Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy and Physiology of The Biliary Tree
Enviado por
Marland Faith Dela CruzTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy and Physiology of The Biliary Tree
Enviado por
Marland Faith Dela CruzDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
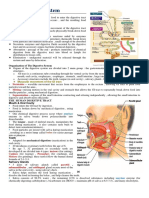
Anatomy and Physiology of the Biliary tree
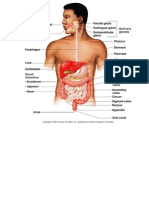
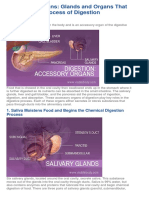
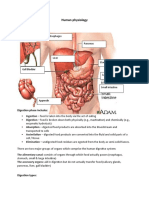
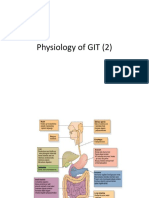
Parts of thee Biliary tree 1) Liver -It is the organ that contains the gall bladder. -Organ that produce bile -It secretes about 700ml of bile each day Function of the Liver - elps in digestion -!"cretion -#utrient conversion -$eto"ification of harmful chemicals %) #ucleases. +) ,all bladder --torage of bile .) /ile -It is a bitter-tasting) dar0 green to yello1ish bro1n fluid) produced by the liver of most vertebrates) that aids the process of digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In many species) bile is stored in the gallbladder and upon eating is discharged into the duodenum. &ancreas -It produced pancreatic en'ymes that helps in digestion such as( Lipase) *mylase)
/ile salts-it emulsify fats) brea0ing the fat globules into smaller droplets) much li0e the action of detergents in dish 1ater $ucts involved in bile flo1 -2he hepatic duct from the liver lobes combines to form common hepatic duct -2he common hepatic duct combines cystic duct from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. -2he common bile duct 3oints the pancreatic duct -2he combined duct empires into the duodenum at the duodenal papilla. -&ancreatic secretions may also may also enter the duodenum through an accessory pancreatic duct) 1hich also empires to the duodenum.
Bile Production 1) /ile is produced by hepatocytes) draining through the many bile ducts that penetrate the liver. $uring this process) the epithelial cells add a 1atery solution that is rich in bicarbonates that dilutes and increases al0alinity of the solution. %) /ile then flo1s into the common hepatic duct) 1hich 3oins 1ith the cystic duct from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. +) 2he common bile duct in turn 3oins 1ith the pancreatic duct to empty into the duodenum. If the sphincter of Oddi is closed) bile is prevented from draining into the intestine and instead flo1s into the gallbladder) 1here it is stored and concentrated to up to five times its original potency bet1een meals. 2his concentration occurs through the absorption of 1ater and small electrolytes) 1hile retaining all the original organic molecules. .) 4holesterol is also released 1ith the bile) dissolved in the acids and fats found in the concentrated solution. 5hen food is released by the stomach into the duodenum in the form of chyme) the duodenum releases cholecysto0inin) 1hich causes the gallbladder to release the concentrated bile to complete digestion. 6-ecretin-released from the duodenum that stimulate bile secretion. 64holecysto0in-stimulates the gall bladder to contract and release bile into the duodenum. 67agus- in parasympathetic stimulation) it stimulates bile secretion and release.
Você também pode gostar
- Digestion Notes Part - 2 (Xi 2020-22) 18 10 21Documento10 páginasDigestion Notes Part - 2 (Xi 2020-22) 18 10 21Ramkrushna khandareAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Biliary System: Click To EnlargeDocumento23 páginasAnatomy of The Biliary System: Click To EnlargeMohit JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System 2022-23Documento28 páginasDigestive System 2022-23Fady Fady100% (1)
- Digestive System A&p BookletDocumento11 páginasDigestive System A&p Bookletnurse1990Ainda não há avaliações
- Nutrition NotesDocumento8 páginasNutrition NotesDC MSME AttendanceAinda não há avaliações
- Name - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsDocumento5 páginasName - Digestive System Worksheet: Salivary GlandsRJ CamarilloAinda não há avaliações
- Avian Digestive SystemDocumento3 páginasAvian Digestive Systemnadz karimAinda não há avaliações
- The Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MDocumento21 páginasThe Huma N Ig e S Tive S Ys Te MJoshua RuntuweneAinda não há avaliações
- Humandigestionteacher 110323090218 Phpapp01Documento45 páginasHumandigestionteacher 110323090218 Phpapp01Lyana AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Bile Salt & Enterohepatic CirculationDocumento27 páginasBile Salt & Enterohepatic Circulationammu 94Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 Biliary System, PSPD, 2013Documento21 páginas8 Biliary System, PSPD, 2013Cox AbeeAinda não há avaliações
- Essay # 4. DigeDocumento9 páginasEssay # 4. DigeAbdul Karim BurkiAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento12 páginasDigestive Systemapi-269652707Ainda não há avaliações
- The Human Digestive SystemDocumento21 páginasThe Human Digestive SystemAshley MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Lea 417 510 2011Documento121 páginasLea 417 510 2011Oliver TalipAinda não há avaliações
- Accessory Organs: Glands and Organs That Facilitate The Process of DigestionDocumento3 páginasAccessory Organs: Glands and Organs That Facilitate The Process of DigestionMaureen PangilinanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 - Digestive SystemDocumento31 páginasUnit 4 - Digestive SystemAbdullah MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Digestion & Digestive SystemDocumento27 páginasDigestion & Digestive SystemAam BhortaAinda não há avaliações
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocumento6 páginasPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanAinda não há avaliações
- Gallbladder & Bile Physiological AspectsDocumento48 páginasGallbladder & Bile Physiological AspectsPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerAinda não há avaliações
- The Digestive System Final 1Documento34 páginasThe Digestive System Final 1Jam DabalosAinda não há avaliações
- Life ProcessesDocumento18 páginasLife ProcessesLal BhaiAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System NotesDocumento10 páginasDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassAinda não há avaliações
- DigestiveDocumento3 páginasDigestivePrishaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Handout 3Documento5 páginasBiology Handout 3djdevils143Ainda não há avaliações
- 09 DigestionDocumento85 páginas09 DigestionSumihar PasaribuAinda não há avaliações
- FenieDocumento32 páginasFenieLilacx ButterflyAinda não há avaliações
- The Digestive SystemDocumento30 páginasThe Digestive SystemUniversal DiscoveringAinda não há avaliações
- Secretion of Bile by The LiverDocumento26 páginasSecretion of Bile by The LiverAmbreen AyubAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry of Liver BCM 412Documento20 páginasBiochemistry of Liver BCM 412onuorahu94Ainda não há avaliações
- Sistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)Documento28 páginasSistem Pencernaan (Digestion System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaAinda não há avaliações
- Science PreDocumento11 páginasScience PreCARL JUSTIN TUMALAAinda não há avaliações
- Digestion SlideDocumento18 páginasDigestion SlideezebelluciAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento8 páginasAnatomy and PhysiologyDanielle V. Cercado100% (1)
- Physiology of Digestive SystemDocumento123 páginasPhysiology of Digestive Systemkidusabeje7Ainda não há avaliações
- Digestive GlandDocumento22 páginasDigestive GlandMalinus TorquatusAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento13 páginasAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04Ainda não há avaliações
- GIT صيدلهphysiologyDocumento38 páginasGIT صيدلهphysiologyAbdo HaiderAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System: Learning ObjectivesDocumento30 páginasDigestive System: Learning Objectivesfatima al neyadiAinda não há avaliações
- Human PhysiologyDocumento26 páginasHuman PhysiologyLaya ShrbagiAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive and Renal SystemsDocumento108 páginasDigestive and Renal SystemsMenalqueAinda não há avaliações
- Intestine. in The Large Intestine, Most of The Water and Some Compounds Such AsDocumento1 páginaIntestine. in The Large Intestine, Most of The Water and Some Compounds Such AsachinparasharAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology: Bile Secretion by The LiverDocumento8 páginasPhysiology: Bile Secretion by The Liverزين العابدين محمد عويشAinda não há avaliações
- Life Process 1Documento4 páginasLife Process 1tanishqmalik20Ainda não há avaliações
- The Digestive SystemDocumento33 páginasThe Digestive SystemHida Az ZahraAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive Glands Structure and FunctionsDocumento24 páginasDigestive Glands Structure and Functionsrustommili01Ainda não há avaliações
- Physiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)Documento67 páginasPhysiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)RISALATUL KHOIROTUNISAAinda não há avaliações
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDocumento66 páginasDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique Gordon100% (1)
- Naan - Unit 4.digestionDocumento45 páginasNaan - Unit 4.digestionNaftal DavidAinda não há avaliações
- Biliary SystemDocumento4 páginasBiliary SystemJesrel DelotaAinda não há avaliações
- DigestDocumento84 páginasDigestBella FebrianAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Nutrition: The MouthDocumento7 páginasAnimal Nutrition: The Moutheugene_970418755Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture21-DigestiveSystem (Spring2020Zeman)Documento50 páginasLecture21-DigestiveSystem (Spring2020Zeman)Sahil ParikhAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Part 6Documento30 páginasAnatomy Part 6Pavan PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Further Digestion Absorption Assimilation and Hormones Final QsDocumento1 páginaFurther Digestion Absorption Assimilation and Hormones Final QsChris WongAinda não há avaliações
- CC 2Documento11 páginasCC 2RMT scientistAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemDocumento54 páginasUnit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemsahilAinda não há avaliações
- The Digestive System MODULEDocumento3 páginasThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- Sle Sle SleDocumento21 páginasSle Sle SleMarland Faith Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- AML Case StudyDocumento44 páginasAML Case StudyMarland Faith Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- HTP of AsthmaDocumento1 páginaHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Varicella - Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasVaricella - Nursing Care PlanMarland Faith Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Working As A Team in Airway Surgery History Pres 2021 Seminars in PediatriDocumento6 páginasWorking As A Team in Airway Surgery History Pres 2021 Seminars in PediatriSavaAinda não há avaliações
- December 2018 Ophthalmic PearlsDocumento2 páginasDecember 2018 Ophthalmic PearlsFathirAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Lab PM10 Sampling in FoodCourtDocumento8 páginasPre-Lab PM10 Sampling in FoodCourtAjlaa RahimAinda não há avaliações
- Homemade MethcathinoneDocumento16 páginasHomemade MethcathinoneDaria Schka100% (1)
- Essentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDocumento143 páginasEssentials of Medical Language 3rd Edition Allan Test BankDebbieCollinsokpzd100% (14)
- Prebiotics Probiotics PDFDocumento40 páginasPrebiotics Probiotics PDFfizalfizalAinda não há avaliações
- 1, 14 PDFDocumento164 páginas1, 14 PDFRudy Nuryadi100% (1)
- Ocular EmergencyDocumento29 páginasOcular EmergencyMohammad Farouq Omar100% (3)
- 9814774723Documento467 páginas9814774723Ortopedia FabioAinda não há avaliações
- Rabbies Health Talk NewDocumento10 páginasRabbies Health Talk NewAmit Ranjan100% (1)
- Om Algora SLE Exam-2 PDFDocumento496 páginasOm Algora SLE Exam-2 PDFGomathy DhanasekarAinda não há avaliações
- Biology WorkbookDocumento526 páginasBiology WorkbookEkaterin90% (10)
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueDocumento76 páginasAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- #MediastinumDocumento4 páginas#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- Scott Foresman Science Grade 4Documento8 páginasScott Foresman Science Grade 4rofi modiAinda não há avaliações
- Nut Ric ScoreDocumento1 páginaNut Ric ScoreClaudia M FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- STS Video ScriptDocumento2 páginasSTS Video ScriptCynthia Y De VeraAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 European Guidance Diagnosis and Management OsteoporosisDocumento42 páginas2018 European Guidance Diagnosis and Management OsteoporosisManel PopescuAinda não há avaliações
- Roche Fact SheetDocumento2 páginasRoche Fact SheetabhijitkumtakarAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive SystemDocumento11 páginasReproductive SystemJohn Matthew ViañaAinda não há avaliações
- Beta BlockersDocumento2 páginasBeta BlockersmetkosdAinda não há avaliações
- L1.clinical ChemistryDocumento37 páginasL1.clinical Chemistrysini gangAinda não há avaliações
- Catalogo Libros Transfusion PDFDocumento44 páginasCatalogo Libros Transfusion PDFmeds1313Ainda não há avaliações
- My Method - E. CoueDocumento236 páginasMy Method - E. Couealex100% (4)
- Butyl CellosolveDocumento1 páginaButyl CellosolvebiosaludquimicaAinda não há avaliações
- PTBD 2Documento4 páginasPTBD 2Alcntara AllenAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology Lec 1Documento16 páginasPathology Lec 1hamadAinda não há avaliações
- STIHL FS 90 Owners Instruction Manual PDFDocumento116 páginasSTIHL FS 90 Owners Instruction Manual PDFCyndi DeatonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan - EthicsDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan - EthicsJustine CasinilloAinda não há avaliações
- Crossectional Anatomy: Ahmed MohammedDocumento26 páginasCrossectional Anatomy: Ahmed Mohammedhawi adugnaAinda não há avaliações