Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Discussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAIN
Enviado por
Kesha GopalDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Discussion MICROBIOLOGY SIMPLE STAIN
Enviado por
Kesha GopalDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
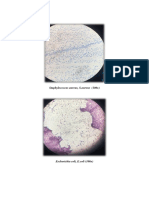
Discussion: SIMPLE STAINS I) Staphylococcus aureus The shape of Staphylococcus aureus is spherical or in other words, they were seen
een in clusters of cocci. The size of this bacteria is small. Staphylococcus aureus is arranged like a bunch of grapes.
II) Candida albicans Candida albicans is oval shaped. It is a yeast that exists in bundle or in a unicellular structure.
III) Escherichia coli Escherichia coli is a rod shaped bacterium. It is short and it has individual arrangement. It is not clustered together like Staphylococcus aureus.
IV) Bacillus subtilis Bacillus subtilis are rod shaped bacteria. Appears to have individual arrangement. Has noticeable space between each bacterium.
Simple staining is a method that is used in microscopy to enhance the visualization of microscopic images. Stains and dyes are the two major chemicals that are often used in simple staining to accentuate the structure and the morphology of the bacterial cell. In this experiment, methylene blue solution was used to stain the bacterial smears. Why is methylene blue used to stain the bacterial cells in this experiment? Since methylene blue is a basic dye, it has a high affinity for acidic substances. The presence of negatively charged molecules in the cells causes it to be attracted to the positively charged dye. Due to the staining procedure, the morphology of the bacterial cell will be clearly seen when examined under the oil immersion. From the observation, we can infer that both Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis are rod shaped bacteria. However, we can note the difference in their arrangment. Escherichia coli is arranged in an individual manner with noticeable space between each cell, whereas for Bacillus subtilis, each rod appears to be longer than of Escherichia coli. The bacteria Staphylococcus aureus appears oval shaped, like a bunched grape like clusters. It is also very small in size compared to the other three bacteria.
Candida albicans is a type of yeast which is found in everyone in small amount. The bacterium is oval in shape and is often the cause of yeast infection known as Candidiasis. Conclusions: I) II) The morphology of the bacteria were observed with the aid of simple stain. Simple staining technique is the best method to observe the morphology, size and the arrangement of bacteria.
DIFFERENTIAL STAINING I) Klebsiella aerogenes Klebsiella aerogenes that were observed were stained red. This indicates that it is a gram negative bacteria.
II) Escherichia coli Escherichia coli are gram negative bacteria. They were observed to be red in colour.
III) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus is a gram positive bacteria. They were observed to be stained blue but with slight hints of pink.
IV) Bacillus subtilis Bacillus subtilis is a gram positive bacteria. The slide observed showed that the bacteria was stained blue with very light tints of pink.
The Gram staining method is a technique that was invented by a Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Joachim Gram in 1884 to classify bacteria into two major classes, that is gram positive bacteria and gram negative bacteria. This technique is still widely used until today. Gram positive bacteria are stained dark blue or violet when observed under the microscope whereas gram negative bacteria are stained pink in colour. Gram negative bacteria are unable to retain the crystal violet stain, thus taking in the colour of the counter stain, safranine (red). Klebsiella aerogenes and Escherichia coli are gram negative bacteria. This is because they have a thin layer of peptidoglycan that causes them to lose the blue colour of the crystal
violet dye (primary stain) when they are decolourized with alcohol(ethanol). Thus, they absorb the red colour of the safranine causing both the bacteria to appear red. However, it should be noted that gram negative bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics compared to gram positive bacteria despite their thin layer of peptidoglycan. This resistance is because the former possess a lipid rich membrane that is relatively impermeable. Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis are gram positive bacteria. Both the bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan that causes them to retain the colour of the crystal violet dye. These bacteria have a high amount of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that enables them to retain the colour of the primary stain. Conclusions : I) II) The Gram staining procedure is the simplest method to classify bacteria into gram positive and gram negative. Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis were identified to be gram positive bacteria. Klebsiella aerogenes and Escherichia coli were identified to be gram negative bacteria.
Questions : 1) What colour would you expect Staph.aureus to be if the iodine step was omitted in the gram staining procedure? The role of iodine in gram stain is to act a mordant (a substance that sets dye). When used in the gram staining procedure, it is also known as a caustic. It functions to form large crystals with the crystal violet dye. When the crystal violet dye mixes with iodine, it will form a crystal violet iodine (CVI) complex. This complex is larger than the crystal violet molecule and is easier for the gram positive bacteria to retain the blue dye. If the iodine step was omitted in the gram staining procedure, the crystal violet dye that is used will not be able to form the CVI complex. Therefore, Staph.aureus will be decolourized by the alcohol and will appear to be red in colour (gram negative) when observed under the microscope. 2) Why would methylene blue not work just as well as safranine for counterstaining in the gram staining procedure? Initially, we use the crystal violet dye to stain the bacterial cells. The colour of this dye can vary from purple to dark blue. If methylene blue was used for counterstaining, it would be difficult to differentiate between a gram positive bacteria and a gram negative bacteria as methylene blue and the crystal violet dye have almost the same colour. Therefore, methylene blue will not work as an effective counter stain. However if safranine is used, we can clearly see the contrast between the blue colour of
the crystal violet dye and the red colour of the safranine making it easier for us to distinguish between a gram positive and a gram negative bacteria.
Você também pode gostar
- Microscopy and Differential Staining of BacteriaDocumento9 páginasMicroscopy and Differential Staining of BacteriaSasha100% (2)
- Gram Staining TechniqueDocumento9 páginasGram Staining TechniqueYusof Sundang100% (1)
- Simple and Gram StainingDocumento4 páginasSimple and Gram Stainingqueenbullex100% (3)
- Experiment 8 Determination of Antimicrobial ActivityDocumento6 páginasExperiment 8 Determination of Antimicrobial ActivityAli Imran Mohamad100% (1)
- Lab Report Exp 5Documento5 páginasLab Report Exp 5api-384913960Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio Gram StainingDocumento7 páginasBio Gram StainingAlexander Sebastian100% (1)
- IMVIC TestDocumento13 páginasIMVIC TestLaksilu Viduraga Peiris100% (5)
- Blood Type Testing Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasBlood Type Testing Lab Reportapi-282851608Ainda não há avaliações
- Identification of Bacteria Using Gram Staining MethodDocumento7 páginasIdentification of Bacteria Using Gram Staining MethodDani MughalAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 1 Microbe Aseptic TechniqueDocumento9 páginasLAB 1 Microbe Aseptic TechniqueYasharudin YusufAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report - BacteriaDocumento5 páginasLab Report - Bacteriadean01602683% (6)
- Aseptic Technique Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasAseptic Technique Lab ReportSleepyHead ˋωˊAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Microbiology Lab Reporting Gram StainingDocumento26 páginasBasic Microbiology Lab Reporting Gram StainingNeayzahn AcesSka100% (1)
- Gram Staining Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasGram Staining Lab ReportAkash MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Isolation of Bacteria To Pure CultureDocumento7 páginasIsolation of Bacteria To Pure CultureMike RelucioAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5 - Microbiology: (Gram Staining)Documento6 páginasLab 5 - Microbiology: (Gram Staining)api-383698554Ainda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Transformation Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasAP Biology Transformation Lab Reportdstaples7100% (17)
- Blood Typing PresentationDocumento39 páginasBlood Typing PresentationNezzeh Clair D. BermejoAinda não há avaliações
- Lab ReportDocumento4 páginasLab Reportfwagner1100% (3)
- 4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFDocumento10 páginas4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFNurul IzzahAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Lab Report on Distribution, Disinfection and SterilizationDocumento5 páginasMicrobiology Lab Report on Distribution, Disinfection and SterilizationFarhinAinda não há avaliações
- Bio pGLO Lab ReportDocumento5 páginasBio pGLO Lab ReportNicole Robertshaw100% (1)
- Unknown Bacteria Lab Report ResultsDocumento11 páginasUnknown Bacteria Lab Report ResultsSanzida Taslim100% (1)
- Lab Report 5 MicrobiologyDocumento8 páginasLab Report 5 Microbiologyapi-384857069100% (1)
- Microbiology Lab Report 2Documento13 páginasMicrobiology Lab Report 2Kah Jun0% (2)
- Ubiquity of Microorganisms RevealedDocumento16 páginasUbiquity of Microorganisms RevealedNichols Amy TarunAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Lab Report AntibioticsDocumento8 páginasBiology Lab Report AntibioticsLoore Liflander100% (1)
- Disc Diffusion Susceptibility MethodsDocumento6 páginasDisc Diffusion Susceptibility MethodswaheedrbhAinda não há avaliações
- Detection and Enumeration of The Most Probable Number of ColiformsDocumento6 páginasDetection and Enumeration of The Most Probable Number of ColiformsLaksilu Viduraga Peiris83% (6)
- Pure Culture TechniqueDocumento6 páginasPure Culture Techniquebetu8137Ainda não há avaliações
- Microbiology-Disinfectants Lab ReportDocumento2 páginasMicrobiology-Disinfectants Lab Reportsaraebo25% (4)
- Aseptic Technique Lab ReportDocumento7 páginasAseptic Technique Lab ReportEugenTutunaru100% (2)
- EnumerationDocumento7 páginasEnumerationSikin Sikin100% (1)
- SDS-PAGE Separates Proteins by SizeDocumento11 páginasSDS-PAGE Separates Proteins by SizeBantita Treepong100% (1)
- Microbiology Lab QuestionsDocumento12 páginasMicrobiology Lab QuestionsKumar KP100% (2)
- Unknown Lab ReportDocumento12 páginasUnknown Lab Reportnkuligowski90% (29)
- Quantitative protein analysis: Determining protein concentration using Bradford assayDocumento3 páginasQuantitative protein analysis: Determining protein concentration using Bradford assaySean Herman100% (1)
- Aseptic Technique: Preventing Harmful Bacterial ContaminationDocumento3 páginasAseptic Technique: Preventing Harmful Bacterial ContaminationMarlene Tubieros - Inducil57% (7)
- Enzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportDocumento4 páginasEnzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportAnthony100% (3)
- Gram Positive & Gram Negative BacteriaDocumento1 páginaGram Positive & Gram Negative BacteriaZubair ShafqatAinda não há avaliações
- CMB Lab Written Report Ex 4Documento5 páginasCMB Lab Written Report Ex 4Fiona SimeonAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Gram Stain Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasMicrobiology Gram Stain Lab Reportnokwanda89% (19)
- (BIO 203 L) Exercise 2 Winogradsky (Preliminary)Documento5 páginas(BIO 203 L) Exercise 2 Winogradsky (Preliminary)Beatrice Del RosarioAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 6Documento12 páginasExperiment 6Keo De Leon100% (3)
- Cellular Respiration Lab ReportDocumento6 páginasCellular Respiration Lab Reportbetojaimes83% (6)
- Types of ImmunofluorescenceDocumento2 páginasTypes of ImmunofluorescenceMuthiah RamanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Fast StainingDocumento4 páginasAcid Fast Stainingchaudhary TahiraliAinda não há avaliações
- MacConkey AgarDocumento12 páginasMacConkey Agardessy asandraAinda não há avaliações
- Isolate Pure Cultures Streak PlatingDocumento8 páginasIsolate Pure Cultures Streak PlatingRoan Eam TanAinda não há avaliações
- Streak PlatesDocumento0 páginaStreak PlatesJenry Reyes TrispaAinda não há avaliações
- Fermentation Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasFermentation Lab ReportSarah Sulon77% (13)
- Starch HydrolysisDocumento3 páginasStarch HydrolysisWiwit ArumAinda não há avaliações
- Unknown Lab Report 13Documento20 páginasUnknown Lab Report 13jordan holstAinda não há avaliações
- Microscope 1. Objective Learn The Basic Techniques For The BacterialDocumento4 páginasMicroscope 1. Objective Learn The Basic Techniques For The Bacterialbnu-robert83% (12)
- Prac 8 Micro 2 S2 Lab Report 2020Documento5 páginasPrac 8 Micro 2 S2 Lab Report 2020NkosinathiAinda não há avaliações
- Gram Simple Stain PDFDocumento5 páginasGram Simple Stain PDFmalasuriAinda não há avaliações
- School of Food Science and Environmental Health Lab Report Gram StainDocumento8 páginasSchool of Food Science and Environmental Health Lab Report Gram StainOliaAinda não há avaliações
- Gabinete - 2A - Laboratory Activity 2Documento5 páginasGabinete - 2A - Laboratory Activity 2Nathaniel GABINETEAinda não há avaliações
- Result:: Staphylococcus Aureus, S.aureus (100x)Documento3 páginasResult:: Staphylococcus Aureus, S.aureus (100x)Ayuni Nadrah Bt KamarujamanAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 6,7,8,9,10,11Documento26 páginasLab Report 6,7,8,9,10,11Rani anak matAinda não há avaliações
- Report On COVID-19 Outbreak at Holyoke Soldiers' HomeDocumento174 páginasReport On COVID-19 Outbreak at Holyoke Soldiers' HomeGreg Saulmon100% (8)
- Meckel's DiverticulumDocumento2 páginasMeckel's Diverticulumlorenz_gtlAinda não há avaliações
- LMMJ1M Medicolegal Aspects of Physical Injuries 1Documento7 páginasLMMJ1M Medicolegal Aspects of Physical Injuries 1Nat HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation on Trachoma with Slit Lamp Examination FindingsDocumento20 páginasCase Presentation on Trachoma with Slit Lamp Examination Findingsdimple alluriAinda não há avaliações
- (13360329 - Endocrine Regulations) Pheochromocytoma, Diagnosis and Treatment - Review of The LiteratureDocumento14 páginas(13360329 - Endocrine Regulations) Pheochromocytoma, Diagnosis and Treatment - Review of The LiteratureNi Nyoman Indirawati KusumaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition Essentials for Medical StudentsDocumento53 páginasNutrition Essentials for Medical StudentsJerahmeel Sombilon GenillaAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamin b12 Deficiency Associated With Depression PDFDocumento7 páginasVitamin b12 Deficiency Associated With Depression PDFRocco LamponeAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction 1 RC PDocumento19 páginasIntroduction 1 RC PMark S.PAinda não há avaliações
- Condylar Fracture - 2Documento72 páginasCondylar Fracture - 2Saranya MohanAinda não há avaliações
- NCLEX - Fluids and ElectrolytesDocumento4 páginasNCLEX - Fluids and ElectrolytesissaiahnicolleAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Architectural Spaces For The Mobility ImpairedDocumento30 páginasDesigning Architectural Spaces For The Mobility ImpairedWayne Anthony MorrisAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Rules and Regulations For Swimming Pool UsageDocumento3 páginasSample Rules and Regulations For Swimming Pool UsageImee S. YuAinda não há avaliações
- Post Test On Needle Stick InjuryDocumento4 páginasPost Test On Needle Stick InjurysunitapuniaAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Guide to Sleep DisordersDocumento23 páginasClinical Guide to Sleep DisordersBEA RADAAinda não há avaliações
- Homeo For SeniorsDocumento17 páginasHomeo For SeniorsAngela100% (1)
- World Health DayDocumento2 páginasWorld Health DaySahilAinda não há avaliações
- Enrichment Utbk SBMPTN: Tes Bahasa Inggris 2Documento5 páginasEnrichment Utbk SBMPTN: Tes Bahasa Inggris 2Bagus DentasAinda não há avaliações
- Sputum Specimen CollectionDocumento14 páginasSputum Specimen CollectionHoneylouAzOpondaAinda não há avaliações
- Gall StonesDocumento26 páginasGall StonesNia SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Health Illness ContinuumDocumento15 páginasHealth Illness ContinuumJeyarani Karunanithi100% (1)
- B.3 Lesson 10 Assessment Genetics Transfer TaskDocumento5 páginasB.3 Lesson 10 Assessment Genetics Transfer TaskknealAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study of Patient With CholelithiasisDocumento3 páginasCase Study of Patient With CholelithiasisBer AnneAinda não há avaliações
- Globin Genes and Thalassemia (Class)Documento44 páginasGlobin Genes and Thalassemia (Class)Naman MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Parameters Marked Are Under The Scope of NABL M (EL) TDocumento3 páginasParameters Marked Are Under The Scope of NABL M (EL) TTanmay SitokeAinda não há avaliações
- Unique UVC Light Bot Deep Cleans Any Space in MinutesDocumento7 páginasUnique UVC Light Bot Deep Cleans Any Space in Minutessutan IskandarsyahAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge and Attitudes of Patients Towards Elephantiasis at Rukunyu Health Centre-Iv Kamwengye DistrictDocumento50 páginasKnowledge and Attitudes of Patients Towards Elephantiasis at Rukunyu Health Centre-Iv Kamwengye DistrictBayo Kakyinire100% (1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis OrenciaDocumento8 páginasRheumatoid Arthritis OrenciavishwanathAinda não há avaliações
- Insert Bioelisa SYPHILIS 3.0Documento8 páginasInsert Bioelisa SYPHILIS 3.0Ika Afriliya WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- The Right Equipment For Each Job: 3M Speedglas Welding Safety Catalogue 2022Documento63 páginasThe Right Equipment For Each Job: 3M Speedglas Welding Safety Catalogue 2022wegigok769 dekaps.comAinda não há avaliações
- Fever in Children With ChemoteraphyDocumento23 páginasFever in Children With ChemoteraphyImanuel Far-FarAinda não há avaliações