Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Definition:: Structure of Mucosa
Enviado por
Roshni MahajanDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Definition:: Structure of Mucosa
Enviado por
Roshni MahajanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Specialized Mucosa
Definition:
Mucosa: a mucous membrane comprised of epithelium, basement membrane, and lamina propria. -GPT 8 Mucous membrane is defined as a moist lining of Gastrointestinal tract, nasal passages and other body cavities that communicate with the exterior. In oral cavity this lining is known as the Oral Mucous Membrane or Oral Mucosa. - Ten cate
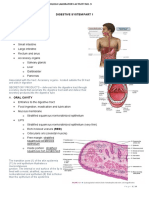
Structure of mucosa:
1. Epithelium( stratified squamous epithelium) Keratinized (masticatory mucosa)
Ortho-keratinized Para-keratinized Non-keratinized (lining mucosa)
2. Lamina propria The connective tissue supporting the oral epithelium is termed lamina propria. Two layers ; 1. PAPILLARY LAYER. 2. Close to epithelial ridges. Arranged loosely. RETICULAR LAYER parallel to epithelium
Specialized Mucosa
fibers are very thick. form network It consists of cells , blood vessels , neural elements & fibers embedded in amorphous ground substance
3. Submucosa (provides flexibility) Loose fat & glandular tissue with blood vessels & nerves. Consists of connective tissue of various thickness . It attaches the mucous membrane to the underlying structures. It may be a loose or a firm attachment - to glands, blood vessels , nerves, and adipose tissues
Structure of the Mucosa in different regions of Oral Cavity
Soft palate Thin( 150um) Non- keratinized Taste buds +nt Floor of Mouth Very thin-100um Non- keratinized Thick, Elastic fiber + nt, Highly Vascular Some Elastic fiber, Highly vascular Loose C.T, Fat & Minor salivary glands Alveolar Mucosa Thin, Non- keratinized Many Elastic fiber, Capillary loops +nt Loose C.T Minor salivary glands Num. minor salivary glands
Specialized Mucosa
Gingiva
Thick 250um, Ortho / Parakeratinized
Dense C.T, Not highly vascular
Firmly attached cementum & periosteum of alv. process
Hard palate
Thick, Ortho -keratinized
Thick, dense C.T ( under rugae), Moderate vascular supply
Dense C.T, firmly attached, Fat & minor salivary glands +nt
Functions :
1. Protection : Barrier from mechanical trauma and microbiological attack.
2. Sensation : Temperature (hot and cold), touch, pain , taste buds, thirst. reflexes such as swallowing, salivating , gagging and etching 3. Secretion : Salivary secretion
Specialized Mucosa
Classification of oral mucosa on the base of function:
1. Masticatory mucosa Gingiva and hard palate
2. Lining mucosa Lip, cheek, vestibular fornix, alveolar mucosa, floor of mouth and soft palate
3. Specialized mucosa Dorsum of the tongue and taste buds
Specialized mucosa:
The Specialized mucosa (Sensory mucosa) is so called because it bears the taste buds, which have a sensory function. Dorsal surface of tongue Anterior part(papillary) 1. Filiform papillae 2. Fungiform papillae 3. Circumvallate papillae Posterior part(lymphatic) 1. Foliate papillae 2. Lingual follicle
Specialized Mucosa
Anterior part of tongue:
Filiform papillae: Numerous fine-pointed, cone shaped papillae giving a velvety appearance to the tongue. Epithelium is keratinized. NO TASTE BUDS
Fungiform papillae: These are interspersed between the Filiform papillae. Mushroom shaped papillae which are round, reddish prominences and contain few taste buds & rich capillary network. Non-keratinized.
Circumvallate papillae: In front of the V shaped sulcus terminalis,8 10 vallate(walled) papillae are found Lined by keratinized epithelium on superficial surface & non-keratinized epithelium on the lateral surface. Taste buds are seen on lateral surface Von Ebners glands are present in the connective tissue.
Specialized Mucosa
Posterior part of tongue:
Foliate papillae: Present on the lateral margins of posterior tongue Consist of 4 11 parallel ridges that alternate with deep grooves in the mucosa and few taste buds.
Nerve supply: Anterior 2/3 is supplied by lingual nerve for general sensation and chorda tympani for taste. Posterior 1/3 is supplied by glossopharyngeal nerve for both general sensation and taste.
Blood supply: Arterial supply is derived from lingual artery and drains into deep lingual vein.
Specialized Mucosa
Taste and Taste buds:
These are small ovoid or barrel shaped intraepithelial organs Outer surface is covered by few flat epithelial cells which surround the Taste pore. It leads to a narrow space lined by supporting cells
Distribution of taste: there are four basic taste : sour , salty , sweet , bitter & fifth is umami.
Effect of denture on taste and age : As age increases the threshold of taste perception increases. There may be reduction in taste perception in denture wearers because of extension of dentures on hard palate, which covers taste buds of hard palate.
Gustatory salivation it is type of salivary reflex stimulated by different taste. Sour taste, from a solution of citric acid or from lemon drops, is among the most powerful and frequently used stimulants for collection of salivary samples. Parotid saliva collected with sour stimulation had the highest Na+ concentration
Salty taste, Stimulation of parotid saliva by salt in turn induced secretion of saliva with the highest protein content and Ca2+ concentration.
Specialized Mucosa
Other taste sweet , bitter , umami also induce salivation of different quantity and quality.
SOME TONGUE RELATED CONDITIONS:
FISSURED TONGUE Fissured tongue is a condition frequently seen that is characterized by grooves that vary in depth and are noted along the dorsal and lateral aspects of the tongue. The depth of the fissures varies but has been noted to be up to 6 mm in diameter. The fissures or grooves may be interconnected, separating the tongue dorsum into several lobules. Definitive etiology is unknown. GEOGRAPHIC TONGUE Benign migratory glossitis or Erythema migrans or Psoriasiform mucositis is a benign condition that occurs in about 3% of the general population.
Você também pode gostar
- Food ProgramsDocumento23 páginasFood ProgramsVlad ȘovărelAinda não há avaliações
- Oral CavityDocumento30 páginasOral CavityNastiti Fathia MagraAinda não há avaliações
- (F) Chapter 16 - Digestive System I, Oral Cavity and Associated StructuresDocumento5 páginas(F) Chapter 16 - Digestive System I, Oral Cavity and Associated StructuresAisle Malibiran PalerAinda não há avaliações
- Lining MucosaDocumento26 páginasLining MucosaShahid EquabalAinda não há avaliações
- CombinepdDocumento33 páginasCombinepdAhmed ZarifAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 (Oral Cavity) DR DoaaDocumento40 páginasLecture 1 (Oral Cavity) DR DoaakhaledAinda não há avaliações
- Oral MucosaDocumento36 páginasOral MucosaSiphiwe MayindiAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocumento39 páginasHistology of Digestive Systemirakozehugue14Ainda não há avaliações
- Oral Mucosa: Iryn A. LagartoDocumento8 páginasOral Mucosa: Iryn A. LagartoVarenLagartoAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of GitDocumento56 páginasHistology of GitDoc On CallAinda não há avaliações
- @ Histol DigestiveDocumento65 páginas@ Histol DigestiveAyele AsefaAinda não há avaliações
- Histologi Saluran CernaDocumento57 páginasHistologi Saluran CernaAdinda TobingAinda não há avaliações
- Oral MucosaDocumento109 páginasOral Mucosashahzeb memonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 - Digestive System 1Documento58 páginasLesson 1 - Digestive System 1tamemdekAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System (Final)Documento164 páginasDigestive System (Final)aubrey alcantaraAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento44 páginasDigestive SystemMekdelawit AyeleAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 1 GIT Aldi FDocumento86 páginasPemicu 1 GIT Aldi Faldi firdausAinda não há avaliações
- The Digestive System IDocumento55 páginasThe Digestive System IYousef KhallafAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SYSTEMDocumento53 páginasDigestive SYSTEMPrincess AnnAinda não há avaliações
- Mila Amor V. Reyes, MD, FPSP Anatomic and Clinical PathologistDocumento41 páginasMila Amor V. Reyes, MD, FPSP Anatomic and Clinical PathologistFranco Rommel ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3Documento31 páginasAnatomy Histology of The Oral Cavity2 3drsondosAinda não há avaliações
- 17 Tongue,+Esophagus+ +stomachDocumento42 páginas17 Tongue,+Esophagus+ +stomachAbi AntonyAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and ItsDocumento10 páginasDigestive Tract: Esophagus, Stomach, Small and Large Intestines, Rectum, and Anus and Itsحوراء عارف الموسويAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento60 páginasDigestive SystemdrynwhylAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Digestive System: C.T. Reyes, DVM, MSDocumento26 páginas10 Digestive System: C.T. Reyes, DVM, MSKent Solis VicenteAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 12Documento7 páginasLecture 12rahaf alshoumaryAinda não há avaliações
- Histology Lab GITDocumento44 páginasHistology Lab GITkedas70Ainda não há avaliações
- Histologi Upper GI Tract ENGDocumento37 páginasHistologi Upper GI Tract ENGmagfira_al_habsyiAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of Oral CavityDocumento17 páginasHistology of Oral Cavitysaint thuggerAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 1 Blok GIT: Theffany 405120198 Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TarumanagaraDocumento99 páginasPemicu 1 Blok GIT: Theffany 405120198 Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TarumanagaraTheffany KasiranAinda não há avaliações
- Oral MucosaDocumento57 páginasOral MucosaShabariNath R NairAinda não há avaliações
- Histologi Saluran CernaDocumento57 páginasHistologi Saluran CernaAdinda TobingAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Anatomy NotesDocumento20 páginasOral Anatomy NotesMyrian V. Legaspi100% (1)
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocumento227 páginasOral Mucous MembraneDR. ISHITA SINGHALAinda não há avaliações
- MIKROS-GIT-all PDFDocumento106 páginasMIKROS-GIT-all PDFKharisulAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter XI DigestiveDocumento19 páginasChapter XI DigestiveTitoMacoyTVAinda não há avaliações
- Alimentary Canal of HumanDocumento37 páginasAlimentary Canal of Humanمحمد العراقيAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrointestinal System: Anup PanthiDocumento67 páginasGastrointestinal System: Anup PanthiMadhav KhanalAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocumento28 páginasGastrointestinal SystemRein Margaret RogelAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Histology & Embryology-FikreDocumento240 páginasOral Histology & Embryology-FikreHeran A AlhadiAinda não há avaliações
- Cavum Oris & Salivary Gland Block 3Documento63 páginasCavum Oris & Salivary Gland Block 3Muhammad HammamAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive Anatomy of AnimalsDocumento336 páginasDigestive Anatomy of AnimalsTatenda MagejaAinda não há avaliações
- RT Basics Digestive SystemDocumento88 páginasRT Basics Digestive Systemmaricar paracadAinda não há avaliações
- Salivary Gland 1Documento31 páginasSalivary Gland 1Ahmed khanAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 1Documento111 páginasProblem 1Agustina CynthiaAinda não há avaliações
- GIT-Pemicu 1: Rachelle Betsy - 405140052Documento149 páginasGIT-Pemicu 1: Rachelle Betsy - 405140052Michelle Betsy AliantoAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Cavity-Converti-ConvertiDocumento6 páginasOral Cavity-Converti-ConvertihudamAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento16 páginasDigestive Systemراوند اعبيدAinda não há avaliações
- Sistem Pencernaan Makanan PDFDocumento74 páginasSistem Pencernaan Makanan PDFNaufal Sulthan RafiAinda não há avaliações
- Oral Mucosa Gingiva or The GumDocumento43 páginasOral Mucosa Gingiva or The Gumمصطفى احمدAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System Part 1Documento12 páginasDigestive System Part 1عبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحAinda não há avaliações
- CHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Documento83 páginasCHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Areej Fatima100% (2)
- Upper GIT System CPPP Lecture 2020-21Documento33 páginasUpper GIT System CPPP Lecture 2020-21NoraAinda não há avaliações
- Teeth, Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocumento12 páginasTeeth, Tongue and Salivary GlandsGideon WillieAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Digestive System Part 1Documento14 páginas9 Digestive System Part 1Fhayee Sulaik HaronAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of Salivary Gland ShivaniDocumento43 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of Salivary Gland ShivaniDeepika LamichhaneAinda não há avaliações
- Histology DigestiveDocumento87 páginasHistology DigestiveAnang Yanuar RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Histology Lecture NotesDocumento62 páginasVeterinary Histology Lecture NotesDEV3LLS100% (3)
- A Simple Guide to The Laryngitis and Vocal Cord DiseasesNo EverandA Simple Guide to The Laryngitis and Vocal Cord DiseasesAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Ainda não há avaliações
- A New Hylid Frog from Eastern Mexico. University of Kansas Publication, Vol 1, No 15No EverandA New Hylid Frog from Eastern Mexico. University of Kansas Publication, Vol 1, No 15Ainda não há avaliações
- Tridosha VijnanDocumento31 páginasTridosha VijnanSiddharth PatkarAinda não há avaliações
- Food Perception and Aesthetics Linking Sensory Science To Culinary PracticeDocumento45 páginasFood Perception and Aesthetics Linking Sensory Science To Culinary Practicexi si xingAinda não há avaliações
- Sensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersDocumento46 páginasSensation and Perception: A Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersLune NoireAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic ToungueDocumento14 páginasElectronic TounguesonuAinda não há avaliações
- GRE MnemonicsDocumento138 páginasGRE Mnemonicsjc224Ainda não há avaliações
- Journeys With Tibetan MedicineDocumento103 páginasJourneys With Tibetan MedicineEtra Publishing100% (2)
- Compostela Science and Technology High School Cogon Compostela Cebu 1 Periodical Test in Science 7Documento2 páginasCompostela Science and Technology High School Cogon Compostela Cebu 1 Periodical Test in Science 7Nanette Sotto TagalogAinda não há avaliações
- DN Beginning Acting Lesson Plan Younger KidsDocumento18 páginasDN Beginning Acting Lesson Plan Younger KidsAye Garnero100% (1)
- Smoking Session WeeklyDocumento26 páginasSmoking Session WeeklyIrwan HartantoAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry ProjectDocumento22 páginasChemistry Projecthari dasAinda não há avaliações
- Full Download Book Flavor From Food To Behaviors Wellbeing and Health PDFDocumento41 páginasFull Download Book Flavor From Food To Behaviors Wellbeing and Health PDFjeffrey.hemmings786100% (14)
- LAW221 Lecture Notes 2Documento5 páginasLAW221 Lecture Notes 2Tata SajaAinda não há avaliações
- Soal BAHASA INGGRIS - X - KUMER - PAKET 2Documento13 páginasSoal BAHASA INGGRIS - X - KUMER - PAKET 2Agus SuhendraAinda não há avaliações
- Pinaupong ManokDocumento2 páginasPinaupong ManokferdinandAinda não há avaliações
- Sex and Senses & Sexual BehaviorDocumento32 páginasSex and Senses & Sexual BehaviorKhyla PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Banana Heart Summer - Story AnalysisDocumento2 páginasBanana Heart Summer - Story Analysislloyd olimbaAinda não há avaliações
- Benefits of AMPALAYADocumento2 páginasBenefits of AMPALAYALieraSagunAinda não há avaliações
- Influence of Different Levels of Sodium Chloride and of A Reduced-Sodium Salt Substitute On Volatiles Formation and Sdsensory Quality of Wheat BreadDocumento9 páginasInfluence of Different Levels of Sodium Chloride and of A Reduced-Sodium Salt Substitute On Volatiles Formation and Sdsensory Quality of Wheat BreadKevin MesaAinda não há avaliações
- An Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Education Department Eastern Visayas StateDocumento20 páginasAn Undergraduate Thesis Presented To The Faculty of The Education Department Eastern Visayas StateJason R. FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Sensory Evaluation Techniques Lesson 9 Fs'11-12Documento41 páginasSensory Evaluation Techniques Lesson 9 Fs'11-12bi6592Ainda não há avaliações
- V EVS Question Bank For SA-1: by Mazumdar Sankar, PRT (SS), AECS, ManuguruDocumento41 páginasV EVS Question Bank For SA-1: by Mazumdar Sankar, PRT (SS), AECS, Manuguruspanja_barcAinda não há avaliações
- Etag Food ReviewDocumento1 páginaEtag Food ReviewGheoxel Kate CaldeAinda não há avaliações
- Science Form 2Documento20 páginasScience Form 2Nabila YazmineAinda não há avaliações
- Translation Theory Illustrated LecturesDocumento23 páginasTranslation Theory Illustrated LecturesChien VoAinda não há avaliações
- The Metabolic Type Self TestDocumento24 páginasThe Metabolic Type Self TestKrisztina Mészáros100% (4)
- Beer PairingDocumento269 páginasBeer PairingDavid Cortés EncinaAinda não há avaliações
- Feed AdditiveDocumento42 páginasFeed AdditiveNabeel ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- Flavalicious 29 - Tropical Temptation - January - March 2012Documento13 páginasFlavalicious 29 - Tropical Temptation - January - March 2012nickoRiesAinda não há avaliações
- Human and Animal Study Manual 2012Documento95 páginasHuman and Animal Study Manual 2012Andreea Balasa100% (2)