Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Dogfish Dissection
Enviado por
Janine Vega CalayoTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Dogfish Dissection
Enviado por
Janine Vega CalayoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Comparative
Vertebrate Anatomy Exam 1 Study Guide Focus your efforts on the lecture notes and on bold-faced terms in the text if they were mentioned in lecture. Anatomy of a phylogenetic tree branching of major vertebrate groups monophyletic paraphyletic homology homoplasy analogy serial homology notochord dorsal hollow nerve cord endostyle pharyngeal slits post-anal tail coelom myomere tripoblastic germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) and derivatives splanchnic mesoderm paraxial mesoderm Protochordates (Hemichordates, Urochordates, Cephalodchordates) Petromyzontidae Myxiniformes Chordata Vertebrata Agnatha Gnathostomata Amniota Ammocoetes Filter feeder Placoid scales Actinopterygii Sarcopterygii Avian specializations for flight Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny egg types and their development (micro- meso- and macrolecithal) cleavage (holoblastic, meroblastic) blastula blastocoel
archenteron blastopore gastrulation protostomes deuterostomes invagination involution neuralation blastoderm primitive streak Hensens node Neurogenic placode Enterocoely Schizocoely extra-embryonic membranes and functions (yolk sac, amnion, chorion, allantois) spermatogenesis oogenesis fertilization trophoblast Hox Genes Heterochrony Neotony Progenesis Paedomorphosis Peramorphosis Isometry/Allometry Osteocytes, Osteoclasts, Osteoblasts Histogenesis of skeletal materials trabeculae Endochondral bone Dermal bone Cartilage Cortical bone Cancellous bone Epiphysis Diaphysis Epiphyseal plate Skull Autostyly Craniostyly Cranial kinesis neurocranium/chondrocranium dermatocranium
splanchnocranium temporal fenestra (anapsid, synapsid, diapsid, euryapsid) Homologies evolution of jaws Sharks - palatoquadrate, Meckel's cartilage, etc. components of jaw joint at this stage of evolution bony fish - components of jaw joint at this stage of evolution mammals evolutionary/anatomical consequences of chewing evolutionary trend from reptile ancestor to living mammals changing size and role of dentary bone bones that comprise the jaw joint in reptiles and in mammals evolution and homologies of inner ear ossicles importance of secondary palate Components of the axial skeleton Vertebrae basic structural components neural and hemal arch bases centrum categorization of vertebra based on centra Development of vertebrae Variation in lamprey, chondricthes, fish, tetrapods Vertebral regions arcualia Lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis Concept of serial homology applied to vertebrae Atlas, Axis, homologies, and groups in which these vertebrae types occur Rib functions Gastralia Plastron, carapace Myosepta Dorsal, Ventral, and Horizontal Skeletogenous septa tuberculum Capitulum Uncinate processes Pectoral Girdle general evolutionary trend from more dermal than replacement bones to more replacement than dermal bones stylo-, zeugo-, autopodium Ancestral arrangement of bones in fish limb development apoptosis AER
ZPA specializations for running in vertebrates and endurance running in humans Pelvic Girdle Components Innominate bone Muscles Embryonic sources of muscle functions Four characteristics striated skeletal cardiac smooth modifications of epaxial and hypaxial muscles in tetrapods epaxials as a whole sliding filimant theory jaw muscles red and white fibers isometric and isotonic contractions
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Discuss The Radial Nerve and Its Branches in The Forearm Up To Its Terminal Branches in The HandDocumento10 páginasDiscuss The Radial Nerve and Its Branches in The Forearm Up To Its Terminal Branches in The HandJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- 33 Approach To ADocumento6 páginas33 Approach To AJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Med 2 Cd2 Endo - ThyroidDocumento6 páginasMed 2 Cd2 Endo - ThyroidJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- SGD 10 Lower Respi Number 4Documento26 páginasSGD 10 Lower Respi Number 4Janine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- A Disease On Epithelial CellsDocumento6 páginasA Disease On Epithelial CellsJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- SGDDocumento7 páginasSGDJanine Vega Calayo100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Specifications: FeaturesDocumento2 páginasSpecifications: FeaturesJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Be Proactive!!Documento23 páginasBe Proactive!!Janine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- World LiteraturesDocumento40 páginasWorld LiteraturesJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- mRNA-Based Identification For Forensic ApplicationDocumento27 páginasmRNA-Based Identification For Forensic ApplicationJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Botany Chapter 4Documento4 páginasBotany Chapter 4Janine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- A History of WindowsDocumento7 páginasA History of WindowsJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
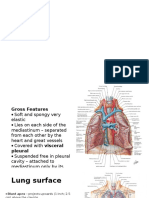
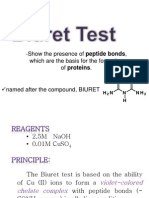
- Biuret TestDocumento10 páginasBiuret TestJanine Vega Calayo100% (1)
- mRNA-Based Identification For Forensic ApplicationDocumento27 páginasmRNA-Based Identification For Forensic ApplicationJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Dissection Walk ThroughDocumento24 páginasDissection Walk ThroughJanine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Biuret TestDocumento10 páginasBiuret TestJanine Vega Calayo100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Dev't of Phil Lit.Documento3 páginasDev't of Phil Lit.Janine Vega CalayoAinda não há avaliações
- 300 BLK WhitepaperDocumento28 páginas300 BLK Whitepapereric desentis100% (1)
- 5l PDFDocumento2 páginas5l PDFSamuel ZambranoAinda não há avaliações
- Gear SelectionDocumento34 páginasGear SelectionManny AnacletoAinda não há avaliações
- Chandigarh Media ListDocumento23 páginasChandigarh Media ListJuhi Jain100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- PrepositionsDocumento1 páginaPrepositionsAzeneth SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Carrozas - de - Fuego - Partitura CompletaDocumento10 páginasCarrozas - de - Fuego - Partitura Completajose andres manchadoAinda não há avaliações
- Mahindra Scorpio-N Review - Page 2 - Team-BHPDocumento13 páginasMahindra Scorpio-N Review - Page 2 - Team-BHPRavi DhingraAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Gilbert BremsethDocumento9 páginasGilbert Bremsethapi-291362084Ainda não há avaliações
- Mario Blasone - Triple Threat Part 2Documento23 páginasMario Blasone - Triple Threat Part 2paffi12345678Ainda não há avaliações
- Novijen, Heart of Progress The Great Henge Cosi's Trickster: Growing Rites of ItlimocDocumento1 páginaNovijen, Heart of Progress The Great Henge Cosi's Trickster: Growing Rites of ItlimocFelizpe RodríguezAinda não há avaliações
- Strength Training / Muscle Building: The Fitness WikiDocumento5 páginasStrength Training / Muscle Building: The Fitness WikiRajulapati VinodkumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Ecto-Meso-Endo-Dermal LayersDocumento3 páginasEcto-Meso-Endo-Dermal LayersCarissa NicholsAinda não há avaliações
- Nobull 23Documento35 páginasNobull 23B D Cook100% (2)
- Assignment in Pathfit 4Documento3 páginasAssignment in Pathfit 4shinamaevAinda não há avaliações
- WoJ XInput Emulator - User Guide - EnglishDocumento10 páginasWoJ XInput Emulator - User Guide - EnglishBrayAndres CastañoAinda não há avaliações
- Cutthroat: Life On The HighwayDocumento11 páginasCutthroat: Life On The HighwayAlexandre HenriquesAinda não há avaliações
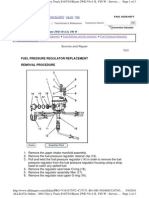
- 2001 Chevy Truck s10 t10 Blazer Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement Removal ProcedureDocumento3 páginas2001 Chevy Truck s10 t10 Blazer Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement Removal ProcedureKidd100% (1)
- Distribution - Excel & Access PackagesDocumento2 páginasDistribution - Excel & Access Packagesumer plays gameAinda não há avaliações
- PN Saw Eng Wah (Chief) en Ong Beng Soon Pn. Retnamala: and The Timekeeper Respectively For Each LevelDocumento3 páginasPN Saw Eng Wah (Chief) en Ong Beng Soon Pn. Retnamala: and The Timekeeper Respectively For Each LevelHazman GhazaliAinda não há avaliações
- Malzeme Cetveli̇Documento1 páginaMalzeme Cetveli̇sitehabAinda não há avaliações
- Punch PowerDocumento2 páginasPunch PowerguidocesanoAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Pe Q1 To Q3Documento109 páginas7 Pe Q1 To Q3ASHYJOE28Ainda não há avaliações
- #53 February 2015Documento76 páginas#53 February 2015OutdoorUAEAinda não há avaliações
- The White Stripes - Seven Nation Army - Cifra ClubDocumento4 páginasThe White Stripes - Seven Nation Army - Cifra ClubGoveanAinda não há avaliações
- LYCOMING O & LO-360 (76 Series) Parts Catalog PC-123 PDFDocumento29 páginasLYCOMING O & LO-360 (76 Series) Parts Catalog PC-123 PDFBrunoAinda não há avaliações
- 60 Day Speed Training PlanDocumento101 páginas60 Day Speed Training Planxceelent100% (7)
- Solo RepertoireDocumento5 páginasSolo RepertoirehywkjyAinda não há avaliações
- (1942) FM 21-150 Unarmed Defense For The American SoldierDocumento75 páginas(1942) FM 21-150 Unarmed Defense For The American SoldierSamurai_Chef100% (3)
- Dungeon Magazine 195 PDFDocumento5 páginasDungeon Magazine 195 PDFGuillaumeRicherAinda não há avaliações
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouNo EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (62)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)