Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Content Health Ed
Enviado por
Anna FoxDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Content Health Ed
Enviado por
Anna FoxDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
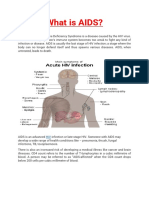
I. Definition HIV HIV infection is a condition caused by the human immunaodeficiency virus (HIV).
The condition gradually destroys the immune system, which makes it harder for the body to fight infections. HIV causes AIDS. HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It breaks down the immune system our body's protection against sdisease. HIV causes people to become sick with infections that normally wouldn't affect them. AIDS is short for acquired immune deficiency syndrome. It is the most advanced stage of HIV disease.
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can be spread by the following: Through sexual contact -- including oral, vaginal, and anal sex Through blood -- through blood transfusions, accidental needlesticks, or needle sharing From mother to child -- a pregnant woman can transmit the virus to her fetus through their shared blood circulation, or a nursing mother can pass it to her baby in her breast milk Rare ways the virus may be spread include: Accidental needle injury Artificial insemination with infected semen Organ transplantation with infected organs Blood banks and orang donor programs screen donors, blood, and tissues thoroughly to prevent the risk of infection. HIV is NOT transmitted to a person who DONATES blood or organs. People who donate organs are never in direct contact with people who receive them. Likewise, a person who donates blood is never in contact with the person receiving it. In all these procedures, sterile needles and instruments are used. People at highest risk for getting HIV include: Injection drug users who share needles Infants born to mothers with HIV who didn't receive HIV therapy during pregnancy People who have unprotected sex, especially with people who have other high-risk behaviors, are HIV-positive, or have AIDS People who received blood transfusions or clotting products between 1977 and 1985 (before screening for the virus became standard practice) Sexual partners of those who participate in high-risk activities (such as injection drug use or anal sex)
Without theraphy, there will be:
1. Initial invasion of the virus - mild, flulike symptoms 2. Seroconversion - woman converts from having no HIV antibodies in her blood serum to having antibodies against HIV - happens 6 weeks to 1 year after exposure 3. Asymptomatic Period - woman appears to be disease free except for symptoms such as weight loss and fatigue - continue replication - average 3-11 years 4. Symptomataic period - CD4 count <200 cells/mm - woman develops opportunistic infections and possibly malignancies Diagnostic Procedures Several tests can find antibodies or genetic material (RNA) to the HIV virus. These tests include: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) . This test is usually the first one used to detect infection with HIV. If antibodies to HIV are present (positive), the test is usually repeated to confirm the diagnosis. If ELISA is negative, other tests are not usually needed. This test has a low chance of having a false result after the first few weeks that a person is infected. Western blot. This test is more difficult than the ELISA to perform, but it is done to confirm the results of two positive ELISA tests. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This test finds either the RNA of the HIV virus or the HIV DNA in white blood cells infected with the virus. PCR testing is not done as frequently as antibody testing, because it requires technical skill and expensive equipment. This test may be done in the days or weeks after exposure to the virus. Genetic material may be found even if other tests are negative for the virus. The PCR test is very useful to find a very recent infection, determine if an HIV infection is present when antibody test results were uncertain, and screen blood or organs for HIV before donation. Treatment Anti-retroviral Therapy (ART) - zidovudine(AZT) (azidothymidine) a. Prolong Life b. Reduce risk of opportunistic infections c. Prolong incubation period For pregnant women with HIV: If ZDZ(zidovudine) is administered at the beginning of the 14 th week and newborn recdeives the drug for 6 weeks after birth, risk for perinatal transmission can be reduced to 8%-10%
Health teachings For infected persons 1. Avoid infections 2. Use latex condom to protect partner during sexual intercourse 3. Do not donate blood, sperm, organs, or other body tissues 4. Do not share items with other persons that may be contaminated with blood and other body fluids 5. Do not breast fed infant For non-infected persons 1. stick to one partner, practice monogomous relationship 2. Use condoms 3. Avoid oral and anal sex 4. Practice good personal hygiene 5. Practice healthful living: exercise, adequate rest, nutritional diet, safer sex 6. Be aware of the signs and symptoms of infections: -weight loss -chronic diarrhea -prolonged fever
Você também pode gostar
- AIDS in The PhilippinesDocumento29 páginasAIDS in The Philippinesjaninasuzette100% (1)
- Hiv AidsDocumento36 páginasHiv AidsNaman Jain100% (1)
- Presented By:dr - Anita Chaudhari Roll No: 2Documento22 páginasPresented By:dr - Anita Chaudhari Roll No: 2younismushtaq100% (1)
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus Case AnalysisDocumento5 páginasHuman Immunodeficiency Virus Case AnalysisAllen Bugarin CabadingAinda não há avaliações
- Plasmapheresis For AutoimmunityDocumento14 páginasPlasmapheresis For AutoimmunityEliDavidAinda não há avaliações
- Spondylo ArthropathyDocumento89 páginasSpondylo ArthropathyJen NeeAinda não há avaliações
- AdisDocumento27 páginasAdisANIL KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyDocumento39 páginasKendriya Vidyalaya Ambernath BiologyROHIT SIHRAAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnDocumento24 páginasHiv Aids: Presented By: Chavez - Galang - Kaur - Noguera 2DcnKate ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- HIV and Its TreatmentDocumento24 páginasHIV and Its Treatmentaathira_kAinda não há avaliações
- 8A Nosocomial InfectionDocumento15 páginas8A Nosocomial InfectionSuminaShrestha100% (1)
- Hiv Notes 2021Documento24 páginasHiv Notes 2021Vïñy KïñgzAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv Aids The BasicsDocumento3 páginasHiv Aids The BasicsHyrum KamandeAinda não há avaliações
- H4 2Documento4 páginasH4 2Patricia CaladoAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Investigatory Project: TopicDocumento24 páginasBiology Investigatory Project: Topicattishya1104100% (1)
- Infection With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: ELISA/Western Blot Tests For HIVDocumento6 páginasInfection With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: ELISA/Western Blot Tests For HIVBianca de GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- S.N0 Topic: IndexDocumento9 páginasS.N0 Topic: Indexashishkoshy12Ainda não há avaliações
- Ate KrissiaDocumento15 páginasAte Krissiaroan marie isaacAinda não há avaliações
- Aids FileDocumento13 páginasAids Fileayansiddiqui0422Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is Hiv?: Aids and HivsDocumento8 páginasWhat Is Hiv?: Aids and Hivscarlous brathwateAinda não há avaliações
- Types of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XDocumento19 páginasTypes of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XronojerutomAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv/Aids: Preventing Testing TreatingDocumento8 páginasHiv/Aids: Preventing Testing TreatingReza Badruun Syahrul HakimAinda não há avaliações
- STDs HIVsAIDsDocumento26 páginasSTDs HIVsAIDsMarco AvenillaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 MillionDocumento11 páginasWhat Is Hiv?: 3 Yearstrusted Source 1.2 Millionhilja shipenaAinda não há avaliações
- ROHITDocumento17 páginasROHITDivyansh kAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv/Aids: Wagiyo, SKP., M.Kep., SP MatDocumento34 páginasHiv/Aids: Wagiyo, SKP., M.Kep., SP MatNettha Bintang DhiafakhriAinda não há avaliações
- Bio BirjuDocumento17 páginasBio BirjuDivyansh kAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv / Aids Education & Prevention ProgramDocumento51 páginasHiv / Aids Education & Prevention ProgramFaeza ZackyAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam TDocumento100 páginasHiv and Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission (PMTCT) : by Gebremaryam THambal AhamedAinda não há avaliações
- HIv FactsDocumento5 páginasHIv Factslarrybeechey3792Ainda não há avaliações
- Hiv 101Documento33 páginasHiv 101Hend Al-RamahiAinda não há avaliações
- Health & Diseases: Topic: AIDSDocumento19 páginasHealth & Diseases: Topic: AIDSkakaramAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report (Swati Dogra)Documento8 páginasProject Report (Swati Dogra)onlinebaijnathAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv/Aids: Masroni, S.Kep., NS., M.S. (In Nursing)Documento19 páginasHiv/Aids: Masroni, S.Kep., NS., M.S. (In Nursing)Sherly OctaviaAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv Aidslecture 170325113424Documento39 páginasHiv Aidslecture 170325113424dAinda não há avaliações
- HIV in PregnancyDocumento26 páginasHIV in Pregnancyairahibrahim23Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 21 - Aids2Documento31 páginasChapter 21 - Aids2Sanjeevan Aravindan (JEEV)Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is AIDS?Documento7 páginasWhat Is AIDS?Bhavya PAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv Immunology Study CaseDocumento7 páginasHiv Immunology Study Casetan choonAinda não há avaliações
- Screenshot 2023-09-05 at 9.24.20 PMDocumento17 páginasScreenshot 2023-09-05 at 9.24.20 PMThanvi EraparajuAinda não há avaliações
- What Are HIV & AIDS?: Last Updated: November 15, 2019Documento16 páginasWhat Are HIV & AIDS?: Last Updated: November 15, 2019MansikhaAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv NotesDocumento6 páginasHiv NotesMartin De Haro GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv NotesDocumento6 páginasHiv NotesMartin De Haro GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking ExerciseDocumento2 páginasCritical Thinking ExerciseDelle KairuzAinda não há avaliações
- HIV and PregnancyDocumento2 páginasHIV and PregnancyMagdalena Dwiyani HutajuluAinda não há avaliações
- Bio ProjectDocumento22 páginasBio Projectrakeshkiran2007100% (1)
- Lecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVDocumento6 páginasLecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVreginaamondi133Ainda não há avaliações
- HIV DocumentationDocumento10 páginasHIV DocumentationSpidyAinda não há avaliações
- HIV Infection Fact SheetDocumento38 páginasHIV Infection Fact SheetYu Mong LeeAinda não há avaliações
- AidsDocumento2 páginasAidsMei-mei ZhuangAinda não há avaliações
- English Hiv LeafletDocumento2 páginasEnglish Hiv LeafletVega HapsariAinda não há avaliações
- End Stage AidsDocumento33 páginasEnd Stage AidsMichael T GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is HIVDocumento18 páginasWhat Is HIVTaufik KhanAinda não há avaliações
- AIDS - Intro & PathophysiologyDocumento24 páginasAIDS - Intro & Pathophysiologykcnit trainingAinda não há avaliações
- By: Glenda Zapata, Maria Leticia Zarazua HernandezDocumento17 páginasBy: Glenda Zapata, Maria Leticia Zarazua HernandezMaria Leticia Zarazua HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology: IntroductionDocumento5 páginasMicrobiology: IntroductionNimra AmeenAinda não há avaliações
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Documento7 páginasHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)Ambar WulanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is HIVDocumento14 páginasWhat Is HIVmariam miladAinda não há avaliações
- The Difference Between HIV and AidsDocumento14 páginasThe Difference Between HIV and AidsAnonymous bq4KY0mcWGAinda não há avaliações
- Hiv NSDocumento17 páginasHiv NSdarraAinda não há avaliações
- Patient Education PDFDocumento12 páginasPatient Education PDFAgustinaAinda não há avaliações
- STD Screening Recommended by The Centers of Disease Control and PreventionDocumento6 páginasSTD Screening Recommended by The Centers of Disease Control and PreventionMonica TrabancoAinda não há avaliações
- PRM - Ma5 BookletDocumento25 páginasPRM - Ma5 BookletVan LabasanoAinda não há avaliações
- Immunology Study Sheet For The Final ExamDocumento3 páginasImmunology Study Sheet For The Final ExamDenizDerenAinda não há avaliações
- 1 No Sop General NformetionDocumento11 páginas1 No Sop General NformetionMANORANJANAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatitis BDocumento25 páginasHepatitis BJevon AndraAinda não há avaliações
- Git, Liver & GB: by Dr. Thameem SaifDocumento119 páginasGit, Liver & GB: by Dr. Thameem SaifGirija VirkarAinda não há avaliações
- ACTINOMYCETESDocumento22 páginasACTINOMYCETESDaniel WaweruAinda não há avaliações
- Animal BiteDocumento51 páginasAnimal BiteJo-Ann Marie MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Staphylococcus EpidermidisDocumento12 páginasStaphylococcus EpidermidisSim M ChangAinda não há avaliações
- STIs Part ADocumento3 páginasSTIs Part AMihaela EneAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Bukhar Ka Ilaj Lakshan Karan Bachne Ke Upay in HindiDocumento2 páginasDengue Bukhar Ka Ilaj Lakshan Karan Bachne Ke Upay in HindiSumit upayAinda não há avaliações
- A Concept Paper: HIV: By: Nichol Niño H. BanaagDocumento2 páginasA Concept Paper: HIV: By: Nichol Niño H. Banaaglhuk banaagAinda não há avaliações
- Tata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALDocumento27 páginasTata Laksana Rinitis Alergi Pada Dewasa FINALNikko Khairul DafaAinda não há avaliações
- Corynebacterium DiphtheriaeDocumento21 páginasCorynebacterium DiphtheriaehercolaniumAinda não há avaliações
- India's COVID-19 Vaccina On Program: CFM Individual Wri/en Assignment 1Documento3 páginasIndia's COVID-19 Vaccina On Program: CFM Individual Wri/en Assignment 1Ayushi ThakkarAinda não há avaliações
- Procedures For Submitting Samples For Testing For Ebola Virus InfectionDocumento3 páginasProcedures For Submitting Samples For Testing For Ebola Virus InfectionssucbbaAinda não há avaliações
- Grid AbcdeDocumento1 páginaGrid AbcdeStephanieDardaAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Alang-AlangDocumento10 páginasJurnal Alang-AlangFransLei Vadoel SaelAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatic Transaminitis and AnakinraDocumento2 páginasHepatic Transaminitis and AnakinraSean GreenAinda não há avaliações
- Fast Facts On Dengue FeverDocumento13 páginasFast Facts On Dengue Fevermuhammad aslamAinda não há avaliações
- Loa Loa, OnchocercaDocumento28 páginasLoa Loa, Onchocercabindu dhanapalAinda não há avaliações
- Abo System-Simply Classifies Human Blood Based On The Inherited Properties of RbcsDocumento2 páginasAbo System-Simply Classifies Human Blood Based On The Inherited Properties of RbcsClaire Angelie RuayaAinda não há avaliações
- Imci Booklet For CHN Pages 64 71 Pages 1,8Documento2 páginasImci Booklet For CHN Pages 64 71 Pages 1,8Xyryl BagagunioAinda não há avaliações
- Tugasan Epraktikal XBDM4103 Mei 2021Documento6 páginasTugasan Epraktikal XBDM4103 Mei 2021norfilzahAinda não há avaliações
- Fungal RhinosinusitisDocumento5 páginasFungal RhinosinusitisigorAinda não há avaliações
- John Bunyan (1628-1688) : The Captain of All These Men of Death'Documento56 páginasJohn Bunyan (1628-1688) : The Captain of All These Men of Death'Johir ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- C. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 13: Organ Transplantation Principles of Organ Transplantation J. R. Botha and L. P. MargoliusDocumento28 páginasC. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 13: Organ Transplantation Principles of Organ Transplantation J. R. Botha and L. P. MargoliusGordana UzelacAinda não há avaliações