Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Belajar Pemrograman Android by IM2
Enviado por
cocy_imyutDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Belajar Pemrograman Android by IM2
Enviado por
cocy_imyutDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
I.
What is Android Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. The Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language, since 2008. Now android is the best mobile platform application powered by Google, http: //developer.android.com/.
II. Features a. Application framework components enabling reuse and replacement of
b. Dalvik virtual machine optimized for mobile devices c. Integrated browser based on the open source WebKit engine d. Optimized graphics powered by a custom 2D graphics library; 3D graphics based on the OpenGL ES 1.0 specification (hardware acceleration optional) e. SQLite for structured data storage f. Media support for common audio, video, and still image formats (MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, PNG, GIF)
g. GSM Telephony (hardware dependent)
Android Training Session
Page 1
h. Bluetooth, EDGE, 3G, and WiFi (hardware dependent) i. j. Camera, GPS, compass, and accelerometer (hardware dependent) Rich development environment including a device emulator, tools for debugging, memory and performance profiling, and a plugin for the Eclipse IDE
III. System Architecture
Picture 1: System Architecture
Android Training Session
Page 2
IV. Other Information a. Android will ship with a set of core applications including an email client, SMS program, calendar, maps, browser, contacts, and others. All applications are written using the Java programming language. b. By providing an open development platform, Android offers developers the ability to build extremely rich and innovative applications. Developers are free to take advantage of the device hardware, access location information, run background services, set alarms, add notifications to the status bar, and much, much more. c. Android includes a set of C/C++ libraries used by various components of the Android system. These capabilities are exposed to developers through the Android application framework. Some of the core libraries such as system C library, Media library, 3D library etc.
V. Getting Started with Android a. Eclipse installed as GUI editor android http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/, Eclipse Packages, Eclipse Classic 3.4.2 / Galileo 3.5 platform, go to Classic, GanyMede
b. Android SDK installed as emulator, basic platform and environment android style, go to http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html c. Eclipse Update Manager install plugins for Android Development Tools (ADT) go to link https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/eclipse/, Eclipse Help Software Updates, Available Software Tab, Add Site d. Open Eclipse, Window Preferences. Configure Android path installation from folder android SDK downloaded earlier. https://dl-ssl.google.com/android/repository/repository.xml
Android Training Session Page 3
VI. Life Cycles Android
Picture 2: Life Cycles
VII. Subject Material Android Training Session
A. Beginner Level; (2 sessions) 1. What is Android 2. Features, System Architecture, Life Cycle Application 3. Getting Started, Requirement Development (ECLIPSE, AVD, ADT, SDK) 4. Create First App (HelloWorld), File Project Structure 5. Create *.apk Installer File Project, Install (command shell) 6. Simple ListView (Object Android XML), Simple Activity, Intent Android Training Session Page 4
B. Intermediate Level; (3 sessions) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Customize ListView, Thread, Sync Method ProgressBar ImageLoader ListView, Simple HTTP Connection Menu, Create Dialog, Icon, Click Listener, get default R icon Simple TabWidget, get content URI list embed, admobView Simple Phone Sim Card Activity, Simple Database SQL Lite WebView, AutoCompleteTextView, CheckBoxView, GalleryView (Object View) Customize Database SQL Lite, RSS Parsing, Simple MusicPlayer SharedPreferences, Simple JSON, using API google
C. Advanced Level; (2 sessions) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. SMS, Receive SMS, EMAIL other Phone Activities Customize Database SQL Lite, SharedPreferences Access Device (Bluetooth, WIFI, GPS), VideoView Project Advanced MapActivities, GPS access Project Advanced, Mobile News RSS Reader Project Advanced, Translator Powered by Google Project Advanced, Twitter, Facebook API integrated Project Advanced Membership Client Server Side, Transaction Case
Android Training Session
Page 5
VIII.
First Application (Eclipse GUI opened)
A. Update Environment Site SDK, plug-in ADT (Android Developer Tool) 1. Update Site plug-in ADT (Help -> Software Updates)
Picture 3: Update ADT
Picture 4: Install - Update ADT
Android Training Session
Page 6
2. Update SDK & AVD Manager (Window -> Preferences)
Picture 5: Install SDK
3. Update SDK & AVD Manager (Window -> Android SDK and AVD Manager)
Picture 6: SDK Manager
Android Training Session
Page 7
Picture 7: Update SDK Manager
4. Create AVD Emulator
Picture 8: Create AVD Android Training Session Page 8
B. Create The First App -> Helloworld
Picture 9: Create First Project
C. Project Variable Input a. b. c. d. e. f. Project Name: HelloWorld Build Target: Android 2.1 Application Name: HelloWorld Package Name: im2.org.sample.main Create Activity: HelloActivity Min SDK Version: 7
Android Training Session
Page 9
Picture 10: Script HelloActivity
D. Run As Android Application
Picture 11: Run Project in Emulator
Android Training Session
Page 10
Picture 12: Display Run Project in Emulator
E. Project Structure
Picture 13: Project Structure
Android Training Session
Page 11
Project Name: HelloWorld Src Gen Asset Res->drawable Res->layout Res->string AndroidManifest.xml => Source Script => Auto-generate Id Unique Variable Local => Storage File (movie, sound etc) => Storage picture layout => XML layout => definition variable global
F. AndroidManifest XML
Picture 14: AndroidManifest XML Android Training Session Page 12
G. Uses-Permission AndroidManifest.xml Permission. http://developer.android.com/reference/android/Manifest.permission.html
Picture 15: Uses-Permission
H. Res -> Layout
Picture 16: Layout Main.xml
Android Training Session
Page 13
I. Res -> Drawable (lpi, mpi, hpi), gen R.java
Picture 17: Drawable R.java
J. Src (Code Behind) HelloActivity.java
Picture 18: HelloActivity.java Android Training Session Page 14
IX. Next First Project (Two Activities Combined)
a. Create layout login.xml (right click in folder res-layout)
Picture 19: Create Layout
Picture 20: Create Layout login.xml
Android Training Session
Page 15
Picture 21: login.xml script
Picture 22: login.xml graphical layout
Android Training Session
Page 16
Picture 23: main.xml script
Picture 24: main.xml graphical layout Android Training Session Page 17
Picture 23: HelloActivity (main.xml)
Android Training Session
Page 18
Picture 24: LoginActivity (1)
Android Training Session
Page 19
Picture 25: LoginActivity (2)
Android Training Session
Page 20
Picture 26: AndroidManifest.XML
Picture 27: Running HelloActivity Android Training Session Page 21
Picture 28: Running LoginActivity
Guidance: http://developer.android.com/resources/tutorials/hello-world.html
Summary: 1. Android Platform Description 2. Installation GUI & Editor 3. Create First Android App 4. Structure Android Project 5. Improvement First Android App
6.
Developer Guidance
Android Training Session
Page 22
Você também pode gostar
- Daftar Kursus Udemy For Government Subtitle Bahasa Indonesia PDFDocumento15 páginasDaftar Kursus Udemy For Government Subtitle Bahasa Indonesia PDFcocy_imyutAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Kursus Udemy For Government Subtitle Bahasa IndonesiaDocumento15 páginasDaftar Kursus Udemy For Government Subtitle Bahasa Indonesiacocy_imyutAinda não há avaliações
- Adwise 4.5 REST API DocumentationDocumento127 páginasAdwise 4.5 REST API Documentationcocy_imyutAinda não há avaliações
- Claims Administration ServicesDocumento4 páginasClaims Administration Servicescocy_imyutAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- XML and Web Technologies For Data Sciences With R-Springer-Verlag New York (2014)Documento677 páginasXML and Web Technologies For Data Sciences With R-Springer-Verlag New York (2014)Carlos Barco100% (1)
- Jira GuideDocumento104 páginasJira Guideioana_nekAinda não há avaliações
- Tascam TD 4000 Fatal - Error - HintDocumento3 páginasTascam TD 4000 Fatal - Error - HintDias Adr100% (1)
- Manual Pic 18F2550Documento430 páginasManual Pic 18F2550Pancho NuncioAinda não há avaliações
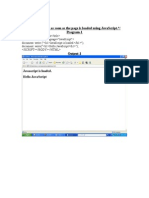
- Display Hello As Soon As The Page Is Loaded Using Javascript. / Program-1Documento25 páginasDisplay Hello As Soon As The Page Is Loaded Using Javascript. / Program-1arun1974Ainda não há avaliações
- Java Program For Banking Management System: Learn MoreDocumento8 páginasJava Program For Banking Management System: Learn MorevibinAinda não há avaliações
- Modbus Il NT, Ic NT, Id LiteDocumento30 páginasModbus Il NT, Ic NT, Id LiteGeorge BarsoumAinda não há avaliações
- Hardwired Control UnitDocumento12 páginasHardwired Control UnitMuzaFar100% (1)
- Lecture - 15 Dynamic Interconnection NetworksDocumento13 páginasLecture - 15 Dynamic Interconnection NetworksmohsinmanzoorAinda não há avaliações
- Embedding Assembly Instructions Inside C-Source Code: Technical Note TN-18Documento3 páginasEmbedding Assembly Instructions Inside C-Source Code: Technical Note TN-18Mothaiba TacungmuaAinda não há avaliações
- Sfha Notes 51sp1rp2 LinDocumento122 páginasSfha Notes 51sp1rp2 LinCaSimiro CarrinoAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering: Lab Manual in Computer Programming LabDocumento49 páginasDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering: Lab Manual in Computer Programming Labmadhu2270Ainda não há avaliações
- Software Notes2018Documento159 páginasSoftware Notes2018AshleyAinda não há avaliações
- PROGRAM1Documento119 páginasPROGRAM1Rahul DeswalAinda não há avaliações
- ONOS OverviewDocumento10 páginasONOS OverviewDIBYARUPAinda não há avaliações
- Cubic SplineDocumento19 páginasCubic SplineCindy Chris KePochiAinda não há avaliações
- WebsitePanel Integration APIDocumento6 páginasWebsitePanel Integration APIxrootd@yahoo.comAinda não há avaliações
- Delete Last: Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1Documento3 páginasDelete Last: Gursharan Singh Tatla Page No. 1Ghanesh RSAinda não há avaliações
- Data Warehousing - CS614 Power Point Slides Lecture 07Documento9 páginasData Warehousing - CS614 Power Point Slides Lecture 07N GullAinda não há avaliações
- CA2E ToolkitConcepts ENU PDFDocumento277 páginasCA2E ToolkitConcepts ENU PDFsangili2005Ainda não há avaliações
- A Novel Hybrid Classification Model For The Loan Repayment Capability Prediction SystemDocumento6 páginasA Novel Hybrid Classification Model For The Loan Repayment Capability Prediction SystemRahul SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 15 PDFDocumento9 páginasLecture 15 PDFattiqueAinda não há avaliações
- Geh 6703 PDFDocumento1.186 páginasGeh 6703 PDFJair TrzynadlowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Agraph TutorialDocumento22 páginasAgraph TutorialJose Perez GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- 76Documento30 páginas76adeelasghar091Ainda não há avaliações
- ImageJ Manual For Image Processing and Analysis.Documento45 páginasImageJ Manual For Image Processing and Analysis.acr3656100% (1)
- Artificial VisionDocumento5 páginasArtificial VisionLalith KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- 2D Viewing: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRDocumento61 páginas2D Viewing: CGVR - Korea.ac - KRSangeetha BajanthriAinda não há avaliações
- Published By: National Electrical Manufacturers AssociationDocumento21 páginasPublished By: National Electrical Manufacturers AssociationJuhani Mikael KumaraAinda não há avaliações
- 8086 Lab ProgramsDocumento6 páginas8086 Lab ProgramsWalter White0% (1)