Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Intro To Biomes
Enviado por
api-235669157Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Intro To Biomes
Enviado por
api-235669157Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Objective: Understand the plants, animals and climate that characterize each biome of the world. Site: http://mbgnet.mobot.
org/ Missouri Botanical Gardens
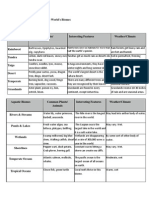
Browse each biome and fill out the chart below and answer the questions below about each individual biome Terrestrial Biome Rainforest Common Plant/Animals Gorilla, Peacock plant Interesting Features There are two types of rainforest: Temperate and Tropical Permanent ice layer Long winters and short, wet summers Little precipitation Weather/Climate Temperate: Cold Tropical: Warm-HOT
Tundra Taiga Desert
Caribou, Lichen Moose, Evergreen Trees Coyote, Cactus
Temperate
Hares, Tall and short Grass
Season changes.
Grasslands
Lion, wildflowers
These are called prairies in the United States
Subfreezing or freezing temperature Winters: cold Summers: warm HOT during day, and temperature decreases during nighttime Moderate temperature depending on the season HOT, dry summers and cold snowy winters
Rainforests 1: What are the two types of rainforests? In the United States, where are our rainforests located? (Be specific). What percentage of our original rainforests does this represent? The two types of rainforests are temperate and tropical. In the United States, the rainforests are located in the Pacific Northwest and there are only 25% of our original rainforest left. Tundra 2: Where is the Tundra Biome located? What is permafrost? What percentage of the Earths surface is covered by Tundra?
The tundra biome is located near the North Pole. Permafrost means that a layer of ground is permanently frozen. 20% of the Earths surface is covered by Tundra. Taiga 3: Where is the Taiga Biome located? What is the soil like in the Taiga- why? The Taiga biome is located in many parts of Canada, Europe, and Asia. The soils in the Taiga are thin and lack nutrients due to slow decomposition. Desert 4: How much rainfall is characteristic of deserts? Explain where most deserts are located and the RAINSHADOW Effect. The average amount of rain in deserts is 10 inches. Most deserts are located in the midlatitude. The rainshadow effect occurs when air travels up the windward side of a mountain range causing it to expand and the temperature decreases due to pressure. Then when it sinks on the leeward side of the mountains, the air begins to compress causing the air to heat up. Temperate Deciduous Forest 5: What is special about this biome? Deciduous trees have special leaves that are adapted to the biome- explain. This biome has all four seasons. Deciduous trees have special leaves that are adapted to the biome because during the autumn, the leaves falls off, then it regrows during springtime. Grasslands 6: Grasslands are found on every continent except for one- which? How much rainfall do grasslands get- why is this important? What are the 3 types of grasslands that are found in North America? What are grasslands called in other places in the world? Grasslands are found on every continent except for Antarctica. It usually receives 10 to 30 inches of rainfall per year. It is important that this biome only receive that much amount of rain because if there is too much amount of it, then it will be a forest and too little amount of it, then it will be a desert. Tall Grass Prairie, Mixed Grass Prairie and Short Grass Prairie are the three types of grasslands found in North America. Grasslands are called Savannas in Africa and Steppes in Europe.
Rivers & Streams 7: How much water on Earth does running water represent? What is a watershed? What are the two main processes that happen to surface water? What is the longest river in the world? What is the longest river in the United States? What is a hydroelectric dam? Running water represents .3% of all water on earth. A watershed is an area of land that contains a common set of streams and rivers that all drains into a single larger body of water. Surface runoff and infiltration are the two main processes that happen to surface water. The Nile River is the longest river in the world. The Mississippi-Missouri River is the longest river in the United States. A hydroelectric dam is a dam that takes water and converts it to hydroelectric power. Ponds & Lakes 8: What is the difference between a pond and lake? Name the four stages of succession of a pond. Explain how an Oxbow Lake is formed. What is the largest lake in the world? What is the largest lake in the United States? What is the deepest lake in the world? What is Lake Effect Snow? Explain. What is the cause of summerkill in some lakes? A lake is larger than a pond and lakes are big enough to produce waves. The largest lake in the world is the Caspian Sea. The largest lake in the United States is Lake Superior. Lake Baikal is the deepest lake in the world. Lake Effect Snow occurs when moisture from warm lakes gets picked up by cold winds and cooled down as it travels up. Eventually, the moisture will condense and precipitate as snow. Too much amount of sunlight is the cause of summerkill in some lakes. Four stages of succession of a pond: o Seeds are dropped by pond pioneers, birds and land animals that inhabits the area around the pond o As the debris increases, vegetation also increases o Emergent then appears o As time advances, the bottom is close enough to the pond floor allowing emergent to grow across the pond floor, which eventually becomes a marsh.
Wetlands 9: What are the types of freshwater wetlands- name and define them. Explain why wetlands are so important. What is happening to our wetlands? Types of freshwater wetlands: o Marshes- an inland area with one to six feet of water o Swamp- slow moving streams o Bog- a wetland that accumulates peat o Prairie Pothole- shallow depressions of water o Riparian Marsh- marshes along rivers Wetlands are important because it prevents floods by acting as a sponge and purifies water. The wetlands are disappearing at a rapid rate of 300,000 acres annually in the United States. Shorelines 10: What kind of lifeforms will you find in the intertidal zone? What is a barrier island? What is an estuary? What is life like in an estuary? What is a salt marsh? What is the Mangrove Forest? How are the trees specially adapted to living in that environment? Why are they important? Seashells and clams are usually found in intertidal zones. A barrier island is formed from multiple islands separate by a main body of water, sizes may vary. An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where seawater is mixed with freshwater from the land. Life in an estuary contains of many diverse organisms from sea and land. A salt marsh is when land approaches the sea. Mangrove forests are where river deltas provide a lot of sediments near the mouth of large rivers. Trees adapted to living in that environment by having aerial roots and salt tapping roots. They are important because those trees protect the coastline and prevent erosion. Temperate Ocean Zones 11: Name and describe the different zones of the ocean and how they are divided. Describe the different photic zones of the ocean. What are kelp forests? Where are they
found? Zones of the ocean: o Benthic- bottom of the ocean o Pelagic zone- water o Neritic zone- extends from high and low tides o Oceanic- water thats deeper than 600 feet o Sunlit zone- the top layer of the ocean o Twilight zone- the zone that gets only small amounts of sunlight o Midnight zone- the zone that contains no light for 90% of the time Kelp forest is an abundance of kelp that grows up to 125 feet. They are usually found in the Atlantic Coast and Pacific waters. Tropical Ocean Zones 12: What is coral made of? Explain. Where are most coral reefs located? Where is the largest coral reef? Coral is made of polyp. Polyp attaches itself to the floor of the reef and is column shaped. Most coral reefs are located near the equator in tropical oceans. The largest coral reef is the Great Barrier Reef.
Você também pode gostar
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds BiomesDocumento4 páginasApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomesapi-235647128Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To The WorldDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To The Worldapi-235617848Ainda não há avaliações
- Apes - Introduction To The Worlds BiomesDocumento6 páginasApes - Introduction To The Worlds Biomesapi-236697820Ainda não há avaliações
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes RepairedDocumento7 páginasApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes Repairedapi-235658421Ainda não há avaliações
- Biomes: How Many Biomes Are There?Documento12 páginasBiomes: How Many Biomes Are There?Branlie RuetasAinda não há avaliações
- Ecosystems and Types of EcosystemsDocumento42 páginasEcosystems and Types of EcosystemsIbrahim AliAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - Lesson 3 ActivityDocumento4 páginasModule 1 - Lesson 3 ActivityKirstelle SarabilloAinda não há avaliações
- GK PDFDocumento14 páginasGK PDFManjeet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Class-7 Ncert Chapter-5 Water Terrarium: It Is An Artificial Enclosure For Keeping Small House PlantsDocumento33 páginasClass-7 Ncert Chapter-5 Water Terrarium: It Is An Artificial Enclosure For Keeping Small House PlantssatyamksspAinda não há avaliações
- BiomesDocumento117 páginasBiomesgeissingert93% (14)
- White Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationDocumento17 páginasWhite Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationZyra AbordsAinda não há avaliações
- Biomes: Thinking QuestionsDocumento21 páginasBiomes: Thinking QuestionsUsman MaukAinda não há avaliações
- Biomes 110821050021 Phpapp02Documento26 páginasBiomes 110821050021 Phpapp02Sendaydiego Rainne GzavinAinda não há avaliações
- Terrestrial EcosystemDocumento27 páginasTerrestrial EcosystemCamille FaustinoAinda não há avaliações
- Tema 11: La EcosferaDocumento10 páginasTema 11: La EcosferaAinhoa Pérez GiménezAinda não há avaliações
- Review Questions Biosphere (KEY)Documento6 páginasReview Questions Biosphere (KEY)owls_1102Ainda não há avaliações
- Wide World of Weather: Weather and Climate Around the WorldNo EverandWide World of Weather: Weather and Climate Around the WorldAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Science - Desert and Aquatic EcosystemDocumento7 páginasEnvironmental Science - Desert and Aquatic EcosystemShruthiDevar100% (1)
- Types of BiomeDocumento8 páginasTypes of Biomelizzie_mcgAinda não há avaliações
- Extremes Desert Science PDFDocumento24 páginasExtremes Desert Science PDFMia SamAinda não há avaliações
- OceanDocumento3 páginasOceanT chAinda não há avaliações
- Kinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesDocumento18 páginasKinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesBelmas CarbonellAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityDocumento68 páginasChapter 7 Climate and BiodiversityBernard DayotAinda não há avaliações
- The Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsNo EverandThe Complete U.S. Army Survival Guide to Tropical, Desert, Cold Weather, Mountain Terrain, Sea, and NBC EnvironmentsAinda não há avaliações
- Geografía Tema 5Documento10 páginasGeografía Tema 5Rocío MadolellAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Textbook Section 3 Temperate and Polar ZonesDocumento7 páginasInteractive Textbook Section 3 Temperate and Polar Zonesapi-249771030Ainda não há avaliações
- Scientists Usually Say That An Area Is Desert If An Average of Less Than 250 Millimetres of Rain Falls EachDocumento9 páginasScientists Usually Say That An Area Is Desert If An Average of Less Than 250 Millimetres of Rain Falls EachSu Myat NoeAinda não há avaliações
- HandOut (World Biomes)Documento7 páginasHandOut (World Biomes)Jonel BarrugaAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental ScienceDocumento5 páginasEnvironmental ScienceJhupoor GargolesAinda não há avaliações
- Envi-Sci Activity 7Documento8 páginasEnvi-Sci Activity 7Loren Mae DetaloAinda não há avaliações
- Desert Eco SystemDocumento6 páginasDesert Eco SystemSiva PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- BiomesDocumento14 páginasBiomesJerico MarcosAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 2 - People and Biomes 3Documento12 páginasCHAPTER 2 - People and Biomes 3juliussayoansus ansusAinda não há avaliações
- Taiga (: Citation NeededDocumento4 páginasTaiga (: Citation NeededLyraAinda não há avaliações
- 14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute BookNo Everand14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute BookNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- aCT 7 EnviSciDocumento6 páginasaCT 7 EnviSciYaj Naitsirhc LD AlyuhadAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Biomes - CompiledDocumento7 páginasTypes of Biomes - CompiledToni GutzAinda não há avaliações
- Lakes and Ponds EcosystemDocumento55 páginasLakes and Ponds EcosystemRelie ArambuloAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Forest Ecosystems 2Documento13 páginasTypes of Forest Ecosystems 2Karthick Ramamoorthy100% (1)
- Unlocking the Secrets of Rivers, Lakes, Oceans and TreesNo EverandUnlocking the Secrets of Rivers, Lakes, Oceans and TreesAinda não há avaliações
- Unit V BiomesDocumento14 páginasUnit V BiomesHyramae CuacoAinda não há avaliações
- 14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute Book: Educational VersionNo Everand14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute Book: Educational VersionAinda não há avaliações
- Panel SolarDocumento13 páginasPanel SolarRosa Andrea CumezAinda não há avaliações
- Biosphere: Group 4Documento61 páginasBiosphere: Group 4Juliana Marie SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Natural and Human-Made EcosystemsDocumento84 páginasNatural and Human-Made EcosystemsRose Anne ConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Apes-Terrestrial Biomes ReviewDocumento6 páginasApes-Terrestrial Biomes Reviewapi-235959158Ainda não há avaliações
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes 1Documento9 páginasApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes 1api-264479456Ainda não há avaliações
- ENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldDocumento20 páginasENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldFatima Therese ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- Desert Eco SystemDocumento5 páginasDesert Eco SystemSiva PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- The Aquatic BiomeDocumento4 páginasThe Aquatic BiomeAngelie LapeAinda não há avaliações
- L8 Human Environment InteractionsDocumento11 páginasL8 Human Environment InteractionsAARUSH SHIRBHATEAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide For Exam 4.doc - 0.odtDocumento14 páginasStudy Guide For Exam 4.doc - 0.odtMattAinda não há avaliações
- G 4 PPT Wala Pang Ano YanDocumento21 páginasG 4 PPT Wala Pang Ano YanPyrrhus John BagamaspadAinda não há avaliações
- Apes BiomeDocumento23 páginasApes BiomeAnonymous EOCiFiAinda não há avaliações
- Biomes and BioGeoChemical CycleDocumento4 páginasBiomes and BioGeoChemical CycleMel Angelo Ayala OrigAinda não há avaliações
- The Og of KearnyDocumento4 páginasThe Og of Kearnyapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Ozone Good and BadDocumento3 páginasOzone Good and Badapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Week FourteenDocumento1 páginaWeek Fourteenapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbon Cycle and The Greenhouse EffectDocumento2 páginasCarbon Cycle and The Greenhouse Effectapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- NotesssDocumento2 páginasNotesssapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Soil NotesDocumento1 páginaSoil Notesapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Should We Grow GM CropsDocumento1 páginaShould We Grow GM Cropsapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- GaslandDocumento2 páginasGaslandapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Water DiversionsDocumento4 páginasWater Diversionsapi-235669157100% (1)
- Personal Water UseDocumento1 páginaPersonal Water Useapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Facing The Freshwater CrisisDocumento2 páginasFacing The Freshwater Crisisapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Virtual Water Testing LabsDocumento3 páginasVirtual Water Testing Labsapi-235669157Ainda não há avaliações
- Enginerring Room Resource Management Section III/1-2 and STCW Code Section A III/1 Paragraph 1-10Documento1 páginaEnginerring Room Resource Management Section III/1-2 and STCW Code Section A III/1 Paragraph 1-10Global Inovasi BersamaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of Sports PhysiologyDocumento10 páginasIntroduction of Sports PhysiologyRoop Inder ShergillAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Listrik Statis Dan Kelistrikan Pada Makhluk SedangDocumento10 páginasSoal Listrik Statis Dan Kelistrikan Pada Makhluk SedangRifatiMasrurohAinda não há avaliações
- Getting Things Done With ADHDDocumento74 páginasGetting Things Done With ADHDhfuqueneAinda não há avaliações
- Tle InterventionDocumento8 páginasTle InterventionNorman T. Regal100% (1)
- Production Logging Tools and InterpretationsDocumento34 páginasProduction Logging Tools and InterpretationsRizwan FaridAinda não há avaliações
- Of Studies: Francis BaconDocumento9 páginasOf Studies: Francis BaconAfreen FaiyazAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Intellectualization of FilipinoDocumento3 páginasMeasures of Intellectualization of Filipinolevine millanesAinda não há avaliações
- Stay!: Suspended SuspendedDocumento17 páginasStay!: Suspended Suspendedjeongin yangAinda não há avaliações
- XY Power 30kW Power Module For Fast EV Charging StationsDocumento2 páginasXY Power 30kW Power Module For Fast EV Charging StationsSam GuoAinda não há avaliações
- Pseudalert Iso 13843 Validation ReportDocumento38 páginasPseudalert Iso 13843 Validation ReportVoThiAnhLoanAinda não há avaliações
- S TypeDocumento29 páginasS TypedenisAinda não há avaliações
- MATLAB Basic Functions and Commands: Ece120L - Introduction To Matlab Laboratory Activity #2Documento7 páginasMATLAB Basic Functions and Commands: Ece120L - Introduction To Matlab Laboratory Activity #2Michelle TagalogAinda não há avaliações
- Parts Catalogue For Detroit DieselDocumento27 páginasParts Catalogue For Detroit DieselEduardo CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Sailor Moon Vol 1 - Naoko TakeuchiDocumento204 páginasSailor Moon Vol 1 - Naoko TakeuchiKate Yati100% (4)
- Original PDF Introduction To Logic by Paul Herrick PDFDocumento41 páginasOriginal PDF Introduction To Logic by Paul Herrick PDFpearl.zinn592100% (35)
- S9 Q2 HYBRID MODULE 1 Week 1 FinalDocumento19 páginasS9 Q2 HYBRID MODULE 1 Week 1 FinalEunnamae VillardeAinda não há avaliações
- Arihant Kota Teachers - KVPY 11 Years Solved Papers 2019-2009 Stream SA For Class 11 Arihant (2020, Arihant Career Helper) - Libgen - LiDocumento257 páginasArihant Kota Teachers - KVPY 11 Years Solved Papers 2019-2009 Stream SA For Class 11 Arihant (2020, Arihant Career Helper) - Libgen - LiAtharv AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Gravel Sealing: Prospects & ChallengesDocumento29 páginasGravel Sealing: Prospects & ChallengesRajendra K KarkiAinda não há avaliações
- Who Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsDocumento82 páginasWho Guideline On Use of Ferritin Concentrations To Assess Iron Status in Individuals and PopulationsLima NetAinda não há avaliações
- Human Computer Interaction - Evaluation TechniquesDocumento26 páginasHuman Computer Interaction - Evaluation TechniquesUrooj AkhlaqAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Potential EnergyDocumento3 páginasElectric Potential EnergykruvanhAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter09 Mathematics of CryptographyDocumento14 páginasChapter09 Mathematics of CryptographytartarAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Finite-Difference Method For The 1D Heat Equation: 1.1 Domain DiscretizationDocumento5 páginas1 Finite-Difference Method For The 1D Heat Equation: 1.1 Domain Discretizationoverdose500Ainda não há avaliações
- QHSE Training Answers FIELD PERSONNELDocumento1 páginaQHSE Training Answers FIELD PERSONNELMhanna AYAinda não há avaliações
- Spectral Triad (AS7265x) Hookup Guide - SparkFun LearnDocumento13 páginasSpectral Triad (AS7265x) Hookup Guide - SparkFun LearnFrancisco BoteroAinda não há avaliações
- The Dark Eye - Character SheetsDocumento6 páginasThe Dark Eye - Character SheetsVergil Hamlet100% (1)
- CV Emil SatriaDocumento1 páginaCV Emil SatriaazmiazfarAinda não há avaliações
- Molavi Faby Kaye P. UTSDocumento5 páginasMolavi Faby Kaye P. UTSAshlyne Joy BalanayAinda não há avaliações
- OI Calidades FinalesDocumento8 páginasOI Calidades FinalesMarcelo VizcayaAinda não há avaliações