Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Tcp/Ip Model: Application Layer
Enviado por
Vikas SharmaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Tcp/Ip Model: Application Layer
Enviado por
Vikas SharmaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
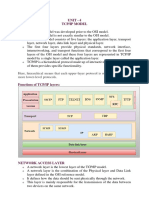
TCP/IP MODEL
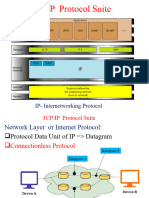
TCP/IP is the most popular protocol stack, which consist of large no of protocol. According to the OSI model TCP/IP consist of only four layers. TCP/IP model is modified form of DOD (Department of Defense) model. A P S T TCP | UDP Internet Protocol N ARP| RARP | ICMP | IGMP | RIP | OSPF | BGP DL All common Lan/Wan Technologies Ph Network Access Internet Transport (Host to Host) Http Smtp Dns Ftp Tftp Telnet Ntp Snmp Ssl Rdp & many more 80 25 53 20 69 23 123 443 3389 pop3 imap Application
Application Layer
This layer contains a large no. of protocols. Each protocol is designed to act as server & client. Some of protocol will need connection oriented. TCP and others may need connection less UDP for data transfer. Application layer use port no.s to identity each application at Transport layer. This layer performs most of functions, which are specified by the Application, Presentation, and Session layer of OSI model.
Transport Layer
Two protocols are available on Transport layer 1) Transmission Control Protocol 2) User Datagram Protocol 1) Transmission Control Protocol TCP performs connection-oriented communication. Its responsibilities are: i) Error Checking ii) Acknowledgement iii) Sequencing iv) Flow Control v) Windowing
TCP Header (24 bytes) Bytes 4 Source port 16 bits ( Randomly generated) (1024) Sequence no. 32 bits (100) Acknowledgement no. 32 bits (500) Header length Reserved 4 bits 6 bits Checksum 16 bits Options 0 or 32 Data (varies) 2) User Datagram Protocol UDP is connection less protocol, which is responsible for error checking and identifying applications using port numbers. UDP Header (8 bytes) Bytes 4 4 Source port 16 bits Length 16 bits Data Destination port 16 bits Ckecksum 16 bits Code bits 6 bits Window 16 bits (512 bytes onwards 1024) Destination port 16 bits ( Fixed ) (80)
Bytes 4 4
4 4
Urgent 16 bits
Internet Layer
The main function of Internet layer is routing and providing a single network interface to the upper layers protocols. Upper or lower protocols have not any functions relating to routing. To prevent this, IP provides one single network interface for the upper layer protocols. After that it is the job of IP and the various Network Access protocols to get along and work together. The main protocols are used in Internet layer:1) Internet Protocol (IP) 2) Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) 3) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) 4) Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) 2
5) Proxy ARP Internet Protocol This protocol works at internet layer. It is responsible for logical addressing, defining type of service and fragmentation. IP Header (20 24 bytes) IP version (4bits) Header length (4) Flag (3) Protocol (8) Source IP (32) Destination IP (32) Options (0 or 32 bits if any) Segment data Type of service (8) Total length(16) Fragmentation offset (13) Header checksum (16)
Identification no (16) Time to live (8)
Você também pode gostar
- Overview Mind Map PDFDocumento2 páginasOverview Mind Map PDFRa Bab50% (2)
- How TCP-IP WorksDocumento29 páginasHow TCP-IP WorksJames GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Durbin Feeling - CWY English DictionaryDocumento396 páginasDurbin Feeling - CWY English DictionaryWyman Kirk83% (6)
- The Passive Voice: Year 7 Sentence StartersDocumento20 páginasThe Passive Voice: Year 7 Sentence StartersMuhammad KholikAinda não há avaliações
- Future of e-Sports: Exploring Benefits of Next Generation InfrastructureDocumento7 páginasFuture of e-Sports: Exploring Benefits of Next Generation InfrastructureRight LuckAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Model PresentationDocumento11 páginasTCP/IP Model PresentationArpitmaan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan SpeakingDocumento20 páginasLesson Plan SpeakingKatia LeliakhAinda não há avaliações
- Topic TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDocumento23 páginasTopic TCP/IP Protocol Suitemalik hadiaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Network Basics: ProtocolsDocumento93 páginasUnderstanding Network Basics: Protocolsnishasaiyed2304Ainda não há avaliações
- Internet ProtocolDocumento120 páginasInternet Protocoldeepsj1988100% (1)
- Tcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP ProtocolsDocumento5 páginasTcp/Ip: How The TCP/IP Protocol Stack Maps To The OSI Model OSI Layers TCP/IP Protocolsajithcoumar351Ainda não há avaliações
- Npms Unit-1Documento36 páginasNpms Unit-1Karthik RaviAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Protocols and URL BasicsDocumento7 páginasTCP/IP Protocols and URL BasicsNandgulabDeshmukhAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Four: TCP/IP Network ManagementDocumento57 páginasChapter Four: TCP/IP Network ManagementYomif NiguseAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Fundamentals: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento27 páginasTCP/IP Fundamentals: Chapter Objectiveschetana sidigeAinda não há avaliações
- 18CSC302J Syllabus - Unit I OverviewDocumento172 páginas18CSC302J Syllabus - Unit I OverviewPraveen SaravananAinda não há avaliações
- OSI & TCP/IP Reference ModelsDocumento33 páginasOSI & TCP/IP Reference ModelsJaishan KashyapAinda não há avaliações
- TCP IP & AddressesDocumento18 páginasTCP IP & Addresses366VEDANTI BACHCHUWARAinda não há avaliações
- Protocol NotesDocumento11 páginasProtocol NotesThiba SivanaihAinda não há avaliações
- CCN Unit-01 (B)Documento56 páginasCCN Unit-01 (B)Basavaraj ShellikeriAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 03Documento21 páginasLecture 03Riju ChatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Etti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSDocumento25 páginasEtti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSbeiculescugeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- ProtocolsDocumento22 páginasProtocolssharkapproachAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Protocols: Web TechnologyDocumento37 páginasInternet Protocols: Web TechnologyMobewtime StylesAinda não há avaliações
- Ebooks - 12 IS-W3D2-SCR200309121203031818Documento12 páginasEbooks - 12 IS-W3D2-SCR200309121203031818shubham sahaiAinda não há avaliações
- #17 TCP-IP ModelDocumento11 páginas#17 TCP-IP ModelPatel NayakAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3 TCP - IP Protocol Suite NotesDocumento9 páginas1.3 TCP - IP Protocol Suite NotesMAGESH K SEC 2020Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction to TCP/IP ProtocolsDocumento27 páginasIntroduction to TCP/IP ProtocolsSandesh ShiwakotiAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Network - TCP - IP ModelDocumento5 páginasComputer Network - TCP - IP ModelAMARJEET KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelDocumento5 páginasTCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelGreen ZoneAinda não há avaliações
- Internet ProtocolDocumento19 páginasInternet ProtocolDaniel AbaraAinda não há avaliações
- The TCP - IP Reference ModelDocumento1 páginaThe TCP - IP Reference ModelFAYSAL AhamadAinda não há avaliações
- Modulator and demodulator functions in data transmissionDocumento51 páginasModulator and demodulator functions in data transmissionANKITAinda não há avaliações
- IP Addressing and Protocols ExplainedDocumento22 páginasIP Addressing and Protocols Explainedmelkamu debasAinda não há avaliações
- IP Router Software Reference GuideDocumento189 páginasIP Router Software Reference Guideniko67Ainda não há avaliações
- IETF Internet Fundamentals Chapter 2 OverviewDocumento78 páginasIETF Internet Fundamentals Chapter 2 OverviewShabil MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Network Chapter ThreeDocumento46 páginasNetwork Chapter ThreeDaniel AshagrieAinda não há avaliações
- Ipv6 AddressDocumento51 páginasIpv6 AddressWeb TestAinda não há avaliações
- OSI LayersDocumento37 páginasOSI LayersAjit WaderAinda não há avaliações
- Acn May 2018Documento45 páginasAcn May 2018shraddha_mundadadaAinda não há avaliações
- TCP IP ModelDocumento31 páginasTCP IP ModelJaveed AhamedAinda não há avaliações
- ICMP MisbehaviourDocumento34 páginasICMP Misbehavioural-amin shohag100% (1)
- Mansoura University Faculty of Computers and Information Department TCP/IP CourseDocumento20 páginasMansoura University Faculty of Computers and Information Department TCP/IP Coursesaher waleedAinda não há avaliações
- Internet Protocol SuiteDocumento854 páginasInternet Protocol SuiteDilys CheungAinda não há avaliações
- W1 HO Networking Concepts PDFDocumento31 páginasW1 HO Networking Concepts PDFRttc PuneAinda não há avaliações
- Group Assignment For 4 Year IT StudentsDocumento15 páginasGroup Assignment For 4 Year IT StudentsAnonymous NNRdxSCpAinda não há avaliações
- Link Layer Overview of TCP/IP ProtocolsDocumento6 páginasLink Layer Overview of TCP/IP Protocolsgani525Ainda não há avaliações
- TCP - IP ProtocolDocumento38 páginasTCP - IP ProtocolShanu SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- TCP and UDP Communication Protocols ExplainedDocumento19 páginasTCP and UDP Communication Protocols ExplainedsawonAinda não há avaliações
- TCP IpDocumento4 páginasTCP IpsukhbirpablaAinda não há avaliações
- Explain About TCP/IP Model.: TCP/IP Supports The Internetworking Protocol. IP, in Turn, Uses Four SupportingDocumento2 páginasExplain About TCP/IP Model.: TCP/IP Supports The Internetworking Protocol. IP, in Turn, Uses Four SupportingYogesh GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- List of Network ProtocolsDocumento5 páginasList of Network Protocolsanon_563889070Ainda não há avaliações
- The Internet NotesDocumento91 páginasThe Internet NotesTejas Raghavendra Bhat MAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Transmission Control Protocol /internet ProtocolDocumento9 páginasPresentation On Transmission Control Protocol /internet ProtocolKide BayAinda não há avaliações
- Functions of ARPDocumento4 páginasFunctions of ARPCherry Mae Dela RosaAinda não há avaliações
- TCP-IP Full SlidesDocumento106 páginasTCP-IP Full SlidesmehdiAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Model ExplainedDocumento10 páginasTCP/IP Model ExplainedNandkumar KhachaneAinda não há avaliações
- 10 - TCP IP ModelDocumento6 páginas10 - TCP IP ModelAbdourahmane BaAinda não há avaliações
- Network and Transport Layers: Tcp/Ip and OsiDocumento42 páginasNetwork and Transport Layers: Tcp/Ip and OsiSomnath LahaAinda não há avaliações
- 17EC64 - Module4 - Network Layer Protocol and Unicast RoutingDocumento52 páginas17EC64 - Module4 - Network Layer Protocol and Unicast RoutingShashidhar krAinda não há avaliações
- TCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Network Interface LayerDocumento3 páginasTCP/IP Protocol Architecture: Network Interface Layersimon sylvesterAinda não há avaliações
- It First ChapterDocumento76 páginasIt First ChapterRohan RathoreAinda não há avaliações
- Network Layer FundamentalsDocumento42 páginasNetwork Layer FundamentalsEwa LisekAinda não há avaliações
- LAN SwitchingDocumento2 páginasLAN SwitchingVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulse Code ModulationDocumento2 páginasPulse Code ModulationVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Old Man Ant The SeaDocumento1 páginaThe Old Man Ant The SeaVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- IP Subnet: Why To Sub?Documento3 páginasIP Subnet: Why To Sub?Vikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulse Code ModulationDocumento2 páginasPulse Code ModulationVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Answer For Study Question 1Documento2 páginasAnswer For Study Question 1Vikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Time Division MultiplexingDocumento2 páginasTime Division MultiplexingVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- All All: For For End EndDocumento2 páginasAll All: For For End EndVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- ASK modulation and demodulationDocumento3 páginasASK modulation and demodulationVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Themes Are The Fundamental and Often Universal Ideas Explored in A Literary WorkDocumento2 páginasThemes Are The Fundamental and Often Universal Ideas Explored in A Literary WorkVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- What Kind of Racism Is Going On in The Book Kim?Documento1 páginaWhat Kind of Racism Is Going On in The Book Kim?Vikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Major CharactersDocumento2 páginasAnalysis of Major CharactersVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- ASK modulation and demodulationDocumento3 páginasASK modulation and demodulationVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Data Structures and AlgorithmsDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To Data Structures and AlgorithmsVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Hill ClimbingDocumento1 páginaHill ClimbingVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 1Documento24 páginasCcna 1Vikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Internal Energy of An Isolated System Is ConstantDocumento12 páginasThe Internal Energy of An Isolated System Is ConstantVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Geometric TransformationDocumento8 páginasGeometric TransformationDaljeet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Bubble SortDocumento6 páginasBubble SortVikas SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade PlanDocumento3 páginas6th Grade PlanMarlon Ramirez JamesAinda não há avaliações
- Matric Exam Timetable Changed To Accommodate Elections.15.9.2021Documento2 páginasMatric Exam Timetable Changed To Accommodate Elections.15.9.2021eNCA.comAinda não há avaliações
- Argumentative Essay (Social Media)Documento2 páginasArgumentative Essay (Social Media)Juviel Ellah Mae Vecinal100% (1)
- Advantages & Disadvantages Extracurricular ActivitiesDocumento3 páginasAdvantages & Disadvantages Extracurricular ActivitiesPaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaAinda não há avaliações
- 3g Research PaperDocumento21 páginas3g Research Paperm_wakte100% (1)
- Marketing MixDocumento4 páginasMarketing Mixpraveenpathak130390Ainda não há avaliações
- Im A Hoop Dancer Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasIm A Hoop Dancer Lesson Planapi-308896998Ainda não há avaliações
- Distance Education: Definitions, Generations, Key Concepts and Future DirectionsDocumento17 páginasDistance Education: Definitions, Generations, Key Concepts and Future Directionsalvin castroAinda não há avaliações
- Vol 8 No 6 - December 2016Documento58 páginasVol 8 No 6 - December 2016IJHSSAinda não há avaliações
- Overview TOEFL IBT WritingDocumento10 páginasOverview TOEFL IBT WritingAmmar AnasAinda não há avaliações
- Cls 6Documento5 páginasCls 6popalina24Ainda não há avaliações
- Plato - The Phaedrus of Plato, With English Notes and Dissertations by W. H. ThompsonDocumento252 páginasPlato - The Phaedrus of Plato, With English Notes and Dissertations by W. H. Thompsonsomebodyelses100% (1)
- Politics and Profit in The Fake News Factory: Four Work Models of Political Trolling in The PhilippinesDocumento27 páginasPolitics and Profit in The Fake News Factory: Four Work Models of Political Trolling in The PhilippinesChritian Laurenze LauronAinda não há avaliações
- Membership Guide CiscoDocumento21 páginasMembership Guide CiscoaassaanmkAinda não há avaliações
- Subject: English Grade Level: 7 UNIT/STRANDS: First Quarter Teachers: Ms. Karen Mae P. Coca, LPTDocumento5 páginasSubject: English Grade Level: 7 UNIT/STRANDS: First Quarter Teachers: Ms. Karen Mae P. Coca, LPTKaren Yen CocaAinda não há avaliações
- The Domain of Psycholinguistics InquiryDocumento34 páginasThe Domain of Psycholinguistics InquiryRogel BelvestreAinda não há avaliações
- Analyse how writers use linguistic devicesDocumento4 páginasAnalyse how writers use linguistic devicesEseel AlsammarraieAinda não há avaliações
- Counting Cars Is Fun FKB Kids Stories PDFDocumento22 páginasCounting Cars Is Fun FKB Kids Stories PDFEko GandaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To SentencesDocumento20 páginasIntroduction To Sentencestahar.kabeAinda não há avaliações
- Alcatel-Lucent 9600 USY: Sdhmedium-Orhigh-CapacitydigitalmicrowavelinksDocumento4 páginasAlcatel-Lucent 9600 USY: Sdhmedium-Orhigh-Capacitydigitalmicrowavelinksaltus_aryaAinda não há avaliações
- Eden Stanley For Brac - Global Communications Strategy - Sep17Documento27 páginasEden Stanley For Brac - Global Communications Strategy - Sep17Noor E Tazrian KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment On Tech AbuseDocumento4 páginasAssignment On Tech AbusesrinidhiAinda não há avaliações
- PTE & AccentDocumento2 páginasPTE & AccentHung NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Siska 3Documento23 páginasJurnal Siska 3Anonymous 3LwVkUsdAinda não há avaliações
- Dictionary of IdiomsDocumento2 páginasDictionary of IdiomsAlexander International100% (1)