Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Assignment No - 2 TE Div - B
Enviado por
Subhash KDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Assignment No - 2 TE Div - B
Enviado por
Subhash KDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
D. Y.
PATIL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, AKURDI, PUNE - 44
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Assignment No 02
Power Screws
Submission last Date: 19-08-2013 Sub: Machine Design-I
Qes.cNo Q. 1 ]
Questions Discuss the various types of power threads. Give at least two practical applications for each Type. Discuss their relative advantages and disadvantages. Write down in detail Terminology used in Power screw. Write down any -10 [Ten] Application of Power screw. Write down Standard Dimensions for Square thread in Tabular Foam. Which includes Points are - d, dc, Pitch(P) and range 22mm to 120mm Derive the expression for maximum efficiency of square threads. Derive formula for torque required to raise the load and torque required to lower the load by a square threaded power screw. What does mean by self locking screws? Explain the condition for self-locking. Also give applications of self locking screw.
Q. 2 ] Q. 3 ] Q. 4 ]
Q. 5 ] Q. 6 ]
Q. 7 ]
Q. 8 ] An electric motor driven power screw moves a nut in a horizontal plane against a force of 75 kN at a speed of 300 mm / min. The screw has a single square thread of 6 mm pitch on a major diameter of 40 mm. The coefficient of friction at screw threads is 0.1. Estimate power of the motor. [ Problem No: 17.02 - R.S Khurmi Page No : 636 ] Q. 9 ] Vertical two start square threaded screw of a 100 mm mean diameter and 20 mm pitch supports a vertical load of 18 kN. The axial thrust on the screw is taken by a collar bearing of 250 mm outside diameter and 100 mm inside diameter. Find the force required at the end of a lever which is 400 mm long in order to lift and lower the load. The coefficient of friction for the vertical screw and nut is 0.15 and that for collar bearing is 0.20. [ Problem No: 17.04 - R.S Khurmi Page No : 638 ]
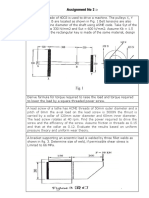
Q. 10 ] A power screw having double start square threads of 25 mm nominal diameter and 5 mm pitch is acted upon by an axial load of 10 kN. The outer and inner diameters of screw collar are 50 mm and 20 mm respectively. The coefficient of thread friction and collar friction may be assumed as 0.2 and 0.15 respectively. The screw rotates at 12 r.p.m. Assuming uniform wear condition at the collar and allowable thread bearing pressure of 5.8 N/mm2, find: 1. the torque required to rotate the screw; 2. the stress in the screw; and 3. the number of threads of nut in engagement with screw. [Example 17.7. - R.S Khurmi Page No : 646 ] Q. 11 ] A C-clamp, as shown in Fig.(a), has Trapezoidal threads of 12 mm outside diameter and 2 mm pitch. The coefficient of friction for screw threads is 0.12 and for the collar is 0.25. The mean radius of the collar is 6 mm. If the force exerted by the operator at the end of the handle is 80 N, find: 1. The length of handle; 2. The maximum shear stress in the body of the screw and where does this exist; and 3. The bearing pressure on the threads. [Example 17.11. - R.S Khurmi Page No : 652 ] A vertical two start square threaded screw of 100 mm mean diameter and 20 mm pitch supports a vertical load of 18 kN. The nut of the screw is fitted in the hub of a gear wheel having 80 teeth which meshes with a pinion of 20 teeth. The mechanical efficiency of the pinion and gear wheel drive is 90 percent. The axial thrust on the screw is taken by a collar bearing 250 mm outside diameter and 100 mm inside diameter. Assuming uniform pressure conditions, find, minimum diameter of pinion shaft and height of nut, when coefficient of friction for the vertical screw and nut is 0.15 and that for the collar bearing is 0.20. The permissible shear stress in the shaft material is 56 MPa and allowable bearing pressure is 1.4 N/mm2. [Example 17.13. - R.S Khurmi Page No : 655 ]
Q. 12 ]
Você também pode gostar
- Introduction to Power Screws and Welded JointsDocumento23 páginasIntroduction to Power Screws and Welded JointssathiaAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Machine Elements - IIDocumento8 páginasDesign of Machine Elements - IIprasaad26Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine Elements Tutorial on Screw Design and EfficiencyDocumento2 páginasMachine Elements Tutorial on Screw Design and EfficiencydvarsastryAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics of Machine Tutorial on Friction ProblemsDocumento1 páginaKinematics of Machine Tutorial on Friction Problemspatelsandip1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine Component Design QuestionsDocumento6 páginasMachine Component Design Questionssuneel kumar rathoreAinda não há avaliações
- DMM Question BankDocumento2 páginasDMM Question Bankzubair ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Design1 SheetsDocumento9 páginasDesign1 SheetsYou channelAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engineering Design QuestionsDocumento4 páginasMechanical Engineering Design QuestionsSoham MisalAinda não há avaliações
- MD Tut PDFDocumento6 páginasMD Tut PDFNelsan PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank - DMEDocumento6 páginasQuestion Bank - DMEBdhdhshAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Quest Ut-2Documento9 páginasDme Quest Ut-2aadhithyarajasekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Automobile Design Rev2015Documento6 páginasAutomobile Design Rev2015Rithik Raj RanjuAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank Numericals DMEDocumento3 páginasQuestion Bank Numericals DMEVanessa SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Power Screw SheetDocumento4 páginasPower Screw SheetMohamed GamalAinda não há avaliações
- TE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFDocumento4 páginasTE - 2019 - Design of Machine Elements PDFonkar nikamAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third YearDocumento4 páginasAssignment No. 3 &4 B.Tech Mechanical Engineering Third Yearharish_kumar201301Ainda não há avaliações
- Design of Machine ElementsDocumento10 páginasDesign of Machine ElementsMahalingam NanjappanAinda não há avaliações
- DMM Ii (2015)Documento35 páginasDMM Ii (2015)gorijalaAinda não há avaliações
- Gtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankDocumento5 páginasGtustudies - FMD IMP Question BankJaideep ZalaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial No.6 DMEDocumento1 páginaTutorial No.6 DMEOnkarAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDocumento2 páginasTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Design of Machine Element-IIDocumento53 páginasDesign of Machine Element-IIPramod R Bidve100% (1)
- Dme Model Key 2019Documento25 páginasDme Model Key 2019Siva RamanAinda não há avaliações
- FinallDocumento175 páginasFinallremeceldo dagamac100% (1)
- 13 ME AssignmentDocumento2 páginas13 ME AssignmentMuhammad Sharif JamaliAinda não há avaliações
- 07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIDocumento11 páginas07a6ec05 Designofmachinemembers IIzahid_polyAinda não há avaliações
- Common Subject Code: Shivaji University, KolhapurDocumento10 páginasCommon Subject Code: Shivaji University, Kolhapursatyamchgl2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Chp4 2 - BrakesDocumento36 páginasChp4 2 - BrakesAzhar BaigAinda não há avaliações
- Dme-22 6 15Documento8 páginasDme-22 6 15VIGNESH L RAinda não há avaliações
- ME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFDocumento15 páginasME6503-Design of Machine Elements PDFkarthikAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Elements Question BankDocumento3 páginasMachine Elements Question BanksonawanepmsAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01Documento10 páginasMachine Design & Industrial Drafting SUBJECT CODE:-2141907 Tutorial - 01The AIRS CreationsAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Machine Members II R5320305 Set 3Documento2 páginasDesign of Machine Members II R5320305 Set 3Ravi Kumar KamarthiAinda não há avaliações
- R7310305 Design of Machine Members - IDocumento1 páginaR7310305 Design of Machine Members - IsivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocumento6 páginas4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Assignment 2Documento3 páginasAssignment 2sonawanepmsAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Question BankDocumento4 páginasDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- Dme Question Bank 2Documento4 páginasDme Question Bank 2Ronak HadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- LabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Documento23 páginasLabManual MDID2016 2016 02 24 16 29 36Rajat MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- MDDocumento5 páginasMDYogesh DanekarAinda não há avaliações
- MD II Machine Design AssignmentsDocumento5 páginasMD II Machine Design Assignmentsrishabhk28995Ainda não há avaliações
- Possible Exercise On Machine Element Two Flat BeltDocumento4 páginasPossible Exercise On Machine Element Two Flat BeltAbebaw AyeleAinda não há avaliações
- Me8593 Iq R17Documento4 páginasMe8593 Iq R17Vaideesh LJAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Design I TutorialDocumento3 páginasMachine Design I TutorialbngelotrAinda não há avaliações
- DME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)Documento7 páginasDME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)honeyfunnyAinda não há avaliações
- DME Question BankDocumento4 páginasDME Question BankILAYAPERUMAL KAinda não há avaliações
- Friction 2 Marks and Important ProblemsDocumento2 páginasFriction 2 Marks and Important ProblemsSachi DhanandamAinda não há avaliações
- Dme Model 2Documento6 páginasDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiAinda não há avaliações
- Projects For Lab BDocumento91 páginasProjects For Lab BPeter AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- MD2 Model QuestionsDocumento2 páginasMD2 Model Questionsmanish sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Imp Qoestions MDDocumento3 páginasImp Qoestions MDvenuedAinda não há avaliações
- Pointers For ReviewDocumento3 páginasPointers For ReviewAdriel JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Dmm2 Mar2006Documento8 páginasDmm2 Mar2006Abdul Saleem MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- gupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9Documento3 páginasgupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9mahendra babu mekalaAinda não há avaliações
- DME QB All UnitsDocumento11 páginasDME QB All UnitsPrakash ThangavelAinda não há avaliações
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesNo EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- How to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheNo EverandHow to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Prompting Science and Engineering Students in Practical TrigonometryNo EverandPrompting Science and Engineering Students in Practical TrigonometryAinda não há avaliações
- 11 - Chapter 2 PDFDocumento30 páginas11 - Chapter 2 PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- FEM Análise para Engrenagens HelicoidaisDocumento12 páginasFEM Análise para Engrenagens HelicoidaisFelipe_PalmeiroAinda não há avaliações
- 12 - Chapter 1 PDFDocumento10 páginas12 - Chapter 1 PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- 07 - Chapter 2 PDFDocumento19 páginas07 - Chapter 2 PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Cotter Joint: Fig 01: Assembled Cottered JointDocumento7 páginasCotter Joint: Fig 01: Assembled Cottered JointSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment ClutchDocumento624 páginasAssignment ClutchSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Optimization of multiple EDM performance characteristics for SS 316 using Grey relational analysisDocumento25 páginasOptimization of multiple EDM performance characteristics for SS 316 using Grey relational analysisSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No: 2: Date:-Dept: - Mechanical EngineeringDocumento1 páginaAssignment No: 2: Date:-Dept: - Mechanical EngineeringSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- 05 Chapter-2 PDFDocumento44 páginas05 Chapter-2 PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Avon Electronics, Pune PDFDocumento1 página1) Avon Electronics, Pune PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Cotter Joint Failure Modes AnalysisDocumento7 páginasCotter Joint Failure Modes AnalysisSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento1 páginaAssignment 1Subhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Course Outcomes by Cad CamDocumento2 páginasCourse Outcomes by Cad CamSubhash K0% (1)
- META Lab PDFDocumento1 páginaMETA Lab PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- New Microsoft Office Word Document PDFDocumento5 páginasNew Microsoft Office Word Document PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- PLC Programming: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocumento6 páginasPLC Programming: Department of Mechanical EngineeringSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Quotation Requirement of Mechatronices Lab PDFDocumento2 páginasQuotation Requirement of Mechatronices Lab PDFSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Magnetic Bearing Technology:: 4) Introduction To Mechanical VibrationsDocumento1 página1) Magnetic Bearing Technology:: 4) Introduction To Mechanical VibrationsSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- When Is The Report DueDocumento2 páginasWhen Is The Report DueSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Work Reports: Goals of Practical Work Report WritingDocumento4 páginasWork Reports: Goals of Practical Work Report WritingSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Mechatronics Unit Test Question BankDocumento1 páginaMechatronics Unit Test Question BankSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Selection Subject RelatedDocumento1 páginaSelection Subject RelatedSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Transducers Explained: Classification, Examples and PrinciplesDocumento32 páginasTransducers Explained: Classification, Examples and PrinciplesSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Study of LVDTDocumento10 páginasStudy of LVDTSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Calibration of Temperature SensorsDocumento13 páginasCalibration of Temperature SensorsSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report Writing Format - FinalDocumento13 páginasProject Report Writing Format - FinalSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Supreme Inustrial Visit Report 2012 NewDocumento26 páginasSupreme Inustrial Visit Report 2012 NewSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- MECHATRONISCDocumento2 páginasMECHATRONISCSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Vaccum Braking SystemDocumento16 páginasVaccum Braking SystemSubhash KAinda não há avaliações
- Alina Dawood - QS - Long AssignmentDocumento11 páginasAlina Dawood - QS - Long AssignmentK AndreAinda não há avaliações
- SP 90 00Documento78 páginasSP 90 00aminAinda não há avaliações
- Sr. Project Manager / SuperintendentDocumento5 páginasSr. Project Manager / Superintendentapi-121459116Ainda não há avaliações
- ISICC Press CTB 2007 2.1.PRS2833 PDFDocumento117 páginasISICC Press CTB 2007 2.1.PRS2833 PDFsairamas07Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 Intro To Project Management StudentrevPFDocumento33 páginasLecture 1 Intro To Project Management StudentrevPFSyed Farjad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Sample - 87lDocumento2 páginasSample - 87lAnonymous dH3DIEtzAinda não há avaliações
- UdoDocumento136 páginasUdoSindhu RamAinda não há avaliações
- Tumile Hack Generator Coins No Human VerificationDocumento3 páginasTumile Hack Generator Coins No Human VerificationMark yoz100% (1)
- HealthSouth Case StudyDocumento41 páginasHealthSouth Case StudyAlex D. Padilla100% (1)
- Manil West 1sept13 DoenDocumento310 páginasManil West 1sept13 DoenRumelaSamantaDattaAinda não há avaliações
- Ford's Vision and Mission Drive Global LeadershipDocumento2 páginasFord's Vision and Mission Drive Global LeadershipstandalonembaAinda não há avaliações
- Conference Proceedings of The Design Management Academy 2017 Volume 2Documento276 páginasConference Proceedings of The Design Management Academy 2017 Volume 2Erik BohemiaAinda não há avaliações
- Aero SemDocumento182 páginasAero SemNaveen Singh100% (1)
- G SaminathanDocumento6 páginasG SaminathanSantoshkumar GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- 2Documento102 páginas2nesamil6941Ainda não há avaliações
- Difference Between 60439 and 61439 (Siemens)Documento1 páginaDifference Between 60439 and 61439 (Siemens)Heera JanAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Pulling Schemes For Iindian Oil CoorporationDocumento35 páginasCustomer Pulling Schemes For Iindian Oil Coorporationsharma3066334Ainda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Filter Classes According EN 779, EN 1822 and ASHRAE 52.2Documento4 páginasComparison of Filter Classes According EN 779, EN 1822 and ASHRAE 52.2gowrish80_bmsAinda não há avaliações
- CP Mining Heavy Machinery CatalogDocumento56 páginasCP Mining Heavy Machinery Catalogfdpc1987Ainda não há avaliações
- BlendingDocumento15 páginasBlendingFrancis GodoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment NoDocumento4 páginasAssignment NoEmmi YfhAinda não há avaliações
- Lean Manufacturing Key BenefitsDocumento12 páginasLean Manufacturing Key BenefitsSundaravignesh 1809Ainda não há avaliações
- 2016-08-07 MM IM Batch TransferPosting MovTypes BloggedDocumento17 páginas2016-08-07 MM IM Batch TransferPosting MovTypes BloggedRahul JainAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engg Classes at Jyothis AcademyDocumento14 páginasMechanical Engg Classes at Jyothis AcademyRAMA RAJU PYDIAinda não há avaliações
- Thread Basics - GO-No GoDocumento2 páginasThread Basics - GO-No GoKundan Kumar MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Saes-Z-002 Locked by BadrDocumento8 páginasSaes-Z-002 Locked by Badrsalic2013Ainda não há avaliações
- Apollo 13 Mission AS-508Documento143 páginasApollo 13 Mission AS-508Aviation/Space History LibraryAinda não há avaliações
- Gripper of FTV Invisio Panels For Horizontal FacadeDocumento16 páginasGripper of FTV Invisio Panels For Horizontal FacadefghfAinda não há avaliações
- Training Report On Cement Factory Sub StationDocumento18 páginasTraining Report On Cement Factory Sub Stationlalit kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Khusna 1805 5275 1 Ed Cipto 6Documento8 páginasKhusna 1805 5275 1 Ed Cipto 6AROTE ADVENTUREAinda não há avaliações