Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Final Probes (P3)
Enviado por
augustlundbergDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Final Probes (P3)
Enviado por
augustlundbergDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Development of probes
Programme of investigation
The hypothesis being that the environment [Rain] & [Sunshine] functions as catalyst for erosion >>><<< growth, developing a series of probes will test this statement. The investigation is set out to explore how the different types of membranes [Materiality] affect the perception of space / the bodily spatial experience. A catalogue of different membranes will be produced. The following parameters will frame the perfomance of experiments; _Time; how materials change over time (Since we have a limited time-frame of Phase3 and therefore cannot examine and verifcate the longterm effect, this will be a data collection) _Orientation/angles (Investigation of phenomena in relation to this) _Structure; application of different membranes
> Change of material over TIME Estimated growth >>><<< erosion Potential growth (moss and sedum)
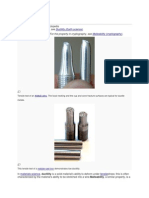
Copper oxidation Brass [3]
Concrete porosity increases
medium for growth
Acrylic
relatively weather-resistant/waterproof, but easily flammable Forex [4] [5]
[2] [1] & [2] ZAHNER, L. Williams (2005) Architectural metal surfaces. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, p. 300 & 308 [3] LAMPENS, Julian (1960) Own residence. Photo by KEMPENAER, Jan (2010) on Domus [Online] http://www.domusweb.it/en/architecture/2010/06/15/juliaan-lampens.html [accessed: 11.10.2013 [4] VIPPERD, Tagdkning Aps (2013) [Online] http://viptag.dk/pages/gronne-tage/sedumtag.php [accessed: 24.10.2013] [5] BIG, Bjarke Ingels Group (2013 - ongoing project) 8-tallet. [Online] http://www.8tallet.dk/billeder-html [accessed 24.10.2013]
[1]
Probe # 1
Parameter: Orientation/angles & Materiality Phenomenon: Sunshine
Materiality 1)
0 22,5 45 67,5 90
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
12)
The tested materials: 1) Copper 2) Perforated messing [staggered grid; large] 3)Perforated messing [straight grid; large] 4) Perforated messing [staggered grid; small] 5) Perforated messing [straight grid; small] 6) Acrylic 7) Forex 8) Cast [striped] 9) Cast [sandpaper] 10) Cast [wood] 11) Cast [plastic] 12) Cast [MDF]
Probe # 1
Conclusion//Discovered effects
Materiality
On a smooth surface (e.g. copper) specular reflection of visible light occurs
On a rough surface (e.g. concrete casted with rough texture) reflection is diffused/light is scattered Furthermore, shadowplay occurs
Perforated or translucent material filters light
Orientation/angles
Depending on the material properties reflection will vary according to the angle of which light reaches the surface (e.g. an acrylic membrane will only be visible from certain angles)
Probe # 2
Parameter: Orientation/angles & Materiality Phenomenon: Rain Materiality 0 45 Conclusion//Discovered effects
1)
Copper
2)
Perforated messing [straight grid; large] Materiality On a smooth surface water will easier be shed off. In general, waters surface tension makes it stick onto any material until gravity overcomes it
3)
Forex
4)
Acrylic
5)
Perforated messing [staggered grid; small] Materiality On a rough surface water will stick due to its texture
6)
Cast [striped]
7)
Cast [sandpaper]
8)
Cast [wood] Orientation/angles Due to gravity water moves vertically from its weight If the horizontally angled material is not rigid enough, the waters weight will bow it
9)
Cast [plastic]
Probe # 3
Structure; application of membranes
Probe # 3
Conclusion//Discovered effects
This probe investigates the relation between modularity versus variation. The three-dimensional units can facilitate double layer of membranes. In this probe the application of different membranes are limited to a single module. If each module in a larger/whole structure is applicated with variating membranes, different spatial experiences can take place within the same structure.
Probe # 4
The intended effect of the constructed membrane // A kaleidoscopic space
Você também pode gostar
- Scientific American - February 2019Documento112 páginasScientific American - February 2019Frankling AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Nearmiss Trending AnalysisDocumento40 páginasNearmiss Trending AnalysisTayyab MayoAinda não há avaliações
- Building MaterialsDocumento13 páginasBuilding MaterialsPriyanka BasuAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento50 páginasUnit 2Ravichandran GAinda não há avaliações
- Linde H16DDocumento2 páginasLinde H16Dfox mulderAinda não há avaliações
- Call Center MetricsDocumento16 páginasCall Center MetricspratimAinda não há avaliações
- Fiber Reinforced Plastics & Laminates GuideDocumento32 páginasFiber Reinforced Plastics & Laminates GuideMercyJatindroAinda não há avaliações
- Copper Wire and Cable: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento16 páginasCopper Wire and Cable: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediatanwar_anuj1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Bme Project ReportDocumento16 páginasBme Project ReportAditya RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Jared Diamond. Guns Germs and Steel 1999 PDFDocumento3 páginasJared Diamond. Guns Germs and Steel 1999 PDFSabah MushtaqAinda não há avaliações
- Piaggio Xevo 400 Workshop Manual PDFDocumento376 páginasPiaggio Xevo 400 Workshop Manual PDFsamasca_serban100% (1)
- UTHM confidential final exam for Engineering GeologyDocumento26 páginasUTHM confidential final exam for Engineering GeologyBryan LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Publications: Geochemistry, Geophysics, GeosystemsDocumento15 páginasPublications: Geochemistry, Geophysics, GeosystemsVAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Assignment 4Documento5 páginasMaterials Assignment 4maitham100Ainda não há avaliações
- Nbsir78 1575 PDFDocumento146 páginasNbsir78 1575 PDFAnonymous uCYIu1Ainda não há avaliações
- Modeling and Experimental Studies of Diffusion Bonding of Inconel 600 To Pyrolytic GraphiteDocumento23 páginasModeling and Experimental Studies of Diffusion Bonding of Inconel 600 To Pyrolytic GraphiteTJPRC PublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Ce 225 IntroductionDocumento51 páginasCe 225 IntroductionEdison SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Treatment Effects on Carbon Steel Microstructure & HardnessDocumento7 páginasHeat Treatment Effects on Carbon Steel Microstructure & Hardnessputri nur shahidaAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Science and Engineering: Dr. Abdulla Al-ShaterDocumento46 páginasMaterials Science and Engineering: Dr. Abdulla Al-ShaterAli ZbayelAinda não há avaliações
- Cleaning The Basis Metal PDFDocumento6 páginasCleaning The Basis Metal PDFAzizAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Atmospheric Corrosion Research in China: Junhua Dong, Enhou Han, Wei KeDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To Atmospheric Corrosion Research in China: Junhua Dong, Enhou Han, Wei KeArdian Kris BramantyoAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Temperature On The Impact Behaviour of Glass Polycarbonate LaminatesDocumento23 páginasThe Effect of Temperature On The Impact Behaviour of Glass Polycarbonate LaminatesRaphael Aragonês LeiteAinda não há avaliações
- Télé Star, Apr 2011Documento4 páginasTélé Star, Apr 2011emediageAinda não há avaliações
- Art:10 1007/BF00619084 PDFDocumento6 páginasArt:10 1007/BF00619084 PDFelectro242Ainda não há avaliações
- Simulation of Chloride Diffusivity For Cracked Concrete Based On RBSM and Truss Network ModelDocumento13 páginasSimulation of Chloride Diffusivity For Cracked Concrete Based On RBSM and Truss Network ModelBandula PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Characterization of WCCo Coatings On Metal SubstratesDocumento3 páginasCharacterization of WCCo Coatings On Metal SubstratesSayra MedellínAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum DotsDocumento14 páginasQuantum DotsSofie YeAinda não há avaliações
- 15 - Chapter 7 PDFDocumento24 páginas15 - Chapter 7 PDFpavan_1988Ainda não há avaliações
- Shridevi 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 989 012024Documento11 páginasShridevi 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 989 012024ron_danyAinda não há avaliações
- Strain Hardening MechanismsDocumento9 páginasStrain Hardening MechanismsRho AsaAinda não há avaliações
- Nanomechanical Testing of Gum Metal: # Society For Experimental Mechanics 2009Documento9 páginasNanomechanical Testing of Gum Metal: # Society For Experimental Mechanics 2009yerly ramirezAinda não há avaliações
- Wear of CeramicDocumento3 páginasWear of CeramicGhaith MdljAinda não há avaliações
- 11IJAERS 1020209 Studyon PDFDocumento10 páginas11IJAERS 1020209 Studyon PDFIJAERS JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Bourne Et Al - 2004 - Propagation of Waves Through A Float Glass LaminateDocumento5 páginasBourne Et Al - 2004 - Propagation of Waves Through A Float Glass LaminatehsuehungAinda não há avaliações
- Fracture Toughness K1c and Toughness GCDocumento5 páginasFracture Toughness K1c and Toughness GCEric Arriaga AltamiranoAinda não há avaliações
- Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Cellular Materials Via Three-Dimensional PrintingDocumento10 páginasAdditive Manufacturing of Metallic Cellular Materials Via Three-Dimensional Printingnewkid2202Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch.1 and Ch2Documento21 páginasCh.1 and Ch2omar TahaAinda não há avaliações
- Fluidity of Molten MetalDocumento18 páginasFluidity of Molten Metalbittu kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Nano ParticleDocumento99 páginasNano ParticleAnonymous gUjimJKAinda não há avaliações
- 1985 Laura Peffect of Icrostruc R On The Erosion of Steel byDocumento21 páginas1985 Laura Peffect of Icrostruc R On The Erosion of Steel byanuragAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Minerals Rocks PR PDFDocumento10 páginas10 Minerals Rocks PR PDFJimmy Torres0% (1)
- Fretting Wear of Thin Diamond Films on SteelDocumento9 páginasFretting Wear of Thin Diamond Films on SteelDersein SaraozAinda não há avaliações
- I Will Explain One Scientific Principle For The Following Failure (Discussed in p1.1) That Happen in Construction MaterialsDocumento5 páginasI Will Explain One Scientific Principle For The Following Failure (Discussed in p1.1) That Happen in Construction MaterialsamiraAinda não há avaliações
- The Surface Self-Organization in Process Friction and Corrosion of Composite MaterialsDocumento4 páginasThe Surface Self-Organization in Process Friction and Corrosion of Composite MaterialsWalber BragaAinda não há avaliações
- Casting-Experiment PDF 1Documento6 páginasCasting-Experiment PDF 1Motasem MrwanAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Analysis of Delamination in Laminated Composite PlatesDocumento44 páginasFinite Element Analysis of Delamination in Laminated Composite PlatesSrini RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Part I PDFDocumento8 páginasPart I PDFJohn WoodAinda não há avaliações
- Identifying An Effective Binder For The Stabilisation of Allophanic SoilsDocumento18 páginasIdentifying An Effective Binder For The Stabilisation of Allophanic SoilsBesim QelajAinda não há avaliações
- Exploring tarnished daguerreotypes with synchrotron light: XRF and μ-XANES analysisDocumento12 páginasExploring tarnished daguerreotypes with synchrotron light: XRF and μ-XANES analysisMANUEL NIÑO JIMENEZAinda não há avaliações
- Forms of corrosion classification and typesDocumento13 páginasForms of corrosion classification and typesAli AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Fracture Mechanics 1 EBB 334Documento37 páginasFracture Mechanics 1 EBB 334Luiz CordeiroAinda não há avaliações
- Nanostructured Surface Layer On Metallic Materials Induced by Surface Mechanical Attrition TreatmentDocumento8 páginasNanostructured Surface Layer On Metallic Materials Induced by Surface Mechanical Attrition TreatmentLalu SuhaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Corrosion in Concrete Lecture on Corrosion Processes and Protection MeasuresDocumento23 páginasCorrosion in Concrete Lecture on Corrosion Processes and Protection MeasuresSunil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- P Diffusion Welding of Commercial Aluminum To Carbon Steel: Hassan Abdellatif OsmanDocumento4 páginasP Diffusion Welding of Commercial Aluminum To Carbon Steel: Hassan Abdellatif OsmanerpublicationAinda não há avaliações
- 4534-Article Text-21129-1-10-20240207Documento6 páginas4534-Article Text-21129-1-10-20240207sandeepAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Descaling of Wire Rod Using Reverse Bending and BrushingDocumento10 páginasMechanical Descaling of Wire Rod Using Reverse Bending and BrushingTịch MịchAinda não há avaliações
- HTM Part A PDFDocumento13 páginasHTM Part A PDFRobotics HodAinda não há avaliações
- Duct IlityDocumento14 páginasDuct IlityMehman NasibovAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Network Topology On Cationic Diffusion and Hardness of Borate Glass SurfacesDocumento7 páginasImpact of Network Topology On Cationic Diffusion and Hardness of Borate Glass SurfacesDiogo Ramon BritoAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Laser Radiation on Wetting and Diffusion of Kovar Alloy and Borosilicate GlassDocumento11 páginasEffects of Laser Radiation on Wetting and Diffusion of Kovar Alloy and Borosilicate GlassBill WhiteAinda não há avaliações
- Geography - Geography Form 1 - Marking SchemeDocumento9 páginasGeography - Geography Form 1 - Marking SchemeJoy TechAinda não há avaliações
- Frost Resistance of Concrete Surfaces Coated With Waterproofing MaterialsDocumento9 páginasFrost Resistance of Concrete Surfaces Coated With Waterproofing MaterialsAshfaq AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Elaboration and Characterization of Facing Blocks Made of Laterite and Cement: Influence of Cement On StrengthDocumento6 páginasElaboration and Characterization of Facing Blocks Made of Laterite and Cement: Influence of Cement On Strengthbrahiman TRAOREAinda não há avaliações
- Nature and Properties of Construction MaterialsDocumento60 páginasNature and Properties of Construction MaterialsBiruk AkliluAinda não há avaliações
- Construction and Building Materials: Lorenzo Miccoli, Urs Müller, Patrick FontanaDocumento13 páginasConstruction and Building Materials: Lorenzo Miccoli, Urs Müller, Patrick FontanaasdfjuanAinda não há avaliações
- Homework Materials5Documento2 páginasHomework Materials5adahrenelleAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Loads, Sliding Speeds and Times On The Wear Rate For Different Materials - Hani Aziz AmeenDocumento8 páginasEffect of Loads, Sliding Speeds and Times On The Wear Rate For Different Materials - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenAinda não há avaliações
- 8.. - Study of Tin .FullDocumento8 páginas8.. - Study of Tin .FullTJPRC PublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Academic English for Materials: Academic EnglishNo EverandAcademic English for Materials: Academic EnglishAinda não há avaliações
- Contoh Spoof TextDocumento7 páginasContoh Spoof TextIndrayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Staring Index PagesDocumento7 páginasStaring Index PagesKolte RushikeshAinda não há avaliações
- My Life - An Illustrated Biograp - A.P.J. Abdul KalamDocumento76 páginasMy Life - An Illustrated Biograp - A.P.J. Abdul KalamAnonymous OJsGrxlx6100% (1)
- CIS ch.5 NotesDocumento4 páginasCIS ch.5 NotesClarize R. MabiogAinda não há avaliações
- DS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishDocumento16 páginasDS150 Simon RO Service Manual EnglishJosé AdelinoAinda não há avaliações
- 1.4404 enDocumento5 páginas1.4404 enyraju88Ainda não há avaliações
- Avoid Simple Mistakes: Cost Breakdown of Shipping Container HomesDocumento25 páginasAvoid Simple Mistakes: Cost Breakdown of Shipping Container Homesalfredo herrejon0% (1)
- Article - Content Management Maturity ModelDocumento4 páginasArticle - Content Management Maturity Modelprasannalaldas100% (3)
- Ekspanzioni VentilDocumento6 páginasEkspanzioni VentilNevena AksićAinda não há avaliações
- Korea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Documento8 páginasKorea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Cesar GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Sharp Lc-46d65u & Lc-52d65u Final LCD TV SMDocumento56 páginasSharp Lc-46d65u & Lc-52d65u Final LCD TV SMDan PrewittAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics CalculationsDocumento3 páginasFluid Mechanics CalculationsandreagassiAinda não há avaliações
- Tiempos de entrega y actividades de aprendizajeDocumento2 páginasTiempos de entrega y actividades de aprendizajejuanAinda não há avaliações
- Armstrong Ambience Plus 8 MMDocumento30 páginasArmstrong Ambience Plus 8 MMPreethi RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- LbiDocumento13 páginasLbiAac AacAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Circuit SimulatorDocumento7 páginasDigital Circuit SimulatorPratik V PandhareAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Organization & Assembly Language: 1 - An IntroductionDocumento35 páginasComputer Organization & Assembly Language: 1 - An IntroductionAhmad NaeemAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Pre Bid MeetingDocumento23 páginasPresentation On Pre Bid MeetinghiveAinda não há avaliações
- Uid Common Tech-Spec 08-13Documento5 páginasUid Common Tech-Spec 08-13Nasir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Subcooling Flow BoilingDocumento8 páginasSubcooling Flow BoilingBokiAinda não há avaliações
- Design and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Documento7 páginasDesign and analyze a non-inverting op-amp circuit with gain of 10Mandeep KaloniaAinda não há avaliações