Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Legend As
Enviado por
tobiasmattei0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
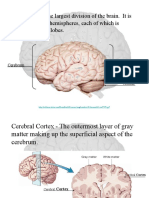
17 visualizações2 páginasFrontal lobe is often depicted as being split into three gyri, superior, middle, and inferior, by two sulci, superior and inferior. The precentral gyrus is located lateral to the posterior part of the body of the ventricle. The postcentral sulcus wraps around the upturned posterior end of the sylvian fissure.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoFrontal lobe is often depicted as being split into three gyri, superior, middle, and inferior, by two sulci, superior and inferior. The precentral gyrus is located lateral to the posterior part of the body of the ventricle. The postcentral sulcus wraps around the upturned posterior end of the sylvian fissure.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
17 visualizações2 páginasLegend As
Enviado por
tobiasmatteiFrontal lobe is often depicted as being split into three gyri, superior, middle, and inferior, by two sulci, superior and inferior. The precentral gyrus is located lateral to the posterior part of the body of the ventricle. The postcentral sulcus wraps around the upturned posterior end of the sylvian fissure.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
SLIDE 4
Continued exposures along the sylvian fissure. The anterior
horizontal ramus of the sylvian fissure separates the pars orbitalis
and triangularis and the anterior ascending ramus separates the
pars triangularis and opercularis. C, another right hemisphere. The
lower end of the precentral gyrus is located behind a somewhat
lobulated pars opercularis. The postcentral gyrus is located at the
anterior edge of the supramar ginal gyrus, which wraps around the
upturned posterior end of the sylvian fissure. D, the part of the right
frontal and parietal lobes in front of and behind the pre- and
postcentral gyri and central sulcus has been removed. The
precentral gyrus is located lateral to the posterior part of the body
of the ventricle. The postcentral gyrus is located lateral to the
anterior part of the atrium. Both gyri adjoining the sylvian fissure
are positioned lateral to the splenium of the corpus callosum. E-G,
sulci and gyri of the frontal lobe. E, superolateral view of the left
frontal lobe. The frontal lobe is often depicted as being split into
three gyri, superior, middle, and inferior, by two sulci, superior and
inferior. Often, as shown, the superior frontal gyrus is split into
medial and lateral segments by irregular sulci and gyri. The middle
frontal gyrus does not have a smooth, unbroken surface, but is
broken up into multiple, tortuous segments. On the inferior frontal
gyrus, formed by the pars orbitalis, triangularis, and opercularis,
there can be multiple variations in the size and shape of the
contributions from each part. The precentral gyrus, in this case, is
broken up into several segments by limbs of the precentral sulcus.
F, anterior view. A portion of the right superior frontal gyrus is
broken into two longitudinal gyral strips. The left superior frontal
gyrus is composed of multiple gyri that extend medially and
laterally across the superior frontal area. The superior frontal sulci
are continuous along both frontal lobes. The middle frontal gyri on
both hemispheres are made up of numerous worm-like gyral
segments. G, lateral view of another right frontal lobe. The pars
triangularis and opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus have a
somewhat similar triangular appearance. Usually there is a gyral
bridge at the lower margin of the central sulcus, but in this case the
central sulcus opens into the sylvian fissure. The precentral gyrus is
continuous from its lower to its upper margin and is not broken up
into multiple segments as shown in B and E. The middle frontal
gyrus is made up of multiple irregular convolutions. H-J, variations in
the sulcal and gyral patterns of the temporal lobe. H, right temporal
lobe with a more typical pattern in which the three temporal gyri,
superior, middle and inferior, are separated by two sulci, superior
and inferior. The sulci have an irregular, tortuous course, but are
largely continuous along the lateral temporal lobe from anterior to
posterior. I, the superior temporal gyrus located above the superior
temporal sulcus is easily identifiable. The part of the temporal lobe
below the superior temporal sulcus is broken up into multiple
obliquely oriented gyri that do not fit easily into a pattern of the
expected middle and inferior gyri. J, the superior temporal gyrus is
broken up into several segments but is fairly continuous. The middle
and inferior temporal regions are formed by multiple obliquely
oriented gyri and there is no clear inferior temporal sulcus
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- A New Understanding of ADHD in Children and Adults Executive Function Impairments (PDFDrive)Documento230 páginasA New Understanding of ADHD in Children and Adults Executive Function Impairments (PDFDrive)Willian vieira Pereira100% (3)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Accelerated Learning Techniques by Joe McCulloughDocumento172 páginasAccelerated Learning Techniques by Joe McCulloughelitely100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Biological Psychology Ninth EditionDocumento614 páginasBiological Psychology Ninth EditionAikido Euroget100% (15)
- Stephen M Stahl Laurence Mignon Stahl S Illustrated ADHD - 1Documento175 páginasStephen M Stahl Laurence Mignon Stahl S Illustrated ADHD - 1May Rc100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Neuroanatomy McqsDocumento20 páginasNeuroanatomy McqsNuman Khan0% (1)
- The Brain QuestionsDocumento4 páginasThe Brain QuestionsBibbyAinda não há avaliações
- #Human BrainDocumento28 páginas#Human BrainDharaa GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Remote Neural Monitoring - en CognitiveDocumento13 páginasWhat Is Remote Neural Monitoring - en CognitiveSimon Benjamin100% (1)
- DementiaDocumento26 páginasDementianadya100% (4)
- Fractal Neurodyamics and Quantum Chaos: Resolving The Mind-Brain Paradox Through Novel BiophysicsDocumento24 páginasFractal Neurodyamics and Quantum Chaos: Resolving The Mind-Brain Paradox Through Novel Biophysicskhanverse100% (1)
- Unit 5 The Nervous System: PretestDocumento5 páginasUnit 5 The Nervous System: PretestAmiel Richie BadiangAinda não há avaliações
- 0301a AllDocumento3 páginas0301a AllWiendha LiendriasariAinda não há avaliações
- The Student's Guide To Cognitive Neuroscience - GlossaryDocumento22 páginasThe Student's Guide To Cognitive Neuroscience - GlossaryDzungAinda não há avaliações
- Early Onset Psychotic DisordersDocumento51 páginasEarly Onset Psychotic Disordersdrkadiyala2100% (1)
- Brain and LearningDocumento13 páginasBrain and Learningvaishali@lets.org.in100% (1)
- Neuroscience: Science of The Brain in PolishDocumento72 páginasNeuroscience: Science of The Brain in PolishInternational Brain Research Organization100% (1)
- Ospe PyDocumento20 páginasOspe Pyipop_001Ainda não há avaliações
- BrainSpan Reference AtlasDocumento12 páginasBrainSpan Reference AtlasCarlos Alb SeAinda não há avaliações
- Lifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1Documento36 páginasLifespan Development Canadian 5th Edition Boyd Solutions Manual 1justinfleminggfcqziaonr100% (24)
- Pengantar Anatomi NBSDocumento65 páginasPengantar Anatomi NBSHa HaAinda não há avaliações
- Localization FunctionDocumento5 páginasLocalization Functionapi-188978784100% (1)
- The Atypical Social Brain Network in Autism Curr Op Neurol 2018Documento5 páginasThe Atypical Social Brain Network in Autism Curr Op Neurol 2018Diego Ignacio TelloAinda não há avaliações
- PTSD Prefrontal Cortex and AmigdalaDocumento13 páginasPTSD Prefrontal Cortex and AmigdalaMeryem FilizAinda não há avaliações
- Art-Habibi Et Al-Music Training and Child Development-2018Documento9 páginasArt-Habibi Et Al-Music Training and Child Development-2018Birgita Solange SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Auriculotherapy ManualDocumento9 páginasAuriculotherapy ManualpluigiaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 AssignmentDocumento11 páginasWeek 3 AssignmentJenneriza DC Del RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Outcome and Prognosis GDDDocumento20 páginasOutcome and Prognosis GDDIfah Inayah D'zatrichaAinda não há avaliações
- Eng World Psychiatry June 2015Documento148 páginasEng World Psychiatry June 2015diablero999Ainda não há avaliações
- Cerebral Cortex and Higher Cortical FunctionsDocumento14 páginasCerebral Cortex and Higher Cortical FunctionsAcid ManaAinda não há avaliações