Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Fluphenazine
Enviado por
Karen T. CeletariaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Fluphenazine
Enviado por
Karen T. CeletariaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
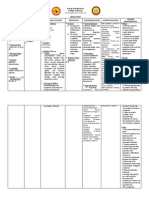
Cebu Normal University College of Nursing Osmea Boulevard, Cebu City DRUG STUDY
DRUG DATA
CLASSIFICATION
MECHANISM OF ACTION
INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS Contraindications Blood dyscrasias, bone marrow depression, cerebral arteriosclerosis, coma, concomitant use of large amounts of another CNS depressant, coronary artery disease, hepatic dysfunction, hypersensitivity to phenothiazines, myeloproliferative disorders, severe CNS depression, severe hypertension or hypotension, subcortical brain damage Precautions Cardiovascular diseases, Parkinsons disease, angle-closure glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, prostatic hyperplasia; seizure disorders; OB, Lactation: safety not established; enters breat milk, not
ADVERSE REACTIONS
CNS: Ataxia, cerebral edema, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, lightheadedness, nervousness, seizures, slurred speech, syncope, worsening psychotic symptoms CV: AV conduction disorders, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, orthostatic hypotension, QT-interval prolongation, shock, STsegment depression, tachycardia EENT: Blurred vision, dry mouth, glaucoma, increased salivation, laryngeal edema, laryngospasm, miosis, mydriasis, nasal congestion, papillary hypertrophy of the tongue, parotid gland enlargement, photophobia, pigmentary retinopathy, ptosis ENDO: Breast
Generic Name Therapeutic Fluphenazine Antipsychotic, hydrochloride/Fluphenazine decanoate Pharmacologic Phenothiazines Trade Name Modecate (CAN), Modecate Pregnancy Concentrate (CAN), Prolixin Category Decanoate C Patients Dose N/A Minimum Dose 2.5 to 10 mg/day in divided doses every 6 to 8 hr. PO Maximum Dose 20 mg/dose with caution PO in divided doses Contents Fluphenazine decanoate/ Fluphenazine hydrochloride Availability Injection, tablets, concentrates,
Pharmacokinetics General Absorption: Acute and Well-absorbed after PO/IM chronic administration, deconoate salt pyschoses in in sesame oil has delayed onset and prolonged action Patients because of delayed release Actual from oil vehicle and Indication subsequent release from fatty N/A tissues Distribution Widely distributed; crosses blood-brain barrier; crosses placenta; enters breast milk Metabolism and Excretion Mostly metabolized by liver ; undergo enterohepatic recirculation Onset PO- 1 hour IM- 24-72 hours Peak PO- unknown IM- 48-96 hours Duration PO- 6-8 hours IM- >4 weeks Half-life: 33 hours; 6.8-9.6 days Action: May block postsynaptic
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES Before 1. Monitor patients blood pressure routinely. 2. Assess mental status (mood, behavior, orientation). 3. Assess weight and BMI. 4. Assess positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. 5. Assess fluid intake and bowel function 6. Prepare drug aseptically and verify the right dose. Render health teaching as appropriate. During 1. Verify patients identity using the chart and other patient and nurses confirmation. 2. Administer oral doses with food, milk, or a full glass of water. 3. For I.M. and subcutaneous injection, use at least a 21G needle.
elixir,
Routes of Administration
PO, IM
dopamine receptor sites in the CNS. This action may depress areas of the brain that control activity and aggression, including the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, and limbic system. Therapeutic Effects Diminished signs and symptoms of psychoses
recommended; Geri: dosage reduction Drug Interactions Drug-Drug
magnesium-containing antacids: Possibly inhibited absorption of fluphenazine amantadine, anticholinergics: Possibly intensified adverse effects of both drugs amphetamines: Possibly decreased therapeutic effects of both drugs antihypertensives: Possibly severe hypotension antithyroid drugs: Increased risk of agranulocytosis beta blockers: Possibly increased blood levels and risk of adverse effects of both drugs bromocriptine: Decreased bromocriptine effects CNS depressants: Possibly prolonged and intensified CNS depression erythromycin: Possibly inhibited fluphenazine metabolism guanethidine: Decreased hypotensive effect of guanethidine levodopa: Possibly decreased antidyskinetic effect of levodopa
engorgement (females), galactorrhea, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, mastalgia, syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion GI: Anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, fecal impaction, ileus, increased appetite, nausea, vomiting GU: Amenorrhea, bladder paralysis, decreased libido, enuresis, menstrual irregularities, polyuria, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence, urine retention HEME: Anemia, aplastic anemia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic or nonthrombocytopenic purpura RESP: Bronchospasm, dyspnea, increased respiratory depth SKIN: Contact dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythema, jaundice, photosensitivity, pruritus, seborrhea Other: Heatstroke, hyponatremia, lupuslike symptoms, weight gain
4. To prevent contact dermatitis, avoid getting solution ion hands. 5. Advise patient not to mix oral solution with beverages that contain caffeine (coffee, cola), tannins (tea), or pectins (apple juice). 6. Observe patient carefully when administering medication to ensure that medication is taken not hoarded or cheeked. After 1. Document medication given. 2. Dont let patient sit or stand up until blood pressure and heart rate have returned to baseline. 3. Notify prescriber if patient develops tardive dyskinesia or urinary incontinence. 4. Instruct to frequently do good oral hygiene. 5. Be alert for and immediately report signs of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. 6. Notify prescriber
lithium: Possibly neurotoxicity (disorientation, extrapyramidal reactions, unconsciousness) meperidine: Excessive sedation and hypotension metrizamide: Increased risk of seizures when injected in subarachnoid area during fluphenazine therapy oral anticoagulants: Possibly decreased anticoagulant effects pimozide, other drugs that prolong QT interval: Prolonged QT interval and risk of arrhythmias thiazide diuretics: Increased risk of hyponatremia, hypotension, and water intoxication tricyclic antidepressants: Possibly prolonged and intensified sedation
about worsening psychotic symptoms: agitation, catatonic state, confusion, depression, hallucinations, lethargy, paranoid reactions. 7. Monitor temperature; a significant, unexplained rise can indicate intolerance and a need to discontinue drug. Notify prescriber immediately if this occurs.
Drug- Activities
alcohol use: Possibly increased CNS depression and increased risk of heatstroke
SOURCE: Deglin, J.H., Vallerand, A.H. (2009). Daviss Drug Guide for Nurses. Ed.11. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company pp. 568-570 Lippincotts Nurses Drug Handbook , ed. 10. 2011, pp. 451-453
Você também pode gostar
- STABLE Resource Toolkit-BipolarDocumento67 páginasSTABLE Resource Toolkit-Bipolardidiisafitri100% (1)
- Drug Study SertralineDocumento5 páginasDrug Study SertralineJose Luis Hernandez50% (2)
- Drug Study (Olanzapine)Documento1 páginaDrug Study (Olanzapine)Eden Marie Francisco100% (1)
- ChlorpromazineDocumento2 páginasChlorpromazineevalyn dane50% (2)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasRisperidone Drug StudyNajmah Saaban77% (13)
- HALOPERIDOL Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasHALOPERIDOL Drug Studyanreilegarde89% (9)
- ChlorpromazineDocumento3 páginasChlorpromazineMarinel Agulto100% (1)
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasHaloperidol Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (5)
- Drug Study HaloperidolDocumento2 páginasDrug Study HaloperidolRobert Martin Rivera PuertaAinda não há avaliações
- Clozapine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasClozapine Drug Studymilkv100% (8)
- Biperiden Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasBiperiden Drug StudyFielMendoza100% (1)
- Psych Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Biperiden (Drug Study)Documento3 páginasBiperiden (Drug Study)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study AmoxicillinDocumento4 páginasDrug Study AmoxicillinKaren T. Celetaria75% (12)
- Presentation by Prof Katya Rubia - The Change Within: Sustainable Effects Ofsustainable Effects of Meditation On Healthmeditation On HealthDocumento24 páginasPresentation by Prof Katya Rubia - The Change Within: Sustainable Effects Ofsustainable Effects of Meditation On Healthmeditation On Healthtanaha100% (3)
- Deep Brain StimulationDocumento54 páginasDeep Brain StimulationNarinder AroraAinda não há avaliações
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasChlorpromazine Drug StudyEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- BiperidenDocumento3 páginasBiperidenKaren T. Celetaria100% (1)
- Fluphenazine Drug Study!Documento3 páginasFluphenazine Drug Study!EmJay Balansag100% (3)
- FluphenazineDocumento4 páginasFluphenazineimthebossAinda não há avaliações
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyTarquin Tomada100% (2)
- Clozapine (Drug Study)Documento2 páginasClozapine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilDocumento2 páginasGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasChlorpromazine Drug StudyPeyjey100% (1)
- RisperidoneDocumento2 páginasRisperidoneKeij Araneta0% (1)
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia67% (3)
- DRUG STUDY PsycheDocumento1 páginaDRUG STUDY Psychejulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoAinda não há avaliações
- FluoxetineDocumento3 páginasFluoxetineArnzz Agbulos100% (1)
- Name of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandDocumento1 páginaName of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandkarenmichellelecarozAinda não há avaliações
- Prozac FluoxetineDocumento2 páginasProzac FluoxetineEAinda não há avaliações
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocumento3 páginasSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study ZiprasidoneDocumento2 páginasDrug Study ZiprasidoneArnzz Agbulos100% (1)
- Drug Study Valproate SodiumDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Valproate SodiumLouie Danielle SegarraAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocumento2 páginasDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJezzy Ann F. SarrozaAinda não há avaliações
- Benztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasBenztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyHamimah Bint AliAinda não há avaliações
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Documento2 páginasClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Ainda não há avaliações
- DisulfiramDocumento1 páginaDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocumento4 páginasQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - ClozapineDocumento5 páginasDrug Study - ClozapinecutemaibearAinda não há avaliações
- Paroxetine Hydro ChlorideDocumento3 páginasParoxetine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study CLOZAPINEDocumento6 páginasDrug Study CLOZAPINESandra ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Valproic AcidDocumento2 páginasValproic AcidRoshleen Ann De PedroAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyKeanu ArcillaAinda não há avaliações
- DRUG STUDY LamotrigineDocumento1 páginaDRUG STUDY LamotrigineP B0% (2)
- BiperidenDocumento2 páginasBiperidenALmik HussinAinda não há avaliações
- Haloperidol DRUG STUDYDocumento2 páginasHaloperidol DRUG STUDYaaron tabernaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Drug Study.Documento20 páginasFinal Drug Study.Bobbie Sison67% (3)
- Lithium DrugstudyDocumento2 páginasLithium DrugstudyShedrann Johan100% (1)
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocumento4 páginasEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study ClonazepamDocumento3 páginasDrug Study ClonazepamJohn Rey AbadAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Documento3 páginasDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)Documento5 páginasDrug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)kuro hanabusa100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY (FLUoxetine)Documento2 páginasDRUG STUDY (FLUoxetine)Diana Villanueva100% (1)
- 5 MG Iv BidDocumento17 páginas5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherAinda não há avaliações
- QuetiapineDocumento3 páginasQuetiapineMichael KuzbytAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento12 páginasDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreAinda não há avaliações
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087Ainda não há avaliações
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Documento5 páginasANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteAinda não há avaliações
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDocumento4 páginasDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocumento3 páginasClinical Medications WorksheetsVinz OñoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocumento2 páginasDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- New DSDocumento2 páginasNew DSKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Commu DiseasesDocumento11 páginasCommu DiseasesKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug Study: AbsorptionDocumento2 páginasCebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug Study: AbsorptionKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Cebu Normal University: Progress ReportDocumento4 páginasCebu Normal University: Progress ReportKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Progress ReportDocumento4 páginasProgress ReportKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient StandardsDocumento16 páginasNutrient StandardsKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento4 páginasAnatomy and PhysiologyKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Dia NoDocumento4 páginasAssignment Dia NoKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 2Documento7 páginasActivity 2Karen T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Blue Cross InsuranceDocumento4 páginasBlue Cross InsuranceKaren T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 2Documento7 páginasActivity 2Karen T. CeletariaAinda não há avaliações
- A Randomized Controlled Trial of Medication and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For HypochondriasisDocumento9 páginasA Randomized Controlled Trial of Medication and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For HypochondriasisDewina Dyani Rosari IIAinda não há avaliações
- Berry (2004) The Relationship Between Depression and Emerging AdulthoodDocumento17 páginasBerry (2004) The Relationship Between Depression and Emerging AdulthoodAlex JozaviAinda não há avaliações
- Overcoming Agoraphobia A Self-Help ManualDocumento41 páginasOvercoming Agoraphobia A Self-Help ManualvasilikiserAinda não há avaliações
- Infographics (Mental Health)Documento1 páginaInfographics (Mental Health)martine soileilAinda não há avaliações
- Bipolar DisordersDocumento63 páginasBipolar DisorderselvinegunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Culture Illness and CareDocumento9 páginasCulture Illness and CareIncaOreAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatry Exam Questions 1Documento4 páginasPsychiatry Exam Questions 1Roxana Mădălina Jojă-AlgeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento3 páginasUntitledMARICHU M. LIGANAinda não há avaliações
- Persuasive Speech - EditedDocumento4 páginasPersuasive Speech - EditedAlex WafulaAinda não há avaliações
- Quinn, PO. Girls and ADHDDocumento10 páginasQuinn, PO. Girls and ADHDAarushi AgniAinda não há avaliações
- The Relationship Between Happiness and Depression Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicDocumento6 páginasThe Relationship Between Happiness and Depression Among Senior High School Students Amidst The COVID-19 PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalAinda não há avaliações
- Radix RauwolfiaeDocumento11 páginasRadix RauwolfiaeDestiny Vian DianAinda não há avaliações
- Med Surg 1 Exam 1Documento23 páginasMed Surg 1 Exam 1Breeana MooreAinda não há avaliações
- Pocketbook of Mental Health 3rd EditionDocumento184 páginasPocketbook of Mental Health 3rd Editionjcartusio38Ainda não há avaliações
- Love and AttractionDocumento19 páginasLove and Attractionalpu_alp20100% (1)
- Labor Pain Is Reduced by MaDocumento6 páginasLabor Pain Is Reduced by MamfhfhfAinda não há avaliações
- Eficacia de La Amisulprida para Los Síntomas Depresivos en Personas Con Trastornos Mentales Revisión Sistemática y MetanálisisDocumento11 páginasEficacia de La Amisulprida para Los Síntomas Depresivos en Personas Con Trastornos Mentales Revisión Sistemática y MetanálisisIVAN ALVAREZAinda não há avaliações
- McIntyreStrength Based Intake Assessment Guide REVISEDDocumento12 páginasMcIntyreStrength Based Intake Assessment Guide REVISEDIsaac FullartonAinda não há avaliações
- SSRIs and Athletic PerformanceDocumento4 páginasSSRIs and Athletic PerformanceGuille monsterAinda não há avaliações
- Potential Therapeutic Effects of PsilocybinDocumento7 páginasPotential Therapeutic Effects of Psilocybindaniel_jose_skateAinda não há avaliações
- MCT With ChineseDocumento14 páginasMCT With ChineseJohn TaylorAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Partum Depression Effect On Child Health and DevelopmentDocumento6 páginasPost-Partum Depression Effect On Child Health and DevelopmentEndang JunaelaAinda não há avaliações
- p-11 aamembersMedDrugDocumento24 páginasp-11 aamembersMedDrugJason WinfieldAinda não há avaliações
- Spiegel Et Al 1999 Psycho OncologyDocumento12 páginasSpiegel Et Al 1999 Psycho Oncologyfatimaramos31Ainda não há avaliações
- APA Fact Sheet Native AmericansDocumento6 páginasAPA Fact Sheet Native AmericansAprilMRosierAinda não há avaliações
- A Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge Regarding The Rights of Mentally Ill Person Among Care Givers Attending OPD of Mental Hospital Selaqui Dehradun, Uttarakhand" AffiliationDocumento11 páginasA Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge Regarding The Rights of Mentally Ill Person Among Care Givers Attending OPD of Mental Hospital Selaqui Dehradun, Uttarakhand" AffiliationKuldeep singhAinda não há avaliações
- New Finished Capstone Annotated BibliographyDocumento10 páginasNew Finished Capstone Annotated Bibliographyapi-256450274Ainda não há avaliações