Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Sandra Enn Bahinting Homework 2
Enviado por
Sandra Enn BahintingDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sandra Enn Bahinting Homework 2
Enviado por
Sandra Enn BahintingDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sandra Enn Bahinting
Homework 2
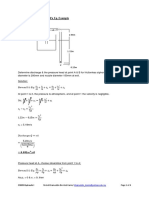
1. Consider the problem of coquette flow between parallel plates for a non-newtonian fluid. ( )
Assuming constant pressure and temperature, solve for the velocity distribution u(y) between the plates for a)n<1 and b) n>1. Plot the velocity profile. Compare with the Newtonian solution Solution: NON-NEWTONIAN Conservation of momentum at x-direction:
Assumptions are follows: Flow is infinite in the x-z plane and steady: Steady-state:
No flow in z direction:
Constant Velocity:
Boundary conditions: ( ( Simplifying the momentum equation: ) ) ( ( ) )
Where
( )
Substituting the said equation to the simplified momentum equation we have;
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) Boundary conditions:
) (
( ( Since pressure is constant, ( ) ( )
) )
) ( )
Therefore, ( ) NEWTONIAN Conservation of momentum at x-direction:
Assumptions are follows: Flow is infinite in the x-z plane and steady: Steady-state:
No flow in z direction:
Constant Velocity:
Boundary conditions: ( ( Simplifying the momentum equation: ) ) ( ( ) )
Where
( )
Substituting the said equation to the simplified momentum equation we have; ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Boundary conditions: ( ( Since pressure is constant, ( ) ( ) ( ) ) ) ( ) ; n=1
Therefore, ( )
This shows that given the same the set of assumptions and conditions the Non-newtonian and Newtonian have the same the velocity distribution. Furthermore, the plot for the velocity profile would be same.
1.5
Y h
1 0.5 0 0 -0.5 -1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 Series1
Linear velocity profile
u(y)
2. Stokes drag on a sphere a. Obtain BSL Equation (2.6-9) from BSL Equation (2.6-7) b. Obtain BSL Equation (2.6-12) from BSL Equation (2.6-10) Solution: a.
( )
[ (
Eqn. 2.6-7
where
and the normal stress
is zero at r=R
( )
[ (
( )
Let
Let =
( )
( )
( )
( )
Eqn. 2.6-9
b.
( )
) =
The shear stress distribution on the sphere surface,
( )
Eqn. 2.6-10
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
Eqn. 2.6-12
3. A sphere of specific gravity 7.8 is dropped into an oil of specific gravity of 0.88 and viscosity = 0.15 Pa-sec. Estimate the terminal velocity of the sphere if its diameter is a. 0.1 mm b. 1 mm c. 10 mm Which of these is creeping motion? Solution: Equation for terminal velocity is given in equation 2. 6-17 ( )
Substituting the values for each variable in the equation above, we have; a. 0.1 mm ( ) ( )
Solving for the Reynolds Number, we obtained;
)(
)(
For b and c, same equations are used for terminal velocity and Reynolds number. b. 1 mm
c. 10 mm
Therefore, it can be said that the 3 spheres having different diameters are the creeping motion. Since these obey the condition for a creeping motion which is to have a Reynolds number that is less than 0.1.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Solids (V 1) 3bh) ConeDocumento13 páginasSolids (V 1) 3bh) ConeSandra Enn Bahinting0% (1)
- Writing A Thesis ProposalDocumento4 páginasWriting A Thesis ProposalSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsDocumento29 páginasLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Convective Mass TransferDocumento46 páginasConvective Mass TransferSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Documento48 páginasLectures 7 - Solids (V BH)Sandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Solids HandlingDocumento13 páginasSolids HandlingSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- The Set of Real Numbers and Its PropertiesDocumento29 páginasThe Set of Real Numbers and Its PropertiesSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugal Separation Processess: Prepared by Engr. Sandra Enn BahintingDocumento31 páginasCentrifugal Separation Processess: Prepared by Engr. Sandra Enn BahintingSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Hazard: Industrial Process SafetyDocumento11 páginasChemical Hazard: Industrial Process SafetySandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Process IndustriesDocumento29 páginasChemical Process IndustriesSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Equation Solution and Solution SetsDocumento17 páginasEquation Solution and Solution SetsSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Shell Momentum BalanceDocumento13 páginasShell Momentum BalanceSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Vsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometryDocumento16 páginasVsepr: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular GeometrySandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- SET IdentitiesDocumento21 páginasSET IdentitiesSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Factoring PolynomialsDocumento2 páginasFactoring PolynomialsSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Homework 1Documento5 páginasHomework 1Sandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Mindanao State University-Iligan Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering College of EngineeringDocumento7 páginasMindanao State University-Iligan Institute of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering College of EngineeringSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Transient Response of Simple Control SystemsDocumento8 páginasTransient Response of Simple Control SystemsSandra Enn BahintingAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ReportDocumento16 páginasLab ReportSandra Enn Bahinting100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Conversion of Earth-Centered Earth-Fixed Coordinates To Geodetic CoordinatesDocumento6 páginasConversion of Earth-Centered Earth-Fixed Coordinates To Geodetic CoordinatesAlex PavloffAinda não há avaliações
- Futaba 6EX 2.4 GHZDocumento38 páginasFutaba 6EX 2.4 GHZMarcelo CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 0663 PaperDocumento5 páginas2014 0663 PaperKlop KlopensonnAinda não há avaliações
- CabacDocumento12 páginasCabacAmit VijayvargiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bell Peak Plane CrashDocumento11 páginasBell Peak Plane CrashKevinMurgatroydAinda não há avaliações
- IPC CheckDocumento1 páginaIPC ChecktailwindflightcenterAinda não há avaliações
- F-14B Afms Bombcat PP 47Documento47 páginasF-14B Afms Bombcat PP 47SpazSinbad2100% (3)
- Runways: Bergen Lufthavn, Flesland Norway Aerodrome Chart IcaoDocumento1 páginaRunways: Bergen Lufthavn, Flesland Norway Aerodrome Chart IcaoEmmaAinda não há avaliações
- Reciprocating Piston Engine Lubrication SystemDocumento39 páginasReciprocating Piston Engine Lubrication SystemccoyureAinda não há avaliações
- AeroelasticityDocumento24 páginasAeroelasticityShanthipriya Guru100% (1)
- P2 Rating: Flight Fundamentals (Part 1: Basics of Flight) Lesson 10: Lifting Me Higher and HigherDocumento6 páginasP2 Rating: Flight Fundamentals (Part 1: Basics of Flight) Lesson 10: Lifting Me Higher and HigherThar LattAinda não há avaliações
- Passenger Boarding Bridges AdelteDocumento8 páginasPassenger Boarding Bridges AdelteIsmail SayyedAinda não há avaliações
- JHON FREDDY MARBUN (Resume) - 1Documento2 páginasJHON FREDDY MARBUN (Resume) - 1jhonfreddymarbunAinda não há avaliações
- Airworthiness Compliance Checklists For Common Part 23 Supplemental Type Certificate (STC) ProjectsDocumento68 páginasAirworthiness Compliance Checklists For Common Part 23 Supplemental Type Certificate (STC) ProjectsJaime Duque PerezAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 2-Basics AerodynamicsDocumento23 páginasUNIT 2-Basics Aerodynamicspiravi66Ainda não há avaliações
- CPL Procedure NewDocumento5 páginasCPL Procedure NewShibin JohneyAinda não há avaliações
- III. Solid Propellant Rocket MotorsDocumento18 páginasIII. Solid Propellant Rocket MotorsdAinda não há avaliações
- C3009 Hydraulic I: Bernoulli's Eq. Example Ex.1Documento4 páginasC3009 Hydraulic I: Bernoulli's Eq. Example Ex.1Marzs MarAinda não há avaliações
- ATP IndexDocumento2.352 páginasATP IndexRicardo zafra100% (1)
- Angular Projectile MotionDocumento16 páginasAngular Projectile MotionwscienceAinda não há avaliações
- Genesys Aerosystems VFR HeliSAS Helicopter Autopilot +++++Documento7 páginasGenesys Aerosystems VFR HeliSAS Helicopter Autopilot +++++NickAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Atpl 11 Npa 29 PBN 22Documento1 páginaEbook Atpl 11 Npa 29 PBN 22BirilloAinda não há avaliações
- Aviation Management Master ThesisDocumento5 páginasAviation Management Master ThesisLindsey Sais100% (2)
- Nasa CR 142379 Detailed Test Objectives For Mercury Atlas Vehicle 67 D NASA Mission MA 2 1975066485Documento111 páginasNasa CR 142379 Detailed Test Objectives For Mercury Atlas Vehicle 67 D NASA Mission MA 2 1975066485LohnJittleAinda não há avaliações
- CSS Capabilities OverviewDocumento24 páginasCSS Capabilities OverviewPankajatSIBMAinda não há avaliações
- Kalpana ChawlaDocumento5 páginasKalpana ChawlaSamarth ParmarAinda não há avaliações
- 062 - Radio Navigation - QuestionsDocumento44 páginas062 - Radio Navigation - QuestionsEASA ATPL Question Bank67% (3)
- BA-31 32 Pilot Standardization R6 PDFDocumento137 páginasBA-31 32 Pilot Standardization R6 PDFCamilo Restrepo100% (1)
- Smart MaterialDocumento19 páginasSmart MaterialSanthuCivilAinda não há avaliações
- AVI-9 Digital Map System-Tactical Situation DisplayDocumento36 páginasAVI-9 Digital Map System-Tactical Situation DisplayIvan LeonardoAinda não há avaliações