Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
AP 20 Prepaid Expenses and Other Assets PDF
Enviado por
myangel_peach3305Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AP 20 Prepaid Expenses and Other Assets PDF
Enviado por
myangel_peach3305Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Form AP 20
Index Reference__________ Audit Program for Prepaid Expenses and Other Assets Legal Company Name Client:
Balance Sheet Date: Instructions: The auditor should refer to the audit planning documentation to gain an understanding of the financial reporting system and the planned extent of testing for prepaid expenses and other assets. Modification to the auditing procedures listed below may be necessary in order to achieve the audit objectives. All audit work should be documented in attached working papers, with appropriate references noted in the right column below.
Audit Objectives Balances of prepaid expenses, deferred charges, intangibles, and other assets are being allocated to future periods and/or realized in the ordinary course of business. Amortization or loss in value is recorded correctly with respect to accounts, amounts, and periods. Amortization methods and periods are reasonable and systematic. Prepaid expenses, deferred charges, intangibles, and other assets with no continuing value are removed from the books in a timely manner. Prepaid expenses, deferred charges, intangibles, and other assets are properly classified and presented in the financial statements and adequate disclosures are made with respect to amortization method and period and accumulated amortization for intangible assets.
Financial Statement Assertions Existence or occurrence Completeness Rights and obligations Valuation or allocation Valuation or allocation
Valuation or allocation
Presentation and disclosure
Performed By 1. If account balances for prepaid expenses, deferred charges, intangibles, and other assets are not material to the overall financial statements, limit testing to only performing analytical review procedures as follows: a. Compare current-period ending balance per the general ledger to the prior-period balance and investigate any unusual variations. b. Compare actual amounts to budgeted amounts. c. Review general ledger account activity and investigate any entries which appear unusual. 2. If prepaid insurance balance is material to the overall financial statements, perform the following procedures: a. Prepare or obtain from the client an analysis of prepaid insurance and related expense showing (1) insurance company name, (2) policy number, (3) type and amount of insurance coverage, (4) insurance coverage period, (5) premium amount, (6) monthly amortization amount, (7) prepaid insurance balance at the beginning of the period, (8) current-period payments or refunds, (9) current-period insurance expense, and (10) prepaid insurance balance at the end of the period. b. Test the arithmetical accuracy of the analysis and determine the reasonableness of the unamortized prepaid insurance balance at the end of the period. c. On a test basis, examine insurance policies in force and agree terms and coverage to detail information per the analysis. d. Consider obtaining independent confirmation of insurance coverage and terms from the insurance company or broker. e. Reconcile insurance expense per the analysis to the general ledger.
Workpaper Reference
Performed By f. Determine whether insurance premiums are being financed and, if so, if the related liabilities and finance costs have been recorded. g. Vouch significant premiums to premium notices. h. Determine whether all significant insurable risks have been considered. 3. If prepaid property taxes balance is material to the overall financial statements, perform the following procedures: a. Prepare or obtain from the client an analysis of prepaid property taxes and related expense showing (1) taxing authority, (2) property location and description, (3) assessed value, (4) total tax paid, (5) payment date, (6) period covered, (7) prepaid property taxes balance at the beginning of the period, (8) current-period payment, (9) current-period expense, and (10) prepaid property taxes balance at the end of the period. b. Examine tax bills and record of payment and agree information to the detail analysis. c. Test the arithmetical accuracy of the analysis and determine whether the prepaid balance at the end of the period is appropriate. d. Reconcile property tax expense per the analysis to the general ledger. e. Determine the extent of any property taxes assessed by taxing authorities but delinquent as of the balancesheet date. 4. If intangible assets are material to the overall financial statements, perform the following procedures: a. For intangible assets acquired from others, examine supporting documentation for the consideration paid.
Workpaper Reference
Performed By b. For intangible assets acquired in connection with the acquisition of another company, determine that the allocation of the purchase price is in accordance with IAS. c. Verify that major transactions resulting in the recording of intangible assets were properly authorized. d. Determine if the amortization period is reasonable. e. Reconcile amortization expense to the general ledger. f. Evaluate whether any events or changes in circumstances have occurred indicating that the carrying amount of intangible assets may not be recoverable and whether an impairment loss should be recognized. 5. For other prepaid expenses, deferred charges, and other assets that are material to the overall financial statements, perform the following procedures: a. Prepare or obtain from the client an analysis of such assets showing (1) description of the asset, (2) period covered, (3) balance at the beginning of the period, (4) additions, (5) amount charged to expense, and (6) balance at the end of the period. b. Trace significant additions to supporting documents such as invoices, purchase contracts, minutes, etc. c. If any costs are allocated to future periods, evaluate the appropriateness of such allocation. d. Determine the reasonableness of the remaining unamortized asset balance and the remaining amortization period. 6. Confirm material deposit balances and other similar assets held by third parties.
Workpaper Reference
Performed By 7. Determine if there has been an impairment of value for the assets and make appropriate adjustments. 8. Determine whether balances are properly classified in the financial statements as current and noncurrent assets and adequate disclosures are made with respect to amortization method and period and accumulated amortization for intangible assets. 9. If the auditor is concerned about the risk of fraud, audit procedures such as the following should be considered in addition to the ones listed above: a. Scrutinize documentation supporting amounts capitalized. b. Vouch and trace transactions to original documents (not copies), including examination of payment orders and bank statements. c. Confirm significant deposits and assets held by others. d. Obtain a list of the detail of all suspense accounts and scrutinize activity for unusual or large items. e. Review journal entries made to the general ledger accounts.
Workpaper Reference
Based on the procedures performed and the results obtained, it is my opinion that the objectives listed in this audit program have been achieved. Performed by Reviewed and approved by Conclusions: Date Date
Comments:
Você também pode gostar
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocumento2 páginasQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- North American Indians - A Very Short IntroductionDocumento147 páginasNorth American Indians - A Very Short IntroductionsiesmannAinda não há avaliações
- Management Reporting A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo EverandManagement Reporting A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Program-MSBPLDocumento21 páginasAudit Program-MSBPLTasdik MahmudAinda não há avaliações
- Audit of Expenditure Cycle TestsDocumento19 páginasAudit of Expenditure Cycle Teststankofdoom 4100% (1)
- Audit Program For Fixed Assets: Form AP 35Documento9 páginasAudit Program For Fixed Assets: Form AP 35Adrianna LenaAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Program For InvestmentsDocumento3 páginasAudit Program For Investmentsxstljvll100% (1)
- SQM-Crop Kit Pepper L-EnDocumento96 páginasSQM-Crop Kit Pepper L-EnPavel Lilian100% (3)
- Clinical Audit Report FormatDocumento4 páginasClinical Audit Report Formatmyangel_peach3305Ainda não há avaliações
- IIA Working PapersDocumento4 páginasIIA Working Papersboludu100% (1)
- Audit Program Revenues Expenses (AP70Documento4 páginasAudit Program Revenues Expenses (AP70hossainmz100% (1)
- Audit of The Payroll and Personnel CycleDocumento31 páginasAudit of The Payroll and Personnel Cyclerico_putra_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Internal Control On Notes PayableDocumento13 páginasInternal Control On Notes PayableAmelia LadromaAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Program For EquityDocumento12 páginasAudit Program For EquityIra Jean DaganzoAinda não há avaliações
- 5.0 Audit For InventoriesDocumento20 páginas5.0 Audit For InventoriesChristine JotojotAinda não há avaliações
- Senior Internal Auditor Promotion Exam ReviewDocumento8 páginasSenior Internal Auditor Promotion Exam Reviewwondimeneh AsratAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 Evidence Substantive TestsDocumento148 páginasChapter 10 Evidence Substantive Testsfalculan_delsie100% (2)
- Richard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Documento274 páginasRichard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Juan Manuel ContrerasAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - Audit of Purchasing Disbursement CycleDocumento71 páginas5 - Audit of Purchasing Disbursement CycleJericho Pedragosa100% (1)
- The Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocumento32 páginasThe Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingsablcsAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6 AUDIT OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS Lecture Notes 2020Documento11 páginasUnit 6 AUDIT OF INTANGIBLE ASSETS Lecture Notes 2020Marynelle Labrador Sevilla100% (1)
- Correction of Error LECTUREDocumento3 páginasCorrection of Error LECTUREKobe bryantAinda não há avaliações
- Transaction CyclesDocumento7 páginasTransaction CyclesJames LopezAinda não há avaliações
- Substantive Testing Cash Receivables InventoriesDocumento7 páginasSubstantive Testing Cash Receivables InventoriesCamille Francisco AgustinAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Fixed AssetsDocumento1.204 páginasOracle Fixed AssetsYudha Prayoga100% (1)
- Audit Program For Property, Plant and Equipment Agency Name: Balance Sheet DateDocumento7 páginasAudit Program For Property, Plant and Equipment Agency Name: Balance Sheet DateZosimo Solano100% (3)
- PSP by AccountsDocumento23 páginasPSP by AccountsatuanainiAinda não há avaliações
- Audit of Sale and Collection Cycle!!!Documento14 páginasAudit of Sale and Collection Cycle!!!ashiakas82730% (1)
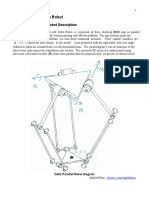
- Revolute-Input Delta Robot DescriptionDocumento43 páginasRevolute-Input Delta Robot DescriptionIbrahim EssamAinda não há avaliações
- Auditing Theory Review Course Pre-Board Exam - FinalDocumento11 páginasAuditing Theory Review Course Pre-Board Exam - FinalROMAR A. PIGAAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Program - Breeding StockDocumento4 páginasAudit Program - Breeding StockNanette Rose HaguilingAinda não há avaliações
- Audit PPE Substantive Test ModuleDocumento65 páginasAudit PPE Substantive Test Modulejulia4razoAinda não há avaliações
- Linux OS MyanmarDocumento75 páginasLinux OS Myanmarweenyin100% (15)
- Quiz 1 AuditingDocumento1 páginaQuiz 1 AuditingSashaAinda não há avaliações
- Audit of LiabsDocumento2 páginasAudit of LiabsRommel Royce CadapanAinda não há avaliações
- Testing Internal Controls for Revenue CycleDocumento4 páginasTesting Internal Controls for Revenue CyclestillwinmsAinda não há avaliações
- Auditing AssignmentDocumento17 páginasAuditing Assignmentihsan278Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 01 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocumento74 páginasChapter 01 - Auditing and Assurance ServicesBettina OsterfasticsAinda não há avaliações
- p7-10 HelpDocumento8 páginasp7-10 HelpAJ SuttonAinda não há avaliações
- Auditing Debt Obligations TransactionsDocumento9 páginasAuditing Debt Obligations TransactionsBeatrize ValerioAinda não há avaliações
- Audit 2 - TheoriesDocumento2 páginasAudit 2 - TheoriesJoy ConsigeneAinda não há avaliações
- Capital BudgetingDocumento4 páginasCapital Budgetingrachmmm0% (3)
- Chapter10 - AnswerDocumento21 páginasChapter10 - Answershanerikim100% (1)
- Long Term Debt ProgramDocumento10 páginasLong Term Debt ProgramSyarif Muhammad Hikmatyar100% (1)
- AUDITINGDocumento20 páginasAUDITINGAngelieAinda não há avaliações
- Audits of special purpose and single financial statementsDocumento6 páginasAudits of special purpose and single financial statementsRachel LeachonAinda não há avaliações
- Session 3 AUDITING AND ASSURANCE PRINCIPLESDocumento29 páginasSession 3 AUDITING AND ASSURANCE PRINCIPLESagent2100Ainda não há avaliações
- AUDIT PROCEDURES: 8 STEPSDocumento3 páginasAUDIT PROCEDURES: 8 STEPSManish Kumar Sukhija50% (2)
- Substantive Tests of Expenditure Cycle Accounts Substantive TestsDocumento3 páginasSubstantive Tests of Expenditure Cycle Accounts Substantive TestsJuvelyn RedutaAinda não há avaliações
- Auditing The Finance and Accounting FunctionsDocumento19 páginasAuditing The Finance and Accounting FunctionsMark Angelo BustosAinda não há avaliações
- AC414 - Audit and Investigations II - Audit of Non-Current AssetsDocumento21 páginasAC414 - Audit and Investigations II - Audit of Non-Current AssetsTsitsi AbigailAinda não há avaliações
- MAS Lauderbach 1 PDFDocumento210 páginasMAS Lauderbach 1 PDFIllion IllionAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 05 PRTC AUDP LECS AP.1601 Audit of Inventories PDFDocumento9 páginas2014 05 PRTC AUDP LECS AP.1601 Audit of Inventories PDFTed Bryan D. CabaguaAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer For Auditing TheoryDocumento10 páginasReviewer For Auditing TheoryMharNellBantasanAinda não há avaliações
- Expenditure CycleDocumento33 páginasExpenditure CycleGerald Salvador MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Notes From Sir Red Sirug Handouts On Auditing TheoryDocumento104 páginasNotes From Sir Red Sirug Handouts On Auditing TheoryAmithy GuevarraAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Revenue Cycle AssertionsDocumento57 páginasAudit Revenue Cycle AssertionsRia CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Accounting 1 Final Exam ReviewDocumento13 páginasAdvance Accounting 1 Final Exam ReviewTina LlorcaAinda não há avaliações
- Audit of InvestmentsDocumento3 páginasAudit of InvestmentsJasmine Marie Ng Cheong50% (2)
- Home Office Branch and Agency Accounting QuestionsDocumento32 páginasHome Office Branch and Agency Accounting QuestionsMichaela Quimson100% (1)
- Auditing TheoryDocumento27 páginasAuditing Theorypenz8_ahl9763Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 10 Control Self AssessmentDocumento24 páginasWeek 10 Control Self AssessmentMark Angelo BustosAinda não há avaliações
- Audit of LiabilitiesDocumento5 páginasAudit of LiabilitiesGille Rosa Abajar100% (1)
- Auditing in Computer Environment in WordDocumento2 páginasAuditing in Computer Environment in WordLotte CabreraAinda não há avaliações
- Substantive Tests of Transactions and Account Balances EditedDocumento85 páginasSubstantive Tests of Transactions and Account Balances EditedPiaElemos100% (2)
- Pre EngagementDocumento2 páginasPre EngagementCM LanceAinda não há avaliações
- AP.3401 Audit of InventoriesDocumento8 páginasAP.3401 Audit of InventoriesMonica GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Audit procedures and evidenceDocumento7 páginasAudit procedures and evidenceJun Ladrillo100% (1)
- External Audit Staff A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo EverandExternal Audit Staff A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Audit Ar EngDocumento26 páginasAudit Ar EngRahul PalAinda não há avaliações
- 19 - April - 2012-Item 11 - Internal Audit Report On Credit Cards5 PDFDocumento14 páginas19 - April - 2012-Item 11 - Internal Audit Report On Credit Cards5 PDFmyangel_peach3305Ainda não há avaliações
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocumento14 páginasFinancial Ratio AnalysisPrasanga WdzAinda não há avaliações
- Deloitte - IfRSs in Your Pocket 2012Documento136 páginasDeloitte - IfRSs in Your Pocket 2012syedtahaaliAinda não há avaliações
- HAAD-Policy Scope of Practice For Practical Nurse PDFDocumento4 páginasHAAD-Policy Scope of Practice For Practical Nurse PDFmyangel_peach3305Ainda não há avaliações
- HAAD-Policy Scope of Practice For Practical Nurse PDFDocumento4 páginasHAAD-Policy Scope of Practice For Practical Nurse PDFmyangel_peach3305Ainda não há avaliações
- Sample Questions PDFDocumento14 páginasSample Questions PDFmyangel_peach3305Ainda não há avaliações
- ME Flowchart 2014 2015Documento2 páginasME Flowchart 2014 2015Mario ManciaAinda não há avaliações
- CvSU Vision and MissionDocumento2 páginasCvSU Vision and MissionJoshua LagonoyAinda não há avaliações
- Grecian Urn PaperDocumento2 páginasGrecian Urn PaperrhesajanubasAinda não há avaliações
- SAP HANA Analytics Training at MAJUDocumento1 páginaSAP HANA Analytics Training at MAJUXIAinda não há avaliações
- Khin Thandar Myint EMPADocumento101 páginasKhin Thandar Myint EMPAAshin NandavamsaAinda não há avaliações
- GUIA REPASO 8° BÁSICO INGLÉS (Unidades 1-2)Documento4 páginasGUIA REPASO 8° BÁSICO INGLÉS (Unidades 1-2)Anonymous lBA5lD100% (1)
- Classroom Rules and RegulationsDocumento1 páginaClassroom Rules and RegulationsASHYJO28Ainda não há avaliações
- Importance of SimilesDocumento10 páginasImportance of Similesnabeelajaved0% (1)
- MOTOR INSURANCE TITLEDocumento5 páginasMOTOR INSURANCE TITLEVara PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Hitachi Loader Lx70 Lx80 Service Manual KM 111 00yyy FTT HDocumento22 páginasHitachi Loader Lx70 Lx80 Service Manual KM 111 00yyy FTT Hmarymurphy140886wdi100% (103)
- Reviews: Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery: A Shift in Eligibility and Success CriteriaDocumento13 páginasReviews: Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery: A Shift in Eligibility and Success CriteriaJulia SCAinda não há avaliações
- Eng Listening Integrated Hkdse2022 UmayDocumento21 páginasEng Listening Integrated Hkdse2022 UmayHoi TungAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Distribution: X e X FDocumento30 páginasNormal Distribution: X e X FNilesh DhakeAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment OUMH1203 English For Written Communication September 2023 SemesterDocumento15 páginasAssignment OUMH1203 English For Written Communication September 2023 SemesterFaiz MufarAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Tricks - Frequency Demodulation AlgorithmsDocumento3 páginasDSP Tricks - Frequency Demodulation Algorithmsik1xpvAinda não há avaliações
- LAWHIST - Week1 - Codamon Lim Tan PDFDocumento32 páginasLAWHIST - Week1 - Codamon Lim Tan PDFMargell TanAinda não há avaliações
- Productivity in Indian Sugar IndustryDocumento17 páginasProductivity in Indian Sugar Industryshahil_4uAinda não há avaliações
- Identifying States of Matter LessonDocumento2 páginasIdentifying States of Matter LessonRaul OrcigaAinda não há avaliações
- Modbus Quick StartDocumento3 páginasModbus Quick StartNash JungAinda não há avaliações
- Rak Single DentureDocumento48 páginasRak Single Denturerakes0Ainda não há avaliações
- Direct Shear TestDocumento10 páginasDirect Shear TestRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Optics Part-1Documento14 páginasWave Optics Part-1Acoustic GuyAinda não há avaliações
- Medical StoreDocumento11 páginasMedical Storefriend4sp75% (4)
- Contribution Sushruta AnatomyDocumento5 páginasContribution Sushruta AnatomyEmmanuelle Soni-DessaigneAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5 ADHAVANDocumento29 páginasExperiment 5 ADHAVANManoj Raj RajAinda não há avaliações