Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Simple Present Tense
Enviado por
Meto FirmansyahDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Simple Present Tense
Enviado por
Meto FirmansyahDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
UNIT I SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE / PRESENT TENSE ( Bentuk Sekarang Kebiasaan / kenyataan ) A. Penggunaan 1. Untuk menyatakan peristiwa atau perbuatan yang berlangsung setiap hari / berulang-ulang / kebiasaan sehari-hari (habitual action). 2. Untuk menyatakan suatu kejadian atau peristiwa yang merupakan kebenaran umum (general truth). B. Keterangan waktu Keterangan waktu yang menunjukkan tenses adalah : 1. Adverb of frequency always usually generally habibually normally often frequency - sometimes - occasionally - seldom - rarely - never - ever
2. Every every hour every day every week every month every year every morning every afternoon every evening - every night - every Sunday - every Monday - every Wednesday - every Saturday - every January - every December
3. Once once a day once a week - once a month - once a year
4. Twice 5. three times
6. four time 7. at noon 8. at night 9. at midnight 10. on Sunday, Monday 11. in the morning 12. in the afternoon 13. in the evening
C. Susunan kalimat 1. Positive (+) : Subject + Verb I (s/es) Subject Verb I (KK I) Object I write a story You buy a shirt We clean the room They play tennis He goes to school She gives a present It swims very fast 2. Negative (-) : Subject + do/does + not + verb I Subject I You We They He She It 3. Interrogativ (?) Do/does do/does not Verb I write buy clean play goes gives swims Verb I write buy clean play goes gives swims Object a story a shirt the room tennis to school a present very fast Object a story| a shirt? the room? tennis? to school? a present? very fast?
do not does
Do
Does
Subject I You We They He She It
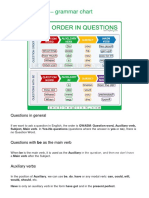
Present Simple Tense
I sing
How do we make the Present Simple Tense?
subject + auxiliary verb + main verb do base There are three important exceptions: 1. For positive sentences, we do not normally use the auxiliary. 2. For the 3rd person singular (he, she, it), we add s to the main verb or es to the auxiliary. 3. For the verb to be, we do not use an auxiliary, even for questions and negatives. Look at these examples with the main verb like: subject I, you, we, they + He, she, it I, you, we, they do He, she, it Do ? Does he, she, it like coffee? does I, you, we, they not like like coffee. coffee? likes not like coffee. coffee. auxiliary verb main verb like coffee.
Look at these examples with the main verb be. Notice that there is no auxiliary: subject I main verb am French. French. French. not old. not old. not old. late? late? late?
+ You, we, they are He, she, it I is am
- You, we, they are He, she, it Am ? Are Is is I you, we, they he, she, it
How do we use the Present Simple Tense?
We use the present simple tense when:
the action is general the action happens all the time, or habitually, in the past, present and future the action is not only happening now the statement is always true John drives a taxi. past present future
It is John's job to drive a taxi. He does it every day. Past, present and future. Look at these examples:
I live in New York. The Moon goes round the Earth. John drives a taxi. He does not drive a bus. We meet every Thursday. We do not work at night. Do you play football?
Note that with the verb to be, we can also use the present simple tense for situations that are not general. We can use the present simple tense to talk about now. Look at these examples of the verb "to be" in the present simple tense - some of them are general, some of them are now: Am I right? Tara is not at home. You are happy. past present future
The situation is now. I am not fat. Why are you so beautiful? Ram is tall. past present future
The situation is general. Past, present and future. This page shows the use of the present simple tense to talk about general events. But note that there are some other uses for the present simple tense, for example in conditional or if sentences, or to talk about the future. You will learn about those later. The simple present tense is used to discuss permanant situations and the frequency of events. To have Short form Other Verbs (to work)
I have he has she has it has
I've he's she's it's
I work He works She works It works you work we work they work Questions Do I work? Short answer Short answer + Yes, I do. No, I don't.
you have you've we have we've they have they've
Statements Statements + I work. I don't work. He works. It works. We work.
He doesn't work. Does he work? Yes, he does. No, he doesn't. It doesn't work. We don't work. Does it work? Do we work? Yes, it does. Yes you do. Yes we do. No, it doesn't. No, you don't. No, we don't. No, they don't.
She works. She doesn't work. Does she work? Yes, she does. No, she doesn't. You work. You don't work. Do you work?
They work. They don't work. Do they work? Yes they do. Regular or permanent situations
When something happens regularly or is a permanent situation we usually use the simple present tense. When using the simple present the verb (with the exception of the auxiliary verbs) remains in the dictionary form (verb + s with he/she/it). Simple Present Timeline For example: Q) "Where do you live?" A) "I live in Germany." Q) "Where does he live?" A) "He lives in Germany." Q) "What do you do?" A) "I'm a teacher." Q) "What does he do?" A) "He's a teacher."
Frequency
The simple present tense is also used to show how often something happens with adverbs of frequency - always, usually, often, sometimes, occasionally, seldom, rarely, never, etc.... And when discussing daily, weekly, monthly etc. routines. For example: "I always get up at 6.00." "I never drink coffee before 12.00." "I work on my website every day." "Every Monday and Thursday I go to the gym." We also use the simple present to ask for and give instructions or to discuss a series of actions. For example: Q) How do I make pancakes?" A) Well, first you take 4 eggs and crack them into a bowl, then you weigh out 4 oz. of flour and sieve it into the eggs. etc. The simple present tense can also be used to discuss future events.
Você também pode gostar
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present TenseDocumento3 páginasSimple Present TenseAbad DuaAinda não há avaliações
- English Tense SystemDocumento26 páginasEnglish Tense SystemJordan CruzAinda não há avaliações
- TensesDocumento50 páginasTensesAndinipuspitasariAinda não há avaliações
- Virtual Class Present TenseDocumento4 páginasVirtual Class Present Tensekunta_kAinda não há avaliações
- PET GRAMMAR POINTSDocumento69 páginasPET GRAMMAR POINTSTatiana ZaraAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple TenseDocumento3 páginasPresent Simple Tenseapi-304729893Ainda não há avaliações
- Present Tense - Reading MaterialDocumento14 páginasPresent Tense - Reading MaterialMs Chikoti Sai Vaishnavi IPEAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present TenseDocumento9 páginasSimple Present TenseTJRAinda não há avaliações
- Progressive TensesDocumento7 páginasProgressive TensesAinin SofiaAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present TenseDocumento5 páginasSimple Present TenseChristine KimAinda não há avaliações
- The simple guide to English verb tensesDocumento30 páginasThe simple guide to English verb tensesBakiyaraj BalasubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple TenseDocumento18 páginasPresent Simple TenseirmafpdAinda não há avaliações
- Active VoiceDocumento13 páginasActive VoiceIan Iswara MadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Tenses English GrammarDocumento50 páginasTenses English GrammarAbhishek TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Documento8 páginasHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Syazwan ZentAinda não há avaliações
- Present TensesPresent SimpleDocumento16 páginasPresent TensesPresent SimpleHarsha SusarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present Tense: From Group 2Documento7 páginasSimple Present Tense: From Group 2Yuliah AsrumAinda não há avaliações
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Documento3 páginasHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?RafitArjeniAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present TenseDocumento33 páginasSimple Present TensenorAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Rules - TenseDocumento13 páginasGrammar Rules - TenseElia Miranda CorralesAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Grammar Guide for Present Tense, Passive Voice & PrepositionsDocumento23 páginasSimple Grammar Guide for Present Tense, Passive Voice & PrepositionsRisa Nanda YusarAinda não há avaliações
- Eng Gram Mod 5 TensesDocumento5 páginasEng Gram Mod 5 Tensesvikas1onlyAinda não há avaliações
- Present Tense PaperDocumento18 páginasPresent Tense PaperMega PuspiytaAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd YearDocumento70 páginas3rd YearAndrea RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- English 2mothDocumento78 páginasEnglish 2mothMichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present Tense Guide - Form, Use & ExamplesDocumento5 páginasSimple Present Tense Guide - Form, Use & ExamplesMaria FerrebuAinda não há avaliações
- GrammarDocumento11 páginasGrammarPedro MarsiAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation EnglishDocumento49 páginasPresentation EnglishribasdAinda não há avaliações
- GrammarDocumento25 páginasGrammarPedro MarsiAinda não há avaliações
- General, Never, Often, Rarely, Sometimes, Usually.: The Simple Present Tense-Affirmative StatementsDocumento12 páginasGeneral, Never, Often, Rarely, Sometimes, Usually.: The Simple Present Tense-Affirmative StatementsMefi-x XtremAinda não há avaliações
- The Simple Present TenseDocumento15 páginasThe Simple Present TenseangelAinda não há avaliações
- Present Tense OverviewDocumento27 páginasPresent Tense OverviewPUSPA A/P MUNIANDY KPM-GuruAinda não há avaliações
- WALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesDocumento56 páginasWALKTHROUGH English Verb TensesLaurentiu IonescuAinda não há avaliações
- All About Simple PresentDocumento6 páginasAll About Simple PresentShameerAinda não há avaliações
- Inglês- aidaDocumento10 páginasInglês- aidamuchuaneosvaldo4Ainda não há avaliações
- The Present Perfect Simple TenseDocumento6 páginasThe Present Perfect Simple Tensealucario92Ainda não há avaliações
- Verbs Must Be Conjugated For Each of These Subject PronounsDocumento1 páginaVerbs Must Be Conjugated For Each of These Subject PronounsAngkol Chris M HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Verbs Must Be Conjugated For Each of These Subject PronounsDocumento1 páginaVerbs Must Be Conjugated For Each of These Subject PronounsAngkol Chris M HassanAinda não há avaliações
- How Do We Make The Simple Past Tense?: Subject + Main VerbDocumento13 páginasHow Do We Make The Simple Past Tense?: Subject + Main VerbGrand OverallAinda não há avaliações
- The 12 Basic English TensesDocumento15 páginasThe 12 Basic English TensesRuben De Jesus Peñaranda MoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of EnglishDocumento10 páginasSummary of Englishfernanda23enfAinda não há avaliações
- Past Simple: Time Adverb Regular Verb Irregular VerbDocumento11 páginasPast Simple: Time Adverb Regular Verb Irregular VerbIngaVilutyteaAinda não há avaliações
- Inglês LeonorDocumento10 páginasInglês Leonormuchuaneosvaldo4Ainda não há avaliações
- Verb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsDocumento43 páginasVerb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsRoxana TudoseAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Hey There 2Documento29 páginasGrammar Hey There 2Kenny Valdez FelipeAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple and Continuous TensesDocumento116 páginasPresent Simple and Continuous TenseskpmadhunAinda não há avaliações
- Bahasa Inggris - Materi Presentasi ''Simple Present + Past Tense''Documento14 páginasBahasa Inggris - Materi Presentasi ''Simple Present + Past Tense''Tyas Rahmaditia100% (3)
- PortafolioDocumento6 páginasPortafolioSunny 95Ainda não há avaliações
- Present SimpleDocumento3 páginasPresent SimpleyepurilaAinda não há avaliações
- Active / Passive Verb FormsDocumento37 páginasActive / Passive Verb FormshusnaAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple: Quick ExamplesDocumento2 páginasPresent Simple: Quick ExamplesIonuţ Dumitru100% (1)
- Leaf StudyDocumento5 páginasLeaf StudyNatália DiasAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Present: Do You Speak English?Documento27 páginasSimple Present: Do You Speak English?Andreea GîleaAinda não há avaliações
- Materi TensesDocumento37 páginasMateri TensesNoviartiAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Guide to English TensesDocumento49 páginasSimple Guide to English TensesHazel GaylanAinda não há avaliações
- Traditiile Romei AnticeDocumento13 páginasTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris-Felicia TambaDocumento11 páginasTugas Bahasa Inggris-Felicia TambaIvon IdaAinda não há avaliações
- AWK and SED Command Examples in LinuxDocumento2 páginasAWK and SED Command Examples in Linuximranpathan22Ainda não há avaliações
- 4th Summative Test Science 6Documento5 páginas4th Summative Test Science 6ANNALIZA FIECASAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento4 páginasUntitledMOHD JEFRI BIN TAJARIAinda não há avaliações
- 001 Gace Early Childhood TestDocumento3 páginas001 Gace Early Childhood Testapi-265795386Ainda não há avaliações
- Opamp TIDocumento5 páginasOpamp TIAmogh Gajaré100% (1)
- Online Music QuizDocumento3 páginasOnline Music QuizGiang VõAinda não há avaliações
- Talon Star Trek Mod v0.2Documento4 páginasTalon Star Trek Mod v0.2EdmundBlackadderIVAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Tools Cutting FluidsDocumento133 páginasMachine Tools Cutting FluidsDamodara MadhukarAinda não há avaliações
- Gamma World Character SheetDocumento1 páginaGamma World Character SheetDr8chAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study, g6Documento62 páginasCase Study, g6julie pearl peliyoAinda não há avaliações
- Goes 300 S Service ManualDocumento188 páginasGoes 300 S Service ManualШурик КамушкинAinda não há avaliações
- Confined Space SafetyDocumento33 páginasConfined Space SafetyEneyo VictorAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Investigation On The Properties of Compressed Earth Blocks Stabilised With A Liquid ChemicalDocumento7 páginasExperimental Investigation On The Properties of Compressed Earth Blocks Stabilised With A Liquid ChemicalDeb Dulal TripuraAinda não há avaliações
- 114 ArDocumento254 páginas114 ArJothishAinda não há avaliações
- BL3B User Manual PDFDocumento142 páginasBL3B User Manual PDFRandy VanegasAinda não há avaliações
- Offshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientDocumento4 páginasOffshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientCristian Jhair PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Benefits of Eating OkraDocumento4 páginasBenefits of Eating Okraama931Ainda não há avaliações
- Data Sheet FC SIDocumento2 páginasData Sheet FC SIAndrea AtzeniAinda não há avaliações
- 2113T Feasibility Study TempateDocumento27 páginas2113T Feasibility Study TempateRA MagallanesAinda não há avaliações
- Afrah Summer ProjectDocumento11 páginasAfrah Summer Projectاشفاق احمدAinda não há avaliações
- EasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130Documento4 páginasEasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130ٍJordan SportAinda não há avaliações
- Plumbing Arithmetic RefresherDocumento80 páginasPlumbing Arithmetic RefresherGigi AguasAinda não há avaliações
- Where Are The Women in The Water Pipeline? Wading Out of The Shallows - Women and Water Leadership in GeorgiaDocumento7 páginasWhere Are The Women in The Water Pipeline? Wading Out of The Shallows - Women and Water Leadership in GeorgiaADBGADAinda não há avaliações
- AP World History: Islamic Empires and Scientific AdvancementDocumento55 páginasAP World History: Islamic Empires and Scientific AdvancementJa'TasiaAinda não há avaliações
- Verification of First Law V-SonometerDocumento3 páginasVerification of First Law V-SonometerRick astley's microphoneAinda não há avaliações
- Shell Omala S2 G150 DatasheetDocumento3 páginasShell Omala S2 G150 Datasheetphankhoa83-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Sci7 Q1 Wk-5 Module-5Documento15 páginasSci7 Q1 Wk-5 Module-5Lester Noel RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 04Documento3 páginasChapter 04gebreAinda não há avaliações
- Thinking and Acting Outside The BoxDocumento36 páginasThinking and Acting Outside The BoxMariecris GatlabayanAinda não há avaliações
- Heads of Departments - 13102021Documento2 páginasHeads of Departments - 13102021Indian LawyerAinda não há avaliações