Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
B.tech (Hons) Mechanical Course Outline
Enviado por
Tableegi TehreekTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
B.tech (Hons) Mechanical Course Outline
Enviado por
Tableegi TehreekDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
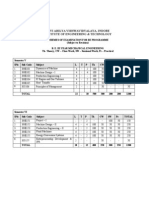
RECOMMENDATION OF CURRICULUM The management of Asian College of Technology, Bahawalpur with the help of Advisory Committee and other
teaching staff, vetted the curriculum of B.Tech Honours Mechanical Technology Programme fourth year class (Annual). The Advisory Committee founded the curriculum suitable and recommended to teach in the academic session 2011-12 starting from September-2011. CURRICULUM FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY B-TECH (HONS) 4 th YEAR Class Sr No. Code Page No. 1. 01 2. 02 3. 03 4. 04 5. 05 6. 06 7. 07 8. 09 9. 10 10. 11 11. 12 MT 408 Production Planning & Control Instrumentation & Control Project MT 407 Power Plants & Energy Resources MT 406 Computer Integrated manufacturing MT 405 Machine Design MT 404 Material Forming MT 403 Tool Design-II MT 402 Thermodynamics & Air Conditioning Math 401 Mathematics-II IS Subject Islamiat & Pakistan Studies
MT 409 MT 410
CURRICULUM FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY B-TECH (HONS) 4 th YEAR Sr. No Marks Code Subject T P C Theor y 50 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 Practic al 0 0 50 50 50 50 50 50 0 50 100 Tot al 50 100 150 150 150 150 150 150 100 150 100 125 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
IS
Islamiat & Pakistan Studies
1 2 & 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 0
0 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 0 3 6
1 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 3 2
Math 401 MT 402 MT 403 MT 404 MT 405 MT 406 MT 407 MT 408
Mathematics-II Thermodynamics Air Conditioning Tool Design-II Material Forming Machine Design Computer Integrated Manufacturing Power Plants & Energy Resources Production Planning & Control Instrumentation & Control Project
10 MT 409 11 MT 410
Total
17
24
25
850
400
Math 401 C Note:
Mathematics-II 2 0
T 2
Common for Civil & Mechanical Technology
1. Differential Equations: Solution of Linear Differential Equations of First and Second order. The S-Operators, complementary functions and particular integrals. Special types of Second and Fourth order Differential Equations Applications to relevant engineering problems. Analytical Geometry of three Dimensions. Equations of line, planes and sphere. 2. POLAR COORDINATES: Polar Coordinates 3. LAPLACE TRANSFORMS: Laplace and inverse Laplace Transforms of Elementary functions and their applications solution of ordinary differential equations. 4. VECTOR ANALYSIS: Vector Differentiation and integration. Gradient, Divergence and Curl 5. Complex Numbers: Algebra of Complex Number, Complex plane, Exponential and Polar form, D' Moiver's Theorem, and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions, Complex Functions, Limit and Continuity, Complex Differentiation, Cauchy Theorem and Chauchy's Integral formula. 6. Integral Calculus: Integration as Reverse process of Differentiation, different techniques of Integration, Definite Integrals. 7. Application of Integration: Area between curves, volume of solids, (prism, cylinder, pyramid, cone and sphere), Momentum, Curvature and radius of curvature. 8. Differential Equations: Classification of Differential Equation, formation of Differential Equation, Initial Value and Boundary Value conditions, Homogeneous Equations, Exact Equations, non homogeneous Linear Equations, application to the physical and engineering problems. 9. Numerical Analysis: (a) importance of Numerical Analysis, solution of Algebraic Equations in one variable, (Bisection Method, Interpolation, Newton's Raphson Method, Secant Method, One point Integration Method, Modified Newton's Method). (b) Finite Differences: Forward difference, Difference of Polynomial, Back ward Differences, Central differences, Interpolation, and Inverse Interpolation. (c) Numerical Integration: Rectangular and Mid Point Rule, Trapezoidal Rule, 1/3 Simpson's Rule, 3/8 Simpson's Rule. Books: Calculus and Analytical geometry by Thomas, G. B. and Finney R. L. (Latest Edition). Advance Engineering Mathematics, by Er. Win Kresyzig. Advance Engineering Mathematics, by C. R. Wylie
Text 1. 2. 3.
4. Practical Mathematics Vol II, by Troft and Mcey. Reference Books: 1. 2. 3. 4. Peter Kuffiting, Technical Mathematics with Calculus. Engineering Mathematics by K. A. Stroud. Mathematical Methods by Dr. S. M. Yousaf and Dr. Abdul Majeed. Calculus and-Analytical geometry by Dr. M.N.M. Talpur. 5. An Introduction to Numerical Analysis by Dr. Muhammad Iqbal.
MT 402 P Part-1 1.
THERMODYNAMICS C
& AIR CONDITIONING 2 3
T 3
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
THERMODYNAMICS Introduction and revision of basic topics: Thermodynamic systems, Thermodynamic properties, Energy and work, Properties of vapor and steam. Properties of ideal and real fluid and their relationships Applications of thermodynamic principles to these fluids. First Law of Thermodynamics and applications ,Closed System and, Open systems. Steady flow energy equation applications to Nozzles, Diffusers, Compressors and, Turbines. Second Law of Thermodynamics ,Irreversibility, Application to heat engines performance. Entropy : Use in heat engines calculations, entropy and irreversible processes. Heat and work exchange, Different closed and, Open systems used in Vehicular engines design.
Part-2 AIR CONDITIONING
1. Air-conditioning and Ventilation: Use of the psychometric charts, Calculation of heat to be removed by an air-conditioning plant, Air-conditioning requirements for comfort and industrial processes. 2. Air distributing systems, Design and sizing of ducts, water cooler, Dehumidifiers, Humidifiers, Automatic temperature and humidity control systems, Pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic systems, Complete calculations for a simple air conditioning system, prevention of noise and vibration. PRACTICALS 1. Study of Four Stroke & Two Stroke Engines
2. Study of Heat Exchanger 3. Duct Designing 4. Air conditioning system Text Book: 1. Thermodynamics and engineering approach. 3rd Ed. {1998) Y Cengel and M Boles 2. Applied Thermodynamics for Engineering Technologist by TD Eastop, A McCONKEY. Reference Book: 1. Engineering thermodynamics work and heat transfer- G.G.C. Rogers and Y.R. Mayhew,
MT 403
TOOL DESIGN-II 2 3
P 3
COURSE CONTENTS:
1. Types of Press working Operations Cutting Operations, Bending Operations, Drawing Operations, Forming Operations, Rubber and Hydraulic Pressing, 2. Power Presses Basic Terminology, Classification, Press Accessories, Press Standards, Press Capacities, 3. Design of Metalworking Dies Basic Terminology, Cutting Dies, Draw Dies, Compression Dies, Progressive Dies, Bulging Dies, Die-Casting Dies 4. Design of Plastic Processing Dies Plastic Moulding Machines, Injection Moulding Dies, Blow Moulding Dies, Compression Moulding Dies, Extrusion Dies 5. Die Manufacturing Die Materials, Manufacturing Processes List of Practicals: 1. To design a blanking and piercing die for the given component 2. To design a trimming and shaving die for the given component 3. To make a three-dimensional solid model of a compound die, 4. To make a three dimensional solid model of a progressive die, 5. To make a three dimensional solid model of a bending die, 6. To make a three dimensional solid model of a single acting and double acting drawing die for the given component. 7. To design a permanent metal mould for the casting of a given component. 8. To design a centrifugal metal mould for the casting of a given
component. 9. To design a semi-centrifugal metal mould for the casting of a given component. 10. To make a three dimensional solid model of the die designed for die-casting of a given component. 11. To make a three dimensional solid model of the injection mould designed for the production of a given plastic component and to demonstrate its functioning. 12. To make a three dimensional solid model of the compression mould designed for the production of a given plastic component and to demonstrate its functioning. 13. To make a three dimensional solid model of the blow mould designed for the production of a given plastic component and to demonstrate its functioning Text Books: 1. Donaldson, Tool Design 2. ASTME TOOL ENGINEER'S Handbook Reference Book: 1. Pollack H W. Tool Design. Prentice Hall, USA.
MT 404 C
MATERIAL FORMING TECHNOLOGY 2
T 3
P 3
COURSE CONTENTS: 1.
Forging:
2. 3. 4. 5.
6.
Introduction, Open Die and Closed Die Forging, Forging Machines, Die Material and Lubrication, Forgability, Forging Defects, Applications, Rolling: Flat Rolling, Shape Rolling, Rolling Mills, Continuous Casting and Rolling, Rolling Defects, Applications Drawing: The Drawing Process, Drawing Equipment, Properties of Drawn Products, Drawing Defects, Applications Extrusion: The Extrusion Process, Hot and Cold Extrusion, Types of Extrusion, Extrusion Presses, Extrusion Defects, Application, Sheet Metal Forming: Sheet Metal Characteristics, Formability Tests, Bending and Shearing, Deep Drawing, Equipment for Sheet Metal Forming, Nonconventional Forming Techniques Powder Metallurgy: Introduction, Production of Powder, Compacting, Sintering and Finishing, Equipment, Design Conside5ration, Advantages and Applications
7. 8. 9.
Forming of Plastics: Injection Moulding, Compression Moulding, Blow Moulding, Extrusion, Reaction Moulding, Forming of Ceramics. Forming of Fiberglass.
List of Practicals. 1. Familiarization with the tools and equipment used in open die forging. 2. To perform open Die Forging Operations (Upsetting, Drawing Down, Setting Down, Bending) 3. The practice to prepare appropriate forged components using Drop Forging Process. 4. The practice to prepare appropriate forged components using press Forging Process. 5. The practice to prepare appropriate forged components using Upset Forging Process. 6. To practice blanking, piercing and bending operations using the power press. 7. To perform formability tests on different grades of sheet metal. 8. Familiarization with the extruding equipment. Text Books: 1. Milenik E M. Metalworking Science and Engineering. McGraw Hill, UK. 2. Lindbeek J.R. Williams M W and Wygant R M Manufacturing Technology. Prentice Hall, UK. Reference Books: 1. Bruce RG. Mileta MT .Neely J E and Kibbe R R. Modern Materials and Manufacturing Processes Prentice Hall, USA.
MT 405 Part I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
MACHINE DESIGN 2
T 3
C 3
Kinematics, force analysis Design of belts, ropes and chains drives. Design of mechanical springs. Design of gears. Design of rolling bearing. Design of Journal Bearings. Stress Concentration in members. Contact stresses in balls and rollers
Practicals
1. Study of belts & chain drives 2. Study of spur gear 3. Study of Journal bearing Recommended Books 1. Mechanical Engineering Design, by J. E. Shigley and Mischke, McGraw Hill. 2. Advance Mechanics of materials by S & Smith 3. Mechanics of Solids & Strength of Materials by P.V. Warnock & P.P. Benham 4. Machine Design by Paul H Black, O. Eugene Adam
MT 406 C
COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING 2
T 3
P 3
COURSE CONTENTS: Part I: COMPUTER APPLICATIONS 1. BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION: Major building blocks; their functions & inter connections. Number Systems, Number conversion, Data Representation & Data structure. Memory & I/O of a computer, Introduction to Languages, High level & Low Level Languages, Compilers interpreters, operating systems, computer programming. 2. APPLICATION PACKAGES: Practice in using Micro Soft Word Practice in using MS Excel Part II 1. 2. COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING
3. 4. 5.
6.
Introduction: History, Goals & Objectives, Cost Justifications, Scope, Computers in Manufacturing: Computer Aided Engineering, Computer Aided Manufacturing, Computer aided Process Planning, Computer simulation of Manufacturing Processes and Systems. Manufacturing Systems. Flexible Manufacturing, Group Technology, Just-in-time Production, CAD/CAM. Production Automation: Strategies, Economics of Automation, Flow Lines, Mathematical Models, Storage Buffers, Balancing, Manufacturing System Design: Process Planning, Facility Design, Production Planning and Scheduling, Manufacturing Communication Networks, System Integration, Evaluation, Artificial Intelligence & CIM:
Practicals 1. To study the construction and operation of an automated guided vehicle. 2. Programming an automated guided vehicle to transport the material within a CIM system. 3. To study the construction and operation of an automated storage and retrieval system. 4. Programming an automated storage and retrieval system within a CIM system. 5. To study the construction and operation of a CMM. 6. Use of CMM for the measurement of flat and angular surfaces. 7. Use of CMM for the measurement of circular surfaces and holes. 8. Use of CMM for the measurement of irregular contoured parts. 9. Use of visual part recognition system for quality assurance 10. Preparing a part program for CNC milling center. 11. Programming a robot within a CIM system. 12. Programming a conveyer within a CIM system. 13. Preparing and programming the sequence of operations within a CIM system.
14. Simulation and analysis of the sequence of operations. 15. Running and debugging the CIM system for required sequence of operations Text Books: 1. Foston A L, Au A and Smith C. Fundamentals of Computer Integrated Manufacturing. Prentice Hall, UK. 2. Mitchell F H. CIM SYSTEMS: Introduction to Computer Integrated Manufacturing. Prentice Hall, UK. 3. Hunter R. Automated Process Control System: Concepts and Hardware. Prentice Hall, UK. Reference Books: 1. Edney R.C. Computer-Aided Engineering for Mechanical Engineers. Prentice Hall, UK. 2. Besant C B. and Lui C W K. Computer Aided Design and Manufacture. Prentice Hall, UK.
MT 407 T
POWER PLANTS AND ENERGY RESOURCES P C 2 3 3
1. Energy Resources: Fossil fuel resources, coal, oil and gas resources of energy, supply and demand. 2. Alternative energy resources: Tidal and geo thermal. Nuclear, Solar, Wind, Ocean,
3. Steam power plants: Modern steam plants, reheat and regenerative Turbines, flow through steam nozzles, Impulse and reaction turbines; pressure compounding, Velocity compounding, extraction and back pressure turbines. Boiler makeup and treatment. 4. Gas Turbine Power Plants: Practical Gas turbine cycle. Isentropic efficiency of compressor and turbines, inter-cooling and reheating. 5. Combine Cycle Power Plants: General-combined cycle with heat recovery boilers. 6. Jet Propulsion Plant: Aircraft Jet engine, efficiency and performance of turbojet plant, ram jet-comparison of plants for subsonic and supersonic flights. 7. Nuclear Power Plant: Introduction, power from nuclear energy, nuclear fusion and fission, Radioactivity, Decay rates and half-life, converting mass into energy by fission. Thermal-Fission Reactors and Power Plants, Pressurized water reactor (PWR), the boiling water reactor (BWR) Practicals:
1. Visits to Thermal Power Plants. 2. Design & Fabrication of workable models of: a) Wind Mill b) Solar
MT 408 C
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL 2 0
T 2
COURSE CONTENTS: 1. Forecasting: Introduction, Forecasting Approaches, Time Series Forecasting Techniques, Casual Forecasting Techniques, Role of Computer in Forecasting 2. Inventory Management: Inventory Systems, Economic Lot Size, Quantity Discounts, Safety Stock Level 3. Just-in-Time Systems: JIT Production, Kanban, 4. Supply-Chain Management: Significance, Purchasing Strategies, Purchasing Management, Materials management, 5. MRP and MRP-II: Master Production Schedule, Bill of Materials, Resource Requirements, MRP Management, 6. Short Term Scheduling Tactics: Job Shop Scheduling, Shop Loading, Sequencing, Line Balancing 7. Queuing Theory: Introduction, Queue Characteristics, Queuing Models, Introduction to Simulation Text Books: 1. Render B and Heizer J PRINCIPLES OF OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT. Prentice-Hall, Inc. USA. 2. Littlechild S. OPERATIONS RESEARCH IN MANANGEMENT. Prentice Hall, UK. Reference Books: 1 Tersine RJ. Principles of Inventory and Materials Management. Prentice Hall, UK. 2 Adam E E and Eber R J. Prodctution and Operations Management. Prentice Hall, UK.
MT 409 C
INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL 2 3
T 3
Course Contents: 1. Basic concepts, characteristics, 2. Function of instruments special for indicating and recording: a) temperature, b) pressure, c) flow, level, d) measuring errors & calibration. 3. Boiler control system, 4. Air compressor controls. 5. Introduction to the principles of automatic system open-loop and closed loop systems. 6. Feed back mode of operation of hydraulic pneumatic and electrical components. 7. Amplifier, servomotors, process controller, regulating value positions. 8. Laboratory experiments on instruments and control components. 9. Measurements of actual system, Design of simple control system. Practicals: 1. Study of pyrometer 2. Calibration of Pressure gauges 3. Stroboscope 4. Study of tachometer Book Recommended: 1. Hand Book of Instrument and Control by Howard P. Kalien 2. Industrial Process Measuring Instruments by Sarroll. 3. Process Instruments and Control (Hand Book by Sarroll)
MT 410
PROJECT
T 0
P 6
C 2
Objectives: 1. To review the knowledge and practice the skills acquired. 2. To apply the acquired knowledge and skill to solve practical problems. 3. To work independently in an object oriented situation 4. To fabricate a project, Description: Students will be assigned different tasks and will be required to work out independently on the details such as: 1. design calculations of project 2. working drawings of project & 3. material specifications, 5. process planning, 6. cost estimation and 7. manufacturing
Você também pode gostar
- Discrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsNo EverandDiscrete Element Method to Model 3D Continuous MaterialsAinda não há avaliações
- Third Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueDocumento8 páginasThird Year Second Semester: Department of Mechanical Engineering - Course CatalogueSudeep GamerAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus - BE Mech II Wef 2012-13 PDFDocumento28 páginasSyllabus - BE Mech II Wef 2012-13 PDFPavan KishoreAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationNo EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertAinda não há avaliações
- Me Manufacturing Curriculum-2Documento11 páginasMe Manufacturing Curriculum-2Arun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech 3rd Sem Exam Scheme Mechanical EngineeringDocumento144 páginasB.Tech 3rd Sem Exam Scheme Mechanical EngineeringPrad UpAinda não há avaliações
- Nanotechnology Commercialization: Manufacturing Processes and ProductsNo EverandNanotechnology Commercialization: Manufacturing Processes and ProductsAinda não há avaliações
- ManuDocumento67 páginasManuidocipetchennaiAinda não há avaliações
- Multiscale Modeling of Additively Manufactured Metals: Application to Laser Powder Bed Fusion ProcessNo EverandMultiscale Modeling of Additively Manufactured Metals: Application to Laser Powder Bed Fusion ProcessAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Design SyllabusDocumento49 páginasEngineering Design SyllabusanandandmeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Power Cycles: Carnot Cycle, Diesel Cycle, Dual Cycle, Brayton Cycle, Cyclecalculations & Analysis Unit-IiiDocumento6 páginasGas Power Cycles: Carnot Cycle, Diesel Cycle, Dual Cycle, Brayton Cycle, Cyclecalculations & Analysis Unit-Iiiapi-19815017Ainda não há avaliações
- Details of Syllabus: Mechanical Engineering LaboratoryDocumento12 páginasDetails of Syllabus: Mechanical Engineering LaboratoryReinhold Seth Jnr100% (3)
- Mechanical Engineering Subject Duration - Maximum Marks Section I-Objective PapersDocumento4 páginasMechanical Engineering Subject Duration - Maximum Marks Section I-Objective Paperssudheer92Ainda não há avaliações
- MACHINEDESIGNDocumento35 páginasMACHINEDESIGNBrandon AllenAinda não há avaliações
- PANJAB UNIVERSITY B.E. MBA MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SCHEMEDocumento42 páginasPANJAB UNIVERSITY B.E. MBA MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SCHEMEcoolratheeAinda não há avaliações
- Anna Univ Part Time Mech SylabusDocumento69 páginasAnna Univ Part Time Mech SylabusmayilsamythangarajuAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engineering CurriculumDocumento20 páginasMechanical Engineering CurriculumMuhammad Saqib Swati100% (1)
- ManufacturingDocumento35 páginasManufacturingMichael EnglishAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Plan For Vth-Semester Mae (2011-12) : Subject: Microprocessor and Applications Subject Code: ETME-301Documento5 páginasAcademic Plan For Vth-Semester Mae (2011-12) : Subject: Microprocessor and Applications Subject Code: ETME-301Jayesh KatariaAinda não há avaliações
- Btech 2Documento17 páginasBtech 2Divyesh SindhiAinda não há avaliações
- Rajiv Gandhi Technological University, Bhopal (MP) : B.E. (ME) Mechanical EngineeringDocumento15 páginasRajiv Gandhi Technological University, Bhopal (MP) : B.E. (ME) Mechanical EngineeringneerajvidishaAinda não há avaliações
- Uet Lahore CourseDocumento23 páginasUet Lahore CourseSufian AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- APEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalDocumento22 páginasAPEGBC Eng Syllabus MechanicalbaljinderAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Semester Mechanical Engineering: Course No. Course Name Credits L T PDocumento8 páginas7 Semester Mechanical Engineering: Course No. Course Name Credits L T PAJAinda não há avaliações
- Elective - IDocumento33 páginasElective - IMohit RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme - e Fourth Semester - Ce, CS, CR, CVDocumento34 páginasScheme - e Fourth Semester - Ce, CS, CR, CVprafullaAinda não há avaliações
- Me Manufacturing EngineeringDocumento33 páginasMe Manufacturing EngineeringsumikannuAinda não há avaliações
- Me Manufacturing CurriculumDocumento37 páginasMe Manufacturing CurriculumJeyaram kumarAinda não há avaliações
- M.E. MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING AU SyllabusDocumento35 páginasM.E. MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING AU SyllabusJoswa CaxtonAinda não há avaliações
- IIT Jodhpur Proposed ME M.Tech Program CurriculumDocumento8 páginasIIT Jodhpur Proposed ME M.Tech Program CurriculumAmit AAinda não há avaliações
- Rajasthan Technical University (RTU) Mechanical Engineering YEAR II / SEMESTER III THEORY AND PRACTICALSDocumento52 páginasRajasthan Technical University (RTU) Mechanical Engineering YEAR II / SEMESTER III THEORY AND PRACTICALSappannusaAinda não há avaliações
- Karanataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)Documento35 páginasKaranataka State Open University: M Tech in Mechanical (Computer Integrated Manufacturing)nav1278Ainda não há avaliações
- Final BTech MechanicalDocumento31 páginasFinal BTech MechanicalAniket GaikwadAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech Degree Course in CSE Scheme of ExaminationsDocumento78 páginasB.Tech Degree Course in CSE Scheme of ExaminationsBobin babyAinda não há avaliações
- B.E. CSEgbDocumento98 páginasB.E. CSEgbjyotsnaroopAinda não há avaliações
- JNTUK-DAP-B.tech (Mechanical Engineering) - Syllabus of B.tech III Year - I SemesterDocumento20 páginasJNTUK-DAP-B.tech (Mechanical Engineering) - Syllabus of B.tech III Year - I SemesterSwamy RakeshAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus - B.E. Mechanical - 2009 RegulationDocumento161 páginasSyllabus - B.E. Mechanical - 2009 RegulationshivakumarAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd SemesterDocumento13 páginas3rd SemesterRed-KanAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Design and Fluid Mechanics Qualifying Exam GuideDocumento15 páginasEngineering Design and Fluid Mechanics Qualifying Exam GuideAnastasiya DobrovaAinda não há avaliações
- B.Tech II Year Mechanical Engineering Study Scheme for Sem IVDocumento6 páginasB.Tech II Year Mechanical Engineering Study Scheme for Sem IVRoshan Virat PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Gtu Be Civil First YearDocumento14 páginasGtu Be Civil First YearHR Divya RanaAinda não há avaliações
- B.E. CseDocumento114 páginasB.E. Cseselva136832Ainda não há avaliações
- Simulation of Heat Transfer in Steel Billets During Continuous CastingDocumento14 páginasSimulation of Heat Transfer in Steel Billets During Continuous CastingFahrgerusteAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Simulation of Chip Flow in Metal MachiningDocumento15 páginasFinite Element Simulation of Chip Flow in Metal MachiningArul KirubakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogyDocumento20 páginasDevi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogySonal MahajanAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Graphics2Documento7 páginasEngineering Graphics2ILAYAPERUMAL KAinda não há avaliações
- MC512 Mechanical Drawing IIDocumento2 páginasMC512 Mechanical Drawing IIEduardo RAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engg RM PET SyllabusDocumento5 páginasMechanical Engg RM PET SyllabusAnil MagareAinda não há avaliações
- M.tech - NIT WarangalDocumento68 páginasM.tech - NIT Warangalrudey18Ainda não há avaliações
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For 1st Sem B.TechDocumento6 páginasElements of Mechanical Engineering Syllabus For 1st Sem B.TechDebarshi BaruahAinda não há avaliações
- ME Syllabus OddDocumento47 páginasME Syllabus OddPrajwalAinda não há avaliações
- MTECH Manufacturing EnggDocumento10 páginasMTECH Manufacturing EnggSudhir KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Jain Un Syllabus 4th SemDocumento13 páginasJain Un Syllabus 4th SemAnshul LallAinda não há avaliações
- DFDGGGDGDGDDocumento54 páginasDFDGGGDGDGDAnil MaliAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 1: Introduction:: 5 July 2010 34Documento15 páginasUNIT 1: Introduction:: 5 July 2010 34don024Ainda não há avaliações
- Course Structure and Teaching Schedule (5 Semester)Documento12 páginasCourse Structure and Teaching Schedule (5 Semester)Gladiatordiv OutlawAinda não há avaliações
- Mech3 - 8 Mdu On Apr 11Documento130 páginasMech3 - 8 Mdu On Apr 11Shanmugavel MallaiahAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Hybrid PowerplantDocumento29 páginasSolar Hybrid PowerplantSulaim Abdul LatheefAinda não há avaliações
- Ap 1000Documento115 páginasAp 1000Shafi MarwatAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento29 páginasChapter 1Ranjan DhungelAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroelectric-Energy - 20231018 000533 0000Documento15 páginasHydroelectric-Energy - 20231018 000533 0000alcuirezjane2Ainda não há avaliações
- Eskom, 2021, "Cooling Techniques at Eskom Power Stations"Documento1 páginaEskom, 2021, "Cooling Techniques at Eskom Power Stations"Tanatswa MoyoAinda não há avaliações
- 1760 Power Plant House Equipment ListDocumento4 páginas1760 Power Plant House Equipment ListJessica DeanAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Builder Logic Test 3 75 QuestionsDocumento10 páginasStrategy Builder Logic Test 3 75 QuestionssarveshaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics of Turbines: Reference:Water Resources Engineering by LarrymaysDocumento12 páginasHydraulics of Turbines: Reference:Water Resources Engineering by LarrymaysCarlos Henry BarcenalAinda não há avaliações
- R41024112018 JNTUK Question PaperDocumento2 páginasR41024112018 JNTUK Question PaperYellaji AllipilliAinda não há avaliações
- Full Summer Training Report On Power PlantDocumento27 páginasFull Summer Training Report On Power PlantAnurag Chand60% (5)
- BGRDocumento84 páginasBGRMustafa LokhandwalaAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution and Components of Diesel Power PlantsDocumento51 páginasEvolution and Components of Diesel Power PlantsJed Alcantara100% (2)
- Ultra Mega Thermal Power PlantDocumento10 páginasUltra Mega Thermal Power PlantAshish VermaAinda não há avaliações
- CA 2 (2021) MCQ Non Conventional EEE7Documento2 páginasCA 2 (2021) MCQ Non Conventional EEE7anupnaskar naskarAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS1003 Cheat SheetDocumento8 páginasPHYS1003 Cheat Sheetwin winwinAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheet 5Documento2 páginasTutorial Sheet 5Syed YousufuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Copenhagen Climate PlanDocumento32 páginasCopenhagen Climate PlanPaula EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- Non-conventional energy sources and techniquesDocumento17 páginasNon-conventional energy sources and techniquesSaidulla MeerAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Actuators for Automating Industrial ValvesDocumento84 páginasElectric Actuators for Automating Industrial ValvesbenyakiAinda não há avaliações
- Evaporative CoolerDocumento6 páginasEvaporative Coolersujiv_sujiv1278Ainda não há avaliações
- Super Trishuli Hydroelectric Project GTSDocumento154 páginasSuper Trishuli Hydroelectric Project GTSDipeshAinda não há avaliações
- Power and EnergyDocumento24 páginasPower and EnergySuman RegmiAinda não há avaliações
- Basic of Boiler DesignDocumento186 páginasBasic of Boiler DesignArielKST100% (2)
- Meghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportDocumento13 páginasMeghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportmadhueeAinda não há avaliações
- Report On GoingDocumento165 páginasReport On Goingnitin lagejuAinda não há avaliações
- 156 Power English PDFDocumento23 páginas156 Power English PDFEmdad MunnaAinda não há avaliações
- Abb Solar Inverters Brochure Bcb.00076 en Rev. D LowresDocumento112 páginasAbb Solar Inverters Brochure Bcb.00076 en Rev. D LowresVIJAYKAGRE100% (1)
- Me419 Ehs Ppe DPPDocumento51 páginasMe419 Ehs Ppe DPPAhsanul haque JoyAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of Grid-Connected Photovoltaics in The Libyan Power SystemDocumento9 páginasA Study of Grid-Connected Photovoltaics in The Libyan Power SystemAbdalmoedAlaiashyAinda não há avaliações
- ATOMEX Europe 2011: Sigma Group A.SDocumento35 páginasATOMEX Europe 2011: Sigma Group A.StomognAinda não há avaliações
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAinda não há avaliações
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthNo EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (197)
- The Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsNo EverandThe Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (131)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityNo EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (115)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkNo EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNo EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceNo EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (9)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessAinda não há avaliações
- Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeNo EverandProof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (165)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNo EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.No EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryNo EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksNo EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCNo EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationNo EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Coastal Alaska & the Inside Passage Adventure Travel GuideNo EverandCoastal Alaska & the Inside Passage Adventure Travel GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsNo EverandDesign and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsMarco CecarelliAinda não há avaliações
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNo EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceAinda não há avaliações
- Building Server-side and Microservices with Go: Building Modern Backends and Microservices Using Go, Docker and KubernetesNo EverandBuilding Server-side and Microservices with Go: Building Modern Backends and Microservices Using Go, Docker and KubernetesAinda não há avaliações