allow air to escape. This phase is known as the release phase. The fourth phase is what happens immediately after the release phase and is called post-release phase.
There are also types of stops or plosives. [ p ] and [ b ]are bilabial plosives in which the airstream stopped at the mouth by the complete closure of the lips. [ t ] and [d] are produced with the constriction of the blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge behind the upper front teeth; thus are known as alveolar plosives. While, [ k ] and [g] are produced by raising the back of the tongue to the soft palate or velum. They are known as velar plosives.
To define a consonant, we must also be familiar with the voicing. A pair of words such as rope and robe is sufficient to establish that English has contrastive voicing in plosives, since the final consonants in these two words are both bilabial plosives and they only differ in one being voiceless and the other voiced (Maddieson, 2011). The
plosives [ p ], [ k ] and [ t ] are unvoiced or voiceless which is determined by the lack of vibration in the vocal folds as compared to [ b ], [ g ] and [ d ] plosives which are voiced.
Voiced plosives are characterized by complete closure in the oral cavity, a buildup of pressure during which vibration of the vocal folds continues, and sudden release (Kaiser, 2004). In initial position, the release of [ p ], [ k ] and [ t ] is followed by audible plosion or a burst of noise that is a period during which air escapes through the vocal folds. This is called aspiration. On the other hand, the release of [ b ], [ g ] and [ d ] is followed by a weak plosion and thus is characterized as not aspirated.
As a conclusion, we classify plosives consonants according to where in the vocal tract the airflow restriction occurs which is called the place of articulation; and voicing.
Você também pode gostar
- Phonetics ActivitiesDocumento20 páginasPhonetics ActivitiesFreddyUcinfAinda não há avaliações
- Feature Geometry and Palatalization: Małgorzata Ewa ĆavarDocumento22 páginasFeature Geometry and Palatalization: Małgorzata Ewa ĆavarplavaadresaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 12Documento11 páginasAssignment 12Mai NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- International Phonetic Alphabet IPA PDFDocumento19 páginasInternational Phonetic Alphabet IPA PDFSalvatore RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- OGDEN. An Introduction To English Phonetics. 2009Documento209 páginasOGDEN. An Introduction To English Phonetics. 2009Renata Bennech100% (1)
- English ConsonantsDocumento28 páginasEnglish ConsonantsIzzati AzmanAinda não há avaliações
- The Role of Memory in Wordsworths PoetryDocumento7 páginasThe Role of Memory in Wordsworths PoetrySneha PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- International Phonetic Alphabet - IPADocumento19 páginasInternational Phonetic Alphabet - IPAseety2100% (2)
- What is a Fricative ConsonantDocumento16 páginasWhat is a Fricative ConsonantFannyCubillos100% (1)
- An Essay of Dramatic PoesyDocumento6 páginasAn Essay of Dramatic PoesyNainanluoAinda não há avaliações
- English Phonetics - Task 2 - Practical ExercisesDocumento5 páginasEnglish Phonetics - Task 2 - Practical ExercisesJuan Esteban Zea TiradoAinda não há avaliações
- WK 5 Vowels, Dipthongs Sounds and ConsonantsDocumento40 páginasWK 5 Vowels, Dipthongs Sounds and ConsonantsShamil UsrahAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 8 Kachru Model "The Three Circles of English"Documento2 páginasLesson 8 Kachru Model "The Three Circles of English"JenAinda não há avaliações
- Outline of AristotleDocumento3 páginasOutline of AristotleSaakshi GummarajuAinda não há avaliações
- A Silent Song and Other Stories Edited by Godwin Siundu : Volume One: A Guide to Reading A Silent Song and Other Stories ed. by Godwin Siundu, #1No EverandA Silent Song and Other Stories Edited by Godwin Siundu : Volume One: A Guide to Reading A Silent Song and Other Stories ed. by Godwin Siundu, #1Ainda não há avaliações
- The Song of The Open RoadDocumento4 páginasThe Song of The Open RoadTanmai NaiduAinda não há avaliações
- The Spanish Tragedy: by Thomas KydDocumento12 páginasThe Spanish Tragedy: by Thomas KydTimi UdvAinda não há avaliações
- 20400-Article Text-73126-1-10-20140910 PDFDocumento12 páginas20400-Article Text-73126-1-10-20140910 PDFRajesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- To Build A FireDocumento5 páginasTo Build A FireDonManuelAinda não há avaliações
- ENG Honours PoetryDocumento12 páginasENG Honours PoetryWungreiyon moinao100% (1)
- Rape of The LockDocumento11 páginasRape of The Lockfalak chaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- How Beastly The Bourgeois Is Interpretation ThomasDocumento2 páginasHow Beastly The Bourgeois Is Interpretation Thomasapi-3744071100% (1)
- Mortality Vs ImmortalityDocumento2 páginasMortality Vs Immortalityfarah fouadAinda não há avaliações
- Metaphysical Poets: George Herbert Go To Guide On George Herbert's Poetry Back To TopDocumento10 páginasMetaphysical Poets: George Herbert Go To Guide On George Herbert's Poetry Back To TopEya Brahem100% (1)
- Nature As A Dominant...Documento46 páginasNature As A Dominant...sabri0% (1)
- Post Mid - Lecture 5 - Preface To The Lyrical BalladsDocumento53 páginasPost Mid - Lecture 5 - Preface To The Lyrical Balladsabdullah kakarAinda não há avaliações
- History BS Literature 2nd Semester (2018)Documento33 páginasHistory BS Literature 2nd Semester (2018)IqraAinda não há avaliações
- English Syllabus For UG Hons and Pass CourseDocumento57 páginasEnglish Syllabus For UG Hons and Pass CourseGeminiAinda não há avaliações
- The The Various Communicative Methods Practiced by Animals in The WildDocumento2 páginasThe The Various Communicative Methods Practiced by Animals in The WildAmutha AmmuAinda não há avaliações
- "A Psychoanalytical Study of The Tragic History of DR Faustus" by Christopher Marlow"Documento18 páginas"A Psychoanalytical Study of The Tragic History of DR Faustus" by Christopher Marlow"Israr KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Wordsworth's poem captures experience among daffodilsDocumento3 páginasWordsworth's poem captures experience among daffodilsОльга СайчукAinda não há avaliações
- Is Swift A Misanthrope?Documento6 páginasIs Swift A Misanthrope?Shan SumalaniAinda não há avaliações
- Aristotle's Concept of Tragedy and CharacterizationDocumento4 páginasAristotle's Concept of Tragedy and Characterizationmuneeba100% (1)
- Lotus Eaters, Ulyses and Lady of ShalotDocumento12 páginasLotus Eaters, Ulyses and Lady of ShalotReginaldAinda não há avaliações
- 6 - Dover Beach AnalysisDocumento2 páginas6 - Dover Beach AnalysisRobert HammondAinda não há avaliações
- Format. Hum - Transgender Literature in India A Comparative Study of I Am Vidya and A Gift of Goddess LakshmiDocumento8 páginasFormat. Hum - Transgender Literature in India A Comparative Study of I Am Vidya and A Gift of Goddess LakshmiImpact JournalsAinda não há avaliações
- Wordsworth's Appreciation of Time in "Tintern Abbey"Documento4 páginasWordsworth's Appreciation of Time in "Tintern Abbey"Mark Fernandez75% (4)
- DR Faustus As A Religious PlayDocumento6 páginasDR Faustus As A Religious Playshehnila ikramAinda não há avaliações
- Of Revenge by Francis BaconDocumento2 páginasOf Revenge by Francis BaconJeyarajan100% (1)
- Study Material and Model QuestionsDocumento20 páginasStudy Material and Model QuestionsBelenVetteseAinda não há avaliações
- Panini and Modern+ Linguistics PDFDocumento16 páginasPanini and Modern+ Linguistics PDFSudip HaldarAinda não há avaliações
- 13 - Chapter 9 PDFDocumento37 páginas13 - Chapter 9 PDFSwati DuttAinda não há avaliações
- 408 Evavuation (Tariq Imam Sariq)Documento14 páginas408 Evavuation (Tariq Imam Sariq)Masters EDRUAinda não há avaliações
- Places and Manners of ArticulationDocumento14 páginasPlaces and Manners of Articulationcamila100% (1)
- Word Formation: Compounding, Clipping, and BlendingDocumento3 páginasWord Formation: Compounding, Clipping, and BlendingAida TovmasyanAinda não há avaliações
- A Prayer For My Daughter WB YeatsDocumento5 páginasA Prayer For My Daughter WB YeatsTinku ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- 11 2 ET V1 S1 - Introduction PDFDocumento12 páginas11 2 ET V1 S1 - Introduction PDFshahbaz jokhioAinda não há avaliações
- William Blake QuestionsDocumento4 páginasWilliam Blake Questionsmanazar hussainAinda não há avaliações
- Methapor and Idiom of The Poem From The Hollow Men by T S EliotDocumento10 páginasMethapor and Idiom of The Poem From The Hollow Men by T S EliotDDAinda não há avaliações
- Coleridge's Interpretation of Wordsworth's Preface to Lyrical BalladsDocumento14 páginasColeridge's Interpretation of Wordsworth's Preface to Lyrical BalladsJess MtzAinda não há avaliações
- ComparisonDocumento3 páginasComparisonShahid RazwanAinda não há avaliações
- Analysisi of William Blakes Selected Poems PDFDocumento12 páginasAnalysisi of William Blakes Selected Poems PDFZuma100% (1)
- The Faerie Queen (Spenser)Documento2 páginasThe Faerie Queen (Spenser)Amy Fowler100% (1)
- 3 - Wordsworth - The Preface and DaffodilsDocumento8 páginas3 - Wordsworth - The Preface and DaffodilsSarha Fiorenza100% (1)
- Ocean Vuong Poetry Collection Explores Trauma and IdentityDocumento5 páginasOcean Vuong Poetry Collection Explores Trauma and IdentitychappyAinda não há avaliações
- Rupert BrookeDocumento6 páginasRupert BrookehemalogeshAinda não há avaliações
- Anatony and Cleopatra in Shakespear TragedyDocumento43 páginasAnatony and Cleopatra in Shakespear TragedyAnil MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Solitary ReaperDocumento2 páginasSolitary ReaperKirstenalex100% (2)
- Modern drama characteristics and naturalism principlesDocumento1 páginaModern drama characteristics and naturalism principlesКарина Купраш100% (1)
- Characteristics of Marlowe as a DramatistDocumento8 páginasCharacteristics of Marlowe as a DramatistBDAinda não há avaliações
- Kubla KhanDocumento2 páginasKubla Khanvanilla_42kpAinda não há avaliações
- Alas So AllDocumento1 páginaAlas So AllattiqaAinda não há avaliações
- Shakespeares Plays Study QuestionsDocumento6 páginasShakespeares Plays Study QuestionsMirela Strajeriu HrimiucAinda não há avaliações
- Wilde As ParodistDocumento7 páginasWilde As ParodistNeil Nagwekar0% (1)
- Mark Twain'S The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn As A Racist Novel: A StudyDocumento12 páginasMark Twain'S The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn As A Racist Novel: A StudyTriviaAinda não há avaliações
- Victorian+Lit +charDocumento2 páginasVictorian+Lit +charCristina DoroșAinda não há avaliações
- Chaucer's Influence on English LiteratureDocumento8 páginasChaucer's Influence on English LiteratureSumaira MalikAinda não há avaliações
- Themes of Waste LandDocumento24 páginasThemes of Waste LandRaees Ali KhanAinda não há avaliações
- AbstractDocumento1 páginaAbstractSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Pendidikan Sivik LP EnglishDocumento4 páginasPendidikan Sivik LP EnglishSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Task 2 Literature SynthesisDocumento9 páginasTask 2 Literature SynthesisSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Competing Roles of The National Language and English in Malaysia and The PhilippinesDocumento3 páginasCompeting Roles of The National Language and English in Malaysia and The PhilippinesSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- BEHAVIOURISM THEORY IN THE LANGUAGE CLASSROOMDocumento17 páginasBEHAVIOURISM THEORY IN THE LANGUAGE CLASSROOMSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Collective Nouns ExerciseDocumento2 páginasCollective Nouns ExerciseSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Section A From DidikDocumento7 páginasSection A From DidikSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Notes and Short ExercisesDocumento23 páginasGrammar Notes and Short ExercisesSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Animals Word SearchDocumento1 páginaAnimals Word SearchSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Complete the crossword puzzle with wordsDocumento1 páginaComplete the crossword puzzle with wordsSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Esl in The 21 Learning Century in Malaysia: Challenges and OpportunitiesDocumento2 páginasEsl in The 21 Learning Century in Malaysia: Challenges and OpportunitiesSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Bahan Bacaan 1 Minggu 2Documento12 páginasBahan Bacaan 1 Minggu 2MaryumiAinda não há avaliações
- List Three Games You Will Enjoy When You Go To Fun Time FunfairDocumento6 páginasList Three Games You Will Enjoy When You Go To Fun Time FunfairSyafqh100% (1)
- Basic TensesDocumento3 páginasBasic TensesSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Fun Day at the BeachDocumento1 páginaFun Day at the BeachSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Didik 27 Mac PenulisanDocumento4 páginasDidik 27 Mac PenulisanSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Young Entrepreneur S DAY: DATE: 16 AUGUT 2018 TIME: 1.00 - 2.00 PM Venue: School HallDocumento1 páginaYoung Entrepreneur S DAY: DATE: 16 AUGUT 2018 TIME: 1.00 - 2.00 PM Venue: School HallSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- English Year 6 Paper QuestionsDocumento7 páginasEnglish Year 6 Paper QuestionsSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Year 5 Unit 1 Grammar Plural Nouns ExerciseDocumento4 páginasYear 5 Unit 1 Grammar Plural Nouns ExerciseSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Section A Upsr Paper 2Documento2 páginasSection A Upsr Paper 2SyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Section A From DidikDocumento7 páginasSection A From DidikSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Cycling - Friend's House - Punctured - Roadside - Fix: Short ParagraphDocumento1 páginaCycling - Friend's House - Punctured - Roadside - Fix: Short ParagraphSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Jadual Perkhemahan KhamisDocumento2 páginasJadual Perkhemahan KhamisSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Match Phrases and Make SentencesDocumento2 páginasMatch Phrases and Make SentencesSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Collective Nouns Year 5 Unit 2Documento4 páginasCollective Nouns Year 5 Unit 2SyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Easy Grammar Exercise Year 4 /5Documento1 páginaEasy Grammar Exercise Year 4 /5SyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- English Y5-6 Objective Questions (Exercise)Documento7 páginasEnglish Y5-6 Objective Questions (Exercise)SyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Who Is Who in The QueueDocumento1 páginaWho Is Who in The QueueSyafqh75% (4)
- RPT Year 6 EditedDocumento17 páginasRPT Year 6 EditedSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- Plural NounsDocumento1 páginaPlural NounsSyafqhAinda não há avaliações
- 44 Sounds Aus EnglishDocumento2 páginas44 Sounds Aus EnglishAlfie Arabejo Masong LaperaAinda não há avaliações
- Bengali Consonants (: Bænjônbôrnô)Documento3 páginasBengali Consonants (: Bænjônbôrnô)Aarajita ParinAinda não há avaliações
- Laya & Quintana EnglishDocumento8 páginasLaya & Quintana EnglishMaría Andreina DíazAinda não há avaliações
- Describing Consonants Manner of ArticulationDocumento5 páginasDescribing Consonants Manner of ArticulationAtika Ayu NuraniAinda não há avaliações
- The International Phonetic Alphabet KeyboardDocumento3 páginasThe International Phonetic Alphabet KeyboardGabriela CoralAinda não há avaliações
- For Assistance With IPA Transcriptions of Icelandic For Wikipedia Articles, See Help:IPA/IcelandicDocumento9 páginasFor Assistance With IPA Transcriptions of Icelandic For Wikipedia Articles, See Help:IPA/IcelandicJose miguel Sanchez gutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Vowels and Consonants ChartDocumento2 páginasVowels and Consonants ChartVianne Denine TipayAinda não há avaliações
- English Phonetics Task 2 - Consonant Sounds: Nicol Yerixa Ruiz Castañeda Number of The Collaborative Group: 29Documento4 páginasEnglish Phonetics Task 2 - Consonant Sounds: Nicol Yerixa Ruiz Castañeda Number of The Collaborative Group: 29Nicol Yerixa Ruiz CastañedaAinda não há avaliações
- IPA chart 2020 - Меѓународна фонетска азбука - ВикипедијаDocumento1 páginaIPA chart 2020 - Меѓународна фонетска азбука - ВикипедијаFilip CenovskiAinda não há avaliações
- REVIEWDocumento51 páginasREVIEWQuốc Khang100% (2)
- 1969 Tetzcocan Nahuatl Phonology With Lexicon (Rand Bryan Foster)Documento116 páginas1969 Tetzcocan Nahuatl Phonology With Lexicon (Rand Bryan Foster)sakeke87Ainda não há avaliações
- English Phonetics - Task 5 - Written ExercisesDocumento9 páginasEnglish Phonetics - Task 5 - Written ExercisesJuan Esteban Zea TiradoAinda não há avaliações
- Phonotactic Distribution of Consonantal Sounds in Urdu: Arslan Ahmad - Shakil NasirDocumento6 páginasPhonotactic Distribution of Consonantal Sounds in Urdu: Arslan Ahmad - Shakil NasirJones AAinda não há avaliações
- النظام الصوتي المرحلة الاولى الملف الكاملDocumento48 páginasالنظام الصوتي المرحلة الاولى الملف الكاملjyx9sbghgvAinda não há avaliações
- Voiceless Voiced: Bilabial BilabialDocumento4 páginasVoiceless Voiced: Bilabial BilabialAhmed El-SaadanyAinda não há avaliações
- Percussive Consonants Are Produced Without Any Airstream MechanismDocumento11 páginasPercussive Consonants Are Produced Without Any Airstream MechanismAnonymous fDO1fdVAinda não há avaliações
- Mal Phonetic Reader - RemovedDocumento66 páginasMal Phonetic Reader - RemovedReshmi R NairAinda não há avaliações
- Manner of Articulation DefinitionDocumento9 páginasManner of Articulation DefinitionAdmin LinguizAinda não há avaliações
- Phonetic Notation SystemsDocumento20 páginasPhonetic Notation SystemsHishamMaeenAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson3 English Consonants Description PDFDocumento5 páginasLesson3 English Consonants Description PDFsami karemAinda não há avaliações