Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Astronomy Test Review 1
Enviado por
Person McPersonDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Astronomy Test Review 1
Enviado por
Person McPersonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1. When does the full moon rise? a. sunset 2. Why do we see different constellations in different seasons? a. 3.
What is the reason for the seasons? In other words, why is summer warmer than winter, etc. a. because the Earths axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees 4. What are the approximate dates of the equinoxes and solstices? Summer Solstice June 21 Winter Solstice December 21 Autumn Equinox September 21 Spring Equinox March 21 5. What season is the Sun seen highest in the sky at noon? Lowest? a. Highest June 21st Summer Solstice- at noon b. Lowest December 21 Winter Solstice- (at noon?) 6. Suppose you see a certain star rising in the east at 9pm tonight? When will it rise tomorrow night? a. 4 minutes earlier -8:56 pm the next sidereal day 7. What does the word sidereal mean? what is a sidereal day? a. Anything relative to the stars The time is takes for a start to come up in the same position in the sky the next day (approx. 23 hours 56 minutes) 8. Are we closer to the sun in winter or in summer? a. Winter 9. What is the ecliptic? What are the two ways of using it to describe Earth or the Sun seen from the Earth. a. The path of the suns motion as seen from the Earth throughout the year b. Its the plane of Earths orbit is space 10. Define heliocentric and geocentric. a. heliocentric- Sun was center of the solar system proposed by Copernicus b. geocentric earth-centered model, idea that moon, sun, stars, revolve around earth 11. What is the celestial sphere? What are the major lines (circles) and important points on it? a. its as if we expanded the earths equator and north/south poles out into space. b. Celestial equator, North Celestial Pole, South Celestial Pole 12. When is the Sun north of the celestial equator? What change in seasons occur when the sun passes from north to south of the equator? South to North? a. North Spring and Summer b. South Fall and Winter 13. After the winter solstice, which way (N or S) is the sun shifting each day? a. North 14. When does the Sun rise and set almost directly E and W in this part of the world? a. Equinox? 15. Describe the apparent motion of the stars as seen from the North pole. what about the Sun in summer at the N. Pole? Winter? a. Summer Stars are not seen b. Winter- Stars continuously rotate in the sky
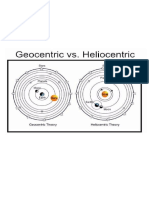
16. Why is the Sun right in your face so often on an E-W road this time of the year? a. Close to an Equinox 17. What happens to the Moon in a Lunar eclipse? Describe the sequence of events in a total lunar eclipe. a. The moon is in the earths shadow 18. What happens to the Moon in a Solar eclipse? Describe the sequence of events in a total lunar eclipse. a. The Eath is in the moons shadow 19. Which type of eclipse is easy to see over a large part of earth at once? a. Lunar 20. Which type of eclipse is very rare to see unless you travel? a. Solar 21. What are the umbra and penumbra? How do they relate to eclipses? a. 22. What was the geocentric model of the universe? a. Earth Centered 23. Who first proposed a heliocentric model in the 1500s? a. Copernicus 24. Who determined the three laws of planetary motion that are still used today? Whos data did he use? a. Keplar used Tychos 25. Who was the most important early user of the telescope? what did he see that confirmed his Copernicanism? a. Galileo 4 moons of Jupiter, phases of Venus 26. What is the shape of a typical closed orbit? a. Ellipse 27. What law of planetary motion les use precisely calculate speeds in an elliptical orbit at differing distances? What does it say about areas? a. 2nd law of Keplar. Describes how planets move faster nearer the Sun. 28. Be able to name and describe briefly the major personalities of the Copernican revolution we have discussed so far: Copernicus, Galileo, Tycho, Brahe, Kepler. a.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Lab - Motion of Celestial BodiesDocumento4 páginasLab - Motion of Celestial BodiesAhmad Makki50% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Autumn Treasures Unit Study & LapbookDocumento86 páginasAutumn Treasures Unit Study & LapbookKim CurulliAinda não há avaliações
- Precession of The Equinoxes and Its Importance in Calendar MakingDocumento13 páginasPrecession of The Equinoxes and Its Importance in Calendar MakingJayesh NehareAinda não há avaliações
- Satellite Parameters Trajectories Module1Documento94 páginasSatellite Parameters Trajectories Module1Gahan A V GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Math Chin CalDocumento39 páginasMath Chin CalMonica Beatriz AmatoAinda não há avaliações
- Back Garden AstronomyDocumento116 páginasBack Garden AstronomyDavid Brown100% (6)
- "More Light!": R. Theron DunnDocumento0 página"More Light!": R. Theron DunnREX666Ainda não há avaliações
- Spherical TrigonometryDocumento23 páginasSpherical TrigonometryPeejay Ollabrac100% (1)
- Climate Weather: B. Compare and Contrast Weather and Climate by Using A Venn DiagramDocumento14 páginasClimate Weather: B. Compare and Contrast Weather and Climate by Using A Venn DiagramMadylyn MacheteAinda não há avaliações
- The Universe and PhysicsDocumento24 páginasThe Universe and PhysicsTrizia ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Sem 2 Finals Lesson 1 HandoutDocumento8 páginasGrade 11 Sem 2 Finals Lesson 1 HandoutAnthony IlustreAinda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento178 páginasPhysicsJunard AsentistaAinda não há avaliações
- Summer Solstice: - Nick JoaquinDocumento28 páginasSummer Solstice: - Nick Joaquinnai50% (2)
- 1.1 Basic Theory: A Normal SightDocumento22 páginas1.1 Basic Theory: A Normal SightBorislav PetrovAinda não há avaliações
- Geosystems An Introduction To Physical GeographyDocumento39 páginasGeosystems An Introduction To Physical GeographyzemmiphobiaAinda não há avaliações
- Resource Pack Grade 6 SSTDocumento26 páginasResource Pack Grade 6 SSTzobiaumargrade8Ainda não há avaliações
- Guia 4. Mov Aparente SolDocumento4 páginasGuia 4. Mov Aparente SolAlexa ContrerasAinda não há avaliações
- Hipparchus Treatment of Early Greek Astronomy The Case of Eudoxus and The Length of Daytime - Alan C Bowen and Bernard R GoldsteinDocumento22 páginasHipparchus Treatment of Early Greek Astronomy The Case of Eudoxus and The Length of Daytime - Alan C Bowen and Bernard R GoldsteinNandini1008Ainda não há avaliações
- 061 General NavigationDocumento638 páginas061 General NavigationkgyjuhiAinda não há avaliações
- Test Bank For Cosmic Perspective 7th Edition by Bennett ISBN 0321839552 9780321839558Documento36 páginasTest Bank For Cosmic Perspective 7th Edition by Bennett ISBN 0321839552 9780321839558leslielowerygetyfbpxim100% (29)
- Scientific EssayDocumento2 páginasScientific Essay: Dr. EMAD KAYYAM.100% (2)
- Anand 04 PDFDocumento488 páginasAnand 04 PDFPatikshita majhiAinda não há avaliações
- The Hoax Called Vedic Rashichakra and Vedic Astrology!Documento36 páginasThe Hoax Called Vedic Rashichakra and Vedic Astrology!SampathKumarGodavarthiAinda não há avaliações
- Marine Laws and Ship Business Questions and AnswersDocumento70 páginasMarine Laws and Ship Business Questions and AnswersGeorge CarinoAinda não há avaliações
- Date of Mahabharata War Using Planetarium SoftwareDocumento93 páginasDate of Mahabharata War Using Planetarium SoftwareSrini Kalyanaraman100% (2)
- 7HW Seasons Tides EclipsesDocumento4 páginas7HW Seasons Tides EclipsesCally ChewAinda não há avaliações
- Sun and The Design ProcessDocumento28 páginasSun and The Design ProcessJireh Grace100% (5)
- Prehistoric ArchitectureDocumento5 páginasPrehistoric ArchitectureKim ManeAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable Energy Basics OneDocumento46 páginasRenewable Energy Basics OneqiTAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 23 - The Sun-Earth-Moon System PDFDocumento32 páginasChapter 23 - The Sun-Earth-Moon System PDFHeather BlackwellAinda não há avaliações