Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Urinary System Exam 1
Enviado por
Brandon BrownDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Urinary System Exam 1
Enviado por
Brandon BrownDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
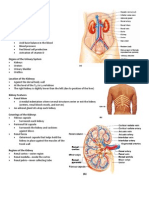
Urinary System Exam 1 1. Urinary system consists of six organs, name them: 2.
The functions of the kidney are a. Filters blood plasma, separates waste from useful chemicals, returns useful substances to blood, eliminates wastes b. Regulate blood volume and pressure by eliminating or conserving water c. Regulate the osmolarity of the body fluids by controlling the relative amounts of water and solutes eliminated d. Secretes enzyme, renin, which activates hormonal mechanisms that control blood pressure and electrolyte balance 3. How is the position of the kidneys maintained in the abdominal cavity? a. overlying peritoneum b. contact with adjacent visceral organs c. supporting connective tissues d. All the above 4. Match the nitrogenous waste with its formation a. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) b. Uric acid c. Urea formation d. Creatinine e. Metabolic waste ____waste substance produced by the body
____Proteins->amino acids-> NH2 removed-> forms ammonia, liver converts to urea ____Product of nucleic acid catabolism _____Product of creatine phosphate catabolism _____expression of the level of nitrogenous waste in the blood
5. Match the three protective connective tissue coverings of kidney a. Renal fascia ____immediately deep to parietal peritoneum _____ cushions kidney and holds it into place ____encloses kidney protecting it from trauma and infection
b. Perirenal fat capsule c. Fibrous capsule
6. Each kidney has about 1.2 million nephrons. TRUEN OR FALSE 7. Each nephron is composed of what two principal parts? _____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________
8. Renal corpuscle consists of the ________and a two-layered glomerular _________ that encloses glomerulus 9. The renal tubule is divided into four regions, name them 10. Match a. Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) b. Nephron loop (loop of Henle) limb and ascending limb) c. Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) cortex d. Collecting duct passes back into the medulla ______ari ses from glomerular capsule ________long U-shaped portion of renal tubule (Descending
______begins shortly after the ascending limb reenters the
______receives fluid from the DCTs of several nephrons as it
11. Trace the flow of fluid from the point where the glomerular filtrate is formed to the point where urine leaves the body, using the terms below urethra papillary duct glomerular capsule proximal convoluted tubule nephron loop distal convoluted tubule collecting duct minor calyx major calyx renal pelvis ureter urinary bladder 12. Cortical nephrons comprise a. 85% of all nephrons b. Short nephron loops
c. Efferent arterioles branch into peritubular capillaries around PCT and DCT d. All the above 13. Juxtamedullary nephrons comprise a. b. c. d. 15% of all nephrons Very long nephron loops Efferent arterioles branch into vasa recta around long nephron loop All the above
14. Renal innervations is by the renal plexus . TRUE OR FALSE 15. Kidneys convert blood plasma to urine in what three stages 16. Glomerular filtration is a special case of the capillary fluid exchange process in which water and some solutes in the blood plasma pass from the capillaries of the glomerulus into the capsular space of the nephron. True or False 17. Proteinuria (albuminuria): presence of protein in urine Hematuria: presence of blood in the urine True or false 18.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- 2.uterine AbnormalitiesDocumento11 páginas2.uterine AbnormalitiesKuleshwar SahuAinda não há avaliações
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocumento35 páginasS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.Ainda não há avaliações
- Human Diseases 8th Edition Zelman Test BankDocumento15 páginasHuman Diseases 8th Edition Zelman Test Bankquatchristabelfa55hd100% (26)
- Renal Histology Biolucida AnswersDocumento6 páginasRenal Histology Biolucida Answersjhk0428Ainda não há avaliações
- Urine Formation Steps Filtration: Dr. Sumaiya KhanDocumento4 páginasUrine Formation Steps Filtration: Dr. Sumaiya KhanZeleen Ann SaberonAinda não há avaliações
- Urology OSCEDocumento9 páginasUrology OSCEJihad Anad75% (4)
- Embryology of The KidneysDocumento18 páginasEmbryology of The KidneysPrincewill SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Latihlah Soal UkomDocumento87 páginasLatihlah Soal UkomDewi Saidatul MAinda não há avaliações
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocumento43 páginasMale and Female Reproductive SystemOre Perez CañeteAinda não há avaliações
- 15 UrinalysisDocumento9 páginas15 UrinalysisJaney Ceniza تAinda não há avaliações
- A&P Coloring Workbook - The Urinary System PDFDocumento19 páginasA&P Coloring Workbook - The Urinary System PDFYuhAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Fabs Post TestDocumento3 páginasRenal Fabs Post Testlorelyn corpuzAinda não há avaliações
- UroflowDocumento41 páginasUroflowSri HariAinda não há avaliações
- Embriologi Alat KelaminDocumento19 páginasEmbriologi Alat KelaminAdi Putra GhifariAinda não há avaliações
- Stress IncontinenceDocumento44 páginasStress IncontinenceswatisinghnigeriaAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology G11 WK13-16 A. TobiasDocumento31 páginasGeneral Biology G11 WK13-16 A. TobiasKristine SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Female Urinary CatheterizationDocumento4 páginasFemale Urinary CatheterizationArdiene Shallouvette GamosoAinda não há avaliações
- System UriDocumento48 páginasSystem UriStef FieAinda não há avaliações
- ANAPHY Lec Session #23 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Documento14 páginasANAPHY Lec Session #23 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care of Client With HypospadiaDocumento21 páginasNursing Care of Client With HypospadiaancoursAinda não há avaliações
- Urogynecology Division AyuDocumento4 páginasUrogynecology Division AyuDwickyAinda não há avaliações
- MORANDocumento3 páginasMORANCubillas P. DerAinda não há avaliações
- Male Reproductive AnatomyDocumento25 páginasMale Reproductive Anatomyisimmonn0% (1)
- Congenital Anomalies of The KidneyDocumento21 páginasCongenital Anomalies of The KidneyRaghu Rajan100% (1)
- Handouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Documento7 páginasHandouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Kelly Trainor100% (2)
- Reflex IncontinenceDocumento3 páginasReflex IncontinenceMezab E RehmatAinda não há avaliações
- Cystoscopy RevisedDocumento9 páginasCystoscopy RevisedRizzi DeveraAinda não há avaliações
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IvDocumento4 páginasA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IvEmiliano Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Erectile Dysfunction PDFDocumento191 páginasTreatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Erectile Dysfunction PDFMontserratAinda não há avaliações
- EAU Pocket On Paediatric Urology 2023Documento54 páginasEAU Pocket On Paediatric Urology 2023Andrea SzaszAinda não há avaliações