Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Julbot 11
Enviado por
gauravTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Julbot 11
Enviado por
gauravDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Syllabus for B.Sc. Botany B.Sc.
I year Session - 2011-12 There will be Three theory papers and a practical examination as follows: Paper I - Diversity of Viruses, Bacteria & Fungi M. M.: 50 Paper II - Diversity of Algae, Lichens, & Bryophytes M. M.: 50 Paper III - Diversity of Pteridophytes & Gymnosperms M. M.: 50 (There will be 9 questions in each paper and candidate has to attempt only 5 questions. Q.1 will be compulsory based on units I - IV. Two questions will be set from each unit of which one question has to be attempted. All questions will carry equal marks. Practicals: Based on papers I - III M. M.: 50 The course detailes are as follows:Paper I: Diversity of Viruses, Bacteria, & Fungi M.M. 50
Unit-I History, nature and classification of Viruses, Bacteria and Fungi. History of virology and bacteriology; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure (bacteria, mycoplasma and yeast); structure, classification and nature of viruses; structure (gram positive and gram negative) and classification (based on cell structure) of bacteria; classification, thallus organisation and reproduction in fungi; economic importance of fungi. Unit-II Viruses:Symptoms of virus infection in plants; transmission of plant viruses; genome organisation, replication of plant virus (tobacco mosaic virus); techniques in plant viruses - purification, serology and electron microscopy; structure and multiplication of bacteriophages; structure and multiplication of viroids. Unit-III Bacteria:Nutritional types of bacteria (based on carbon and energy sources), metabolism in different nutritional types (basics only) and nitrogen cycle; bacterial genome and plasmids; bacterial cell division, variability in bacteria - mutation, principles of genetic recombination; techniques in sterilisation, bacterial culture and staining; economic importance. Unit-IV Fungi:The characteristics and life cycles of the following: Mastigomycotina: Albugo, Pythium,; Ascomycotina: Saccharomyces, Aspergillus; Ascobolus; Basidiomycotina : Ustilago, Puccinia, Polyporus, Agaricus; Deuteromycotina: Fusarium.
Paper II - Diversity of Algae, Lichens, and Bryophytes
M.M. 50
Unit-I General characters. Range of thallus organization, classification, ultrastructure of eukaryotic algal cell and cyanobacterial cell, economic importance of algae. Lichens, classification, thallus organization, reproduction, physiology and role in environmental pollution. Unit-II The characteristics and life cycles of the following:Cyanophyta Microcystis, Oscillatoria :Chlorophyta Volvox, Hydrodictyon, Oedogonium, Coleochaete, Chara; Bacillariophyta Navicula; Xanthopyta Vaucheria; Phaeophyta; Ectocarpus Rhodophyta Polysiphonia
Unit III Bryophytes, general characters, classification, reproduction and affinities. Gametophytic and soporophytic organization of: Bryopsida: Pogonatum; Anthocerotopsida: Anthoceros
Unit - IV Gametophytic and sporophytic organization of Hepaticopsida : Riccia, Marchantia.
Paper III Diversity of Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and elementary Palaeobotany
M.M. 50
Unit - I Pteridophytes: General features, classification, stellar system and its evolution. Comparative study of morphology, anatomy, development, vegetative and reproductive systems of following: Lycopsida - Lycopodium, Selaginella;Psilopsida- Rhynia
Unit II General and comparative account of gametophytic and sprophytic system in Filicopsida -Pteridium, Nephrolepis. Marsilea. Heterospory and seed habit. Unit - III Gymnosperms: General characters, classification. Comparative study of morphology, anatomy, development of vegetative and reproductive parts in: Cycadales: Cycas Unit IV Study of morphology, anatomy, development and reproductive parts in: Coniferales Pinus ; Gnetales - Ephedra Affinities and relationship of Gymnosperms, evolutionary significance. Elementary Palaeobotany: general account, types of fossils, methods of fossilization and geological time scale.
2
Você também pode gostar
- The Third SexDocumento1 páginaThe Third SexgauravAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 A View of Life: Just To UploadDocumento1 páginaChapter 1 A View of Life: Just To UploadgauravAinda não há avaliações
- AwardsDocumento1 páginaAwardsgauravAinda não há avaliações
- SportsDocumento1 páginaSportsgauravAinda não há avaliações
- List of Cable OperatorsDocumento4 páginasList of Cable OperatorsgauravAinda não há avaliações
- One Day WorkshopDocumento1 páginaOne Day WorkshopgauravAinda não há avaliações
- Þ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocumento12 páginasÞ CC) C' (CC& +C++C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCgauravAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Vegetation Analysis and Species Diversity in The Desert Ecosystem of Coastal Wadis of South Sinai, Egypt PDFDocumento14 páginasVegetation Analysis and Species Diversity in The Desert Ecosystem of Coastal Wadis of South Sinai, Egypt PDFRs HawkinsAinda não há avaliações
- Divya Yog - KwathDocumento16 páginasDivya Yog - KwathziponlineAinda não há avaliações
- Cypripedium - Lady Slipper Orchids For The GardenDocumento9 páginasCypripedium - Lady Slipper Orchids For The GardenDennis CareyAinda não há avaliações
- 2021-2022 Stampin' Up! Annual CatalogueDocumento180 páginas2021-2022 Stampin' Up! Annual CatalogueCynthia StevensonAinda não há avaliações
- II1 IB RevisionDocumento3 páginasII1 IB RevisionMedinaAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF TRICHODESMA EHRENBERGII SCHWEINF. EX BOISS.GROWING WIDELY IN GEBEL ELBA, EGYPT Amani M. D. El-Mesallamy, Fatma A. Ahmed, Mohammed H. Elhaw , Taha A. Ibrahim*Documento6 páginasCHEMICAL INVESTIGATION AND EVALUATION OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF TRICHODESMA EHRENBERGII SCHWEINF. EX BOISS.GROWING WIDELY IN GEBEL ELBA, EGYPT Amani M. D. El-Mesallamy, Fatma A. Ahmed, Mohammed H. Elhaw , Taha A. Ibrahim*iajpsAinda não há avaliações
- Volume 12 Issue 1. March, 2012 Issn: 1474-4635Documento24 páginasVolume 12 Issue 1. March, 2012 Issn: 1474-4635C. Javier VazquezAinda não há avaliações
- Wild Edible Plants of Mayurbhanj DistricDocumento10 páginasWild Edible Plants of Mayurbhanj DistricBotany DepartmentAinda não há avaliações
- Reading: WritingDocumento8 páginasReading: WritingSantos ChhetriAinda não há avaliações
- Chestnut Trees Are of Moderate Growth RateDocumento2 páginasChestnut Trees Are of Moderate Growth RateEdrick YapAinda não há avaliações
- Historical Evolution and Current Status of The Taxonomy of Genus Pseudomonas 2009 Infection Genetics and EvolutionDocumento16 páginasHistorical Evolution and Current Status of The Taxonomy of Genus Pseudomonas 2009 Infection Genetics and EvolutionY lepay100% (1)
- Title: Cameron Highland As A Tourist Destination: We Tea Making Process andDocumento4 páginasTitle: Cameron Highland As A Tourist Destination: We Tea Making Process andbirubest86Ainda não há avaliações
- EEB XVIII PerumalDocumento7 páginasEEB XVIII PerumalDr. Prasad B. O.Ainda não há avaliações
- GingerDocumento14 páginasGingerNurhikmah FarahzanaAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 Spring Liner AvailabilityDocumento7 páginas2019 Spring Liner AvailabilityEditaAinda não há avaliações
- Pomegranate: By: Dr. Hera GulDocumento56 páginasPomegranate: By: Dr. Hera GulM ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Anti Vata DieteticsDocumento3 páginasAnti Vata DieteticsNatacha GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- How To See FairiesDocumento3 páginasHow To See Fairiesapi-26210871100% (2)
- Angiosperms BookDocumento278 páginasAngiosperms BookShah RafiqAinda não há avaliações
- The Trees of Florida Second Edition by Gil NelsonDocumento11 páginasThe Trees of Florida Second Edition by Gil NelsonPineapple Press, Inc.0% (1)
- The Alkaloids Chemistry and Physiology v18 VolumeDocumento429 páginasThe Alkaloids Chemistry and Physiology v18 VolumekiranAinda não há avaliações
- To Study The Natural Phenomenon of InheritanceDocumento1 páginaTo Study The Natural Phenomenon of InheritanceDhruv AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Plants Question NATDocumento2 páginasPlants Question NATRachelle Melegrito Bernabe100% (1)
- Portulacaria AfraDocumento4 páginasPortulacaria AfrajvnraoAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento7 páginasUntitledyogeshAinda não há avaliações
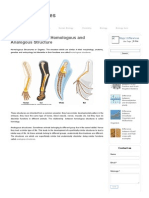
- Difference Between Homologous and Analogous Structure - Major DifferencesDocumento3 páginasDifference Between Homologous and Analogous Structure - Major DifferencesArvind BoudhaAinda não há avaliações
- Sandal WoodDocumento7 páginasSandal WoodSudhakar GanjikuntaAinda não há avaliações
- Research PaperDocumento9 páginasResearch Papercrizel lisay100% (1)
- New Flowers - FlowerMedDocumento5 páginasNew Flowers - FlowerMedAndré CamargoAinda não há avaliações
- Black Pepper: DescriptionDocumento4 páginasBlack Pepper: Descriptionmeet143bmAinda não há avaliações