Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
07 Ups
Enviado por
aimizaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
07 Ups
Enviado por
aimizaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PUSAT A T 1 H A L ~ TEKNOLOGI TINGGI (ADTEC)
, SHAHALAM
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS)
OVerview
~
UPS (Uninterrupted. Power Supply) is used to maintain the power supply to the essential load e.g ..
-senrer, pc and etc in case of power failure: Normally the UPS can provide power supply back up time
from 5 min to 10 min depending to the capacity of the load. Usually within the time, the generator!
generators should be able to take over and continue providingilie: supply sensitive 10att .
Choice of a UPS system
The choice of a UPS system is determined mainly by the following parameters:
i) Rated power, based on: .
- maximum value of actual estimated kV A transitory current peak (motor starting,
energization ofresistive load, transformer)
Ii) Voltage levels upstream (input) and downstream (output) ofthe UPS unit)
iii) Duration of autonomy required (ie. supply from the battery)
iv) F:requencies upstream (input) and down stream (output) offue UPS units
v) Level ofavailability required
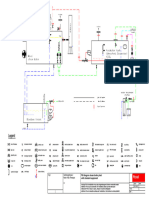
UPS operating theory
UPS operating theory
=
=
I
1.c. power supply network
Rectifier charger
Inverter
Essential load
T
Battery
. Fig. 1 UPS system with constant supply from netWork
1
=
I.e. power supply netWort
Rectifier charger
Inverter
Essential Load
Battery
Fig 2 - WS without constant supply fr9m network
. .
(
......"""j
,
J 0._
t------..
,...., \
c
(
Fig. 3 UPS switching circui1:
RefeI,Ting to Fig 1, UPS system with constant supply from network
The power supply from network is being converter from AC ro DC by the rectifier charger.
The DC supply is now charging the battery.
- The DC supply that flows through inverter is being converter from DC to AC.
- The converted AC supply providing the necessary CUlTent to essential load.
2
:::;;: 11,
..
--
.......
..,.
"'.....oek
Q]
\
i
1-------1 1I1I1
Pusat Latihan Teknologi Tinggi (ADTEC)
ShahAlam
STANDBY POWER SYSTEMS
1. Introduction
Reliability of electrical supply to industrial and commercial undertakings is essential for
continuity of production and safety ofgoods and personnel, and standby power systems
have been in use for many years. Standby power systems also known as emergency
power systems are intended to provide illumination and power to essential circuits in the
event offailure in the normal system supply.
2. Identifying and Assessing Essential Loads
Loads range in sensitivity to loss ofutility power from as little as one half cycle for
computers to minutes or more for heating and air-conditioning systems. Each installation
comprises a range ofload equipment that must be classified by sensitivity before a
system is designed to supply the load in the face ofutility power failure. Three common
(;
alternate sources that can supply power to the loads include the battery directly, the,UPS
from its dedicated battery, and the diesel engine driven generator set. The battery can
supply power with no interruption, or after about a 0.5 second transfer switch operation.
The UPS can supply power with no interruption when the utility source fails.
3 Types of Loads
a. Critical, requiring line voltage with less than one quarter cycle (5 ms) of dip to zero.
b. Essential, requiring line voltage following a 10 second dip to zero.
c. Nonessential, requiring line voltage following a dip to zero lasting minutes to hours.
4 Classification of Loads
a. Equipment Support
C' Necessary to operate an overall system, e.g., a data processing center, power plant boiler,
'--- industrial process, air-traffic control center.
b. People Support
Necessary to maintain a specific group, e.g., the personnel necessary to operate an air
traffic control center or the patients and staff of a hospital.
c. Building Support
Necessary to keep a building functioning, e.g., lights, heat, air-Conditioning, fire alarms,
elevators.
Penjaga Jentera Elektrik
5
Pusat Latihan Teknologi Tinggi CADTEC)
ShahAlam
Loads For Battery Supply
Two types of batteries systems are used for emergency/standby supply_
in the first, the system consists of an ACIDC charger supplying a dc bus with a battery
floating on the dc bus. All ofthe critical loads are supplied from the dc bus.
In the event of utility power failure, the battery supplies the loads on a dc bus. When ac
power is restored, the charger supplies the load on the dc bus and recharges the battery.
Typical loads for battery supply include the following:
a. Power plant and sub.stations, including
Control circuit
Circuit breakers
Contactors
Back-up lubrication pumps
Alarms
Telephone
Emergency light
b. Telephone Systems, including
Center office equipment
Communication Repeater
Satellite Tracking station
Subscribers' equipment
c. Building, including
Emergency lights
Fire alarms
Telephone
Radio Communication
Security
6. Loads For UPS
In assigning loads to categories and to methods of supply, examples of critical loads for
UPS supply include the following: .
a. Data processing, including
Disk drive, Central processor and interfacing
b. Medical electronics, including
Monitor
Instrumentation
Heart / lung machines
In addition, small UPS up to 10 KV A are used for PCs, Laboratory instrumentation,
photo processor and other load equipment whose operation would be costly to interrupt.
Penjaga Jentera Elektrik
Pusat Latihan Teknologi Tinggi (ADTEC)
ShahAlam
c. Loads for diesel- engine generator
Loads -which can tolerate a lO second delay in power after utility failure include the
following:
Elevator
Escalator
Telephone
Facsimile
Ventilation motor
Fan
Blower
Sanitation pump
1 Industrial control, including
Control computer
Programmable controller
Penjaga Jentera Ele1ctrik
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- IEE 16 04 Cables, Conduits and Trunking#Documento30 páginasIEE 16 04 Cables, Conduits and Trunking#aimiza17% (6)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Motor of Pump HandbookDocumento252 páginasMotor of Pump Handbookhithr1Ainda não há avaliações
- SRU Training ModuleDocumento161 páginasSRU Training ModuleArun Kumar PAinda não há avaliações
- EPE 12kV SwitchgearDocumento48 páginasEPE 12kV Switchgearaimiza100% (1)
- Basic Vocational Knowledge Electrical Installation PDFDocumento150 páginasBasic Vocational Knowledge Electrical Installation PDFaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- GE Cycles Lecture Info 2009Documento18 páginasGE Cycles Lecture Info 2009Sayantan Datta Gupta100% (1)
- Naval Reactor Handbook Vol 3Documento523 páginasNaval Reactor Handbook Vol 3Peter AngeloAinda não há avaliações
- Huafengdongli 495 4100 Series Operationmanual PDFDocumento73 páginasHuafengdongli 495 4100 Series Operationmanual PDFSergio Ricardo IbañezAinda não há avaliações
- Areva Transformer ManualDocumento97 páginasAreva Transformer Manualnidnitrkl051296100% (2)
- Areva - HWX VCB - Installation Operation & Maintenance ManualDocumento16 páginasAreva - HWX VCB - Installation Operation & Maintenance Manualaimiza79% (14)
- NH3 Process DescriptionDocumento8 páginasNH3 Process DescriptionMusa KaleemAinda não há avaliações
- Grounding (Slide) PDFDocumento61 páginasGrounding (Slide) PDFaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Training Session 1 Gas Turbine Basics: by Jim Noordermeer, P.Eng. Gryphon International Engineering Services IncDocumento24 páginasTraining Session 1 Gas Turbine Basics: by Jim Noordermeer, P.Eng. Gryphon International Engineering Services IncM Azri Zulkipli100% (1)
- A Guide To Selection of Electrical CableDocumento46 páginasA Guide To Selection of Electrical Cableapi-3808029100% (7)
- ABC Cable Accessories#Documento23 páginasABC Cable Accessories#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Combined Cycle OperationDocumento70 páginasChapter 2 Combined Cycle OperationGloria Del Carmen MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- Acer Aspire E1 ManualDocumento85 páginasAcer Aspire E1 ManualaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Ecm 700Documento2 páginasEcm 700aimiza0% (1)
- Archgon - MH-3621-U3 - ManualDocumento14 páginasArchgon - MH-3621-U3 - ManualaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Sanyo EM-N102 Micowaveoven SMDocumento26 páginasSanyo EM-N102 Micowaveoven SMaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- mk2200 ManDocumento56 páginasmk2200 ManKannan VAinda não há avaliações
- 001 Supply Voltages AC and DC SystemsDocumento17 páginas001 Supply Voltages AC and DC Systemsaimiza100% (1)
- Terman - WTI - MSRT150-WDocumento9 páginasTerman - WTI - MSRT150-Waimiza100% (2)
- Ziehl PTC-resistor Relay MSF 220 V (VU) PDFDocumento8 páginasZiehl PTC-resistor Relay MSF 220 V (VU) PDFaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Why Spike A Cable#Documento1 páginaWhy Spike A Cable#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- GE - LV Cable and BusductDocumento36 páginasGE - LV Cable and BusductaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Multimeter, Measuring DC VoltageDocumento38 páginasAnalog Multimeter, Measuring DC VoltageAlexander BlackAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Standard Kemahiran Pekerjaan Kebangsaan (SKPK)Documento281 páginasDaftar Standard Kemahiran Pekerjaan Kebangsaan (SKPK)Everboleh ChowAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Protective EquipmentsDocumento72 páginasPersonal Protective EquipmentsaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- 06 Instruction and Operation Manual - Power SynchronisingDocumento9 páginas06 Instruction and Operation Manual - Power SynchronisingaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Underground Cables#Documento6 páginasUnderground Cables#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Anode: Flow of ElectronsDocumento3 páginasAnode: Flow of ElectronsaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Low Voltage Twisted Cable#Documento1 páginaLow Voltage Twisted Cable#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- AWG To MM#Documento2 páginasAWG To MM#aimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Conductor Data Size - Stranding - Current RatingDocumento2 páginasCable Conductor Data Size - Stranding - Current RatingaimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Rab Mekanikal Block D - 1Documento21 páginasRab Mekanikal Block D - 1Setyo Tyas JarwantoAinda não há avaliações
- Bernoulli Venturi NozzleDocumento4 páginasBernoulli Venturi NozzleFrank PingolAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Date Sheet Moder-GBD10/options: Performance DataDocumento4 páginasTechnical Date Sheet Moder-GBD10/options: Performance DataFoxAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson BDocumento3 páginasLesson BDavid Mena BrenisAinda não há avaliações
- Hydro Power PlantDocumento41 páginasHydro Power PlantEr Mishal Gandhi100% (1)
- P&I Diagram Steam Boiler Plant With Standard EquipmentDocumento1 páginaP&I Diagram Steam Boiler Plant With Standard Equipmentrachman hardianAinda não há avaliações
- Tank Fire ReportDocumento32 páginasTank Fire ReportAbubucker AshiqAinda não há avaliações
- Steam Power Plant Analysis - Full Run - Example - 4th Ed PK Nag - KSB - UofCanterburyDocumento5 páginasSteam Power Plant Analysis - Full Run - Example - 4th Ed PK Nag - KSB - UofCanterburyRajaramAinda não há avaliações
- Eet-04 GepDocumento2 páginasEet-04 GepNmg KumarAinda não há avaliações
- European Hydrogen Economy FINALDocumento36 páginasEuropean Hydrogen Economy FINALsiaAinda não há avaliações
- Injection Timing Calculator 2020Documento43 páginasInjection Timing Calculator 2020Tim JuddAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Heat Boiler Recovery: YoshimineDocumento12 páginasWaste Heat Boiler Recovery: YoshimineardiansyahhandikaAinda não há avaliações
- Parts Manual Parts Manual Parts Manual Parts Manual: Mfg. No: 613477-2192-J1Documento45 páginasParts Manual Parts Manual Parts Manual Parts Manual: Mfg. No: 613477-2192-J1Stefan CorjucAinda não há avaliações
- ComplicationsDocumento11 páginasComplicationsBoedi SyafiqAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar Presentation On Micro Power GeneratorDocumento25 páginasSeminar Presentation On Micro Power GeneratorDev Kumar100% (5)
- PP FWpumpDocumento10 páginasPP FWpumpMohammad MohseniAinda não há avaliações
- Instruction Manual FCGDocumento38 páginasInstruction Manual FCGDennisAinda não há avaliações
- Pumping & Compression of Co2: Haward Technology Middle East 1 Section 1aDocumento18 páginasPumping & Compression of Co2: Haward Technology Middle East 1 Section 1aVlassis SarantinosAinda não há avaliações
- TurbomDocumento2 páginasTurbomjuchaca36Ainda não há avaliações
- LPG Piping Systems EngDocumento2 páginasLPG Piping Systems EngAbdelfattah ben RagabAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Renewable Energy: Introduction To Common TerminologyDocumento15 páginasBasic Renewable Energy: Introduction To Common Terminologyasmae aminaAinda não há avaliações
- Cashback Model ListDocumento79 páginasCashback Model Listgixabat112Ainda não há avaliações
- Performance Comparison of R32 R410A and R290 Refrigerant in InveDocumento11 páginasPerformance Comparison of R32 R410A and R290 Refrigerant in InveDipin DangAinda não há avaliações