Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I Ms
Enviado por
kingman14Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I Ms
Enviado por
kingman14Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
5.3 TRANSITION METALS HW PART I MS 1.
Does not have an incomplete set of d electrons / does not have a partially filled d orbital / does not have a partially filled d sub-shell / ora (1) Allow use of 3d
1
[1]
2.
(i) (ii)
1s22s22p63s23p63d5 (1) Has an incomplete set of d electrons / partially filled d sub-shell / partially filled d orbital (1) Allow partially filled d shell
1 1
[2]
3.
(a)
1s22s22p63s23p63d5 (1); Has an incomplete set of 3d electrons (1) Allow 3d orbitals are not completely occupied / incomplete 3d sub-shell Allow has half-filled d orbitals Any two from Variable oxidation state / variable valency (1); Act as catalysts (1); Form complexes / form complex ions (1); Form coloured compounds (1) Not high melting point / good thermal and electrical conductors / high density etc Iron (II) ions give a green ppt (1); Iron (III) ions give an orange-rust ppt (1) Precipitate must be used once Allow solid instead of ppt 4Fe2+ + O2 + 4H+ 4Fe3+ + 2H2O Correct reactants and products (1); Correct balancing (1)
(b)
(c)
(d)
2
[8]
4.
(i)
Brown / red-brown / foxy-red / rusty / orange ppt (1) Allow solid instead of precipitate Allow state symbol (s) for precipitate Fe3+(aq) + 3OH(aq) Fe(OH)3(s) Correct equation (1) State symbols for the correct formulae even if spectator ions are present (1) Allow equations using the hydrated iron(III) ion
(ii)
2
[3]
Paddington Academy
5.
Add (aqueous) sodium hydroxide which will give a brown/rusty ppt (1) Allow solid for precipitate or (s) in equation Allow Use aqueous thiocyanate ions which gives a (blood) red colouration
[1]
6.
(i) (ii)
Has a (lone) pair of electrons that can be donated / lone pair that can form a dative bond / pair of electrons that can form a coordinate bond (1) 3D diagram of octahedral structure (1); Bond angle 90 (1) Name octahedral must be present to score two marks Allow use of wedges and dotted lines to indicate three dimensions Allow three dimensions if at least two bond angles of 90 are shown that clearly demonstrate 3D If two different bond angles do not award bond angle mark
1 2
[3]
7.
(i) (ii)
6 Species with (lone) pair of electrons Capable of being donated / forms a dative covalent bond / co-ordinate bond to a metal ion. (allow suitable diagram)
1 1 1
[3]
8.
Any three from Ammonia molecule 1 lone pair (and 3 bond pairs) (1); Ammonia ligand 4 bond pairs / lone pair is now a bond pair / ligand does not have a lone pair (1); Lone pairs repel more than bond pairs (1): In complex equal repulsion between electron pairs (1) Not bonds repel / atoms repel
3
[3]
9.
Water molecule 2 lone pairs (and 2 bond pairs) (1); Water ligand 1 lone pair and 3 bond pairs / lone pair is now a bond pair / water has one less lone pair when it is a ligand (1); Lone pairs repel more than bond pairs (1) Not atoms repel
3
[3]
10.
Mr of [Cu(CH3COO)2]2.Cu(OH)2 = 460.5 (1) Allow ecf from wrong Mr Molar ratio [Cu(CH3COO)2]2.Cu(OH)2 : H2O is 0.182 : 0.906 (1) x = 5 (1) Not full marks for 5 with no working out
[3]
Paddington Academy
11.
Transition element Cu2+ 1s22s22p63s23p63d9 (1); Transition elements have one oxidation state that has an incomplete set of 3d electrons / have one ion with a half-filled 3d orbital (1) Allow has at least one half-filled d orbital / partially filled 3d sub-shell Complex ion Example of a copper complex ion e.g. [Cu(H2O)6]2+ or CuCl42 (1); Diagram of the copper complex showing three dimensions e.g. use of wedges or dotted lines (1); Correct bond angle to match the complex / correct name of the shape of the complex (1); If a copper complex that does not exist is used then first three marks not available If a correct iron complex is given then example mark cannot be awarded Allow square planar where appropriate Ligand is an electron pair donor (1); Copper(II) ion is an electron pair acceptor (1); Dative bond exists between ligand and the copper(II) ion (1) Electron pair donor, electron pair acceptor and dative bond marks can awarded from an appropriate diagram Properties Several oxidation states e.g. copper has +1 and +2 or iron has +2 and +3 (1); Ignore copper has a +3 Ignore iron has a +6 oxidation state Forms coloured compounds e.g. copper(ii) chloride is green or iron(II) sulphate is pale green (1); Element or compound has catalytic properties e.g. Iron is a catalyst in the Haber process (1) Quality of written communication Use of technical terms at least three terms from the following list are used in the correct context ligand dative bond coordinate bond tetrahedral square planar octahedral oxidation (state) catalyst electron pair lone pair orbital sub-shell (1) Put a ring around the technical terms 1
11
Paddington Academy
[12]
12.
(a)
(i) (ii)
(Blue to) yellow (solution) / (blue to) green (solution) (1) Lone pair on chloride ion (1); Donated to copper(II) ion (1) Allow dative bond / coordinate bond (1) Allow marks via a diagram that must show lone pairs and the dative bond
1 2
(b)
(Light) blue precipitate / blue solid (1); With excess (dark) blue solution (1) Not just goes blue
2
[5]
13.
(a) (b)
Number of coordinate / dative covalent bonds attached to metal ion / number of lone pairs accepted (not number of ligands) (i) [Co(H2O)6]2+ is octahedral; [CoCl4]2 is tetrahedral Drawings must be 3 dimensional Acceptable shapes for [Co(H2O)6]2+ include:
C o
Co
C o
Co
Acceptable shapes for [CoCl4]2 include Co C o 2 (ii) (iii) Pink blue Add water. (Allow other suitable suggestions, e.g. add lead nitrate to precipitate Cl as PbCl2) 2
1
[6]
14.
(a) (b)
Ligand able to donate two lone pairs to form dative covalent / co-ordinate bonds
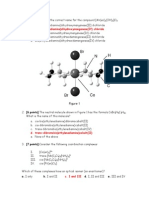
O O O O C C O O O O C C r O C C C O O 3
1 1
3-D diagram with three ethanedioate ligands used correct bonding between ligands and Cr3+ correct charge on ion (3) (Accept O O as minimum for ethanedioate ion)
Paddington Academy
1 1 1
[5]
15.
(a) (b)
1s22s22p63s23p63d8 (Do not accept [Ar]3d8) (i) Ring around O Ring around N (Accept ring around O of C=O as an alternative to O) Lone pair (of electrons) / non-bonding pair
1 1 1 1
[4]
(ii)
16.
(i) (ii)
Cis platin Binds to DNA Prevents cell from replicating / cells die
1 1 1
[3]
17.
(a)
(i)
1 mark for correct 3-D diagram of cis isomer 1 mark for correct 3-D diagram of trans isomer (Allow planar diagrams if two appropriate 90 angles are shown) Allow any suitable 3-D diagrams. Possibilities to include: Co C o C o
1 1
(ii) (b)
Geometric / cis trans
1 1 1
1 mark for using cis isomer 1 mark for correct 3-D diagrams which are mirror images of each other. (If all diagrams are drawn as non-3d do not penalise in (b)) Allow any suitable 3-D diagrams such as: C H 2 CH 2 N H en H 2N C l Co Co or e Cl
n 2
Cl
H 2N CH
C H
Cl
2
NH
[5]
18.
(a) (b)
Two lone pairs/ able to form two dative covalent / co-ordinate bonds Stereoisomerism same atoms with same order of bonds but a different spatial arrangement / same structure but different arrangement of atoms Both isomers drawn for cis / trans Both isomers drawn for optical (must be mirror images) (all diagrams to show 3-D arrangement) Enantiomers/non superimposable mirror images Rotate plane polarised light in opposite direction by same number of degrees (any two for 1 mark)
1 2 2 1 1
[8]
Paddington Academy
Paddington Academy
19.
(a)
(i)
Number of dative bonds / co-ordinate bonds formed with the transition metal (Do not accept number of ligands but allow number of lone pairs bonded to.) Square planar Ligand substitution x = 2 y=0 cis isomer drawn trans isomer drawn (ignore any charges)
N H
3
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
(ii) (b) (i) (ii) (c) (i)
C l
C l
N H
Pt
Pt
C l
N H
N H
C l
(ii) (iii)
cis / trans or geometric Binds with DNA (not binds with cell) Prevents replication/prevents cell dividing/prevents tumour growth (do not allow kills cell)
1 1 1
[10]
20.
(a)
(i) (ii) (iii)
+3 Cis and trans forms drawn in 3-D (only award these marks if C has been chosen) Type of isomerism is cis-trans/geometric (concentrated) hydrochloric acid/sodium chloride/ Other suitable named ionic chloride but not just chloride or Cl Ligand substitution / ligand exchange
1 2 1 1 1
[6]
(b)
(i) (ii)
Paddington Academy
21.
(a)
(i)
transition element: has at least one ion with a partly filled d-orbital (1) example showing electronic configuration with d orbital as between d1 d9 (1) complex ion: a central metal ion surrounded by ligands with an example. (1) ligand: molecule/ion with lone pair of electrons capable of forming coordinate/ dative bonds to a metal ion (1)
(ii)
precipitation: equation (1) colour of precipitate (1) ligand substitution: equation (1) colour of substituted complex (1) redox: equation (1) colour change (1) The candidate clearly links observations to provide evidence for two reactions discussed. (1) 7
(b)
complex ions: octahedral example (1) with 3-D diagram (1) tetrahedral example (1) with 3-D diagram (1) square planar example (see also below) (1) with 3-D diagram (1) stereoisomerism: cis-trans example, e.g. Ni(NH3)2Cl2; platin with 3-D diagram (1) optical example, e.g. Ni(en)32+ (1) with 3D diagrams (1) The candidate clearly links features on the diagrams with a characteristic of the stereoisomerism involved (1) Max: 9
[20]
Paddington Academy
Você também pode gostar
- Problem Set 5 KeyDocumento5 páginasProblem Set 5 KeyYash KumarAinda não há avaliações
- A2 Test 11 Notes - Transition ElementsDocumento11 páginasA2 Test 11 Notes - Transition Elementswill bellAinda não há avaliações
- Metalography and Microstructures of Stainless Steels and Maraging SteelsDocumento32 páginasMetalography and Microstructures of Stainless Steels and Maraging SteelsChaguy VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Soil Science GuideDocumento12 páginasSoil Science GuideSean HooeksAinda não há avaliações
- Investigation of Grey Cast Iron Water Mains To Develop A Methodology For Estimating Service LifeDocumento4 páginasInvestigation of Grey Cast Iron Water Mains To Develop A Methodology For Estimating Service LifeyaofuzhangAinda não há avaliações
- Perfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ANSWERDocumento61 páginasPerfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ANSWERAhmad RawiAinda não há avaliações
- Steel - Equivalent Grades PDFDocumento23 páginasSteel - Equivalent Grades PDFSowmen Chakroborty100% (1)
- Natural Gas Liquids Recovery PDFDocumento65 páginasNatural Gas Liquids Recovery PDFMahathir Che Ap100% (7)
- Pre TreatmentDocumento7 páginasPre TreatmentRascal Silvent100% (1)
- IAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17Documento6 páginasIAL Chemistry SB2 Answers Topic17salmaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 ChemDocumento55 páginasUnit 1 ChemDarly SivanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Transition MSDocumento19 páginasTransition MSiratuzipacifique2Ainda não há avaliações
- A2 Chemistry: Transition Metal Mark SchemeDocumento5 páginasA2 Chemistry: Transition Metal Mark SchemeJake RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- 5.4 Database Part 1 MsDocumento7 páginas5.4 Database Part 1 MsSairah RazakAinda não há avaliações
- 2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Advanced) C (U1) WS01 (Periodic Properties - Chemical Bonding) (NC Sir) Q + SolnDocumento10 páginas2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Advanced) C (U1) WS01 (Periodic Properties - Chemical Bonding) (NC Sir) Q + SolnSooryaAinda não há avaliações
- DPP-13 (Coordination Compound) PDFDocumento3 páginasDPP-13 (Coordination Compound) PDFAvishek BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- Transition Metals Test Mark Scheme /30 Name 1Documento3 páginasTransition Metals Test Mark Scheme /30 Name 1Corey NAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 13 MCQsDocumento8 páginasTopic 13 MCQsJonathan HuiAinda não há avaliações
- CH302 Model AnswersDocumento8 páginasCH302 Model AnswersMike VhurinosharaAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry of ComplexesDocumento8 páginasGeometry of ComplexessnhmaitlaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Unit 5 Organic AnswersDocumento47 páginasChem Unit 5 Organic Answersareyouthere92Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Questions - Chapter 25Documento6 páginasSample Questions - Chapter 25Glenn Farah Faye RausaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter18 Answer KeyDocumento6 páginasChapter18 Answer KeyRavindra KempaiahAinda não há avaliações
- Homework2 - KIM224E - 2020 Inorganic Chemistry 2Documento4 páginasHomework2 - KIM224E - 2020 Inorganic Chemistry 2irembasar2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Bonding AnswerDocumento19 páginasChemistry Bonding AnswerPeaceAinda não há avaliações
- Co-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Documento4 páginasCo-Ordination Compound (Question Paper)Param shahAinda não há avaliações
- 5.co Ordination CompoundsDocumento7 páginas5.co Ordination CompoundsSheetal KoriAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Questions - Chapter 25Documento7 páginasSample Questions - Chapter 25Rasel Islam100% (2)
- Transitn Meta CheDocumento10 páginasTransitn Meta CheAdegunju Adedayo SulaimonAinda não há avaliações
- Group2 and 7 AnswersDocumento44 páginasGroup2 and 7 Answers123456Ainda não há avaliações
- 0620 w13 Ms 31Documento5 páginas0620 w13 Ms 31Haider AliAinda não há avaliações
- Bonding QDocumento19 páginasBonding QhamedAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Cell Structure and Properties of MaterialsDocumento4 páginasUnit Cell Structure and Properties of MaterialsudaysrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER # 6 Remaining + ExerciseDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER # 6 Remaining + ExerciseshahidchemistAinda não há avaliações
- 6687732Documento12 páginas6687732JetNoKunAinda não há avaliações
- Transition Metals H2 QuestionsDocumento7 páginasTransition Metals H2 QuestionskitoniumAinda não há avaliações
- 6241 01 Rms 20050618Documento10 páginas6241 01 Rms 20050618UncleBulgariaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6Documento54 páginasChemistry SL P2 Markscheme Chapter 1-6reneeyeung001Ainda não há avaliações
- Transition Metal Coordination CompoundsDocumento30 páginasTransition Metal Coordination CompoundsImmortal BlackheartAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3/13 Practice IB Chem TestDocumento12 páginasTopic 3/13 Practice IB Chem TestKeyerria HowardAinda não há avaliações
- FEDERAL PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION CHEMISTRY PAPER EXAMDocumento3 páginasFEDERAL PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION CHEMISTRY PAPER EXAMTayyab ZafarAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Bonding SETDocumento3 páginasChemical Bonding SETmridulAinda não há avaliações
- GUJCET - D22 Mar 2024Documento17 páginasGUJCET - D22 Mar 2024aadityabhagchandaniAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Jan Unit 5 Chemistry A Level EdexcelDocumento24 páginas2013 Jan Unit 5 Chemistry A Level EdexcelJames KingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Sample Paper Coordination CompoundDocumento14 páginasChemistry Sample Paper Coordination Compoundbachpankapyar071Ainda não há avaliações
- Chem Unit 5 Transition Metals AnswersDocumento13 páginasChem Unit 5 Transition Metals Answersareyouthere9250% (2)
- C04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kDocumento46 páginasC04as Periodic Table of Elements PDF August 17 2011-5-48 Am 687kMThana Balan0% (1)
- Isomerism in Coordination ChemistryDocumento21 páginasIsomerism in Coordination Chemistrym.nouraldenAinda não há avaliações
- Transition MetalsDocumento19 páginasTransition MetalsBrantAinda não há avaliações
- Review Question On Coordination Compounds 2022Documento6 páginasReview Question On Coordination Compounds 2022Sangay ChodenAinda não há avaliações
- CHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersDocumento10 páginasCHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersAbdul Mueez Lone100% (1)
- Schm312 Ex Memo 2015 - FinalDocumento13 páginasSchm312 Ex Memo 2015 - FinalSandile SynthaxError Mabika100% (1)
- LPP-Transition Elements and Coordination CompoundsDocumento4 páginasLPP-Transition Elements and Coordination CompoundsYash TandonAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry EX - 2 Solution of Class 12th All Sheets RESONANCEDocumento180 páginasChemistry EX - 2 Solution of Class 12th All Sheets RESONANCEGOURISH AGRAWALAinda não há avaliações
- Apc - Pi 18Documento2 páginasApc - Pi 18Pralay MaitiAinda não há avaliações
- Solid-State Chem - ch1-5Documento21 páginasSolid-State Chem - ch1-5VadivelanAinda não há avaliações
- SECTION-I (Multiple Choice Questions) : Faculty Test Topic:Co-Ordination Compounds - 1Documento4 páginasSECTION-I (Multiple Choice Questions) : Faculty Test Topic:Co-Ordination Compounds - 1Sachin DedhiaAinda não há avaliações
- GZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharDocumento4 páginasGZB Xii Ws-9 Chemistry D & F Block Elements October Sarita KhokharSaman PanwarAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Questions - Chapter 15Documento6 páginasSample Questions - Chapter 15Rasel IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 13 Transition Elements ExerciseDocumento6 páginasChapter 13 Transition Elements Exerciseisqma100% (1)
- Molecular Structure, Chemical Bonding and Transition MetalsDocumento13 páginasMolecular Structure, Chemical Bonding and Transition Metalsngah lidwineAinda não há avaliações
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesNo EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneAinda não há avaliações
- Vibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataNo EverandVibrational Spectra of Organometallics: Theoretical and Experimental DataAinda não há avaliações
- Graphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo EverandGraphene Oxide: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAyrat M. DimievAinda não há avaliações
- Electrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceNo EverandElectrodes for Li-ion Batteries: Materials, Mechanisms and PerformanceAinda não há avaliações
- SL2014-587Documento20 páginasSL2014-587Subramoniam MarineAinda não há avaliações
- Agen HematinikDocumento77 páginasAgen HematinikErinaGeraldiAinda não há avaliações
- Engr - Gul-E-Hina: Lecture 10 - Water Distribution SystemDocumento40 páginasEngr - Gul-E-Hina: Lecture 10 - Water Distribution SystemRehan KhanAinda não há avaliações
- DRAGFLOW TECH INFO ON CHROME WEAR PARTS AND SEAL ARRANGEMENTDocumento2 páginasDRAGFLOW TECH INFO ON CHROME WEAR PARTS AND SEAL ARRANGEMENTAlditho PomatayAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Profile and Steel Products OverviewDocumento25 páginasPersonal Profile and Steel Products OverviewrahmanhadiAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Metal Release From Various MetallicDocumento11 páginasComparison of Metal Release From Various MetallicArmando DiazAinda não há avaliações
- PRACTICAL - Iron and Sulphur Class IxDocumento31 páginasPRACTICAL - Iron and Sulphur Class IxPriyanca JunejaAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Alloying Elements On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ductile IronDocumento5 páginasEffect of Alloying Elements On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ductile IronIjabiAinda não há avaliações
- MY2200 Primary Metal 2002Documento52 páginasMY2200 Primary Metal 2002LTE002Ainda não há avaliações
- Sulfur CompoundsDocumento84 páginasSulfur Compoundsjppmj100% (1)
- Lenntech: Ionpure Vnx55-Ep High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (Cedi) ModulesDocumento2 páginasLenntech: Ionpure Vnx55-Ep High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (Cedi) Modulesalper canturkAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluating Iron & Steel in Historic BridgesDocumento8 páginasEvaluating Iron & Steel in Historic BridgesjayaramanrathnamAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/41 October/November 2021Documento11 páginasCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/41 October/November 2021Mahir VasoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Notes v1.6 ExtraDocumento20 páginasChemistry Notes v1.6 Extraarj77Ainda não há avaliações
- Chem MCQ MetalsDocumento8 páginasChem MCQ MetalsArundathyAinda não há avaliações
- Titanium Diboride AMCsDocumento11 páginasTitanium Diboride AMCsbaskaran shanmugavelAinda não há avaliações
- Argon Purging Systems (APS), Applicable To Purging Induction Melting Furnaces and Induction PowerDocumento12 páginasArgon Purging Systems (APS), Applicable To Purging Induction Melting Furnaces and Induction Powernirav patelAinda não há avaliações
- Answer:: Water Supply Engineering - Section 1 C - D - EDocumento3 páginasAnswer:: Water Supply Engineering - Section 1 C - D - EBez SofAinda não há avaliações
- Problem I: Oil Extraction: Theory AnswersDocumento7 páginasProblem I: Oil Extraction: Theory AnswershasanlishamilAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Scheme of Work For SS3 First Term and Second Term. - ITS MYSCHOOL LIBRARYDocumento9 páginasChemistry Scheme of Work For SS3 First Term and Second Term. - ITS MYSCHOOL LIBRARYsagir m. s.Ainda não há avaliações
- Reduction Swelling of Iron OxidesDocumento32 páginasReduction Swelling of Iron OxidesMuykundan MenonAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Materials & Workshop TechnologyDocumento6 páginasEngineering Materials & Workshop TechnologyCaleb MukaviAinda não há avaliações
- Chem181 m2 Experiment5 AbapoDocumento9 páginasChem181 m2 Experiment5 AbapoRyan Angelo AbapoAinda não há avaliações
- Armco Telar 57: Magnetic IronDocumento23 páginasArmco Telar 57: Magnetic IronKarthikeyan LAinda não há avaliações