Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
5 Forces Porter Eng 2 PDF
Enviado por
Proph Timothy Tsaagane100%(2)100% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
179 visualizações2 páginasFive Forces Model
Título original
5-forces-Porter-eng-2.pdf
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoFive Forces Model
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(2)100% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
179 visualizações2 páginas5 Forces Porter Eng 2 PDF
Enviado por
Proph Timothy TsaaganeFive Forces Model
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
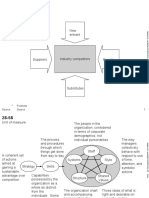
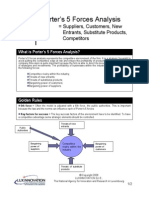
Porters 5 Forces Analysis
= Suppliers, Customers, New Entrants, Substitute Products, Competitors
What is Porters 5 Forces Analysis?
Porters 5 forces analysis represents the competitive environment of the firm. It is a strategic foresight to avoid putting the competitive edge at risk and ensure the profitability of products on a long term. For the company this vision is quite important because the firm is able to direct its innovations in terms of choice of strategies and investments. The profitability of businesses within the industrial structure depends on the following forces: Competitive rivalry within the industry; Threats of new entrants; Threats of substitutes products; Bargaining power of customers; Bargaining power of suppliers.
Golden Rules
6th force = Often the model is adjusted with a 6th force, the public authorities. This is important because the law and the norms can influence each of Porters 5 forces. Key factors for success = The key success factors of the environment have to be identified. To have a competitive advantage some strategic elements should be controlled.
Threats of new entrants
Public Authorities
Bargaining power of suppliers
Competitive rivalry within the industry
Bargaining power of customers
Threats of substitute products
Copyright 2008 LUXINNOVATION G.I.E., The National Agency for Innovation and Research in Luxembourg
1/2
Porters 5 Forces Analysis
= Suppliers, Customers, New Entrants, Substitute Products, Competitors
Structure of Porters 5 Forces Analysis
The competitive rivalry within the industry The competition between firms determines the attractiveness of a sector. Companies are struggling to maintain their power. The competition changes based on sector development, diversity and the existence of barriers to enter. In addition it is an analysis of the number of competitors, products, brands, strengths and weaknesses, strategies, market shares, . The threat of new entrants It is in a companys interest to create barriers to prevent its competitors to enter to market. They are either new companies, or companies which intend to diversify. This barriers can be legal (patent regulations, ), or industrial (products or single brands, ), . The arrival of new entrants also depends on the size of the market (economy of scale), the reputation of a company already installed, the cost of entry, access to raw materials, technical standards, cultural barriers,. The threat of substitute products The substitute products can be considered as an alternative compared to supply on the market. These products are due to changes in the state of technology or to the innovation. The companies see their products be replaced by different products. These products often have a better price/quality report and come from sectors with higher profits. These substitute products can be dangerous and the company should anticipate to cope with this threat. The bargaining power of suppliers The bargaining power of suppliers is very important in a market. Powerful suppliers can impose their conditions in terms of price, quality and quantity. On the other hand if there are a lot of suppliers their influence is weaker. One has to analyze the number of realized orders, the cost of changing the supplier, the presence of raw materials, . The bargaining power of customers If the bargaining power of customers is high, they influence the profitability of the market by imposing their requirements in terms of price, service, quality,. Choosing clients is crucial because a firm should avoid to be in a situation of dependence. The level of concentration of customers gives them more or less power. Generally their bargaining power tends to be inversely proportional to that of the suppliers.
Copyright 2008 LUXINNOVATION G.I.E., The National Agency for Innovation and Research in Luxembourg
2/2
Você também pode gostar
- What Is Deloitte Consulting?: Created August 5, 2004Documento15 páginasWhat Is Deloitte Consulting?: Created August 5, 2004Kapil KaushalAinda não há avaliações
- Consulting Process 1Documento20 páginasConsulting Process 1Tanit Paochinda100% (1)
- ''Summary of What Is Strategy''Documento3 páginas''Summary of What Is Strategy''PradIpta KaphleAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey's 10 Timeless Tests of StrategyDocumento1 páginaMcKinsey's 10 Timeless Tests of StrategyVivek Sarthi100% (1)
- BAIN BRIEF Strategic Planning That Produces Real StrategyDocumento8 páginasBAIN BRIEF Strategic Planning That Produces Real StrategyHoanabc123Ainda não há avaliações
- Strategy Consultants Presentation ToolkitDocumento23 páginasStrategy Consultants Presentation ToolkitMonal Patel100% (4)
- Building A Market Model and Market SizingDocumento12 páginasBuilding A Market Model and Market SizingSTRATICXAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy Consultants Presentation ToolkitDocumento23 páginasStrategy Consultants Presentation ToolkitTomAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Solving StrategiesDocumento5 páginasProblem Solving Strategieslowela becodo100% (1)
- Bain & Co. Writing Style Compilation (Updated)Documento56 páginasBain & Co. Writing Style Compilation (Updated)vinod100% (1)
- Elegant Structures Consulting Toolkit by SlidesgoDocumento80 páginasElegant Structures Consulting Toolkit by SlidesgoAbdías MelgarAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Step Consulting FrameworkDocumento60 páginas7 Step Consulting FrameworkJimmy Parent Jr.100% (4)
- McKinsey MindDocumento1 páginaMcKinsey MindEno Budo100% (2)
- Recrultment Q&A of McKinsey, BCG, A.T. Kearney, BoozDocumento5 páginasRecrultment Q&A of McKinsey, BCG, A.T. Kearney, BoozGen Long100% (1)
- Bain Consutlant Skills Copy 2Documento16 páginasBain Consutlant Skills Copy 2ki100% (2)
- McKinsey PresentationDocumento18 páginasMcKinsey PresentationAman ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- How P&G Presents Data To Decision-Makers - Tom Davenport - Harvard Business ReviewDocumento4 páginasHow P&G Presents Data To Decision-Makers - Tom Davenport - Harvard Business Reviewali4002Ainda não há avaliações
- PSTDocumento8 páginasPSThenreeoktaAinda não há avaliações
- BAIN GUIDE Management Tools 2015 Executives GuideDocumento68 páginasBAIN GUIDE Management Tools 2015 Executives Guidekernelexploit100% (7)
- Valuation Modeling 1.1Documento13 páginasValuation Modeling 1.1Sourav Sharma100% (2)
- Productize Yourself - Wisdom TheoryDocumento136 páginasProductize Yourself - Wisdom Theorypierrej.bachelier100% (1)
- Bain & CoDocumento4 páginasBain & Coebwhitaker67% (9)
- Steering Committee Working DraftDocumento221 páginasSteering Committee Working DraftQUEST100% (2)
- Your Action Plan: Big Picture ProcessDocumento12 páginasYour Action Plan: Big Picture ProcessSusan BvochoraAinda não há avaliações
- The Ten Types of Innovation (Doblin Inc.)Documento1 páginaThe Ten Types of Innovation (Doblin Inc.)Berry CheungAinda não há avaliações
- Bains - On ConsultingDocumento28 páginasBains - On Consultingturkeyegypt100% (2)
- Forces at Work: Unit of MeasureDocumento16 páginasForces at Work: Unit of MeasureaAinda não há avaliações
- Management Consulting Book The Mckinsey MindDocumento23 páginasManagement Consulting Book The Mckinsey Mindthanhkaf50% (2)
- T B C G: Cracking A Bcg-Style CaseDocumento21 páginasT B C G: Cracking A Bcg-Style CaseJamesAinda não há avaliações
- A Unique Selling PropositionDocumento56 páginasA Unique Selling PropositionEdwin B. TaburadaAinda não há avaliações
- EOQ Model: Ken HomaDocumento18 páginasEOQ Model: Ken HomatohemaAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey Survey-Managing SustainabilityDocumento10 páginasMcKinsey Survey-Managing SustainabilityAminur RahamanAinda não há avaliações
- Bain ThanksgivingDocumento12 páginasBain Thanksgivingjgravis100% (1)
- Framing Complex Problem Part 3Documento135 páginasFraming Complex Problem Part 3Kunal Deore100% (2)
- StartingUp McKinsey (1) - NotepadDocumento117 páginasStartingUp McKinsey (1) - Notepadha2am100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Barbara Minto-The Minto Pyramid Principle - Logic in Writing, Thinking, & Problem SolvingDocumento11 páginasChapter 1 Barbara Minto-The Minto Pyramid Principle - Logic in Writing, Thinking, & Problem SolvingfahmynastAinda não há avaliações
- McKinsey On M&ADocumento7 páginasMcKinsey On M&AmfmosmanAinda não há avaliações
- Strategyand The Mandate For Multichannel RetailDocumento20 páginasStrategyand The Mandate For Multichannel RetailHarish BalasubramanianAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Analysis Tools BookDocumento40 páginasStrategic Analysis Tools BookHanh Nguyen89% (9)
- PWC Ma Integration Capturing SynergiesDocumento10 páginasPWC Ma Integration Capturing SynergiesKamalapati BeheraAinda não há avaliações
- Bain Management Tools 2007 StrategyDocumento74 páginasBain Management Tools 2007 Strategyavik_bang100% (2)
- MckinseyDocumento15 páginasMckinseyPawanKumar1984100% (4)
- Frame Issue TreeDocumento38 páginasFrame Issue Treefrankdoyle100% (1)
- Management Consulting 101 So, You Might Want To Be A ConsultantDocumento58 páginasManagement Consulting 101 So, You Might Want To Be A ConsultantTrisha PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Strategyand Commercial Excellence ProgramsDocumento16 páginasStrategyand Commercial Excellence Programspulsar77Ainda não há avaliações
- Bain & Co. StrategyDocumento30 páginasBain & Co. Strategyapi-1096998171% (7)
- Porter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4Documento28 páginasPorter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4mariaAinda não há avaliações
- Bain TrainingDocumento16 páginasBain TrainingRishikesh MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Why Has Strategy Become Irrelevant? Understanding The Complete Strategy LandscapeDocumento12 páginasWhy Has Strategy Become Irrelevant? Understanding The Complete Strategy LandscapeAnish KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Module One: - New Consultant Skill BuildingDocumento16 páginasModule One: - New Consultant Skill Buildingki100% (2)
- Accenture Strategy Breaking Habits PDFDocumento12 páginasAccenture Strategy Breaking Habits PDFAmine AïdiAinda não há avaliações
- Arthur Anderson ToolbookDocumento42 páginasArthur Anderson ToolbookRupee Rudolf Lucy Ha100% (15)
- Growth Strategy Process Flow A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo EverandGrowth Strategy Process Flow A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Business consultant A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo EverandBusiness consultant A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis PorterDocumento2 páginasAnalisis PorterAlim AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- 5forcesporter en PDFDocumento2 páginas5forcesporter en PDFWin BoAinda não há avaliações
- Porter 5 Forces - SWOT - Analyzing The Business EnvironmentDocumento15 páginasPorter 5 Forces - SWOT - Analyzing The Business EnvironmentpuchkishenoAinda não há avaliações
- Porter Analysis ReportingDocumento5 páginasPorter Analysis ReportingMinini NestAinda não há avaliações
- 006.electr - Textual Criticism MethodDocumento9 páginas006.electr - Textual Criticism MethodjltwhtteAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Questions Wise Women Ask - Kingsley Okonkwo PDFDocumento62 páginas7 Questions Wise Women Ask - Kingsley Okonkwo PDFBlessing Chirwa88% (16)
- Work SamplingDocumento25 páginasWork SamplingProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Rate of ReturnDocumento3 páginasAccounting Rate of ReturnDeep Debnath100% (1)
- Kuhn, T - The Function of Dogma in Scientific ResearchDocumento23 páginasKuhn, T - The Function of Dogma in Scientific ResearchDaniel Bernal HiguaAinda não há avaliações
- Productivity MethodologiesDocumento2 páginasProductivity MethodologiesProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Work SamplingDocumento24 páginasWork SamplingProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Xhosa Phrasebook: Pronunciation Guide Vowels Phrase List BasicsDocumento9 páginasXhosa Phrasebook: Pronunciation Guide Vowels Phrase List BasicsProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Taphole Management PDFDocumento7 páginasTaphole Management PDFProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Angelology PDFDocumento16 páginasAngelology PDFProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Introductory Economics (12th Class CBSE)Documento252 páginasIntroductory Economics (12th Class CBSE)Vipul Verma87% (31)
- Employee Training and Development PDFDocumento8 páginasEmployee Training and Development PDFProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Alesis Drum Module Service ManualDocumento39 páginasAlesis Drum Module Service ManualProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- 75583Documento36 páginas75583Memyself MyselfAinda não há avaliações
- Flu or SparDocumento11 páginasFlu or SparProph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- AlesisD4 ManualDocumento50 páginasAlesisD4 ManualgomaticAinda não há avaliações
- Sharp Financial Calculator Manual EL738Documento88 páginasSharp Financial Calculator Manual EL738Proph Timothy TsaaganeAinda não há avaliações
- Powering Up TeamsDocumento19 páginasPowering Up TeamsfziliottiAinda não há avaliações
- Chattanooga Ice Cream DivisionDocumento11 páginasChattanooga Ice Cream DivisionWilliamedia ShephardAinda não há avaliações
- BRTADocumento13 páginasBRTAImam Jafar Sadek SajeedAinda não há avaliações
- Article On Staff TrainingDocumento19 páginasArticle On Staff TrainingAamir SaeedAinda não há avaliações
- 988 - Fencing and Exterior Improvements Essentials - Quality Plan PDFDocumento10 páginas988 - Fencing and Exterior Improvements Essentials - Quality Plan PDFأشرف عليAinda não há avaliações
- Lead Management in Salesforce - EbookDocumento51 páginasLead Management in Salesforce - EbookShashank NaikAinda não há avaliações
- Agile ManufacturingDocumento23 páginasAgile Manufacturingjhpatel100% (1)
- Q1W7 Nature Types Levels PlanningDocumento22 páginasQ1W7 Nature Types Levels PlanningDaisiree PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Serio Availability ManagementDocumento18 páginasSerio Availability ManagementDang Ngoc TrungAinda não há avaliações
- Calyx Case Study Analysis Example PDFDocumento3 páginasCalyx Case Study Analysis Example PDFjohnsobdAinda não há avaliações
- Manual of Works AuditDocumento566 páginasManual of Works Auditsaurabh singh100% (1)
- Buat PPT Liat Jurnal Eproc, Penerapan Lean Manufacturing (PDF), Bookmark Di ChromeDocumento1 páginaBuat PPT Liat Jurnal Eproc, Penerapan Lean Manufacturing (PDF), Bookmark Di ChromeJoice MargarethaAinda não há avaliações
- Julekha Mohanty: ProfileDocumento3 páginasJulekha Mohanty: Profilevikrant sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Employment Opportunities: The Nelson Mandela African Institute of Science and Technology (NM-AIST)Documento8 páginasEmployment Opportunities: The Nelson Mandela African Institute of Science and Technology (NM-AIST)Rashid BumarwaAinda não há avaliações
- Human Resource Management Practices of Bangladesh: IDLC Finance LimitedDocumento20 páginasHuman Resource Management Practices of Bangladesh: IDLC Finance LimitedMahabub AlamAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Engineering Scit B. Tech It/Cse/Cce VI Semester First Mid Term Examination: 2021-22 Data Mining and Warehousing (IT3240)Documento2 páginasFaculty of Engineering Scit B. Tech It/Cse/Cce VI Semester First Mid Term Examination: 2021-22 Data Mining and Warehousing (IT3240)Samarth issarAinda não há avaliações
- Daft Presentation 6 EnvironmentDocumento18 páginasDaft Presentation 6 EnvironmentJuan Manuel OvalleAinda não há avaliações
- AP01-EV04 - "Inglés-Hoja de Vida" PDFDocumento3 páginasAP01-EV04 - "Inglés-Hoja de Vida" PDFcamilo arango50% (2)
- Change in Structure-Notes and QuestionsDocumento5 páginasChange in Structure-Notes and QuestionsBilliee ButccherAinda não há avaliações
- GG Guide To Risk ManagementDocumento43 páginasGG Guide To Risk ManagementSamrat SinghaAinda não há avaliações
- Operations Strategy at GalanzDocumento7 páginasOperations Strategy at GalanzAshishAg91Ainda não há avaliações
- Operations Esterline Case Report Bog1 04 Feb 2012 PDF FreeDocumento4 páginasOperations Esterline Case Report Bog1 04 Feb 2012 PDF FreeJonathan OngAinda não há avaliações
- Rahima KhatunDocumento3 páginasRahima KhatunDewan Khalid Hasan ShuvoAinda não há avaliações
- BSBMKG609 TaskDocumento9 páginasBSBMKG609 TaskJoanne Navarro Almeria33% (3)
- Employee Performance Review - Organic (Sup and Up)Documento4 páginasEmployee Performance Review - Organic (Sup and Up)Paul André OfianaAinda não há avaliações
- IBDP Business Management Subject Guide (First Assessment 2024)Documento77 páginasIBDP Business Management Subject Guide (First Assessment 2024)jadenAinda não há avaliações
- GurgaonDocumento8 páginasGurgaonkshitijsahuAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Analytics Instructional Manual Version 1.0Documento14 páginasMarketing Analytics Instructional Manual Version 1.0fabriAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Auditing Ch11Documento31 páginasModern Auditing Ch11astoeti_sriAinda não há avaliações
- Toor, S.R., & Ogunlana, S. O. (2010) - "Beyond The Iron Triangle' Stakeholder Perception of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) For Large-Scale Public-Sector Development ProjectsDocumento11 páginasToor, S.R., & Ogunlana, S. O. (2010) - "Beyond The Iron Triangle' Stakeholder Perception of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) For Large-Scale Public-Sector Development ProjectsDavid SabaflyAinda não há avaliações