Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Drug Form 2
Enviado por
Kwesi YasayTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Drug Form 2
Enviado por
Kwesi YasayDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
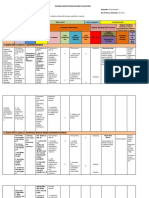
CAPITOL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING Name of Student : Name of Patient:_______________ __________________________ Date of Assignment:______________ Ward:________________________Bed No.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name,
classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
iNDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF THE DRUG
NURSING RESPONISBILITIES
Generic name: lidocaine Brand name: Lidamantle Classification: Anesthetic Dosage: 1ml Route: IM/topical Frequency:
Lidocaine suppresses the automaticity and spontaneous depolarization of the ventricles during diastole by altering the flux of sodium ions across the cell membrane with little or no effect on the heart. Locally, it produces local anesthesia effect by inhibiting the transport of ions across the neural membranes. Thus, initiation and conduction of normal nerve impulses is prevented.
*Intravenous ventricular arrhythmias *Intramuscular selfinjected or when IV is unavailable during transport to local facilities *Local infiltration or mucosal or topical anesthetic *Patch used when pain is present due to postherpetic neuralgia
Hypovolaemia; heart block or other conduction disturbances.
Dizziness, paraesthesia, drowsiness, confusion, respiratory depression and convulsions.
When Lidocaine is administered as an antiarrhythmic the nurse should monitor the ECG continuously. Blood pressure and respiratory status should be monitored frequently during the drug administration. When administered as
an anesthetic, the numbness of the affected part should be assessed. Serum Lidocaine levels should be monitored frequently during prolonged use. Therapeutic serum lidocaine levels range from 1.5 to 5 mcg/ml. If signs of overdose occur (listed above), stop the infusion immediately and monitor the patient closely.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name,
classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
iNDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF THE DRUG
NURSING RESPONISBILITIES
Generic name: Tetanus immunoglobulin(human) Brand name: Classification: Vaccines Dosage: 250 units Route: IM Frequency:
Tetanus immunoglobulin is used for passive immunisation against tetanus. Absorption: Well absorbed.
Tetanus prophylaxis. Tetanus treatment.
Must not be given IV as patient could develop shock. Should not be given in severe thrombocytopenia & in hemostasis.
Chills, headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, allergic reactions, dizziness, low BP, arthralgia & moderate low back pain.
Remove the prefilled syringe from the package. Lift syringe by barrel, not by plunger. Twist the plunger rod clockwise until the threads are seated. With the rubber needle shield secured on the syringe tip, push the plunger rod forward a few millimeters to break any friction seal between the rubber stopper and the glass syringe barrel. Remove the needle shield and expel air bubbles. [Do not remove the rubber needle shield to prepare the product for administration until immediately prior to the anticipated injection time.] Proceed with hypodermic needle puncture. Aspirate prior to injection to confirm that the needle is not in a vein or artery. Inject the medication.
Keeping your hands behind the needle, grasp the guard with free hand and slide forward toward needle until it is completely covered and guard clicks into place. If audible click is not heard, guard may not be completely activated. Place entire prefilled glass syringe with guard activated into an approved sharps container for proper disposal.
CAPITOL UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING Name of Student : Name of Patient:_______________ __________________________ Date of Assignment:______________ Ward:________________________Bed No.
DRUG ORDER (Generic name, brand name,
classification, dosage, route, frequency)
MECHANISM OF ACTION
iNDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF THE DRUG
NURSING RESPONISBILITIES
Generic name: favirab Brand name: Lidamantle Classification: Vaccines Dosage: 40 iu/kg Route: IM Frequency:
Used in a postexposure prophylaxis regimen that includes active immunizatio n with rabies vaccine and passive immunization with RIG. RIG provides immediate, temporary rabies virus-neutralizing antibodies until the patient has an immunologic response to active immunization with rabies vaccine and produces virusneutralizing antibodies.
Seroprophylaxis in individuals exposed to rabies virus, particularly serious exposure (multiple severe bites to the face, head, neck & hands when domestic or wild animal incriminated either cannot be examined or is affected or suspected of being affected by rabies; bites in young childn).
Known history of allergic symptoms to equine proteins.
Immediate reactions: Anaphylactoid reactions w/ hypotension, dyspnea & urticaria. Delayed reactions: Serum sickness-like reactions may occur about 6 days after the beginning of treatment.
Do not administer RIG in the same syringe or at the same injection site as rabies vaccine. Do not administer IV.
Você também pode gostar
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocumento8 páginasDrug Study - Paracetamoldamtere71% (7)
- IFU Stimulate - LFT01 Rev.02Documento9 páginasIFU Stimulate - LFT01 Rev.02Ana ČolovićAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Lidocaine HCL) - TorresDocumento6 páginasDrug Study (Lidocaine HCL) - TorresbabiAinda não há avaliações
- IFU Hydro Deluxe - LFT03 Rev.02Documento9 páginasIFU Hydro Deluxe - LFT03 Rev.02Ana ČolovićAinda não há avaliações
- IFU Intense - LFT06 Rev.02Documento9 páginasIFU Intense - LFT06 Rev.02Ana ČolovićAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3No EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3Ainda não há avaliações
- Viceversa Tarot PDF 5Documento1 páginaViceversa Tarot PDF 5Kimberly Hill100% (1)
- 5 Star Hotels in Portugal Leads 1Documento9 páginas5 Star Hotels in Portugal Leads 1Zahed IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Missouri Courts Appellate PracticeDocumento27 páginasMissouri Courts Appellate PracticeGeneAinda não há avaliações
- Micron Interview Questions Summary # Question 1 Parsing The HTML WebpagesDocumento2 páginasMicron Interview Questions Summary # Question 1 Parsing The HTML WebpagesKartik SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing StrategyDocumento31 páginasManufacturing Strategyrajendra1pansare0% (1)
- Lea 4Documento36 páginasLea 4Divina DugaoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study FormatDocumento13 páginasDrug Study FormatMa'rose Briones100% (1)
- KybellaDocumento14 páginasKybellaErik BrooksAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium BromideDocumento8 páginasDrug Study Clindamycin, Ipatropium Bromidepaupaulala100% (2)
- Sepsis PharmacologyDocumento9 páginasSepsis PharmacologyAlex MarieAinda não há avaliações
- Continuation of PneumoniaDocumento6 páginasContinuation of PneumoniagorresAinda não há avaliações
- CHECKLIST PROCEDURES (Immunization)Documento3 páginasCHECKLIST PROCEDURES (Immunization)Elaine Frances IlloAinda não há avaliações
- Zovirax (1) MsdsDocumento39 páginasZovirax (1) MsdsHenokh Youthjoshers RoryAinda não há avaliações
- CHECKLIST PROCEDURES (Immunization)Documento3 páginasCHECKLIST PROCEDURES (Immunization)Elaine Frances IlloAinda não há avaliações
- A Drug Study On Vincristine SulfateDocumento9 páginasA Drug Study On Vincristine SulfateTrio San LuisAinda não há avaliações
- Tetanus Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Initial Supportive Therapy and Wound Care, Pharmacologic TherapyDocumento11 páginasTetanus Treatment & Management - Approach Considerations, Initial Supportive Therapy and Wound Care, Pharmacologic TherapyFuad Adi PrasetyoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasDrug StudyPeetah PanAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For Sinovac 6301Documento6 páginasGuidelines For Sinovac 6301HaseebPirachaAinda não há avaliações
- DUREMDES KAYLA NICOLE Care For Clients With Rheumatic Disease and Immunodeficiency Critical ThinkinDocumento4 páginasDUREMDES KAYLA NICOLE Care For Clients With Rheumatic Disease and Immunodeficiency Critical ThinkinOPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANOAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For Sinovac Vaccine - 6303Documento6 páginasGuidelines For Sinovac Vaccine - 6303Wpress PressAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines and Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) Sinovac Vaccine (Coronavac)Documento6 páginasGuidelines and Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) Sinovac Vaccine (Coronavac)Rico MaligayaAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For Sinovac Vaccine - 6304Documento6 páginasGuidelines For Sinovac Vaccine - 6304Ali AsgharAinda não há avaliações
- AzzalureTM InstructionsDocumento12 páginasAzzalureTM InstructionspsdsportsdocAinda não há avaliações
- PR Azacitidine For Injection: Submission Control No: 218729Documento38 páginasPR Azacitidine For Injection: Submission Control No: 218729Md. Sazzad HossenAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyArdrina SappariAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study QiDocumento7 páginasDrug Study QiJeremiah Mauricio100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyMenard VelascoAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Rules of VaccinationDocumento15 páginasBasic Rules of VaccinationDr.PRATIBHA VATSAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs StudyDocumento7 páginasDrugs Studymcmac24Ainda não há avaliações
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocumento34 páginasAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsgladioAinda não há avaliações
- Ciprofloxacin: A Drug Study OnDocumento5 páginasCiprofloxacin: A Drug Study Onkarl montanoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingDocumento3 páginasDrug Study: University of Southern Mindanao Department of NursingMizpah DuculanAinda não há avaliações
- Science Behind ZiconotideDocumento3 páginasScience Behind ZiconotideLawrence SiervoAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 2 Updated MurilloDocumento22 páginasActivity 2 Updated MurilloAraw GabiAinda não há avaliações
- Keshav Sir's SatDocumento28 páginasKeshav Sir's SatPreksha SinghaiAinda não há avaliações
- DiclofenacDocumento22 páginasDiclofenacintan kusumaningtyasAinda não há avaliações
- What Are Current Recommendations For Treatment of Drug ExtravasationDocumento13 páginasWhat Are Current Recommendations For Treatment of Drug ExtravasationThắng NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- AzithromycinDocumento10 páginasAzithromycinShaina MentangAinda não há avaliações
- Brand NameDocumento5 páginasBrand NameJunrey AbarcaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Drug StudyDocumento14 páginas5 Drug StudyJennyLapitan100% (2)
- TbactDocumento7 páginasTbactVinay KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Study of The Effect of Topical CorticoDocumento5 páginasComparative Study of The Effect of Topical Corticoririen refrina sariAinda não há avaliações
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocumento33 páginasAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsMohamed AllamAinda não há avaliações
- Annex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocumento33 páginasAnnex I Summary of Product CharacteristicsEva DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- C Ê Ê Ê ! " Ê # $%$ ! ! & Ê ! ' Ê # ! + !, % - Ê - ! / 0 1 Ê # Ê 3 c4 Ê % CC Ê 5 ! C Ê C Ê C" Ê 6 % 7 C& ÊDocumento4 páginasC Ê Ê Ê ! " Ê # $%$ ! ! & Ê ! ' Ê # ! + !, % - Ê - ! / 0 1 Ê # Ê 3 c4 Ê % CC Ê 5 ! C Ê C Ê C" Ê 6 % 7 C& ÊGerry PingenAinda não há avaliações
- 2A - Pasay - Module 7 - ElaborateDocumento21 páginas2A - Pasay - Module 7 - ElaborateTrishaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP and DrugsDocumento7 páginasNCP and DrugsRach AbsalonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study OR AreaDocumento7 páginasDrug Study OR AreaVal FielAinda não há avaliações
- Actemra PM E PDFDocumento142 páginasActemra PM E PDFMuhammad AwaisAinda não há avaliações
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasMetronidazole Drug StudyJC LumayaAinda não há avaliações
- Nuvaxovid Epar Product Information enDocumento31 páginasNuvaxovid Epar Product Information enKiss TiborAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento10 páginasDrug StudyBandana RajpootAinda não há avaliações
- Doxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionDocumento3 páginasDoxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionGeorge FogAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Name: Berirab Contents: Indication / Action:: RabiesDocumento4 páginasBrand Name: Berirab Contents: Indication / Action:: RabiesAbdelmar SusulanAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal MataDocumento11 páginasJurnal MataNovi RatnaAinda não há avaliações
- Actemra PM EDocumento143 páginasActemra PM ELala Nur HidayatullohAinda não há avaliações
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryAinda não há avaliações
- Igpit: 50 Hp-China (78,000) 100 HP - Us (100,000)Documento1 páginaIgpit: 50 Hp-China (78,000) 100 HP - Us (100,000)Kwesi YasayAinda não há avaliações
- Minor or Format TemplateDocumento2 páginasMinor or Format TemplateKwesi YasayAinda não há avaliações
- Capitol University: College of NursingDocumento5 páginasCapitol University: College of NursingKwesi YasayAinda não há avaliações
- Ecg PlacementsDocumento1 páginaEcg PlacementsMucs Rabino LagadanAinda não há avaliações
- Rllii5t,,.u, JT' (I: ( Tli 'NRDocumento1 páginaRllii5t,,.u, JT' (I: ( Tli 'NRKwesi YasayAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Material Nonlinear Problems Using Pseudo-Elastic Finite Element MethodDocumento5 páginasAnalysis of Material Nonlinear Problems Using Pseudo-Elastic Finite Element MethodleksremeshAinda não há avaliações
- Epidemiologi DialipidemiaDocumento5 páginasEpidemiologi DialipidemianurfitrizuhurhurAinda não há avaliações
- Everlube 620 CTDSDocumento2 páginasEverlube 620 CTDSchristianAinda não há avaliações
- Interruptions - 02.03.2023Documento2 páginasInterruptions - 02.03.2023Jeff JeffAinda não há avaliações
- Dike Calculation Sheet eDocumento2 páginasDike Calculation Sheet eSaravanan Ganesan100% (1)
- Seminar On Despute Resolution & IPR Protection in PRCDocumento4 páginasSeminar On Despute Resolution & IPR Protection in PRCrishi000071985100% (2)
- Cs8792 Cns Unit 1Documento35 páginasCs8792 Cns Unit 1Manikandan JAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento97 páginasUnit 2MOHAN RuttalaAinda não há avaliações
- (X-09485) XYLENE RECTIFIED Extra Pure (Mix Isomers)Documento9 páginas(X-09485) XYLENE RECTIFIED Extra Pure (Mix Isomers)Bharath KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Droplet Precautions PatientsDocumento1 páginaDroplet Precautions PatientsMaga42Ainda não há avaliações
- Condition Monitoring of Steam Turbines by Performance AnalysisDocumento25 páginasCondition Monitoring of Steam Turbines by Performance Analysisabuhurairaqazi100% (1)
- PFI High Flow Series Single Cartridge Filter Housing For CleaningDocumento2 páginasPFI High Flow Series Single Cartridge Filter Housing For Cleaningbennypartono407Ainda não há avaliações
- SBL - The Event - QuestionDocumento9 páginasSBL - The Event - QuestionLucio Indiana WalazaAinda não há avaliações
- G.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARDocumento2 páginasG.R. No. 185449, November 12, 2014 Del Castillo Digest By: DOLARTheodore DolarAinda não há avaliações
- Ytrig Tuchchh TVDocumento10 páginasYtrig Tuchchh TVYogesh ChhaprooAinda não há avaliações
- Fidp ResearchDocumento3 páginasFidp ResearchIn SanityAinda não há avaliações
- Privacy: Based On Slides Prepared by Cyndi Chie, Sarah Frye and Sharon Gray. Fifth Edition Updated by Timothy HenryDocumento50 páginasPrivacy: Based On Slides Prepared by Cyndi Chie, Sarah Frye and Sharon Gray. Fifth Edition Updated by Timothy HenryAbid KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Powerpoint Presentation: Calcium Sulphate in Cement ManufactureDocumento7 páginasPowerpoint Presentation: Calcium Sulphate in Cement ManufactureDhruv PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- TAB Procedures From An Engineering FirmDocumento18 páginasTAB Procedures From An Engineering Firmtestuser180Ainda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of Risk Management: An Analysis of Project Risk Planning Across Industries and CountriesDocumento13 páginasThe Effectiveness of Risk Management: An Analysis of Project Risk Planning Across Industries and Countriesluisbmwm6Ainda não há avaliações
- Cabling and Connection System PDFDocumento16 páginasCabling and Connection System PDFLyndryl ProvidoAinda não há avaliações
- Hager Pricelist May 2014Documento64 páginasHager Pricelist May 2014rajinipre-1Ainda não há avaliações
- LOG-2-8-FLEETWAREHOUSE-TEMPLATE-Waybill-Delivery Note-IFRCDocumento1 páginaLOG-2-8-FLEETWAREHOUSE-TEMPLATE-Waybill-Delivery Note-IFRCMAinda não há avaliações
- On CatiaDocumento42 páginasOn Catiahimanshuvermac3053100% (1)