Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Strategy Insight 2013 - 0517 - 17 May 2013
Enviado por
StrategicInnovation0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
36 visualizações7 páginasStrategy Insight May 2013 - Macro economics, Geo-strategy, Systemic risks, Technology, Bio-techs, Energy, Regulation and Culture
Título original
Strategy Insight 2013_0517 - 17 May 2013
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoStrategy Insight May 2013 - Macro economics, Geo-strategy, Systemic risks, Technology, Bio-techs, Energy, Regulation and Culture
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
36 visualizações7 páginasStrategy Insight 2013 - 0517 - 17 May 2013
Enviado por
StrategicInnovationStrategy Insight May 2013 - Macro economics, Geo-strategy, Systemic risks, Technology, Bio-techs, Energy, Regulation and Culture
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Personal Insurance
One team protecting what matters
CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
Signals of Change Scanned by the Strategic Innovation Team
!
Putented Homun Genes
Bitcoin
riverless Curs
ABS utu now in
Google Iurth
Mupping
the
Homun
Insight Highlights
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight: Highlights
Friday May 17, 2013
The Strategic Innovation framework helps us determine the relevance of signals of change for our business.
11 Strategic Risks to the PI business emerge from 7 areas of Structural Change.
--
BRAIN research project
received $100m funding
from the US govt to
develop a comprehensive
map of the human brain.
The US Supreme Court is
deciding whether
companies can patent
human genes and the
Indian Supreme Court has
ruled against Novartis on
HIV drug, both actions
against asymmetries that
have characterised
commercial enterprise.
Bitcoin: a proof of concept
for future digital
currencies?
The use of Google Earth
by the Australian Bureau
of Statistics is another
example of big data
visualisation, becoming
more effective.
Anticipated disruptions
from driverless cars are
being discussed in
mainstream media
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
Alternative systems of value exchange are characteristic of an area of structural change we have called FINANCE 2.0. They
are a constituent element of two of our Strategic Risks RISK 2.0 and GLOBAL. Would we be prepared to do business in a
borderless, user-determined currency?
!
NEW CURRENCIES
Bitcoin: bubble or the future of currency?
In the past weeks the value of the virtual digital currency tripled
before falling 50% in a few hours. Bitcoin has a global circulation worth
more than $US1.4B, yet it belongs to no nation and is issued by no central
bank. It can be used to buy gold in California, hamburger in Tel Aviv or a
house in the US. An important aspect of Bitcoin is that it offers untraceable
transactions. This makes it the currency of choice on black market site Silk
Road, an illegal underground eBay-like site whose url is only accessible via
the Tor encrypted web-browser and network.
Opinions diverge about Bitcoin. Techno enthusiasts and libertarians see
the future in it, whilst other dismiss it as a bubble: eg Paul Krugman sees
its value "conjured out of thin air because contrary to traditional currencies
backed by the power of the state, which defines them as legal tender and
accepts them as payment for taxes, Bitcoins, however, derive their value, if
any, purely from the belief that other people will accept them as payment."
Both views could be valid:
1) In the short-term it is likely to be a bubble. It follows a speculative
pattern, fuelled by media frenzy, as illustrated by the correlation between a
Google Trends search on "bitcoin" and its price chart.
2) In the long-term, whatever the Bitcoin market will look like in 5-10
years, it serves as a proof-of-concept for a decentralized crypto-currency,
which cannot be manipulated by governments nor changed by monetary
policy. Bitcoin shows something entirely new: a true, stateless, virtual
currency rooted in nothing other than confidence in the set of rules that
surround it. It could open a third chapter in the history of money: after
commodity based (e.g. gold), politically based (e.g. dollar), this would be a
math based currency (because it's minted by a computer algorithm). This
would be a response to falling confidence in the soundness of government-
backed fiat money in an era of quantitative easing. Notwithstanding the
many risks and issues, the algorithmic approach to controlling the money
supply used by Bitcoin could go a long way to creating a sound store of
value.
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
In addition to aiding in the treatment of known illnesses (with incidence on Health and Life Insurance), this program will likely deliver
more insight into brain patterns and understanding of human behaviours, such as, for example, consumer choices, risk appetite and
risk choices in multiple situations. It will also accelerate progress in Artificial Intelligence. This suggests an acceleration of one of the
areas of structural change we are following - VIRTUALISATION which drives strategic risks such as RISK 2.0 and ASSETS.
!
HUMAN BEHAVIOUR
Mapping the human brain
Last month, Obama announced the funding of a
$100 million BRAIN program (Brain Research
through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies) to
do for the human brain what has been earlier achieved
for the human genome: funds are intended to develop
a comprehensive map of the human brain, its
functions and networks, that will allow for treatments
for conditions such as epilepsy or Parkinson, but also
dementia and strokes.
The timing matches the readiness of key technologies
that have paved the way and will enable the initiative:
sequencing of the human genome, the development of
new tools for mapping neuronal connections,
increasing resolution of imaging technologies, and the
explosion of nano-science. These technologies
present unprecedented opportunities for integration
across scientific fields. The key technology is the MRI
scan which picks up at the molecular level what is
happening inside brain tissue.
!
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
Cars that have no accidents, mobility that does not depend on individual ownership, the technology that makes that possible and
the consumer demand for it are features of two areas of structural change we are observing VIRTUALISATION and DATA
which are behind two of our Strategic Risks RISK2.0 and ASSETS.
!
NO COLLISIONS
Driverless cars
Mainstream media interest in driverless cars is ramping up: after a comprehensive article in Forbes, the
latest report is from the Economist. The disruptive implications of vehicle technologies for car insurers are
now being called out. Some observers anticipate that the market might be reduced by 75%. Driverless
technology has the potential to reduce accidents by up to 90% and significantly change traditional patterns
of car ownership. Governments are watching the possible healthcare, infrastructure and environmental
benefits of driverless cars, which is possibly why regulators appear to be working quickly to enable the
introduction of driverless cars in the US. Driverless car technology may commercially enter the US market
by 2018.
In a scenario reminiscent of Kodak's research conducted in the 1980s which led it to conclude that digital
photography was still a decade away, insurance executives such as Progressive's CEO believe that
driverless cars are probably not something that need keep anyone awake for quite some time". Their
argument is based on the time it will take to sort out regulatory complexities and for drivers to adopt the
technology.
However analysts believe that disruption will happen well before driverless cars become ubiquitous: even
a 20% adoption of incremental driver-assist and collision avoidance technology might result in material
reduction of premiums. If in the long term, with this technology, car insurance as we know it goes away,
the question is about the medium term scenario. Vehicle to vehicle and vehicle to infrastructure
technologies represent opportunities for new data intermediaries and application providers to enter the
value chain. Market and customer perception of risk and of the need for insurance may change ahead of
full implementation or regulation of the technology. If insurers push away liability and increase prices on
driverless cars, car manufacturers or start-up companies could offer cheaper insurance and eat away at
the edges of the market as disruption grows.
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
These cases are illustrative of growing pressure on asymmetries of information wielded by incumbent industry players looking to
maximise profit. They form part of patterns of structural change we are calling SOCIALISATION and COMPLEXITY, which give rise
to two of our Strategic Risks: ASYMMETRY (information asymmetries in favour of commercial enterprise are actively regulated
against and punished by consumers) and TRIBES (consumers/citizens structure themselves around communal values and
collaborative enterprises, instinctively mutual and adept at self-management, effective in managing open sourcing).
!
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTIES OF THE HUMAN BODY
Patenting human genes
The US Supreme Court is hearing arguments to decide in June
whether companies can patent human genes, in a landmark case
against Myriad Genetics who patented the BRCA1 and BRCA3
genes, indicators of risk of breast and ovarian cancer. The outcome
could alter the course of US medical research. Myriad claim their
patent corresponds to the cost of finding the genes. The American
Civil Liberties Union is challenging that right, arguing that Myriad is
acting as a gatekeeper on all research on those genes, and is
stifling it.
20% to 40% of the Human Genome is covered by patents. Some
are held by companies, while others by institutions committed to
"open source genomics" who hold them "pre-emptively", to stop
commercial companies from having them.
In a similar vein, giant Swiss pharmaceutical company Novartis lost
a court case with the Indian Supreme Court on an HIV-AIDS
drug: patients will now be able to access the generic drug that costs
$170/month rather than $2,200/month for the Novartis brand.
<< BACK TO CONTENTS
Insight
Friday May 17, 2013
This is a classic example of the DATA structural change and the emergence of our ASYMMETRY risk: this information is not only
made public but also presented in a way that enables other companies and customers to do their own analytics. This Google Earth
mash-up illustrates the increasing availability of government data in software that will make it useable, therefore marketable.
!
OPEN SOURCE INFORMATION
Socio-Economic Data from the ABS
Last month the Australian Bureau of Statistics released its measure of the
relative level of advantage and disadvantage across the nation on the
basis of information contained in the 2011 census. The Socio-Economic
Indexes for Areas covers indication of Education and Occupation through
education variables (degrees, occupational skills), Economic Resources
through variables related to income and housing circumstances, and
Relative Socio-economic Advantage and Disadvantage (IRSAD) through
variables such as income but also such aspects as overcrowding in
homes, people's occupations, the number of cars per household, the
number of households with single parents, and also the number with no
internet connection.
The IRSAD index provides a score for each geographical area (the higher
the score the higher the advantage), which allows for areas of various size
to be compared. The ABS has compiled this data down to Statistical Areas
with an average population of 400 people each (which they call SA1). This
allows for an extremely detailed picture of cities and major areas. They
have also produced map overlays that can be uploaded into Google Earth:
dark blue denoting "most advantageous" and dark red "most
disadvantaged".
SEIFA data can be used across a wide range of organisations: by
governments to determine areas that require funding and services, by
political parties who mine the data to assist with their election campaigning.
Suncorp is looking at this data and currently testing to see if it can be
merged to our risk modelling dataset. The question is whether this adds
predictive capability to the existing model.
This data could be used in other business areas to focus local marketing
campaigns, or determine areas in which to open future WorkAtHome Hubs
(meant to be set up such as targeted employee demographic live within
30mins of a Hub).
Você também pode gostar
- Beware The Known Unknowns When Finance Meets AIDocumento7 páginasBeware The Known Unknowns When Finance Meets AIrahulgabdaAinda não há avaliações
- ComputersfreedomDocumento12 páginasComputersfreedomSteven NahdeeAinda não há avaliações
- Global Buisness LawDocumento7 páginasGlobal Buisness LawMuaz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- The Business of Knowing: Private Market Data and Contemporary IntelligenceDocumento24 páginasThe Business of Knowing: Private Market Data and Contemporary IntelligenceHoover InstitutionAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of The Industries of the Future: by Alec Ross | Includes AnalysisNo EverandSummary of The Industries of the Future: by Alec Ross | Includes AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Summary of The Industries of the Future: by Alec Ross | Includes AnalysisNo EverandSummary of The Industries of the Future: by Alec Ross | Includes AnalysisAinda não há avaliações
- Bhavya Wani: Ai in FinanceDocumento5 páginasBhavya Wani: Ai in FinanceScrappy CocoAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Intelligence & Financial ServicesDocumento60 páginasArtificial Intelligence & Financial ServicesPulast S TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- SSRN Id3107123Documento49 páginasSSRN Id3107123FaithAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Virtues, and FlourishingDocumento21 páginasWork, Virtues, and FlourishingAlejo José Sison GalsimAinda não há avaliações
- Data AutonomyDocumento57 páginasData Autonomyssa912918Ainda não há avaliações
- CB Insights - Tech Trends 2022Documento70 páginasCB Insights - Tech Trends 2022Flávio Rabelo BarrosAinda não há avaliações
- 4 - 2018 - MITd - Kiron - Unruh - How AI Will Define New IndustriesDocumento4 páginas4 - 2018 - MITd - Kiron - Unruh - How AI Will Define New IndustriesWesley MarcosAinda não há avaliações
- Sakshi Srivastav - Disruptive TechnologyDocumento4 páginasSakshi Srivastav - Disruptive Technologysakshi srivastavAinda não há avaliações
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): An implementation guideNo EverandThe California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): An implementation guideNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- THE EVOLUTION OF ANTITRUST IN THE DIGITAL ERA: Essays on Competition PolicyNo EverandTHE EVOLUTION OF ANTITRUST IN THE DIGITAL ERA: Essays on Competition PolicyAinda não há avaliações
- Correcting The Record For False Testimony by Justin Brookman Consumer ReportsDocumento5 páginasCorrecting The Record For False Testimony by Justin Brookman Consumer ReportsRoslyn LaytonAinda não há avaliações
- New Rules For Big DataDocumento3 páginasNew Rules For Big DataanniestylAinda não há avaliações
- Algorithms EverywhereDocumento4 páginasAlgorithms EverywhereArielResearchServicesAinda não há avaliações
- Project 2020Documento25 páginasProject 2020dantheman82Ainda não há avaliações
- A World Divided Over Artificial Intelligence-Foreign AffairsDocumento6 páginasA World Divided Over Artificial Intelligence-Foreign Affairs8jynt64h6mAinda não há avaliações
- 05 AWP - 151 - FinalDocumento26 páginas05 AWP - 151 - FinalAmit Kumar PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Digitalali CX Pathway - Transcript - Digital TechnologiesDocumento12 páginasDigitalali CX Pathway - Transcript - Digital TechnologiesN.a. M. TandayagAinda não há avaliações
- Grunes Allen y Stucke Maurice - No Mistake About It - The Important Role of Antitrust in The Era of Big Data (2015)Documento14 páginasGrunes Allen y Stucke Maurice - No Mistake About It - The Important Role of Antitrust in The Era of Big Data (2015)Juan Ignacio BugueñoAinda não há avaliações
- Artikel - 2019 - 3 - Insurtech - Micro-Trends - To - WatchDocumento4 páginasArtikel - 2019 - 3 - Insurtech - Micro-Trends - To - WatchMario Vittoria FilhoAinda não há avaliações
- Firefly DocumentDocumento4 páginasFirefly DocumentTracy Tam NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Debat - Technological ProgressDocumento4 páginasDebat - Technological ProgressfdpAinda não há avaliações
- Key Takeaways: © 2020 Future Today InstituteDocumento2 páginasKey Takeaways: © 2020 Future Today InstituteyudisamaAinda não há avaliações
- Cyber Security Meets National Security: International Perspectives on Digital Era ThreatsNo EverandCyber Security Meets National Security: International Perspectives on Digital Era ThreatsAinda não há avaliações
- The Two Critical Driverless Technologies You Must Own TodayDocumento15 páginasThe Two Critical Driverless Technologies You Must Own TodayblakskorpioAinda não há avaliações
- A Rational Response To The Privacy "Crisis"Documento36 páginasA Rational Response To The Privacy "Crisis"willsinkAinda não há avaliações
- T P B D: Hree Aradoxes of IG ATADocumento6 páginasT P B D: Hree Aradoxes of IG ATAjshen5Ainda não há avaliações
- Examining The Evolving Cyber Insurance Marketplace: HearingDocumento48 páginasExamining The Evolving Cyber Insurance Marketplace: HearingScribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Three Paradoxes of Big DataDocumento6 páginasThree Paradoxes of Big DataFarheen AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Final Research PaperDocumento9 páginasFinal Research PaperA GAinda não há avaliações
- The Journey To Understanding Your Insurance CustomersDocumento17 páginasThe Journey To Understanding Your Insurance CustomersInam Ullah BukhariAinda não há avaliações
- Big Data and The Future of Our Privacy-1Documento14 páginasBig Data and The Future of Our Privacy-1julianAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Economy 2019Documento230 páginasDigital Economy 2019Joan AtupAinda não há avaliações
- How To Tame Big Tech: Kaushik BasuDocumento3 páginasHow To Tame Big Tech: Kaushik BasuSylvieAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Economy Compass 2019Documento230 páginasDigital Economy Compass 2019Khuat Minh QuyenAinda não há avaliações
- The World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil, But Data - The EconomistDocumento7 páginasThe World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil, But Data - The EconomistMartijn van de WeerdtAinda não há avaliações
- Politica MonetariaDocumento11 páginasPolitica MonetariaLetty Fiorella Reto EncaladaAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial IntelligenceDocumento14 páginasArtificial IntelligenceБ. ХуланAinda não há avaliações
- Big Data The Next Frontier For InnovationDocumento4 páginasBig Data The Next Frontier For InnovationJohn evansAinda não há avaliações
- Fintech - The Impact On Consumers and Regulatory ResponsesDocumento6 páginasFintech - The Impact On Consumers and Regulatory Responsesfarazphd88Ainda não há avaliações
- An Ultimate Guide to Launch An SEC Compliant ICONo EverandAn Ultimate Guide to Launch An SEC Compliant ICOAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Intelligence & Cyber SecurityDocumento12 páginasArtificial Intelligence & Cyber Securityrahul_cscAinda não há avaliações
- The World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil, But Data - Regulating The Internet GiantsDocumento5 páginasThe World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil, But Data - Regulating The Internet GiantsOlga GtzAinda não há avaliações
- The Influence of Big Data in The Field of FinanceDocumento5 páginasThe Influence of Big Data in The Field of FinancecoolAinda não há avaliações
- 2007 - Digital Identities and The Promise of The Technology TrioDocumento7 páginas2007 - Digital Identities and The Promise of The Technology TrioAli MohdAinda não há avaliações
- The World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil - But DataDocumento3 páginasThe World's Most Valuable Resource Is No Longer Oil - But DataLvs KiranAinda não há avaliações
- The Five Technological Forces Disrupting Security: How Cloud, Social, Mobile, Big Data and IoT are Transforming Physical Security in the Digital AgeNo EverandThe Five Technological Forces Disrupting Security: How Cloud, Social, Mobile, Big Data and IoT are Transforming Physical Security in the Digital AgeAinda não há avaliações
- Issue AnalysisDocumento10 páginasIssue AnalysisYang YahuiAinda não há avaliações
- Insurance Innovation Report 2016Documento21 páginasInsurance Innovation Report 2016Rishita GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Big Data World: Benefits, Threats and Ethical ChallengesDocumento21 páginasThe Big Data World: Benefits, Threats and Ethical ChallengesNatasha DavidsAinda não há avaliações
- Observe by Forencis Research (FSR) .: Request The Report Sample PDF of Global Market @Documento3 páginasObserve by Forencis Research (FSR) .: Request The Report Sample PDF of Global Market @Patrick Olayinka AdedokunAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 1109 XX High Level Snapshot On ReinsuranceDocumento2 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 1109 XX High Level Snapshot On ReinsuranceStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 1102 XX Storm SandyDocumento1 páginaStrategy Radar - 2012 - 1102 XX Storm SandyStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 1012 XX Potential Housing BubbleDocumento2 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 1012 XX Potential Housing BubbleStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 1005 XX Peak CarDocumento3 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 1005 XX Peak CarStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 0601 XX An Australian MomentDocumento4 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 0601 XX An Australian MomentStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 0413 XX Apple StockDocumento2 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 0413 XX Apple StockStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 0406 XX Oz Housing MarketDocumento3 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 0406 XX Oz Housing MarketStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 0316 XX ChinamericaDocumento3 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 0316 XX ChinamericaStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar - 2012 - 0309 XX Australian WorkforceDocumento3 páginasStrategy Radar - 2012 - 0309 XX Australian WorkforceStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Radar 2012 0323 XX Mining BoomDocumento3 páginasStrategy Radar 2012 0323 XX Mining BoomStrategicInnovationAinda não há avaliações
- Bni DataDocumento15 páginasBni Datatarun kumar100% (1)
- Bike Rental AgreementDocumento2 páginasBike Rental AgreementMallesh Arja100% (1)
- Marine InsuranceDocumento3 páginasMarine InsuranceKirtishbose ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
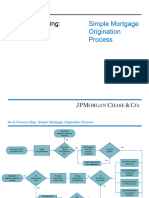
- Mortgage Process Map - Model AnswerDocumento3 páginasMortgage Process Map - Model AnswersdsAinda não há avaliações
- Irda Journal July10Documento96 páginasIrda Journal July10ankurgupta03Ainda não há avaliações
- BFM PDFDocumento30 páginasBFM PDFVarsha Jaisinghani100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Insurable InterestDocumento12 páginasChapter 3 - Insurable Interestaudreydql5Ainda não há avaliações
- Review Handouts and Materials: Semester Auditing Problems INTEGR 2-004 Agriculture and LiabilitiesDocumento8 páginasReview Handouts and Materials: Semester Auditing Problems INTEGR 2-004 Agriculture and LiabilitiesKarlayaanAinda não há avaliações
- English Vocabulary Unit 2 International MarketingDocumento32 páginasEnglish Vocabulary Unit 2 International MarketingMariaBufneaAinda não há avaliações
- Health Advantage BrochureDocumento11 páginasHealth Advantage BrochurevenkatAinda não há avaliações
- Everett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookDocumento46 páginasEverett Association of School Administrators (EASA) Administrative HandbookJessica OlsonAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Custumer Acquisition Through Personal SellingDocumento51 páginasStudy of Custumer Acquisition Through Personal SellingGaurav RajwarAinda não há avaliações
- Health Insurance Fronter Script 3.5Documento3 páginasHealth Insurance Fronter Script 3.5Jolly Silastre100% (2)
- INT Claim Form GeneralDocumento5 páginasINT Claim Form GeneralkarlheinzeAinda não há avaliações
- INSURANCE #1 Aboitiz Shipping Corporation vs. Insurance Company of North AmericaDocumento2 páginasINSURANCE #1 Aboitiz Shipping Corporation vs. Insurance Company of North AmericaAdrian VidalAinda não há avaliações
- An Inchmaree Clause Is A Provision Common in Maritime Insurance Policies That Cover A Ship's Loss or Damage Due To Reasons Such AsDocumento5 páginasAn Inchmaree Clause Is A Provision Common in Maritime Insurance Policies That Cover A Ship's Loss or Damage Due To Reasons Such AsSudhendra SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Examination: Certificate in Practical Financial EconomicsDocumento63 páginasExamination: Certificate in Practical Financial Economicschan chadoAinda não há avaliações
- HKS Tender 2013Documento26 páginasHKS Tender 2013gpraveenroy0% (1)
- BSBRSK501A Manage Risk FCSDocumento139 páginasBSBRSK501A Manage Risk FCSphongvan_DuAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Bill FormDocumento2 páginasHospital Bill FormMeena VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Standard+of+Conduct+Asia 6.30.20Documento7 páginasStandard+of+Conduct+Asia 6.30.20clarence dinoAinda não há avaliações
- GSIS LawDocumento18 páginasGSIS LawJm EjeAinda não há avaliações
- Government of Nepal Ministry of Finance Inland Revenue Department Tax Rates For Natural Person Fiscal Year 2077/78 (2020/21) (Only For Employment Income)Documento3 páginasGovernment of Nepal Ministry of Finance Inland Revenue Department Tax Rates For Natural Person Fiscal Year 2077/78 (2020/21) (Only For Employment Income)shankar k.c.Ainda não há avaliações
- Compound Financial InstrumentsDocumento3 páginasCompound Financial InstrumentsJm atlavs100% (1)
- General Conditions of Contract Qatar May 2007Documento58 páginasGeneral Conditions of Contract Qatar May 2007Leonidas AnaxandridaAinda não há avaliações
- Monthly One Liner Current Affairs PDF JanuaryDocumento49 páginasMonthly One Liner Current Affairs PDF Januaryvishnu pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report On Risk MGT in Life InsuranceDocumento77 páginasProject Report On Risk MGT in Life InsuranceAlpatron shit'sAinda não há avaliações
- Allstate Your Easy Pay Plan Payment NoticeDocumento3 páginasAllstate Your Easy Pay Plan Payment NoticestevemillerfhAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Tax Interview Questions For ArticleshipDocumento15 páginasDirect Tax Interview Questions For ArticleshipAayush GamingAinda não há avaliações
- State Life InsuraceDocumento167 páginasState Life Insuracetyrose88Ainda não há avaliações