Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Energy Resources
Enviado por
Thanusha DhanarajDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Energy Resources
Enviado por
Thanusha DhanarajDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
7I - Energy Resources Summary Notes
Energy is the ability to do work. The units of energy are Joules (J). There are different kinds of energy such as heat energy, light energy, sound energy and electrical energy.
A fuel is a substance that releases energy when it burns.
Most of our energy ultimately comes from the Sun. Only geothermal, nuclear and tidal energy do not originate from the Sun.
Fossil fuels Fossil fuels are coal, oil and natural gas. They are non-renewable because we cannot replace them so they will run out. They were formed millions of years ago from dead plants and animals.
Coal is formed from dead plants that lived millions of years ago. The plants were buried in mud. This stopped air reaching the plants so that the plants did not rot away. This formed peat. Over time more layers of mud built up, squashing the peat. Then heat from inside the Earth combined with the pressure of the earth on top of the peat caused the mud to turn to rock and the peat into coal.
Oil and gas are formed from tiny plants and animals that lived in the sea millions of years ago. When the plants and animals died they fell to the bottom of the sea where they were buried. More layers of mud and debris buried the dead animals. Heat and pressure cause the dead plants and animals to turn into oil and gas. The oil and gas became stuck under a layer of caprock, which would not let them through.
Fossil fuels are relatively cheap to obtain but they produce gases, such as carbon dioxide, which are harmful to our environment.
Conserving energy There are many ways to save energy. This has the following benefits: Saves fossil fuels, so they last longer. Saves money spent on fuels. Reduces pollution.
Renewable energy resources. Renewable energy resources can be expensive but they do not produce harmful gases (except biomass) and they will not run out.
CRD 2013
Types of renewable energy: Type of energy Solar Hydroelectric Wind Tidal Description Uses UV radiation from the Sun to generate electricity in solar cells. A dam traps water which is allowed to flow through tunnels to turn turbines which drive generators. Uses wind movements to turn wind turbines which drive generators. A huge dam (called a "barrage") is built across a river estuary. When the tide goes in and out, the water flows through tunnels in the dam. The ebb and flow of the tides can be used to turn a turbine, or it can be used to push air through a pipe, which then turns a turbine. Wave Geothermal Biofuel Uses the motion of the waves to generate electricity. Uses the heat energy stored within the earth. Fuels made from recently dead matter that can be regenerated. Generally used for transportation. Two common types are bioethanol and biodiesel.
Conservation of energy The law of conservation of energy states that: Energy can never be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another.
Energy transfer Devices are useful because they convert energy from one form to another, for example: a radio converts electrical energy into sound energy. Sometimes there is more than one energy transfer and this is called an energy chain. For example: chemical electrical light In energy transfers some energy is always lost, often to heat. Total energy input = Useful energy + Wasted energy. A couple of important examples of energy transfer: Photosynthesis: The transfer of the suns energy into chemical energy in chloroplasts. carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen Respiration: The release of energy by cells. glucose + water carbon dioxide + water
How to measure food energy The amount of energy in food can be measured by burning a known quantity of food that heats up a known volume of water. As one calorie (4.2 Joules) is the energy required to raise 1 mL of water by one degree, the amount of energy in the food can be calculated.
CRD 2013
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Specimen Paper 4Documento26 páginasSpecimen Paper 4Thanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- 7J - Electrical Circuits Summary Notes: Current Voltage and ResistanceDocumento3 páginas7J - Electrical Circuits Summary Notes: Current Voltage and ResistanceThanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- 7F Simple Chemical ReactionsDocumento24 páginas7F Simple Chemical ReactionsThanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Rotations of ShapesDocumento4 páginasRotations of ShapesThanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- Gcse GeometryDocumento7 páginasGcse GeometryThanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- 7A - Cells Summary Notes: Movement Respiration SensitivityDocumento5 páginas7A - Cells Summary Notes: Movement Respiration SensitivityThanusha DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Name - Date - Energy Summit Poster ProjectDocumento3 páginasName - Date - Energy Summit Poster ProjectPranali Shah AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Solar Company Profile.Documento39 páginasSolar Company Profile.Meleckzedeck MetiliAinda não há avaliações
- SOFC THESIS Compson Charles e 200705 PHDDocumento285 páginasSOFC THESIS Compson Charles e 200705 PHDRajkumar KalmekarAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Parabolic Array Final Report From Kiran-WITH REQUIRED ModificationsDocumento8 páginasParabolic Array Final Report From Kiran-WITH REQUIRED ModificationsveeruduAinda não há avaliações
- Geothermal EnergyDocumento3 páginasGeothermal EnergyKyla Rosana OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- SolarPower Europe Global Market Outlook For Solar 2021 2025 V3Documento136 páginasSolarPower Europe Global Market Outlook For Solar 2021 2025 V3hjacaAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Energy - Definitions, Units, Magnitudes - CourseraDocumento1 páginaEnergy - Definitions, Units, Magnitudes - CourseraFranklin Josue Ticona CoaquiraAinda não há avaliações
- Nanosolar PowersheetDocumento18 páginasNanosolar PowersheetchethanAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Alternative Energy Systems in Building Design Greensource Books Mcgraw Hills Greensource by Peter GevorkianDocumento7 páginasAlternative Energy Systems in Building Design Greensource Books Mcgraw Hills Greensource by Peter GevorkianSatrio PrakosoAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- PROPOSAL Solar TubewellDocumento125 páginasPROPOSAL Solar TubewellSyed Asim Bokhari0% (1)
- Hydroelectric Power Plants in The Philippine 1Documento20 páginasHydroelectric Power Plants in The Philippine 1Gopalakrishnan SekharanAinda não há avaliações
- ICB ClassificationDocumento8 páginasICB Classificationchandra shekharAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- W1P5 Wind Turbine Power CurvesDocumento6 páginasW1P5 Wind Turbine Power CurvesperlenceAinda não há avaliações
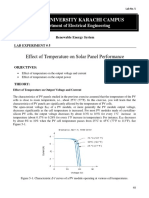
- Effect of Temp PV - Lab 5 PDFDocumento7 páginasEffect of Temp PV - Lab 5 PDFHumayun ArshadAinda não há avaliações
- NCER Syllabus - PTUDocumento2 páginasNCER Syllabus - PTUshalom_pklAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- GWO Annual Report 2018 FinalDocumento16 páginasGWO Annual Report 2018 Finalbravo480Ainda não há avaliações
- Broschuere PID KILLERDocumento12 páginasBroschuere PID KILLERAndrea AtzeniAinda não há avaliações
- PV For Large - Scal Solar Parks in EgyptDocumento18 páginasPV For Large - Scal Solar Parks in EgyptMahmoud A. SalemAinda não há avaliações
- Timbavati Solar Borehole PumpDocumento1 páginaTimbavati Solar Borehole PumpDale RobertsonAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Solar Energy and Its ApplicationsDocumento1 páginaFundamentals of Solar Energy and Its ApplicationsRaja SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- For KnowledgeDocumento4 páginasFor KnowledgeDeepak SashidharanAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Standards On Solar (2019) - 1Documento2 páginasIndian Standards On Solar (2019) - 1akash7strings100% (1)
- Solar Energy PerspectivesDocumento234 páginasSolar Energy PerspectivesFrancisco Javier Alvarez GarzaAinda não há avaliações
- High Efficiency Large PEM Electrolyzers: Giner, IncDocumento22 páginasHigh Efficiency Large PEM Electrolyzers: Giner, IncSyed Mushtaq AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Oslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeDocumento12 páginasOslo Mihai Neacsu, IcpeMihaiNeacsuAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Cell PresentationDocumento26 páginasSolar Cell Presentationraj1090Ainda não há avaliações
- UN-CECAR Renewable Energy Curriculum Development Workshop Group MeetingDocumento18 páginasUN-CECAR Renewable Energy Curriculum Development Workshop Group MeetingRabinAinda não há avaliações
- METKA EGN Company Profile PDFDocumento11 páginasMETKA EGN Company Profile PDFParas NakraAinda não há avaliações
- Solar PV String Guide-1Documento26 páginasSolar PV String Guide-1ankitAinda não há avaliações
- Project Delays / Cancellations Tracker: Date Power Plant NameDocumento10 páginasProject Delays / Cancellations Tracker: Date Power Plant NameSubhrangsu AdhikariAinda não há avaliações