Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chemistry Gen
Enviado por
YekitaSTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chemistry Gen
Enviado por
YekitaSDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chemistry Gen: Course Description Year 2 PART - II CGT 21a Unit I.
Basic physical chemistry I Gaseous state: Gas laws, kinetic theory of gas, collision and gas pressure, derivation of gas laws from kinetic theory, average kinetic energy of translation, Boltzmann constant and absolute scale of temperature, Maxwell's distribution law of molecular speeds (without derivation), most probable, average and root mean square speed of gas molecules, principle of equipartition of energy (without derivation). Mean free path and collision frequencies. Heat capacity of gases (molecular basis); viscosity of gases. Real gases, compressibility factor, deviation from ideality, van der Waals equation of state, critical phenomena, continuity of states, critical constants. Liquid state: physical properties of liquids and their measurements: surface tension and viscosity. Unit II. Basic physical chemistry II Chemical kinetics and catalysis: order and molecularity of reactions, rate laws and rate equations for first order and second order reactions (differential and integrated forms); zero order reactions. Determination of order of reactions. Temperature dependence of reaction rate, energy of activation. Catalytic reactions: homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic reactions, autocatalytic reactions, catalyst poisons, catalyst promoters (typical examples). CGT 21b Unit I. Principles of qualitative inorganic analysis Formation of sublimates; principle of flame test, borax-bead test, cobalt nitrate test, fusion test, chromyl chloride test; analytical reactions for the detection of nitrate, nitrite, halides, phosphate, arsenate, arsenite, sulphide, thiosulphate, sulphate, thiocyanate, borate, boric acid, carbonate. Analytical reactions for the detection of Cr3+, Fe3+, , Ni2+, Cu2+, As3+, Mn2+, Importance of common-ion effect in the separation of Group II cations, and Group III cations. Unit II. Basic inorganic chemistry III
Comparative study of s-block elements: Group trends in electronic configuration, modification of pure elements, common oxidation states, inert pair effect, chemical properties and reactions in respect of the following group elements: i) Li-Na-K ii) Be-Mg-Ca-Sr-Ba 25 Extraction and purification of elements from natural sources: Li, Cr, Ni, Ag, Au. Electroplating, galvanizing and anodizing. CGT 22a Unit I. Basic physical chemistry III Thermodynamics: Definition of thermodynamic terms: Intensive and extensive variables, isolated, closed and open systems. Cyclic, reversible and irreversible processes. Thermodynamic functions and their differentials. Zeroth law of thermodynamics, concept of heat (q) and work (w). First law of thermodynamics, internal energy (U) and enthalpy (H); relation between Cp and Cv, calculation of w, q, U and H for expansion of ideal gas under isothermal and adiabatic conditions for reversible and irreversible processes including free expansion. Joule-Thomson Coefficient and inversion temperature. Application of First law of thermodynamics: standard state, standard enthalpy changes of physical and chemical transformations: fusion, sublimation, vaporization, solution, dilution, neutralization, ionization,. Hess's law of constant heat summation. Bond-dissociation energy, Born haber cycle for calculation of lattice energy. Kirchhoffs equation, relation between H and U of a reaction. Spontaneous processes, heat engine, Carnot cycle and its efficiency, Second law of thermodynamics, Entropy (S) as a state function, molecular interpretation of entropy, entropy changes in simple transformations. Free energy: Gibbs function (G) and Helmholtz function (A), Gibbs-Helmholtz equation, criteria for thermodynamic equilibrium and spontaneity of a process. Unit II. Basic physical chemistry IV Chemical equilibrium: chemical equlibria of homogeneous and heterogeneous systems, derivation of expression of equilibrium constants; temperature, pressure and
concentration dependence of equilibrium constants (KP, KC, KX); Le Chatelier's principle of dynamic equilibrium. Colloids: colloids and crystalloids, classification of colloids, preparation and purification of colloids: ferric hydroxide sol and gold sol. Properties of colloids: Brownian motion, peptization, dialysis, Tyndal effect and its applications. Protecting colloids, gold number, isoelectric points, coagulation of colloids by electrolytes, SchulzeHardy rule. CGT 22b Unit 1. Basic physical chemistry V Acids-bases and solvents: Modern aspects of acids and bases: Arrhenius theory , theory of solvent system, Bronsted and Lowry's concept, Lewis concept with typical examples, applications and limitations. Strengths of acids and bases (elementary idea). Ionization of weak acids and bases in aqueous solutions, application of Ostwald's dilution law, ionization constants, ionic product of water, pH-scale, buffer solutions and their pH values, buffer actions; hydrolysis of salts. Solutions of electrolytes: Electrolytic conductance, specific conductance, equivalent conductance and molar conductance of electrolytic solutions. Influence of temperature and dilution on weak electrolytes. 26 Unit II. Basic physical chemistry VI Electrode potential: Electrode potentials, Nernst Equation, reference electrodes: normal hydrogen electrode and calomel electrodes, Emf of electrochemical cells and its measurement, electrode potential series and its applications. Solutions of non-electrolytes: Colligative properties of solution, Raoult's Law, relative lowering of vapor pressure, osmosis and osmotic pressure; elevation of boiling point and depression of freezing point of solvents. CGP 23 Qualitative Analysis of Single Organic Compound(s) Experiment A: Detection of special elements (N, Cl, and S) in organic compounds. Experiment B: Solubility and Classification (solvents: H2O, dil. HCl, dil. NaOH)
Experiment C: Detection of functional groups -NO2, -NH2, -COOH, carbonyl (-CHO, >C=O), -OH (phenolic) in solid organic compounds. Experiments A - C with unknown (at least 6) solid samples containing not more than two of the above types of functional groups should be done. CGP 24 Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic Mixtures: Experiments A: Preliminary Tests for Acid and Basic radicals in given samples. Experiments B: Wet tests for Acid and Basic radicals in given samples. Experiments C: Confirmatory tests. Acid Radicals: Cl-, Br-, I-, NO2 -1, S2-, SO4 -2, PO4 -3, BO3 3-, H3BO3. Basic Radicals: Na+, K+, Ca+2, Sr+2, Ba+2, Cr+3, Mn+2, Fe+3, Ni+3, Cu+2, NH4 +. Note: At least 6 unknown samples are to be analyzed by each student during the laboratory session.
Você também pode gostar
- Tropical Depression TenDocumento1 páginaTropical Depression TenYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) safety data sheetDocumento7 páginasRegulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) safety data sheetYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- The Cinderella MomentDocumento1 páginaThe Cinderella MomentYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- PART III Syllabus of CUDocumento6 páginasPART III Syllabus of CUYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10Documento8 páginasChapter 10YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Paper, 29.01.08Documento21 páginasAutism Paper, 29.01.08YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- CCC Background PaperDocumento1 páginaCCC Background PaperYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Pyroclastic Igneous Rocks Pumice ScoriaDocumento1 páginaPyroclastic Igneous Rocks Pumice ScoriaYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Consent Form For CCC SurveyDocumento1 páginaConsent Form For CCC SurveyYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Amended Data Formats, 1,2 (1.2.08), Final VersionDocumento2 páginasAmended Data Formats, 1,2 (1.2.08), Final VersionYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Paper, Revised 16.03.08Documento14 páginasAutism Paper, Revised 16.03.08YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Dad, Please Read ThisDocumento1 páginaDad, Please Read ThisYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Paper, Revised 21.03.08Documento14 páginasAutism Paper, Revised 21.03.08YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Paper, Revised 13.03.08Documento15 páginasAutism Paper, Revised 13.03.08YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- A Protocol For Assessment, Investigation & Intervention, Modified 13.03.08Documento20 páginasA Protocol For Assessment, Investigation & Intervention, Modified 13.03.08YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayDocumento1 páginaTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
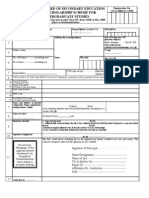
- F-1 Central Board of Secondary Education Merit Scholarship SchemeDocumento3 páginasF-1 Central Board of Secondary Education Merit Scholarship SchemeYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Misconceptions For Ncetm ForumDocumento2 páginasMathematical Misconceptions For Ncetm ForumYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- 12-Principles of Inheritance and Variation-MCQDocumento0 página12-Principles of Inheritance and Variation-MCQYekitaS100% (4)
- Jem 2009 MDocumento3 páginasJem 2009 MYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Interact With Chairman Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) ConsolidatedDocumento27 páginasInteract With Chairman Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) ConsolidatedAbhijit BalanAinda não há avaliações
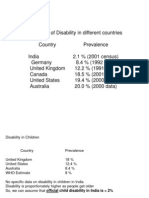
- Census of India 2011: West Bengal Figures at A GlanceDocumento1 páginaCensus of India 2011: West Bengal Figures at A GlanceYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- F-3 Central Board of Secondary Education Merit Scholarship Scheme For Undergraduate StudiesDocumento3 páginasF-3 Central Board of Secondary Education Merit Scholarship Scheme For Undergraduate StudiesMohan LalAinda não há avaliações
- Model Question and Answers For English - Sample 5Documento10 páginasModel Question and Answers For English - Sample 5YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Reaction Kinetics Investigation: Inversion of Sucrose: 1. BackgroundDocumento7 páginasReaction Kinetics Investigation: Inversion of Sucrose: 1. BackgroundYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Change The Positions of The Frogs On Right and Left. Usually It Can Be Done in 3 Minutes If Your IQ Is Not Under 50Documento2 páginasChange The Positions of The Frogs On Right and Left. Usually It Can Be Done in 3 Minutes If Your IQ Is Not Under 50YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Brix Scale for Measuring Sugar SolutionsDocumento1 páginaBrix Scale for Measuring Sugar SolutionsYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation Results:: S/ON Liquid 2BV 0.6L of 33.0 Brix - 0.200 KG "Documento6 páginasEvaluation Results:: S/ON Liquid 2BV 0.6L of 33.0 Brix - 0.200 KG "YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Invert Sugar 17 12 09Documento9 páginasInvert Sugar 17 12 09YekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Inversion of Sucrose 4th CycleDocumento3 páginasInversion of Sucrose 4th CycleYekitaSAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- PENTADOMEDocumento13 páginasPENTADOMERoxana LoredanaAinda não há avaliações
- Note On Backpropagation John Hull: Ith Observation, and yDocumento2 páginasNote On Backpropagation John Hull: Ith Observation, and yOmar BairanAinda não há avaliações
- Petrophysics in Horizontal WellsDocumento13 páginasPetrophysics in Horizontal WellsusuarioAinda não há avaliações
- ME PDC Course PlanDocumento6 páginasME PDC Course PlanBabitha DhanaAinda não há avaliações
- Empirical Correlations Drained Shear Strength For Slope Stability AnalysesDocumento10 páginasEmpirical Correlations Drained Shear Strength For Slope Stability AnalysesPSAinda não há avaliações
- DM Unit 1Documento15 páginasDM Unit 1Rushikesh ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Kotval Mullin Fiscal ImpactDocumento44 páginasKotval Mullin Fiscal ImpactMarkWeberAinda não há avaliações
- Investigation on Pole-Slot Combinations for PM Machines with Concentrated WindingsDocumento6 páginasInvestigation on Pole-Slot Combinations for PM Machines with Concentrated WindingsAnna DrKiss SzűcsnéAinda não há avaliações
- Verification and ValidationDocumento22 páginasVerification and Validationapi-3806986Ainda não há avaliações
- COMPLEX NUMBER SOLUTIONSDocumento22 páginasCOMPLEX NUMBER SOLUTIONSSanjanaAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 336 Bomb Calorimetry Lab ExperimentDocumento3 páginasCHEM 336 Bomb Calorimetry Lab ExperimentSerenityAinda não há avaliações
- The Traditional Theory of CostsDocumento13 páginasThe Traditional Theory of Costsamrendra kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Visit TutorialDocumento83 páginasVisit Tutorialfab1991Ainda não há avaliações
- Quarter 3 Week 9 Math DLL by MpuhiDocumento25 páginasQuarter 3 Week 9 Math DLL by MpuhiCristy AmorAinda não há avaliações
- 15 Atom HidrogenDocumento42 páginas15 Atom HidrogenRahajengAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento41 páginasChapter 1api-268597715Ainda não há avaliações
- Answer: Acceptance (Formalized Acceptance)Documento673 páginasAnswer: Acceptance (Formalized Acceptance)Patty Chacón100% (1)
- Thermal Overload Protection Functional TestDocumento1 páginaThermal Overload Protection Functional TestMihai BancuAinda não há avaliações
- Parachute FormulasDocumento3 páginasParachute FormulaskaranmarwahaAinda não há avaliações
- Business Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Kinds of ProportionDocumento25 páginasBusiness Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 3: Kinds of ProportionZia Belle Bedro - LuardoAinda não há avaliações
- Structures Lab ReportDocumento18 páginasStructures Lab Reportedk5035Ainda não há avaliações
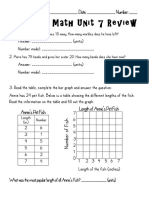
- Everyday Math Unit 7 ReviewDocumento3 páginasEveryday Math Unit 7 ReviewReekhaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingDocumento20 páginasChapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingSiamHashan100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 (AutoRecovered)Documento12 páginasCHAPTER 5 (AutoRecovered)Wilmar AcaboAinda não há avaliações
- A Tutorial On Combinatorics An Enumeration in Music TheoryDocumento22 páginasA Tutorial On Combinatorics An Enumeration in Music TheoryGrandeBoiAinda não há avaliações
- PhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 1Documento3 páginasPhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 1villanuevaparedesaracely4Ainda não há avaliações
- Gumbel DistributionDocumento5 páginasGumbel DistributionAdrian IosifAinda não há avaliações
- Seepage Pressure PDFDocumento8 páginasSeepage Pressure PDFVenance MasanjaAinda não há avaliações
- 19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20Documento22 páginas19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20sai tejaAinda não há avaliações
- PRINCIPLES OF MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM DESIGNDocumento3 páginasPRINCIPLES OF MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM DESIGNKhadga Shrestha50% (2)