Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nursing Care Plan
Enviado por
Joshua PascasioDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Care Plan
Enviado por
Joshua PascasioDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
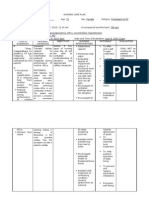
Nursing Care Plan Name: Joshua S. Pascasio Section: BSN 301 Date: July 7, 2013 Patient: Jamila G.
Datuimam
Assessment Subjective Cues: >The Clients mother verbalize minsan pansin mo talaga na nag hahabol siya ng hininga Objective cues: >Coughing >Shallow breathing >Irritable >RR 42
Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange related to build up of secretions as manifested by DOB and coughing
Planning Goal: After the nursing intervention the client will demonstrate a relief in breathing and maintain airway Objective: The parent will be able to verbalize the cause the therapeutic managements.
Participate in actions to maximize oxygenation.
Intervention Assess respiratory rate, depth, and ease. Observe color of skin, mucous membranes, and nailbeds, noting presence of peripheral cyanosis (nailbeds) or central cyanosis (circumoral). Assess mental status. Monitor heart rate/rhythm. Monitor body temperature, as indicated. Assist with comfort measures to reduce fever and chills, e.g., addition/removal of bedcovers, comfortable room temperature, tepid or cool water sponge bath. Maintain bed rest. Encourage use of relaxation techniques and diversional
Rationale Manifestations of respiratory distress are dependent on/and indicative of the degree of lung involvement and underlying general health status. Cyanosis of nailbeds may represent vasoconstriction or the bodys response to fever/chills; however, cyanosis of earlobes, mucous membranes, and skin around the mouth (warm membranes) is indicative of systemic hypoxemia. Restlessness, irritation, confusion, and somnolence may reflect hypoxemia/ decreased cerebral oxygenation. Tachycardia is usually present as a result of fever/dehydration but may represent a
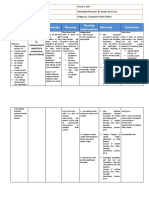
Evaluation After the nursing intervention the client demonstrates a relief in breathing and maintain airway Goal met The parent is able to verbalize the cause the therapeutic managements. Goal met
The client participates in actions to maximize oxygenation. Goal met
Nursing Care Plan Name: Joshua S. Pascasio Section: BSN 301 activities. Elevate head and encourage frequent position changes, deep breathing, and effective coughing. Assess level of anxiety. Encourage verbalization of concerns/feelings. Answer questions honestly. Visit frequently, arrange for SO/visitors to stay with patient as indicated. Observe for deterioration in condition, noting hypotension, copious amounts of pink/bloody sputum, pallor, cyanosis, and change in level of consciousness, severe dyspnea, and restlessness. Monitor ABGs, pulse oximetry. response to hypoxemia. High fever (common in bacterial pneumonia and influenza) greatly increases metabolic demands and oxygen consumption and alters cellular oxygenation. Prevents over exhaustion and reduces oxygen consumption/demands to facilitate resolution of infection. These measures promote maximal inspiration; enhance expectoration of secretions to improve ventilation. Anxiety is a manifestation of psychological concerns and physiological responses to hypoxia. Providing reassurance and enhancing sense of security can reduce Date: July 7, 2013 Patient: Jamila G. Datuimam
Nursing Care Plan Name: Joshua S. Pascasio Section: BSN 301 Administer oxygen therapy by appropriate means, e.g., nasal prongs, mask, Venturi mask. Administer medication as prescribe by the physician. Date: July 7, 2013 Patient: Jamila G. Datuimam the psychological component, thereby decreasing oxygen demand and adverse physiological responses. Shock and pulmonary edema are the most common causes of death in pneumonia and require immediate medical intervention. Follows progress of disease process and facilitates alterations in pulmonary therapy. The purpose of oxygen therapy is to maintain Pao2 above 60 mm Hg. Oxygen is administered by the method that provides appropriate delivery within the patients tolerance. Medications like bronchodilators will help the client to breath normally
Nursing Care Plan Name: Joshua S. Pascasio Section: BSN 301 Date: July 7, 2013 Patient: Jamila G. Datuimam
Você também pode gostar
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocumento6 páginasWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrAinda não há avaliações
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocumento7 páginasCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaAinda não há avaliações
- Pleural EffusionDocumento5 páginasPleural EffusionTerizla MobileAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocumento4 páginasIneffective Airway Clearance Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: IndependentIrish Eunice FelixAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento4 páginasNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiAinda não há avaliações
- BPN NCPDocumento6 páginasBPN NCPJoart EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocumento6 páginasBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPDidith AbanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotAinda não há avaliações
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocumento1 páginaTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeAinda não há avaliações
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADocumento2 páginasNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Planapi-309251523Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP PTBDocumento2 páginasNCP PTBKath TalubanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocumento7 páginas6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocumento3 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPJhel NabosAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LocDocumento2 páginasNCP LocMel RodolfoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocumento2 páginasNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocumento2 páginasNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 1Documento1 páginaNCP 1hsiriaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralRomzy BasañesAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALDocumento1 páginaHyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For ConcussionDocumento3 páginasNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Respiratory Failure NCPDocumento1 páginaRespiratory Failure NCPkyaw100% (1)
- Cva NCP AnxietyDocumento1 páginaCva NCP AnxietyQueenElsaDeVeraAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For CTTDocumento1 páginaNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory DistressDocumento2 páginasAcute Respiratory Distressminaanne100% (3)
- Knowledge Deficit - RegorDocumento3 páginasKnowledge Deficit - RegorAdrian MallarAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PTBDocumento6 páginasNCP PTBJay Dela VegaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan (Bronchiectasis)Documento4 páginasNursing Care Plan (Bronchiectasis)Leah QuiñanolaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP FeverDocumento2 páginasNCP FeverMary Joyce LimoicoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP TbiDocumento4 páginasNCP TbiWyen CabatbatAinda não há avaliações
- Gastrectomy NCP IBPDocumento3 páginasGastrectomy NCP IBPKevin T. Katada100% (1)
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocumento2 páginasAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPEsther RefuncionAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan HyperthermiaDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan Hyperthermiasamanthabox50% (2)
- Hypertension - 5 Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions: Nursing Care Plan For Hypertension Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento7 páginasHypertension - 5 Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions: Nursing Care Plan For Hypertension Decreased Cardiac Outputmelerine16Ainda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Klippel Trenaunay SyndromeDocumento3 páginasNCP Klippel Trenaunay SyndromePaola Marie VenusAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasNursing Care PlanAdreanah Martin RañisesAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllDocumento17 páginasNursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllsreekalaAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Nursing Careplan For FeverDocumento9 páginas1) Nursing Careplan For FeverY. Beatrice AbigailAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Management of PatientDocumento32 páginasNursing Management of PatientNoky KiaAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsDocumento13 páginasChap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsElaine Jean UayanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis For AsthmaDocumento6 páginasNursing Diagnosis For AsthmaTINAIDA33% (3)
- Nursing InterventionsDocumento18 páginasNursing InterventionsMark BellAinda não há avaliações
- PneumoniaDocumento17 páginasPneumoniajustin_saneAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento7 páginasNursing DiagnosisMariya Mikaela Garcia SoledadAinda não há avaliações
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocumento8 páginasBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- The Declaration of Independence Would Show Up 1/16Documento36 páginasThe Declaration of Independence Would Show Up 1/16Joshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st DayDocumento35 páginas1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st Day1st DayJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Job Satisfaction On Nursing Student of UPHSD-Cal Batches 2006-2008Documento13 páginasJob Satisfaction On Nursing Student of UPHSD-Cal Batches 2006-2008Joshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Special Senses (Eye and Ear)Documento2 páginasSpecial Senses (Eye and Ear)Joshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- AssessmentDocumento7 páginasAssessmentJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Qand ADocumento5 páginasQand AJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Histrionic Personality DisorderDocumento2 páginasHistrionic Personality DisorderJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Christine VanguardiaDocumento7 páginasChristine VanguardiaJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Chap 2 FinalThesis Chap 2 FinalDocumento13 páginasThesis Chap 2 FinalThesis Chap 2 FinalJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- World Literature: Mark Pascasio BSIT 801Documento5 páginasWorld Literature: Mark Pascasio BSIT 801Joshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Knowledge DeficitDocumento2 páginasNCP Knowledge DeficitFatima Dorcas Roxas Labausa100% (2)
- Faculty Loading System For Sti College Calamba Faculty UserDocumento1 páginaFaculty Loading System For Sti College Calamba Faculty UserJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- FebuxostatDocumento2 páginasFebuxostatJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Alzheimers Dementia Caregiver Case StudyDocumento9 páginasAlzheimers Dementia Caregiver Case StudyJoshua PascasioAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocumento67 páginasAcute Myocardial InfarctionJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- PI SQC 2015 R3 User GuideDocumento50 páginasPI SQC 2015 R3 User Guideislam ahmedAinda não há avaliações
- 32 EM GreenTechDocumento45 páginas32 EM GreenTechMark Lester RealAinda não há avaliações
- Fish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Documento293 páginasFish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Rodolfo Velazco100% (1)
- 23 Rosales V ERC PDFDocumento2 páginas23 Rosales V ERC PDFelobenia100% (2)
- Public Utility Accounting Manual 2018Documento115 páginasPublic Utility Accounting Manual 2018effieladureAinda não há avaliações
- A Study of Consumer Protection Act Related Related To Banking SectorDocumento7 páginasA Study of Consumer Protection Act Related Related To Banking SectorParag SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- TDS 39987 Easycoat Profile Decor 3MM Euk GBDocumento3 páginasTDS 39987 Easycoat Profile Decor 3MM Euk GBp4pubgwalyAinda não há avaliações
- Softwash ComparatorDocumento5 páginasSoftwash ComparatorFaheem MushtaqAinda não há avaliações
- RJSC - Form VII PDFDocumento4 páginasRJSC - Form VII PDFKamruzzaman SheikhAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction - Types and ApproachesDocumento88 páginasIntroduction - Types and ApproachesAritra DeyAinda não há avaliações
- Business Communication and Behavioural StudiesDocumento10 páginasBusiness Communication and Behavioural StudiesBhujangam NaiduAinda não há avaliações
- Individualism in Marketing CampaignDocumento6 páginasIndividualism in Marketing CampaignTrần Nguyễn Khánh TrangAinda não há avaliações
- Case DigestsDocumento12 páginasCase DigestsHusni B. SaripAinda não há avaliações
- Song FlowDocumento4 páginasSong FlowEhij ZheyAinda não há avaliações
- Thermoplastics Are Defined As Polymers That Can Be Melted and Recast AlmostDocumento5 páginasThermoplastics Are Defined As Polymers That Can Be Melted and Recast AlmostMnemosyneAinda não há avaliações
- Developing The Tourism Sector in The Sultanate of OmanDocumento18 páginasDeveloping The Tourism Sector in The Sultanate of OmanSalma Al-NamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study: Direct Selling ConceptDocumento20 páginasCase Study: Direct Selling Conceptbansi2kk0% (1)
- Law Sample QuestionDocumento2 páginasLaw Sample QuestionknmodiAinda não há avaliações
- BA 238. Berita Acara XCMGDocumento3 páginasBA 238. Berita Acara XCMGRizkiRamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Friday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksDocumento3 páginasFriday Night Mishaps, Listening Plus TasksCristina Stoian100% (1)
- Birhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5Documento50 páginasBirhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5woubshetAinda não há avaliações
- SQL Interview QuestionsDocumento89 páginasSQL Interview QuestionsVaneet Arora100% (2)
- Aci - The Financial Markets Association: Examination FormulaeDocumento8 páginasAci - The Financial Markets Association: Examination FormulaeJovan SsenkandwaAinda não há avaliações
- Apollo Hospital Chennai: NO: 16, BSNL TELESHOPPE, Greams Road 044 2999 1606Documento9 páginasApollo Hospital Chennai: NO: 16, BSNL TELESHOPPE, Greams Road 044 2999 1606Manas ChandaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestDocumento12 páginasUnderstanding The School Curriculum Close Encounter With The School Curriculum SPARK Your InterestJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaAinda não há avaliações
- Pechay Camote Buchi - Aug7Documento36 páginasPechay Camote Buchi - Aug7Rockie Alibio JuanicoAinda não há avaliações
- Cases Torts 7-29-17 DigestDocumento1 páginaCases Torts 7-29-17 Digestczabina fatima delicaAinda não há avaliações
- 2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTDocumento5 páginas2-Port Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DTIbrahim JaberAinda não há avaliações
- ERF 2019 0128 H160 Noise CertificationDocumento10 páginasERF 2019 0128 H160 Noise CertificationHelimanualAinda não há avaliações
- Doanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang CaoDocumento1 páginaDoanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang Caodoanhnghiep100% (1)