Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Kasdkfj
Enviado por
Pravallika KolliparaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Kasdkfj
Enviado por
Pravallika KolliparaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
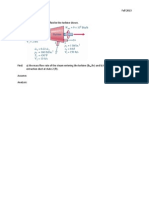
Problem 4.1 Given & Find: a) R-134a at T = 60oC and v = 0.072 m3/kg. Find P and h.
b) Ammonia at P = 8 bar and v = 0.005 m3/kg. Find T and u. c) R-22 at T = -10oC and u = 200 kJ/kg. Find P and v.
Analysis:
Problem 4.2 Given: R-134a is compressed with no heat transfer in a piston-cylinder assembly from 30 lbf/in2, 20oF to 160 lbf/in2. The mass of refrigerant is 0.04 lbm. For the refrigerant as the system, W = -0.56 Btu. Kinetic and potential energy changes may be neglected. Find: The final temperature (oF).
Problem 4.3 Given: Saturated water vapor is contained in a closed rigid tank. The water is cooled to a temperature of 110oC. At this temperature the masses of saturated vapor and liquid are each 1000 kg. Find: The heat transfer for the process (kJ).
Assume: Analysis:
Problem 4.4 Given: 0.5 kg of R-22 is contained in a piston-cylinder assembly, initially saturated vapor at 5 bar. The refrigerant undergoes a process for which the pressure-specific volume relationship is Pv = C to a final pressure of 20 bar. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. Find: a) Work (kJ) and b) heat transfer (kJ) for the process.
Assume: Analysis:
Problem 4.5 Given: A gallon of milk at 68oF is placed in a refrigerator. Energy is removed from the milk at a constant rate of 0.08 Btu/s a the milk cools. Specific heat, cp,milk = 0.94 Btu/lbmoR and density, milk = 64 lbm/ft3. Find: How many minutes will it take for the milk to cool to 48oF? How many minutes to cool another 10oF to 38oF?
Assume: Analysis:
Problem 5.1 Given: Water vapor at 200 bar and 470oC. Find: The compressibility factor using a) the generalized compressibility chart and b) data from the steam tables. Comment on the difference.
Analysis:
Problem 5.2 Given & Find: For the four cases given below, calculate the compressibility factor and comment on whether the ideal gas model is valid for these states. a) water at 700oF and pressures of 1600 lbf/in2 and 160 lbf/in2. b) carbon dioxide at 865 K and pressures of 75 bar and 3 bar. Analysis:
Problem 5.3 Given: A closed, rigid tank fitted with a paddle wheel contains 0.1 kg of air, initially at 300 K, 0.1 MPa. The paddle wheel stirs the air for 20 minutes, with the power input varying with time according = 10t, where W is in Watts and t is in minutes. The final temperature of the air is 1060 K. to W Find: a) the final pressure (MPa), b) work (kJ), and c) heat transfer (kJ).
Assume: 1) Air behaves as an ideal gas.
Analysis:
Problem 5.4 Given: 1.6 kg of air in a piston-cylinder device undergoes two processes in series from an initial state where P1 = 0.5 MPa, T1 = 227oC. Process 1-2: Constant-temperature expansion until the volume is twice the initial volume. Process 2-3: Constant volume heating until the pressure is again 0.5 MPa. Find: a) Sketch the two process on a P-v diagram, b) calculate the pressure at state 2, c) calculate the temperature at state 3, and d) find the work and heat transfer for each process (kJ).
Assume: Analysis:
Problem 5.5 Given: A 0.2 ft3 aluminum block is initially at 200oF. It is placed in a tank with 4 ft3 of liquid water at 70oF. Find: The equilibrium temperature of the block and water. Assume: The heat loss to the surroundings is negligible.
Você também pode gostar
- Tutorial Questions On Thermo 1Documento1 páginaTutorial Questions On Thermo 1MuhammadAizatAinda não há avaliações
- ChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Documento5 páginasChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Irene Kaye AceroAinda não há avaliações
- Test 1 With AnsDocumento4 páginasTest 1 With AnsKavinesh GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank (Numericals)Documento12 páginasQuestion Bank (Numericals)Omid Karimi SadaghianiAinda não há avaliações
- MEG 212 Practise QuestionsdocxDocumento11 páginasMEG 212 Practise Questionsdocxoyetunde ridwanAinda não há avaliações
- Basics of ThermodynamicsDocumento36 páginasBasics of ThermodynamicsYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Important QuestionsDocumento5 páginasImportant Questionstamilselvan nAinda não há avaliações
- ThermoDocumento4 páginasThermowong zhi chengAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics I#5Documento2 páginasThermodynamics I#5Pranjal GaurAinda não há avaliações
- ThermoDocumento5 páginasThermoTerry Clarice DecatoriaAinda não há avaliações
- Solving Week 8Documento14 páginasSolving Week 8Christopher Lennon Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet #7Documento4 páginasSheet #7AHMED BAKRAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheet 6Documento2 páginasTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinAinda não há avaliações
- PR Closed System 2Documento2 páginasPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Engineering Practice Problem 1Documento2 páginasBasic Engineering Practice Problem 1neva000Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Assignment 2 2014Documento5 páginasThermodynamics Assignment 2 2014ravikr950% (1)
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocumento4 páginasThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Documento22 páginasThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiAinda não há avaliações
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Documento3 páginasChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71Ainda não há avaliações
- ThermodynamicsDocumento3 páginasThermodynamicsKanchana RavindranAinda não há avaliações
- QP 12345Documento2 páginasQP 12345Siva ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- AssignmentDocumento2 páginasAssignmentTheod S. VilaAinda não há avaliações
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDocumento2 páginasCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35Ainda não há avaliações
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocumento2 páginasOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromPradeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- ChE Refresher Without Answers PDFDocumento86 páginasChE Refresher Without Answers PDFJulian S.Ainda não há avaliações
- Sheet 2Documento2 páginasSheet 2Ahmed Rabie Abd Elazeem100% (1)
- Tutorial Problems-Ch 6Documento2 páginasTutorial Problems-Ch 6Aryan NayanAinda não há avaliações
- BTD Question Bank1Documento16 páginasBTD Question Bank1Mahantesh ChulakiAinda não há avaliações
- TD ThermalPPDocumento2 páginasTD ThermalPPHectorDavidPreciadoValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- 9A03302 ThermodynamicsDocumento5 páginas9A03302 ThermodynamicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Eme Question Bank 08Documento16 páginasEme Question Bank 08عبدالله عمرAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 6Documento2 páginasTutorial 6LeoThomas0% (1)
- Tut 3Documento4 páginasTut 3SamarthAinda não há avaliações
- ME 63 Prob Set 2Documento2 páginasME 63 Prob Set 2RamonVannCleffRaroAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment EntropyDocumento2 páginasAssignment Entropyme22b009Ainda não há avaliações
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocumento2 páginas16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics With AnswersDocumento2 páginasThermodynamics With AnswersCedric Dela Cruz50% (2)
- AE321 Tut1Documento4 páginasAE321 Tut1Prabhash singhAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 4Documento2 páginasTutorial 4tehpohkee50% (2)
- Thermo 2Documento14 páginasThermo 2Yato QtAinda não há avaliações
- Taller 2 2023-1Documento8 páginasTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemDocumento3 páginasPractice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemNetra PujarAinda não há avaliações
- In A Gas TurbineDocumento7 páginasIn A Gas TurbineANBU RAJ AAinda não há avaliações
- Pset 1 CombustionDocumento13 páginasPset 1 CombustionMicaella Jaime De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Mock Test For Chemistry For Engineers 2Documento2 páginasMock Test For Chemistry For Engineers 2aramikaelatanAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocumento4 páginasThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiAinda não há avaliações
- Tarea 5 TermodinamicaDocumento4 páginasTarea 5 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocumento21 páginasEngineering Thermodynamicsrkrajesh86Ainda não há avaliações
- ETD Important QuestionsDocumento6 páginasETD Important QuestionsRavi KîshôreAinda não há avaliações
- Home Work 3Documento4 páginasHome Work 3Husiyandi HusniAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo 2Documento2 páginasThermo 2kj gandaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1, Autumn 2023Documento2 páginasAssignment 1, Autumn 2023cocodarshi2022Ainda não há avaliações
- QB Unit 1Documento6 páginasQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaAinda não há avaliações
- Work Sheet1Documento4 páginasWork Sheet1Tesfa negaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 J3 PDFDocumento19 páginasChapter 2 J3 PDFPravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Chi-Squared Distribution TableDocumento1 páginaChi-Squared Distribution TablePravallika Kollipara33% (3)
- Figure 1 Screenshot, Axes of The Problem, and Assumed Angle of TakeoffDocumento2 páginasFigure 1 Screenshot, Axes of The Problem, and Assumed Angle of TakeoffPravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 Part 2Documento5 páginasUnit 4 Part 2Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 Part 4Documento5 páginasUnit 4 Part 4Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Homework BDocumento28 páginasHomework BPravallika Kollipara0% (2)
- Unit 4 Part 1Documento5 páginasUnit 4 Part 1Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- HW 12 Solutions Spring 2012Documento4 páginasHW 12 Solutions Spring 2012Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- ENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsDocumento47 páginasENGSC 2333 - ThermodynamicsPravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 6Documento6 páginasProblem 6Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- For Our Thermodynamics Class, We Assume That Mass Is Conserved (Nuclear and Chemical Reactions Change The Mass of A System Very Small Amount)Documento6 páginasFor Our Thermodynamics Class, We Assume That Mass Is Conserved (Nuclear and Chemical Reactions Change The Mass of A System Very Small Amount)Pravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- BIOL-240-75-4138 SyllabusDocumento3 páginasBIOL-240-75-4138 SyllabusPravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Groups in Organic ChemistryDocumento1 páginaFunctional Groups in Organic ChemistrygznmemberAinda não há avaliações
- How To Tell A True War StoryDocumento15 páginasHow To Tell A True War StoryPravallika KolliparaAinda não há avaliações
- Theories of Failure2 PDFDocumento12 páginasTheories of Failure2 PDFDeepak AshokanAinda não há avaliações
- Partial Replacement of Cement With GGBS in ConcreteDocumento10 páginasPartial Replacement of Cement With GGBS in ConcreteE Hammam El MissiryAinda não há avaliações
- Bikesport Micro-Camper PDFDocumento15 páginasBikesport Micro-Camper PDFviocons72Ainda não há avaliações
- Architectural Glass Fixings & Metal SolutionDocumento111 páginasArchitectural Glass Fixings & Metal SolutiondtweetyAinda não há avaliações
- MAAG S Series Brochure English PDFDocumento12 páginasMAAG S Series Brochure English PDFWilliam ValenciaAinda não há avaliações
- A667Documento6 páginasA667IjabiAinda não há avaliações
- KSDB Channagiri Planning 04.08.2022Documento17 páginasKSDB Channagiri Planning 04.08.2022RavikumarAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Frictional ResistanceDocumento35 páginas4 Frictional Resistancebr1404Ainda não há avaliações
- Shell Tellus Oils C: Mild Anti-Wear Hydraulic OilsDocumento3 páginasShell Tellus Oils C: Mild Anti-Wear Hydraulic Oilssamar2090% (1)
- Lighting Design For Green and Adouless Public ToiletsDocumento8 páginasLighting Design For Green and Adouless Public ToiletsSankaranarayanan ChandresekarAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogo Towel RailsDocumento1 páginaCatalogo Towel RailsrodijammoulAinda não há avaliações
- Civic CenterDocumento7 páginasCivic CenterArt BerenguelAinda não há avaliações
- Geotechnical Characteristics of An Erodible Soil Stabilised by LiDocumento229 páginasGeotechnical Characteristics of An Erodible Soil Stabilised by LiRatan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Schedule of Loads and Computations: Riser Diagram/ Details of Circuit BreakersDocumento1 páginaSchedule of Loads and Computations: Riser Diagram/ Details of Circuit BreakersCarl Lou BaclayonAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis and Design Calculation of The Proposed Two Storey Residential BuildingDocumento57 páginasStructural Analysis and Design Calculation of The Proposed Two Storey Residential BuildingErwin ObenzaAinda não há avaliações
- Netsure 531 User ManualDocumento40 páginasNetsure 531 User ManualdmitriyAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 201 9-20: Setting of CementDocumento18 páginasChemistry Investigatory Project 201 9-20: Setting of CementVaibhav GavitAinda não há avaliações
- Limit State Design Flanged BeamsDocumento13 páginasLimit State Design Flanged BeamsRahulRandyAinda não há avaliações
- We Care We CareDocumento8 páginasWe Care We CareRamaKrishna AAinda não há avaliações
- PDF cSsArDocumento19 páginasPDF cSsArALO VIDIAAinda não há avaliações
- Envirotemp 200Documento2 páginasEnvirotemp 200Zoar Damaris PadronAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 - K.Bakshi - Laminated Composite Cylindrical Shell PanelsDocumento12 páginas2019 - K.Bakshi - Laminated Composite Cylindrical Shell PanelsArpita SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- D 129 Ui 4 ß109 U 51 P 4 Ji 1591243 Uj 1 oDocumento20 páginasD 129 Ui 4 ß109 U 51 P 4 Ji 1591243 Uj 1 orobert2pe10unuAinda não há avaliações
- CE6603-Design of Steel Structures QBDocumento7 páginasCE6603-Design of Steel Structures QBAarohiShirkeAinda não há avaliações
- April 16, 1968 L, 4, Derham Et Al 3,378,338: Production of High-Purity Aluminium ChlorideDocumento4 páginasApril 16, 1968 L, 4, Derham Et Al 3,378,338: Production of High-Purity Aluminium ChlorideDimas MitraAinda não há avaliações
- Flat Slab BW 2Documento14 páginasFlat Slab BW 2Kuladeep YalamanchiliAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Natural Fibers As An Admixture For Concrete Mix DesignDocumento9 páginasStudy of Natural Fibers As An Admixture For Concrete Mix DesignJOHN FHILIP ORIT67% (3)
- Code-Designation-Explanations For Cables and Insulated WireDocumento1 páginaCode-Designation-Explanations For Cables and Insulated WirerocketvtAinda não há avaliações
- Positioning of Air Cooled CondensersDocumento9 páginasPositioning of Air Cooled CondensersAlexAinda não há avaliações
- Describe The Shape of The Plastic Zone Ahead of A Crack Tip and Particularly How This Varies Between Plane Stress and Plane Strain SituationsDocumento6 páginasDescribe The Shape of The Plastic Zone Ahead of A Crack Tip and Particularly How This Varies Between Plane Stress and Plane Strain SituationsAndrew SpiteriAinda não há avaliações