Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
WS 2013 04 Advanced Materials Aerospace PDF
Enviado por
Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
WS 2013 04 Advanced Materials Aerospace PDF
Enviado por
Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Dr. Jan Seyfarth
Product Manager Digimat April 2013
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
2
Aerospace Industry
A Very Short Introduction...
Digimat
e-Xstream & Simulation Strategy
Software
Materials
Technology & Applications
From Materials to Structure
Current Status and Ongoing Developments
Structures
Technology & Applications
Summary
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Digimat
e-Xstream engineering
Simulation Strategy
Nonlinear Multi-Scale Simulation Platform
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
3
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
4
Who are we...? A MSC Software Company!
Team of ~30 persons
- PhDs (~65%)
- MS & BS Engineering (~ 25%)
- Marketing, Finance & Admin (~10%)
+ TBH in 2013
Material experts
- Micromechanics
It`s all about...
COMPOSITES
A
m
s
t
e
r
d
a
m
,
O
c
t
o
b
e
r
2
0
1
2
e-Xstream engineering
Digimat
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
5
What are we concerned about?
Inter-dependencies in the Design of a Composite Part
e-Xstream engineering
Digimat
Structural design
influences processing
Manufacturing sets
local microstructure
Local microstructure
sets material
properties
What do we do...? Multi-Scale!
MICRO
- Material
MACRO
- Dumbbell
- Part
- System
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
6
Micro-
structure Material model
Part
performance
Characterization
Process
System level
Simulation Strategy
Digimat
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
7
Material Related Design Challenges
Manage Material Data
- Generate Data (Cost & Time of Test)
- Manage, Trace, Protect (IP)
- Comply (Regulation)
Model (composite) Materials, Part & Systems
- Nonlinearity: Progressive damage & failure
- Anisotropy
- Heterogeneity
- Process dependency
Use
- The optimal mix of material
- The Material(s) as a design parameter to innovate
- The optimal manufacturing process
Simulation Strategy
Digimat
Nonlinear Multiscale Modeling Platform
8
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Nonlinear Multi-Scale Simulation Platform
Digimat
- Performance
- Stiffness
- Failure
- Fatigue
- Technology
- Linear/Nonlinear
- Mean Field/FEA
- Micro/Hybrid
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
9
Nonlinear Multiscale Modeling Platform
Holistic modeling
- Materials
- Chopped Fibers: Short/Long
- Continuous Fibers
- Fillers
- Physics
- (Thermo-) Mechanical
- Thermal Conductivity
- Electric Conductivity
- Manufacturing
- Injection
- Compression
- Draping
- Fiber placement
- MuCell
Nonlinear Multi-Scale Simulation Platform
Digimat
Nonlinear Multiscale Modeling Platform
MICRO
- Virtual Material
MACRO
- Data management
- Reverse Engineering
- FEA Interfaces
- Mapping
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
10
Material Engineering
Structural Engineering
Nonlinear Multi-Scale Simulation Platform
Digimat
Interfaces to MSC Nastran
SOL 101 - linear
- Weak coupling [Nastran material card used]
- Including SOL 103 for vibration
- Including SOL 105 for buckling
SOL 400 - nonlinear
- Implicit
- Strong coupling [Digimat user subroutine]
SOL 700 - nonlinear
- Explicit
- Strong coupling [Digimat user subroutine]
11
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Available in 4.4.1
Specification phase
Under development
Nonlinear Multi-Scale Simulation Platform
Digimat
Materials
Composites
Materials Engineering
Applications
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
12
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
13
A Vast Mix of Different Materials
Metal (Alloys)
- Aluminium / Magnesium
- Molybdenum / Titanium / Tungsten
Reinforced Plastics
- Thermoplastics + Carbon fibers
- Epoxy + Glass / Carbon / Aramid fibers
Ceramics
- Titanium + SiC fibers
Composites
Materials
Complex structures Pores
Stacking Weaving
Structure / Orientation
Random
Material's
Performance (Stiffness, failure, fatigue, ...)
Anisotropy
Digimat-FE
Fast & Efficient Prediction of Composite Material Properties
14
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Materials Engineering
Materials
UD Composites
Defects & influence of processing
- ISEMP
- Integrative Simulation and Engineering of Materials and Processes
Aims at the simulation of material details and not only the
macroscopic overall properties
Aims at considering manufacturing process by the simulation
Uses commercially available software tools
CHALLENGE
- Processing of CFRP results in residual stresses in the material
- Residual stresses lead to micro-damage & failure of CFRP
- Goal is to simulate residual stresses of a carbon fiber composite
material at the micro scale with realistic topology
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
15
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
Defects & influence of processing
- E.g. already generated in the material during processing
- Source for the failure of the composite.
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
16
Segmentation
Matrix enrichment
Pores
Delamination
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
RVE Generation
- Periodic boundary conditions
- Enhanced flexibility
- 45 orientation
And other...
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
17
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
RVE Generation
- Fibers
- Stochastic
- Intersection with
Matrix
Voids
- Voids
- Stochastic
- Complex shapes
- Clustering, control over
Position
Shape
Orientation
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
18
[ 0 / 90 ]
fibers intersecting voids
complex
shapes
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
Curing effects
- Replacement experiment:
- Shrinkage due to temperature decrease
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
19
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
Curing effects
- Delamination due to change in orientation
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
20
Applications
Materials
UD Composites
Curing effects
- Crack propagation due to stochastic distribution of fibers
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
21
Applications
Materials
Strategic Simulation Tool
Digimat
- Recommended tool for investigations
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2012
22
!"#"$%& ()*+,(- .- /0 1(23024 5) 6(1/7 -/.65(- 03 8041,(9 *)6 2(*,5-/58
45820-/2.8/.2(-: %- *) 5);(-/ 5)/0 /7( 3./.2( <( +*-( 0.2 -54.,*/50) *1120*87 0) /7(
!"#"$%& -03/<*2(= +0/7 302 0.2 2(-(*287 *)6 /7( (6.8*/50) 03 * )(< >()(2*/50) 03
-54.,*/50) ()>5)((2- <70 <5,, +( (91(2/- 5) /7( 406(,5)> 03 4*/(25*,-:
"#$%& '()*+, "+$)-*.-*/0 1*#23) 4/5$645 7-(*# %$# 8/94:#(9*;4 <*=3+(9*$/ (/5
>/:*/44#*/: $% ?(94#*(+) (/5 "#$74))4) @666&*)4=A&54B
Applications
Materials
Sandwich Panels
Micross - Stand-Alone Digimat Module
- Input Data @ micro and/or macro scale
- Fast Solution in less than 10 minutes
- Loading
- 3-Point & 4-Point Bending
- In-Plane Shear
Tuesday, 23 April 2013
23
Applications
Materials
Micross
Stand-alone module
- Definition of honeycomb core
- Definition of skin plies
Tuesday, 23 April 2013
24
Applications
Materials
Micross
Stand-alone module
- Visualization of results
- Failure indicators
- Skins: max. stress, Tsai-Wu, Tsai-Hill, Azzi-Tsai-Hill
- Core: shear, compression
Tuesday, 23 April 2013
25
Applications
Materials
From Materials to Structure
Critical Development Phase
Materials Engineering
Current Status
Ongoing Developments
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
26
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Digimat-MF
Fast & Efficient Prediction of Composite Material Properties
27
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Output
Homogenization
DIGIMAT material model
sensitive to composite
microstructure
State-of-the-art
homogenization
methods
Per-phase material
properties +
microstructure
information
Input
a
r
w [%]
matrix
filler
Materials Engineering
From Materials to Structure
Digimat-MX
Material eXchange & Reverse Engineering
28
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Reverse
Engineering
Input
Output
Calibrated DIGIMAT
Material Model, stored in
database and ready to be
shared and used
Calibration of
DIGIMAT models
based on
experimental data
Experimental data,
DIGIMAT material
models stored in
database
Materials Engineering
From Materials to Structure
Multi-Scale Approach
Top Down |
Reverse Engineering
29
Critical Development Phase
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Multi-Scale Approach
Bottom Up |
Prediction of performance
30
Critical Development Phase
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Material Models - Standart
(Thermo-) Elastic
(Thermo-) Elastoplastic
(Thermo-) Viscoelastic
(Thermo-) Elasto-Viscoplastic
31
f(T)
TEMPERATURE
f( )
STRAIN RATES
High strain rates
Creep
f(OT)
ANISOTROPY
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Material Models - Advanced
(Thermal) Creep
- Viscoelasticity
- Elasto-Viscoplasticity
32
time
aligned
VE Matrix Composite
TVE Matrix Composite
G
0
, K
0
and CTE Constant
TVE Matrix Composite
G
0
=G
0
(0), K
0
= K
0
(0) and CTE Constant
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
Eshelby approach for UD & woven composites
- Mean field homogenization
- Glass fibers isotropic
- Carbon fibers transversely isotropic
33
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
UD Composites - RVE definition
- Layered microstructure
34
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Stiffness
Failure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
Woven Composites - Basic model
- Superposition of fibers
35
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
Woven Composites - Advanced model
- Realistic woven structure
36
yarn definition
woven modeler
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
Woven Composites - Advanced model
- Realistic woven structure
37
visualization &
property
computation
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Stiffness
Virtual testing
- Stress & strain
- Tension & compression
- Creep & relaxation
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
38
uniaxial
shear
biaxial
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Stiffness
Input / Definition
- Epoxy matrix
- Density
- Isotropic elastic
Youngs modulus
Poisson ratio
- Carbon fibers
- Density
- Transversely isotropic elastic
In-plane Youngs modulus
Axial Youngs modulus
In-plane Poisson ratio
Transverse Poisson ratio
Transverse shear modulus
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
39
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
ksi
t/mm
3
ksi
t/mm
3
Stiffness
Input / Definition
- Ply
- Microstructure
Continuous fiber
Volume fraction of fibers: 61%
- Laminate
- Stacking sequence
3 different laminates
- Computation of
Laminate
Stress response
Engineering properties
Ply
Engineering properties
Per-phase
Stress response
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
40
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
10/30/60
Laminate 1
60/30/10
Laminate 2
10/40/50
Laminate 3
Stiffness
Output
- Laminate
- Stress response
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
41
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
11
Stiffness
Output
- Laminate
- Stiffness matrix
In coordinate system of the RVE
Tensile direction: 11
Orthotropic
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
42
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Laminate 1
10/30/60
Laminate 2
60/30/10
Laminate 3
10/40/50
11
Stiffness
Output
- Ply level
- Engineering constants
In coordinate system of the ply
Tensile direction: x
Unique for all three laminates
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
43
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Lamlna Angle 0 43 90
?oung
Modulus (ksl)
Axlal (along x-axls) 23.044 2.139 1.318
1ransverse (along y-axls) 1.318 2.139 23.044
Stiffness
Output
- Matrix level
- Microscopic properties
Stress 11 vs. Strain 11 [ksi]
- Per ply information
Different stresses ( ) & strains are reached
Dependent on the ply and sensitive to changes in the laminate design
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
44
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
imposed strain imposed strain imposed strain
0 45 90
matrix strain matrix strain matrix strain
11
Stiffness
Output
- Fiber level
- Microscopic properties
Stress 11 vs. Strain 11 [ksi]
- Per ply information
Dependent on the ply and sensitive to changes in the laminate design
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
45
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
imposed strain imposed strain imposed strain
fiber strain fiber strain fiber strain
11
0 45 90
Stiffness
Coupled Analysis
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
46
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Stiffness
Coupled Analysis - Global Response
- Laminate level
- Force / displacement curve
Digimat-MF Fraction of a second to solve micromechanics
Nastran Minutes for FEA analysis
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
47
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Stiffness
Coupled Analysis - Local Response
- Ply level
- Macroscopic properties in each ply
Max. Princ. Stress [ksi]
Influence of the hole on local behavior
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
48
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Laminate 1
10/30/60
Laminate 2
60/30/10
Laminate 3
10/40/50
Failure
Matrix strain per ply
- Differs from macroscopic strain
- Input for unique strain based failure criteria
49
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
0
45
90
-45
O
r
i
e
n
t
a
t
i
o
n
i
n
p
l
y
No matrix failure in 0 ply
Average matrix strain in other plies
for failure of the composite
Matrix
Macroscopic
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Failure
Per ply definition
- Derived from microstructure
- Stress in fibers / strain in matrix
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
50
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Progressive Failure Analysis
Explicit solver
- Element deletion triggered by
- Stress in fibers / strain in matrix
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
51
Fiber failure
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Progressive Failure Analysis
Validation of stiffness & failure
- Predictive modeling
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
52
RE on ply level of plain
specimen
Prediction of performance
of open whole specimen
Current Status
From Materials to Structure
Progressive Failure Analysis
The idea
- Feed the indicator, control stiffness & failure...
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
53
Ongoing Developments
From Materials to Structure
Indicator
Matrix
Strain
Transverse tensile
Fibers
Stress
Tension
Compression
Matrix
stresses & strains
Fibers
stresses & strains
Composite
stresses & strains
Pre-Failure
Stiffness Reduction
Damage controled by
failure indicator
Failure
Element Deletion
Final composite
failure controled by
critical damage
Progressive Failure Analysis
Preliminary results 2013/02 release
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
54
Ongoing Developments
From Materials to Structure
Partial
failure
No
failure
Complete
failure
Progressive Failure Analysis
Preliminary results 2013/02 release
- Stiffness degradation
- Failure
55
Ongoing Developments
From Materials to Structure
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
Deformation: d11 & d22 Element deletion: progressive & classical
Structures
Structural Engineering
Applications
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
56
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Short Fiber Reinforcement
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
57
Structural Engineering
Structures
fibers
failure
ANISO
Measurements
/ curves
Process Simulation
Orientation data on processing mesh
FEA
Structural analysis
Structural mesh
Mapping
Anisotropic (non)linear
Material Model
ISO
Short Fiber Reinforcement
Fittings
Turbine parts
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
58
Structural Engineering
Structures
UD & Woven
59
Measurements
/ curves
FEA
Structural analysis
Anisotropic (non)linear
Material Model
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
UD
Woven
Draping
Warp/weft angles
Structural Engineering
Structures
Summary
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
60
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
61
Summary
Materials
- In-depth study of a broad range of materials & performances
- SFRP, UD & woven composites, hard metals, ceramics, nano composites
- Complex RVEs - micro stresses & strains
- (Thermo-)Mechanical, thermal & electrical conductivity
From Materials to Structure
- Material property evaluation
- Screening / Selection / Specification / Allowables
Structures
- Influence of processing on final performance
- Injection molding
- Draping
- Fiber placement
- ...
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Digimat 4.4.1 -New Release
Soon available on e-Xstream
FTP!
(see separate email announcement)
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
62
Licensing
sales.admin@e-Xstream.com
Support
support@e-Xstream.com
Training
bernard.alsteens@e-Xstream.com
Software
jan.seyfarth@e-Xstream.com
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Thanks a lot for your attention!
Copyright e-Xstream engineering, 2013
63
Aerospace Industry
Multi-Scale Modeling of Composite Materials & Structures
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Daewoo Lanos Service Manual Full EngDocumento2.038 páginasDaewoo Lanos Service Manual Full EngRafael Hernandez90% (30)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Daewoo Nubira Manual InglesDocumento1.032 páginasDaewoo Nubira Manual Inglesivan_georgiev34793% (15)
- SolidWorks PlasticsDocumento60 páginasSolidWorks PlasticsAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Sa 449Documento8 páginasSa 449Widya widya100% (1)
- Example Quality PlanDocumento11 páginasExample Quality PlanzafeerAinda não há avaliações
- 15 - Hot Stamped Bumper Design PDFDocumento16 páginas15 - Hot Stamped Bumper Design PDFAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics Analysis of Threaded ConnectionsDocumento402 páginasFatigue and Fracture Mechanics Analysis of Threaded ConnectionsAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- A Handbook of Livestock and Poultry Best Management PracticeDocumento87 páginasA Handbook of Livestock and Poultry Best Management PracticeRaymond Katabazi100% (2)
- Brahmss Pianos and The Performance of His Late Works PDFDocumento16 páginasBrahmss Pianos and The Performance of His Late Works PDFllukaspAinda não há avaliações
- BAERD GEN-007 Rev CDocumento27 páginasBAERD GEN-007 Rev CPaulAinda não há avaliações
- Technology A Way of RevealingDocumento24 páginasTechnology A Way of RevealingSheena jhane Magana100% (1)
- Operations Management: William J. StevensonDocumento36 páginasOperations Management: William J. StevensonRubel Barua100% (4)
- Genetic Algorithms - Principles and Perspectives - A Guide To GA TheoryDocumento327 páginasGenetic Algorithms - Principles and Perspectives - A Guide To GA Theoryluis-barrios-941150% (4)
- BBRAUNDocumento9 páginasBBRAUNLuis RosasAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Case StudyDocumento28 páginasEconomics Case StudyZehra KHanAinda não há avaliações
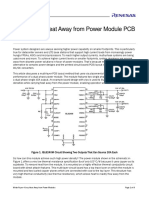
- Carry Heat Away From Power Modules PCBsDocumento8 páginasCarry Heat Away From Power Modules PCBsAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- BISCO Material Selection Guide PDFDocumento9 páginasBISCO Material Selection Guide PDFAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- OTR Installation Instruction - EngDocumento14 páginasOTR Installation Instruction - EngAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Jaguar E PACE Brochure 1X5401810000BCAEN01P Tcm131 413875Documento80 páginasJaguar E PACE Brochure 1X5401810000BCAEN01P Tcm131 413875Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Iron Horse PM DCDocumento6 páginasIron Horse PM DCAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Examination of A Common Assumption in System Availability ComputationsDocumento24 páginasCritical Examination of A Common Assumption in System Availability ComputationsAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- GHGHFDocumento35 páginasGHGHFMetin BlackshotAinda não há avaliações
- Sapa STNDRD Extr Cat 8-10Documento138 páginasSapa STNDRD Extr Cat 8-10Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Diamondback Brochure2013Documento10 páginasDiamondback Brochure2013Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- PART4Documento92 páginasPART4Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts of Model Verification and Validation: LA-14167-MSDocumento41 páginasConcepts of Model Verification and Validation: LA-14167-MSAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Nu-Calgon Application Bulletin: A Complete Family of Gas Leak Detectors From The Leaders in Gas Leak Detection TechnologyDocumento4 páginasNu-Calgon Application Bulletin: A Complete Family of Gas Leak Detectors From The Leaders in Gas Leak Detection TechnologyAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- 550.0029-Diode Pack Info PDFDocumento0 página550.0029-Diode Pack Info PDFAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- 550 0013-SureGripCatalog PDFDocumento21 páginas550 0013-SureGripCatalog PDFAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Apex150 16/18 AWG Female Terminal On 18AWG M1L123A Wire: ESR# AM-030127A Test Request #05-003Documento20 páginasApex150 16/18 AWG Female Terminal On 18AWG M1L123A Wire: ESR# AM-030127A Test Request #05-003Amir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Foundations With Piles For Vibrating Machinery: M. Gohnert, I. Luker and C. MorrisDocumento7 páginasDesigning Foundations With Piles For Vibrating Machinery: M. Gohnert, I. Luker and C. MorrisAmir Hooshang Ghadymi MahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of EbookDocumento14 páginasDefinition of EbookNurul IzzahAinda não há avaliações
- Compact FlashDocumento9 páginasCompact Flashenpr87reddyAinda não há avaliações
- How To Effectively Implement DCIM and Bridge The Gap Between IT and FacilitiesDocumento11 páginasHow To Effectively Implement DCIM and Bridge The Gap Between IT and FacilitiesAbednego TariganAinda não há avaliações
- 12556/gorakhdham Exp Third Ac (3A)Documento2 páginas12556/gorakhdham Exp Third Ac (3A)Lovkesh GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Technical DataSheet (POWERTECH社) -55559-9 (Motormech)Documento2 páginasTechnical DataSheet (POWERTECH社) -55559-9 (Motormech)BilalAinda não há avaliações
- HVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsDocumento5 páginasHVPE Syllabus of Ist Year & IInd Year Degree StudentsReddyvari Venugopal0% (1)
- Bolted Tank Specifications Final 11-5-15Documento6 páginasBolted Tank Specifications Final 11-5-15Rodrigo ZapataAinda não há avaliações
- Graphics in C LanguageDocumento8 páginasGraphics in C LanguagePattabhi RamaraoAinda não há avaliações
- Top Links October 2018Documento122 páginasTop Links October 2018Andrew Richard ThompsonAinda não há avaliações
- Vmware Validated Design 41 SDDC Architecture DesignDocumento226 páginasVmware Validated Design 41 SDDC Architecture DesignmpuriceAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Manual Operator'S and Unit Maintenance Manual FOR Firing Device, Demolition. M122 (NSN 1375-01-021-0606) (EIC: 2NA)Documento7 páginasTechnical Manual Operator'S and Unit Maintenance Manual FOR Firing Device, Demolition. M122 (NSN 1375-01-021-0606) (EIC: 2NA)Михаил НаумовAinda não há avaliações
- Diagram of Vitamix Blade Blade Assembly: InstructionsDocumento5 páginasDiagram of Vitamix Blade Blade Assembly: InstructionsRenato PurcinoAinda não há avaliações
- Marrantz Service Manual Using CS493263 09122113454050Documento63 páginasMarrantz Service Manual Using CS493263 09122113454050Lars AnderssonAinda não há avaliações
- SV50SP2RevB Released User DocumentsDocumento8 páginasSV50SP2RevB Released User DocumentsAhmed RamadanAinda não há avaliações
- Ibps Po Interview Capsule-1Documento8 páginasIbps Po Interview Capsule-1atingoyal1Ainda não há avaliações
- Hydraulic Backhoe MachineDocumento57 páginasHydraulic Backhoe MachineLokesh SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3. Growth of Functions Asymptotic NotationDocumento9 páginasLecture 3. Growth of Functions Asymptotic NotationJasdeep Singh Pardeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Manual de Serviço PDFDocumento394 páginasManual de Serviço PDFMarcos Antonio de Souza JuniorAinda não há avaliações
- Adicionando Mais Um Disco (VG) HPUXDocumento4 páginasAdicionando Mais Um Disco (VG) HPUXVinicius SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Science Ram PresentationDocumento11 páginasComputer Science Ram Presentationapi-268896185100% (3)