Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Or Unit 3
Enviado por
raniTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Or Unit 3
Enviado por
raniDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
UNIT-III: SIMULATION
1. Define simulation Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real world process or system over time. It is a numerical technique for conducting experiments that involve certain types of mathematical and system over extended period of time. 2. What are the areas of applications of simulation 1. Manufacturing systems 2. Public and transportation systems 3. Restaurant and entertainment systems 4. Computer system performance. 3. Define a system and system environment in simulation A system is defined as the collection of objects / ideas which permits identification as a whole coherent logical functional unit. A system is often affected by changes occurring outside the system. Such changes are said to occur in the system environment. 4. .What are the components of a system? The components of a system are (i) Entity (ii) Attribute (iii) Activity (iv) State (v) Variables (vi) Event 5. Define the following (i) Entity (ii) Attribute (iii) Activity (iv) State 6. Define (i) Event (ii) Variables: Variables are those that take different values (i) Event: An event is defined as an instantaneous occurrence that may change the state of the system. (ii) Variables: variables are those that take different values at different times. 7. What are the types of simulation system? System can be categorized as (i) (ii) Discrete system Continuous system. Events Arrival; Departure State variables Number of busy tellers; Number of customer waiting.
8. Give an example of a system and its components System Entities Attributes Activities Banking Customers Checking account balance Making deposits
8. When to use simulation The reasons for selecting simulation other than the known mathematical technique are: It is impossible to develop a mathematical solution Actual observation of a system may be too expensive Simulation may be the only method available because it is difficult to observe the actual environment (d) Actual operation and observation of a real system may be too disruptive. 9. Define discrete system and continuous system with examples Discrete system is one in which the state variables change only as a discrete set of points in time. Example: In a bank, the number of customers changes only when the service is completed for a customer Continuous system is one in which the state variables change continuously over time. 10. What are the types of simulation models? The simulation models are classified into (a) (b) Based on the representation (i) Physical model (ii) Schematic model (iii) Symbolic model Based on timing nature (i) Static (ii) dynamic (a) (b) (c)
Based on the input nature (i) Deterministic nature (ii) Stochastic nature 11.Define Static model and Dynamic model A Static simulation model represents a system at a particular point in time. It does not change with time. A dynamic simulation model represents a system at a particular point in time. It does change with time.
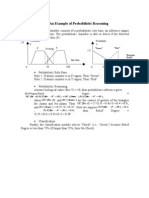
13 What is a deterministic and stochastic simulation model These models have a known set of inputs which will result in a unique set of outputs. This model has one or more random variables at inputs. Since the inputs are random, the outputs lead to random outputs. 14. Explain Monte-Carlo simulation This method is generally used to solve problems which cannot be adequately represented by the mathematical models, or where the problems are too expensive for experimental solutions. This model involves random sampling from a known probability distribution and yields a solution which will be very close to the optimal. 15. Define random number. Random number is a sequence of numbers whose probability of occurrence is the same as that of any other number in the sequence. The sequence of numbers must have two important statistical properties (i.e.) uniformity and independence.
16. Define pseudo random number. Arithmetic operations are used to compute a sequence of random numbers from a recursive equation. The random numbers generated from recursive algorithm is not a true random number. These numbers are called a pseudo (false) random numbers and hence these numbers should be tested for randomness and uniqueness. 17. What are the techniques used for generating random numbers? (i) Mid square method (ii) Mid Product method (iii) constant multiple methods (iv) Mixed congruent method (v) Additives congruent method 18. What are advantageous of simulation technique? 1. Simulation models are relatively free from complicated mathematics and thus can be easily understand by even a non technical managers or semi-skilled operating staff. 2. Simulation models are completely flexible and can be easily modified to accommodate the changing environment of the real system. Computer simulation involves large calculations in to a few minutes of computer running time and thus it reduces the simulation time period. 19. What are the limitations of simulation technique? 1. Simulation results are not optimal. Simulation results are only reliable approximations subject to statistical errors. 2. Since simulation involves repetition of the experiment, it is a time consuming task when manually done. 3. Quantification of variables are not possible in the behavior of the system. 20. Define the model of a system. A model is defined as the actual representation of a system for the purpose of studying the system.
Você também pode gostar
- Applications of StackDocumento7 páginasApplications of StackraniAinda não há avaliações
- AgentsDocumento31 páginasAgentsraniAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Geometric Objects and Transformations - IDocumento67 páginasGeometric Objects and Transformations - IraniAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- CO - Quiz 2Documento3 páginasCO - Quiz 2raniAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Ai SyllabusDocumento2 páginasAi SyllabusraniAinda não há avaliações
- XmlqnsDocumento1 páginaXmlqnsraniAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Q-1. What Are The New Features Introduced in HTML5? AnswerDocumento47 páginasQ-1. What Are The New Features Introduced in HTML5? AnswerraniAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- KannadaDocumento6 páginasKannadaraniAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- AI QZ With AnswerDocumento2 páginasAI QZ With AnswerraniAinda não há avaliações
- Water - Cool PicDocumento1 páginaWater - Cool PicraniAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Map India PoliticalDocumento1 páginaMap India PoliticalraniAinda não há avaliações
- Dbms QnsDocumento1 páginaDbms QnsraniAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- CSE Big Data ReportDocumento15 páginasCSE Big Data ReportMohit SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Europe Outline MapDocumento1 páginaEurope Outline MapraniAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Water FallsDocumento1 páginaWater FallsraniAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- BDA Streaming QuestionsDocumento1 páginaBDA Streaming QuestionsraniAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- PHPDocumento43 páginasPHPraniAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Sample Question in Big Data IntroDocumento1 páginaSample Question in Big Data IntroraniAinda não há avaliações
- Viva For 7th Sem Web LabDocumento22 páginasViva For 7th Sem Web LabDhanush V AacharAinda não há avaliações
- JsDocumento29 páginasJsraniAinda não há avaliações
- IBM: in The Next 5 Years Computers Will Learn, Mimic The Human SensesDocumento9 páginasIBM: in The Next 5 Years Computers Will Learn, Mimic The Human SensesraniAinda não há avaliações
- AI QuizDocumento23 páginasAI Quizrani100% (1)
- HCIDocumento64 páginasHCIraniAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- HolidaysDocumento1 páginaHolidaysraniAinda não há avaliações
- Image of Red FortDocumento1 páginaImage of Red FortraniAinda não há avaliações
- Pictures of Medieval PeriodDocumento1 páginaPictures of Medieval PeriodraniAinda não há avaliações
- UncertaintyDocumento1 páginaUncertaintyAbdul Hafeez KhanAinda não há avaliações
- AI 2 MarksDocumento14 páginasAI 2 MarksraniAinda não há avaliações
- Ai BioDocumento1 páginaAi BioArpit GargAinda não há avaliações
- A) Write A C Program To Find The Sum of Individual Digits of A PositiveDocumento1 páginaA) Write A C Program To Find The Sum of Individual Digits of A PositiveraniAinda não há avaliações
- Rock Mechanics ASSGN 2Documento7 páginasRock Mechanics ASSGN 2ankeshAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Default passwords for 3COM network devicesDocumento42 páginasDefault passwords for 3COM network devicesJamey ParkerAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile Virtual Reality ServicesDocumento11 páginasMobile Virtual Reality ServicesRahul MaraviAinda não há avaliações
- MS 2400 1 2010 P-TocDocumento7 páginasMS 2400 1 2010 P-Tocfauzirohani0% (1)
- Ias Public Administration Mains Test 1 Vision IasDocumento2 páginasIas Public Administration Mains Test 1 Vision IasM Darshan UrsAinda não há avaliações
- Bip 0072-2014 PDFDocumento94 páginasBip 0072-2014 PDFgrAinda não há avaliações
- Altera 5M1270ZF256C5N DatasheetDocumento30 páginasAltera 5M1270ZF256C5N DatasheetIonut Daniel FigherAinda não há avaliações
- Report on Industrial Visit to ACC Limited Chaibasa Cement WorksDocumento8 páginasReport on Industrial Visit to ACC Limited Chaibasa Cement WorksRohit Vishal PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Essentials For A Good Night'S Sleep: Mattresses, Duvets and PillowsDocumento4 páginasEssentials For A Good Night'S Sleep: Mattresses, Duvets and PillowselizondomaruAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation Framework GuideDocumento126 páginasCalculation Framework GuidedeeptiakkaAinda não há avaliações
- Valvulas Solenoides - Parker - SkinnerDocumento148 páginasValvulas Solenoides - Parker - SkinneraspoiaspoiAinda não há avaliações
- Training Estimator by VladarDocumento10 páginasTraining Estimator by VladarMohamad SyukhairiAinda não há avaliações
- Document 1Documento14 páginasDocument 1Lê Quyên VõAinda não há avaliações
- 32LS3400 KoreaDocumento60 páginas32LS3400 KoreaNightin VargheseAinda não há avaliações
- Implementasi Pembelajaran Pendidikan Jasmani Dan Olahraga Kesehatan Dalam Perspektif Standar Nasional Pendidikan Di SMP Negeri 46 PalembangDocumento20 páginasImplementasi Pembelajaran Pendidikan Jasmani Dan Olahraga Kesehatan Dalam Perspektif Standar Nasional Pendidikan Di SMP Negeri 46 PalembangDionisius Marcel GintingAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To CPHQDocumento24 páginasIntroduction To CPHQmonir61Ainda não há avaliações
- CERAWeek 2012Documento28 páginasCERAWeek 2012kentselveAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Calculatio For Design of Structures and Foundations For Vibrating MachinesDocumento6 páginasSample Calculatio For Design of Structures and Foundations For Vibrating MachinesRay LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabDocumento6 páginasCalculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabДејан ПејовскиAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Based Task Dfc2043Documento3 páginasProblem Based Task Dfc2043player6675100% (1)
- Kohler Tt1584PIMDocumento20 páginasKohler Tt1584PIMJohn ElyAinda não há avaliações
- 1017 Daa Aa Aa Duplex Steam Pump PDFDocumento3 páginas1017 Daa Aa Aa Duplex Steam Pump PDFBelesica Victor ValentinAinda não há avaliações
- MD 5 SumDocumento47 páginasMD 5 SumBabay Si TagamaAinda não há avaliações
- ME116P Weeks 1-4Documento243 páginasME116P Weeks 1-4Ska dooshAinda não há avaliações
- MagazineDocumento34 páginasMagazineAhmed Khalil100% (1)
- Problems - SPCDocumento11 páginasProblems - SPCAshish viswanath prakashAinda não há avaliações
- Elizabeth Hokanson - Resume - DB EditDocumento2 páginasElizabeth Hokanson - Resume - DB EditDouglAinda não há avaliações
- 2715 Top BracingDocumento41 páginas2715 Top BracingValentin-Madalin Voica100% (2)
- C3Documento14 páginasC3mee myyAinda não há avaliações
- Bhatia CPD 20001Documento1 páginaBhatia CPD 20001bilalaimsAinda não há avaliações
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNo EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveAinda não há avaliações
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldNo EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (54)
- Who's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesNo EverandWho's Afraid of AI?: Fear and Promise in the Age of Thinking MachinesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAinda não há avaliações