Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Calcul Higrotermic
Enviado por
Vlad SpataruDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Calcul Higrotermic
Enviado por
Vlad SpataruDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Hygrothermal design
Characteristics:
The building is situated in the city Iasi, in the climatic zone III, with a respective
exterior temperature T
e
=-18
0
C. It has a height of 14m(from ground level) (S+P+4E) and a
structure of reinforced concrete frames with cladding of BCA masonry with a thickness
of 25 cm. The top of the building has a non-circulable terrace.
The purpose of thermal dimensioning is the meeting of confort requirements, the
reduction of fuel consumption necessary to assure a confortable temperature and the
reduction of pollution from fuel consumption.
The thermal dimensioning calculus for the exterior walls and the terrace is made
in agreement with the conforming standards. According to the normative C107/1-1997
the thermal verification is made using the relation :
GN G
Where :
- GN is the normated global coefficient of thermal insulation [W/m
2
K]
- G is the global coefficient of thermal insulation [W/m
2
K]
The factor of thermal insulation reflects the sum of all thermal loss trough all the
building envelope elements for a thermal difference of 1 Kelvin () plus the losses
because of ventilation and air infiltration.
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Thermal Design
1. Calculus of the global coefficient of thermal insulation
(Romanian Code C107/1,2,3,4-2005)
1.1 Specific thermal resistance
Thermal resistance of the material of construction is determined by the
relationship:
0 i e
R R R R + +
, where:
i e
R
, - means the thermo transfer resistance through internal surface, respective
external of the construction element[m
2
K/W].
Ri =
i
1
=
8
1
=0,125 m
2
K/W
R
e
=
e
1
=
24
1
= 0,042 m
2
K/W
R the thermo permeability resistance of a layer from the construction element, which
has homogeneousness by both directions .
n
i j
j
d
R
1
where:
dj- the layers thickness(m).
j- coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material from layer j(W/m K).
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Finally, the relationship is obtained for calculating the thermal resistance of the
element of construction:
+ +
n
i
e
j
j
i
R
d
R R
1
0
(
2
/ m K W ).
a)Exterior walls
According to C107/2005, in case of the external walls we have the followings:
R
si
= 0.125[m
2
K/W];
R
se
= 0.042[m
2
K/W];
R
min
= 1.80[m
2
K/W]; (from 10.6.2011)
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
2
0.125 (0.017 0.085 2.273 0.017) 0.042 2.786( / )
i e
d
R R R m K W
+ + + + + + +
b)lower slab:
According to C107/2005, for slab over basement we have:
R
si
= 0.167[m
2
K/W];
R
se
= 0.125[m
2
K/W];
R
min
= 2.90[m
2
K/W]; (from 10.6.2011)
No
crt
Name of the material layer
d (m) (W/mK)
d/
1. Interior plaster M50T 0.01
5
0.87 0.017
2. Brickwork BCA 0.25 0.34 0.085
3. Thermal Insulation 0.10 0,044 2.273
4. Exterior plaster M100 0.01
5
0.87 0.017
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Nr.
crt
Name of the material
layer
d (m)
(W/m
K)
d/
1 Ceiling plaster M50T 0.015 0.87 0.017
2 Thermal insulation 0.20 0.044 4.545
3 Reinforced Concrete
Plate
0.15 1.74 0.086
4 Equlizing cement
flooring (M100)
0.03 0.93 0.032
5
Sand Stone 0.01 1.2 0.083
2
0.125 (0.017 4.545 0.086 0.032 0.083) 0.167 4.93( / )
i e
d
R R R m K W
+ + + + + + + +
c)Roof floor:
According to C107/2005 we have the followings:
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
R
si
= 0.125[m
2
K/W];
R
se
= 0.048[m
2
K/W];
R
min
= 5 [m
2
K/W]; (from 10.6.2011)
Nr.
crt
Name of the
material layer
d (m) (W/mK) d/
1 Ceiling Plaster
M50T
0.015 0.87 0.017
2 Reinforced
Concrete Plate
0.15 1.74 0.086
3 Equlizing cement 0.03 0.93 0.032
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
flooring (M100)
4 Vapor barrier - - -
5 Protection layer - - -
6 Support layer 0.03 0.93 0.032
7 Diffusion layer - - -
8 Protection layer - - -
9 Thermal insulation 0.2 0.048 4.5
10 Protection screed 0.03 0.91 0.032
11 Waterproofing
- - -
12 Gravel - - -
2
0.125 (0.017 0.086 0.032 0.032 4.5 0.32) 0.167 5.326( / )
i e
d
R R R m K W
+ + + + + + + + +
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
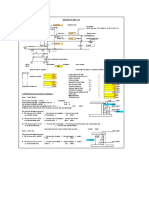
1.2. Thermal bridges
Calculation of areas of building elements (closing). These areas are calculated
from their inner face.
2
.
3
. .
2
. .
4 1 .
int
int
7 . 20 1 2 . 2 8 . 1 2 1 . 2 9 . 0 2 2 . 1 9 . 0 4 6 . 0 6 . 0 4 2 . 1 2 . 1 2 2 . 1 5 . 1
81 . 2735 4 8 . 2 93 . 160 8 . 2 93 . 160 3 93 . 160 5
4 . 972 4 8 . 2 2 . 57 8 . 2 2 . 57 3 2 . 57 5
; 2 . 57 ; 2 . 57 ; 2 . 57
93 . 160
7 . 7
9 . 20
m S
m h S h S h S V
m h P h P h P S
m P m P m P
m S
m l
m L
woodwork fl
floor floor floor gr floor gr basement basement
floor floor floor gr floor gr basement basement
floors floor gr basement
floor
+ + + + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
] [ 47 . 0
81 . 2735
26 . 1294
26 . 1294 93 . 160 5 . 103 9 . 868 93 . 160
9 . 868 5 . 103 4 . 972
5 . 103 7 . 20 5
3
2
2
. inf
2
.
2
.
m
m
V
A
m S S S S A
m S S S
m S
T wood opac pl
T wood opac
T wood
+ + + + + +
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Determination of the length of thermal bridges
Thermal bridges are parts of elements covering the construction with non-
homogenous structures, through which the propagation of heat is more intense.
a. Vertical joint (end or corner exiting)
m h n l 56 8 . 2 20
05 . 0
int
2 1
b. Vertical joint intersection between the reinforced concrete columns and the
exterior wall of BCA
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
m h l 112 8 . 2 40 10
04 . 0
int
2 1
c.Horizontal joint roof floor -attic terrace and exterior wall of BCA
m l 20 . 57
27 . 0
01 . 0
2
1
d.Horizontal joint intersection between current floor and main girder
1=0.10
2=0.15 L=286 m
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
e.Horizontal joint intersection between inferior floor over foundation and exterior wall
m l 2 . 57 1 2 . 57
25 . 0
06 . 0
2
1
f.Jamb for windows and doors
m l 75
25 . 0
1
g.Horizontal joint current floor with balcony
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
m l 79
21 . 0
2 . 0
2
1
Specific thermal resistance corected
'
R
(mk/W):
/
/
1
R
U
/
U - coefficient of thermal transfer
/
( )
1
l
U
R A
(mk/W)
R- thermal resistance by category placement element
For exterior wall:
) / ( 478503 . 0
9 . 868
89 . 103
786 . 2
1
2 '
W k m U +
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
For roof floor:
) / ( 28728 . 0
93 . 160
016 . 16
326 . 5
1
2 '
W k m U +
For inferior floor:
) / ( 31302 . 0
93 . 160
732 . 17
93 . 4
1
2 '
W k m U +
For exterior woodwork :
) / ( 1811 . 2
5 . 103
75 . 18
5 . 0
1
2 '
W k m U +
inf
/ / / /
inf
1
0.34
perext acop pl tamplarie
perext acop pl tamplarie
A A A A
G n
V R R R R
1
+ + + +
1
1
]
3 3
1 868.9 160.93 160.93 103.5
1 1 0.5 1 0.34 0.5
2735.81 2.08985 3.4809 3.19468 0.4584
0.4306( / ) 0.61( / )
(0.5 1.5);
G
G W m k GN W m k
n G GN
1
+ + + +
1
]
<
from C107/1 pg.28
]] [ 47 . 0
81 . 2735
26 . 1294
3
2
m
m
V
A
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
3.2 Sweat calculus
3.2.1 Sweat calculus on the interior surface of exterior walls
Sweat on the interior elements of construction is due to increased partial pressure
of vapor on the interior, with a tendency for equalization of the saturation pressure of the
air inside. This is because the interior surface temperature decreases, caused by decreased
air temperature on the outside.
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Sweat on the inside of the building element can be avoided if the inequality is
satisfied:
si r
T f
T
Si
= temperature on the inside of exterior wall
r
= dew temperature and the temperature at which the actual vapor pressure of
water becomes equal to the saturation pressure
( ; )
r i i
f T
Ti = indoor air temperature
i = indoor air humidity
I = outside air temperature
Indoor climate parameters:
20
o
T C
i
- According to SR 1907-2
% 60
1
- According to table VI of normative C107/3
2
8 / W m K
i
- According to normative C 107/3
Outdoor climate parameters:
T
e
= -18
0
C
e
= 85%
2
24 /
e
W m K
Determining the characteristics of the outer wall structure:
Layer I : Interior plaster M50T (interior plaster)
d=0.015m
=1700kg/m
=0.87W/mK
d
=8.5
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Layer II: BCA masonry
d=0.25m
=825kg/m
=0.34W/mK
d
=4.4
Layer III : thermal insulation
150
/ 044 . 0
/ 25
10 , 0
3
d
u
mK W
m kg
m d
layer IV: exterior plaster M100
5 . 8
/ 87 . 0
/ 700 . 1
015 . 0
3
d
u
mK W
m kg
m d
where
d
- permeability factor in resistance to water vapor
- thermal conductivity for calculating j layer
a) Thermal resistances calculus
Thermal resistances of the layers of the elements of construction
R =0.125
si
mk/W - According to normative C 107/3
W k m
d
R
W k m
d
R
W k m
d
R
W k m
d
R
IV
IV
sIV
III
III
sIII
II
II
sII
I
I
sI
/ 0172 . 0
087 . 0
015 . 0
/ 272 . 2
044 . 0
10 . 0
/ 735 . 0
34 . 0
25 . 0
/ 0172 . 0
87 . 0
015 . 0
2
2
2
2
R =0.043
se
mk/W - According to normative C 107/3
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Thermal resistance of the unidirectional element of construction:
W k m R
R R R R
se s si
/ 207 . 3 043 . 0 272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 * 2 125 . 0
2
+ + + +
+ +
b) The temperatures of the exterior wall, setting the saturation pressure
j
T -T k
e
i
T =T - R
k i
R
j=1
where:
T =
k
represents the temperature inside the element of construction of the k surface of
each layer
j
k
R
j=1
permeability amount resistances to heat parts of the layers between the inner
surface and k
R - thermal resistance of the element of construction
0
20
i
T C
2340
si a
p P
C R
R
T T
T T
i
e i
i si
5 . 18 125 . 0
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20
for Pa p C T
ssi si
2132 5 . 18 >
from C107/3 (anexa C)
for:
i
= 60%
C C T
r si
5 . 11 5 . 18 does not produce condensation on the interior surface of
exterior wall
0
si
T ( ) C
12 14 16 18 20 22
0
( )
r
C
4.5 6.4 8.2 10.
1
12.0 13.9
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
3.2.2 Sweat calculus in the inner structure of the exterior wall
Sweat of water vapor in the item of construction will occur in areas where vapor
layer face temperature lower than the dew point. The decrease in the thickness of the
element temperature will lead to a decrease of the saturation pressure. In areas where
partial vapor pressure will be greater than the saturation pressure, vapor will condense.
Pa p
C R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C
R R R R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C R R R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C R R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C R R
R
T T
T T
sse
e
em i
i sse
s
sIV sIII sII sI i
em i
i
s
sIII sII sI i
em i
i
s
sII sI i
em i
i
s
sI i
em i
i
131
49 . 17 ) 043 . 0 207 . 3 (
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20 ) (
131
5 . 17
) 0172 . 0 272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20 ) (
133
3 . 17 ) 272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20 ) (
1195
6 . 9 ) 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20 ) (
2105
3 . 18 ) 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
) 18 ( 20
20 ) (
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + +
+ + +
+ +
+ +
+
+
se
18 p 125
a
o
T C P
e
a) The strength of the exterior wall at the permeability of vapours:
v vI vII vIII vIV
R R R R R + + +
( )
vj j d j
R d M +
8
54 10 M
1
( ) s
diffusion coefficient of water vapor in the air
s m R
s m M d R
s m M d R
s m M d R
s m M d R
v
IV d IV vV
III d III vIII
II d II vII
I d I vI
/ 10 17 . 983
/ 10 885 . 6 10 54 5 . 8 015 . 0 ) (
/ 10 910 10 54 150 05 . 0 ) (
/ 10 4 . 59 10 54 4 . 4 25 . 0 ) (
/ 10 885 . 6 10 54 5 . 8 015 . 0 ) (
8
8 8
8 8
8 8
8 8
b) Calculation of partial pressure of water vapor in the outside and inside air
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
100
i si
vi
p
p
100
e se
ve
p
p
i
;
e
= relative air humidity inside respectively outside
i
= 60%;
e
= 85%
Pa p
Pa p
ve
vi
25 . 106
100
125 85
1218
100
2030 60
3.2.3 Verification of lack of water accumulation in the structure elements of construction
from one year to another
0
20
i
T +
60%
i
0 0
18 8, 5
e em
T T + (Iasi climate area III)
85%
e
We remake the
k
T
calculus inside the construction elements, to restore the saturation
pressure of water vapor.
( 1; )
1
k
i em
k i s j j
j
T T
T T R
R
C R
R
T T
T T
P p C T
si
em i
i
si i
+
5 . 19 125 . 0
207 . 3
5 . 8 20
20
2340 20
1
0
Pa p
C R R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
s
sII sI i
em i
i
s
sI si
em i
i
ssi
1914
8 . 16 ) 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
1324 . 2
5 . 8 20
20 ) (
2268
49 . 19 ) 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
5 . 8 20
20 ) (
2268
2
2
1
1
+ +
+ +
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Pa p
C
R R R R R
R
T T
T T
Pa p
C R R R R
R
T T
T T
s
sIV sIII sII sI i
em i
i
s
sIII sII sI i
em i
i
1117
64 . 8
) 0172 . 0 272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
1324 . 2
5 . 8 20
20 ) (
1125
7 . 8 ) 272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0 (
207 . 3
5 . 8 20
20 ) (
4
4
3
3
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + +
+ + +
Pa p R R
R
T T
T T
sse e
em i
i se
1125 7 . 8 ) ( > +
0
8.5 1119
em sem a
T C p P
We calculate the corrected values of the saturation pressure:
for area III
2
142
s
scorectat s
R
p p
R
1
+
1
]
Pa
R
R R R
p p
Pa
R
R R
p p
Pa
R
R
p p
sII sI si
s cor s
sI si
s cor s
si
ssi ssicor
62 . 1924
207 . 3
735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0
142 1914 142
62 . 2278
207 . 3
0172 . 0 125 . 0
142 2268 142
21 . 2268
207 . 3
125 . 0
142 2268 142
2 2
2 2
2 2
1 1
2 2
,
_
+ +
+
1
]
1
+ +
+
,
_
+
+
1
]
1
+
+
,
_
+
1
]
1
+
Pa
R
R R R R
p p
sIV sII sI si
s cor s
92 . 1347
207 . 3
272 . 2 735 . 0 0172 . 0 125 . 0
142 1211 142
2 2
3 3
,
_
+ + +
+
1
]
1
+ + +
+
Pa
x
R
R R R R R
p p
sV sIV sII sI si
s cor s
01 . 1351
207 . 3
272 . 2 734 . 0 0172 . 0 2 125 . 0
142 1203 142
2 2
4 4
,
_
+ + +
+
1
]
1
+ + + +
+
Pa
R
R R
p p
se si
or s or s
21 . 1263
207 . 3
043 . 0 207 . 3
142 1125 142
2 2
sec sec
,
_
+
1
]
1
+
For area III:
Pa p p
sen mcor se
1261 142 1119 142
3
+ +
Stage 3: Hygrothermal design
___________________________________________________________________
Você também pode gostar
- Discrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsNo EverandDiscrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Insulation ComputationDocumento14 páginasThermal Insulation ComputationBogdan BîngăAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter. Higrothermal Calculation of The BuildingDocumento29 páginasChapter. Higrothermal Calculation of The BuildingChirilianu CosminAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Constructio Ns Project IIDocumento37 páginasCivil Constructio Ns Project IIVennus OvidiuAinda não há avaliações
- Loads Evaluation: TerraceDocumento9 páginasLoads Evaluation: TerracemayanekitaAinda não há avaliações
- RC Deflection & CrackingDocumento27 páginasRC Deflection & CrackingGerald Maginga50% (2)
- Hygrothermal AssessmentDocumento9 páginasHygrothermal AssessmentGeorge LazarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Documento87 páginasChapitre 18 Portiques BA-Exemple Calcul-Corr09Mohamed Bouzidi FSAinda não há avaliações
- Design of MinaretDocumento19 páginasDesign of MinaretJanasheen Bond80% (5)
- Appendix RW - Design of R.C. Cantilever Retaining Wall: Louis Berger in Association With SABA Engineering PLCDocumento12 páginasAppendix RW - Design of R.C. Cantilever Retaining Wall: Louis Berger in Association With SABA Engineering PLCHundeejireenyaAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 11Documento10 páginasProblem Set 11mmccomas08Ainda não há avaliações
- Paper - Determination of Thermal Transmittance of InsulatedDocumento8 páginasPaper - Determination of Thermal Transmittance of Insulatedphillip jinAinda não há avaliações
- Wall Calculation Example EC2Documento15 páginasWall Calculation Example EC2Kristjan Igasta88% (8)
- Shear Wall Design TheoryDocumento15 páginasShear Wall Design TheoryKarish_J89100% (2)
- Structural Steel Beam Calculations For Loft Conversion ExampleDocumento4 páginasStructural Steel Beam Calculations For Loft Conversion ExamplePetar ValevAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Constructions II Project: Student: Mirodone Madalin Group: 3308Documento44 páginasCivil Constructions II Project: Student: Mirodone Madalin Group: 3308Vennus OvidiuAinda não há avaliações
- Bobaru MariusDocumento40 páginasBobaru MariusElena Iulia CucoleaAinda não há avaliações
- Punching of Flat Slabs: Design Example: Fib Model Code 2010Documento13 páginasPunching of Flat Slabs: Design Example: Fib Model Code 2010Bhagirath JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Example 1 Approximate Analysis of Frames Subjected To Lateral LoadsDocumento10 páginasChapter 2 Example 1 Approximate Analysis of Frames Subjected To Lateral LoadsMesfin Derbew100% (1)
- Fin Glass 6Documento6 páginasFin Glass 6EIWAA100% (1)
- 507 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 3Documento11 páginas507 39 Solutions Instructor Manual Chapter 3Arun GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Redi Rock Verification Manual enDocumento23 páginasRedi Rock Verification Manual enAyman ElsayedAinda não há avaliações
- Paper Steel Geodesic Dome PDFDocumento6 páginasPaper Steel Geodesic Dome PDFAngga WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: ConfidentialDocumento8 páginasUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: ConfidentialcalliepearsonAinda não há avaliações
- Contribution To The Modelling of The Structural Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Walls Under ISO Fire ExposureDocumento17 páginasContribution To The Modelling of The Structural Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Walls Under ISO Fire ExposureFarjallah Al-AssãadAinda não há avaliações
- A Theoretical and Numerical Evaluation On The Ductility of Reinforced Concrete Flexural Members Due To The Effects of Varying Structural ParametersDocumento16 páginasA Theoretical and Numerical Evaluation On The Ductility of Reinforced Concrete Flexural Members Due To The Effects of Varying Structural ParametersWai FaiAinda não há avaliações
- For The Dwelling Building Shown Below, Calculate The Anual Necessary Thermal Energy andDocumento15 páginasFor The Dwelling Building Shown Below, Calculate The Anual Necessary Thermal Energy andMoldovan Adrian NeluAinda não há avaliações
- Control of Cracking in Mass Concrete Structures - EM34Documento82 páginasControl of Cracking in Mass Concrete Structures - EM34mivos4100% (1)
- Annex B - Checklist On Impact Assessment ReportDocumento3 páginasAnnex B - Checklist On Impact Assessment ReportmgmgnyeinzawAinda não há avaliações
- Steel Structure AssignmentDocumento11 páginasSteel Structure AssignmentGetaneh HailuAinda não há avaliações
- How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2 - (3) SlabsDocumento8 páginasHow To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2 - (3) Slabsbobbytirona566100% (1)
- U Values Walls OfficeDocumento2 páginasU Values Walls Officeapi-227748796Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary of Equations and Tables - En1992-2 Eurocode 2 - Design of Concrete Structures 2C Part 2 - Concrete BridgesDocumento21 páginasSummary of Equations and Tables - En1992-2 Eurocode 2 - Design of Concrete Structures 2C Part 2 - Concrete BridgesgoawaynowAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Water TanksDocumento71 páginasDesign of Reinforced Concrete Water Tanksace1205100% (3)
- PP AMAS2021Documento7 páginasPP AMAS2021lethao2011Ainda não há avaliações
- Eurocode 2 - BeamsDocumento8 páginasEurocode 2 - Beamsmm507Ainda não há avaliações
- Heat Load Calculation ExampleDocumento5 páginasHeat Load Calculation ExampleJoshua RanjithAinda não há avaliações
- Thermotechnical Calculation of Enclosing Structures of A Standard Type Residential BuildingDocumento8 páginasThermotechnical Calculation of Enclosing Structures of A Standard Type Residential BuildingGogyAinda não há avaliações
- Crack Width Check BS5400 4Documento5 páginasCrack Width Check BS5400 4saravanan4286100% (1)
- Wall DesignDocumento13 páginasWall DesignAnantPawarAinda não há avaliações
- Explanatory Notes For RC Concrete ProjectDocumento32 páginasExplanatory Notes For RC Concrete ProjectJean pierre ManriqueAinda não há avaliações
- UK Afternoon WorkshopDocumento50 páginasUK Afternoon WorkshopanhkhoacgAinda não há avaliações
- Estimation AllDocumento64 páginasEstimation AllAso GardiAinda não há avaliações
- Gravity Wall Verification Manual enDocumento26 páginasGravity Wall Verification Manual enradem3Ainda não há avaliações
- Example 10: Design of Walls of A Building With Cross Waij System of Load-Bearing Construction A 3 Storeyed Building As Shown in Fig. E-38 HasDocumento7 páginasExample 10: Design of Walls of A Building With Cross Waij System of Load-Bearing Construction A 3 Storeyed Building As Shown in Fig. E-38 HasSajidAliKhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento8 páginasChapter 4mwaseem2011Ainda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Behavior of Organic Matrix Composites: Effect of Thermo-oxidative AgeingNo EverandMechanical Behavior of Organic Matrix Composites: Effect of Thermo-oxidative AgeingAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo-hydrodynamic Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsNo EverandThermo-hydrodynamic Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Engineering Structures According to the Eurocodes: Inspection and MaintenanceNo EverandCivil Engineering Structures According to the Eurocodes: Inspection and MaintenanceAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsNo EverandMathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsRoderick MelnikAinda não há avaliações
- Process Intensification for Sustainable Energy ConversionNo EverandProcess Intensification for Sustainable Energy ConversionAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Embedded Controllers: Design and Troubleshooting with the Motorola 68HC11No EverandPractical Embedded Controllers: Design and Troubleshooting with the Motorola 68HC11Ainda não há avaliações
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationNo EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertAinda não há avaliações
- Wind Turbines in Cold Climates: Icing Impacts and Mitigation SystemsNo EverandWind Turbines in Cold Climates: Icing Impacts and Mitigation SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- Jar Test Result ExcelDocumento11 páginasJar Test Result ExcelMuhammad NuruddinAinda não há avaliações
- 440.11-22 PreviewDocumento10 páginas440.11-22 Previewjcunha4740Ainda não há avaliações
- Callister - Concept Check AnswersDocumento58 páginasCallister - Concept Check AnswersGöksun Güven75% (4)
- Hand Portable ExtinguishersDocumento20 páginasHand Portable ExtinguishersJun AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Astm b86.5503 ZamakDocumento7 páginasAstm b86.5503 ZamakJosé SierraAinda não há avaliações
- Paint Chip AnalysisDocumento11 páginasPaint Chip AnalysisIlyana ShalahudinAinda não há avaliações
- Aluminum Bronze, UNS C61300: Component Wt. %Documento3 páginasAluminum Bronze, UNS C61300: Component Wt. %AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Studies For Rock CuttingDocumento11 páginasLaboratory Studies For Rock CuttingAjyant DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- Internship Report For Compounding Department at General Tyre & Rubber Company of PakistanDocumento22 páginasInternship Report For Compounding Department at General Tyre & Rubber Company of PakistanZeeshan Zahid0% (1)
- Nomex Essential: Extreme Protection ColorDocumento2 páginasNomex Essential: Extreme Protection ColorRobert AndrewAinda não há avaliações
- The Gibbs Phase Rule RevisitedDocumento3 páginasThe Gibbs Phase Rule Revisitedleizar_death640% (1)
- Aluminum Crust BreakerDocumento8 páginasAluminum Crust BreakersenamotoAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Workshop - Question Paper CompilationDocumento197 páginasChem Workshop - Question Paper Compilations1672snehil6353Ainda não há avaliações
- Fracture of Ceramics and Glasses: PhysDocumento43 páginasFracture of Ceramics and Glasses: PhysMridanku Shekhar PramanickAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 3Documento11 páginasChapter 1 3Selvin A Crisostomo63% (8)
- Asme Section IxDocumento71 páginasAsme Section Ixranjitkumar1977100% (2)
- Cost Effective Integrated Gas Plant Design Sulfinol MDocumento2 páginasCost Effective Integrated Gas Plant Design Sulfinol Mamirho3ein100% (1)
- Co Ordination CompoundsDocumento9 páginasCo Ordination CompoundsSanket PatilAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Chem Prelim Paper 2Documento28 páginasH2 Chem Prelim Paper 2chuasioklengAinda não há avaliações
- Set 1Documento3 páginasSet 1Niraj ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Painting Procedure: Total Solutions Integrated ServicesDocumento9 páginasPainting Procedure: Total Solutions Integrated ServicesLi LiuAinda não há avaliações
- Ashtamudilake JournalpaperDocumento9 páginasAshtamudilake JournalpaperAnashwara PillaiAinda não há avaliações
- UOP-Mercury-Removal-From-Natural-Gas-and-Liquid-Streams-Tech-Paper 2 PDFDocumento9 páginasUOP-Mercury-Removal-From-Natural-Gas-and-Liquid-Streams-Tech-Paper 2 PDFPedraza Velandia JhonAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Engineering Project Topics and MaterialsDocumento5 páginasCivil Engineering Project Topics and MaterialsCivil Engineering projectAinda não há avaliações
- 1 2 3 Literature Review 4 Experiment Objective 5 Methodology 6 Results 7 Discussions 8 Conclusion & Recommendations 9 References 10 AppendicesDocumento16 páginas1 2 3 Literature Review 4 Experiment Objective 5 Methodology 6 Results 7 Discussions 8 Conclusion & Recommendations 9 References 10 Appendicesmonkeystar12100% (3)
- Measurement of Thin Chromium Coatings by Spot Test: Standard Guide ForDocumento3 páginasMeasurement of Thin Chromium Coatings by Spot Test: Standard Guide ForTuanbk NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Ipcc Waste ModelDocumento98 páginasIpcc Waste ModelJayson VillezaAinda não há avaliações
- Tool Wear Mechanisms in The Machining of Steels and Stainless SteelsDocumento13 páginasTool Wear Mechanisms in The Machining of Steels and Stainless SteelsCarlitosBenalcázarAinda não há avaliações
- Moles and Equations Worksheet and AnswersDocumento3 páginasMoles and Equations Worksheet and AnswersMahumAinda não há avaliações
- Dental Base Resins 2Documento27 páginasDental Base Resins 2Nurzafirah IliasAinda não há avaliações