Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
COMPLETE Project On Networking PDF
Enviado por
Ajit Sangwan100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
65 visualizações128 páginasnetwork
Título original
COMPLETE-Project-on-Networking.pdf
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentonetwork
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(1)100% acharam este documento útil (1 voto)
65 visualizações128 páginasCOMPLETE Project On Networking PDF
Enviado por
Ajit Sangwannetwork
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 128
SWAMI PARMANAND COLLEGE OF
ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
SIX MONTHS INDUSTRIAL TRAINING REPORT
ON
NETWORKING (MCSE & CCNA)
AT
1ETKING
SEC 34 , CHANDIGARH
SUBMITTED AS A PART OF COURSE CURRICULUM
BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY
IN
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Under the Guidance oI
Mr. Baljit singh
Mr. Inder Gulati
Submitted To: Submitted By:
Er. Harpreet Kaur (HOD) Saroj Dogra (697041917)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS &
COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
SWAMI PAMANAND COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING &
TECHNOLOGY, DERA BASSI, MOHALI
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
I Ieel deeply indedted to Mr. Baljit Singh, MicrosoIt trainer who delivered valuable
lesson on MCSE, his indepth knowledge about the subject helped me understand the
subject in better way. His method oI teaching the minute details helped me a lot to
acquire the insight into the subject.
I am also grateIul to Mr. Inder Gulati, CCNA trainer Ior giving best knowledge about
CCNA.the way he instilled knowledge oI the subject was undoubtly praise worthy and
valuable.
I am also thankIul to Jetking institution as a whole that is doing yeoman`s service by
teaching the learner avreast with the computer , networking and hardware knowledge that
is the need oI the day.
I will be Iailing in my duty iI I do not acknowledge my husband Mr. Nardev Singh Rana
who always stood by my side during my studies. I am indepted to my son`s Anirudh
Rana and Romil Rana who never clamed my time and get bore by my long absence rather
silent.
Last but not the least, I thank all my classmates at Jetking Ior extending kind
co-operation.
SARO1 DOGRA
List of Figures
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Figure No. Name of Figure Page No.
1 Computer network 6
2 Local Area Nework 9
3 LAN ClassiIication 9
4 Campus Area Network 10
5 Metropolitan Area Network 11
6 To Iind location oI a computer using FQDN 24
7 Tree structure 25
8 Structure oI domain Iorest and domain tree 36
9 Multi-Master Mode 37
10 Parent child relationship model 40
11 Direct Sharing Scenario 43
12 ICS scenario 44
13 Scenario oI win proxy server 45
14 NAT Server 46
15 VPN server 48
16 LAN routing 52
17 Static routing 53
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
18 Architecture oI router 60
19 Variable Subnet Mask 75
20 Scenario oI Telnet 76
21 Scenario oI Static Routing 81
22 Routing table 86
23 Routing table oI covered networks 86
24 Routing loops 87
25 OSPF Scenario 99
26 VLAN Operation
105
27 VTP ConIiguration 110
28 VTP Pruning 111
29 IEEE 802.11 Standard 114
List of tables
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Table No. Name of table Page No.
1 DiIIerence between Workgroup & Domain 7
2 Comparison between IPv4 and IPv6 12
3 Address Classes 13
4 Category and Speed oI UTP cables 17
5 Colour Coding Ior straight Cable 18
6 Colour Coding Ior Crossover cable 19
7 Colour Coding Ior Rollover Cable 20
8 Operating Systems 21
9 DiIIerence between Workgroup and Domain 34
10 Exchange Server with diIIerent operating systems 56
11 Router interIaces and connectors 62
12 Router Ports 63
13 DeIault address mask in binary & dotted decimals 71
14 Decimal and Binary values oI subnet mask 72
15 Subnet mask, valid hosts, broadcast address 74
16 Routing table 86
17 DiIIerence between RIPV1 & RIPV2 90
18 DiIIerence between IGRP and RIP 91
CONTENTS
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Sr. No. Topic Page No.
1 INTRODUCTION 1
1.1 Company ProIile 1
2 LITERATURE RIEVIEW 5
3 NETWORKING 6
3.1 Introduction to networking 6
3.1.1 Models oI Networking 6
3.1.2 Categories oI network 8
3.2 IP ADDRESSES and MAC Addresses 12
3.2.1 IPAddressClasses 12
3.2.2 MAC Addressing 15
3.3 NETWORKING MEDIA 15
3.3.1 Ethernet Cabling 17
3.4 OPERATING SYSTEM 20
3.4.1 Types oI Operating Systems 20
3.5 DNS SERVER 22
3.5.1 PARTS OF DNS SYSTEM 23
3.5.2 DNS Zone 26
3.6 DHCP SERVER 28
3.6.1 Working oI DHCP Server 29
3.6.2 InstallationStepsoIDHCPServer 31
3.7 ACTIVE DIRECTORY 33
3.7.1ActiveDirectoryServices 34
3.7.2 CHILD DOMAIN 40
3.8 INTERNET SHAREING 42
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.8.1 Direct Sharing 42
3.8.2 ICS (Internet Connection Sharing) 43
3.8.3 Win Proxy Server 45
3.8.4 NAT (Network Address Translation) 45
3.9 VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORK (VPN) 47
3.9.1 VPN components 48
3.9.2 Types oI VPN 49
3.10 ROUTING 51
3.10.1 Types oI Routing 51
3.11 EXCHANGE SERVER 56
3.11.1 Elements oI Exchange Server 56
3.11.2 Exchange Version 56
3.11.3 Requirements Ior Exchange Server 57
3.12 Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model 57
3.12.1 Description oI DiIIerent Layers 58
3.13 ROUTERS 60
3.13.1 Router Architecture and its Key Component 60
3.13.2 Router InterIaces & Ports 62
3.13.3 Modes oI Router 63
3.13.4 ConIiguring Password 65
3.13.5 Managing ConIiguration 66
3.14 SUBNETTING 70
3.14.1 Advantages oI subnetting 70
3.14.2 Types oI Subnetting 73
3.15 TELNET 75
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.15.1 To Access the Device Remotely 75
3.15.2 Commands to assign IP addresses to the interIaces 76
3.16 ROUTING 79
3.16.1 TYPES OF ROUTING 79
3.16.2 Routing Protocol Basics 84
3.1.3 R IP (Routing InIormation Protocol) 88
3.1.4 IGRP ( Interior Gateway Protocol) 91
3.1.5 EIGRP(Enhanced Interior Routing Protocol) 93
3.1.6 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) 95
3.17 LAN SWITCHING 100
3.17.1 SWITCH 100
3.17.1.1 VLAN (Virtual LAN) 103
3.17.1.2 Vlan Trunking Protocol (VTP) 108
3.18 Wi-Fi (WIRELESS FIDELITY) 113
3.18.1 Wireless LAN 113
3.18.2 Wireless Standards 114
3.18.3 Wireless Security 115
4 CONCLUSION 117
5 REFRENCES 118
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
1. INTRODUCTION
This project report pertains to six months industrial training that I had underwent
at JETKING, Chandigarh as part oI curriculum oI degree in Bachelor oI technology in
Electronics and Communication engineering as required by Swami Parmanand College oI
engineering and technology (aIIiliated to Punjab Technical University, Jalandhar) .
I learnt a lot Irom proIessional managers and skilled engineers. I had a great
learning experience as trainee in this Iirm. I learnt a lot about how diIIerent networks are
controlled in the industry or any department with the help oI networking processes, under
MCSE and CCNA.
I have learnt about diIIerent type oI servers like DHCP Server, DNS Server, NAT
Server. Also I have learnt how to control the LAN and MAN networks under MCSE
(MicrosoIt CertiIied System Engineers) and how to control MAN and WAN networks
under CCNA (CISCO CertiIied System Engineers).
JustiIication cannot be done to whatever I have learnt in these six months within a
Iew pages but I have still tried my best to cover as much as possible in this report. In this
report I have tried to sum up the technical knowledge I have gained in my six months oI
training.
1.1 Company Profile
Jetking is an organization came into establishment in1947. Jetking is India`s
number one Computer Hardware and Networking Institute.
Birth and Evolution
It took a lot oI Iailure beIore mankind tasted technological success. Jetking evolved in
tune with the changing Iace oI technology. During 55 years in the Iield oI electronic
technology. Jetking successIully trained thousands oI students to overcome Iailure Ior
high paying careers.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
1947 Birth
1962 Pioneered 'Do-It-YourselI Kits in India
1972 Introduced Asia- 72, Fairchild and Wildcat transistors
1986 Became a Public Limited Company and also introduced
entertainment electronics product-T.V sets, Two-in-ones and
ampliIiers.
1990 Launched Jetking School oI Electronics Technology
1993 Network oI Jetking training centers spread all over India
1994 Opening oI Jetking, Chandigarh
1995 Tie-up with Heath kit Educational System (U.S.A.)
1996 Introduced advanced courses on Pentium, Notebooks, Modems,
Email/Internet, LAN 4.X
1997 Novell Education Academic Partner
1998 Representative Ior International Correspondence School (ICS),
USA in India
1999 Added cyber technology to the curriculum
2003 ISO 9001-2000 company and Authorized MicrosoIt online testing
centre (VUE) Ior MS, CISCO, MCSA, MCSE, CCNA, A etc.
Mr. Suresh G. Bharwani is the CHAIRMAN and MANAGING Director oI
Jetking InIotrain Ltd. India`s leading Computer Hardware and Networking Institute. With
the vision to promote and the conviction to deliver the widespread propagation oI comp-
uter hardware and networking education across the nation, Mr. Bharwani was the Iirst to
set up an training institute oIIering innovative courses in computer hardware in 1990.
Jetking`s core competency lies in providing complete training and developing hardware
engineers and proIessionals with sound technical knowledge. It Iocuses on the overall
development oI personality oI an individual with emphasis on personality development,
presentation and communication skills, leadership skills etc.
Jetking has established more than 125 operational centers and 250 Iaculties across
the country and has trained over 3,50,000 students who have move onto the crave
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
success- Iull career. With its alumni placed in the best oI organizations in India and some
abroad,
Jetking,s vocational training and placement promises has helped build the career
prospects oI many young boys and girls.
The company has been awarded the ISO 9000:2000 certiIication in 2003.The
company has been awarded the ' Maharashtra IT Award Ior a key role in manpower
activities in year 2006-07,it was Ielicitated with Franchise Award as Best Franchisor Ior
the year 2007-08.Also,ranked 4
th
in the list oI 26
th
hot Iranchises as per outlook money
magazine.
Mr. Suresh Bharwani was awarded with 'Pike`s Peak Award by the Bob Pike
Group USA Ior eIIective implementing smart lab plus Ior making technical training Iun,
Iaster and easier Ior non- technical person.
Across all the sectors, industries are upgrading their inIormation technology
system. Industries ranging Irom plastics, chemicals, textiles and power to the automotive
and telecom sector are now IT savy. Government and public sectors are going hi-tech
with EDI and computer networks. The IT industry, soItware companies, data centers, IT-
enabled services providers are all equipped with advance IT system and networks. The
increasing number oI call centers, BPO`s etc., have given a Iurther boost to the hardware
and networking industry.
The courses in jetking comprises lecture and theory session, with a great Iocus on
active participation through smart lab plus ,that Iocuses on audio visual and learning with
hands-on training and equips students with an in depth domain knowledge that is
technical; it also equips students with soIt skills ,to Iace the multi-Iaceted challenges oI
corporate world.
PLACEMENT: Jetking is the Iirst and only institute that promises the 100
jobs guarantee to its students. The companies that have recruited jetkings students
include:
Samsung, Sun Micro system, IBM, Canon, Siement, reliance, TATA, Compaq HP
invent, IT-T solutions, Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited, D-Link, Novell, Dell, Wipro, LG,
ICIC InIotech and several other MNCs.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Any student who has qualiIied his or her HSC/SSC examination is eligible to take
up a course at jetking. The one year program Jetking certiIied hardware and networking
proIessionals give 680 hours oI in-depth knowledge to a student in Basic electronics and
computer applications. Computer hardware and peripherals, window 2003 administrator
and network administrator (soon it will be replaced with window server 2008).Apart
Irame technical knowledge there are personality development sessions which groom the
student`s personality, their ability to perIorm better.
Jetking, India`s leading hardware and networking training institute has trained
over 3,00,000 students Irom its 125 centers spread across India. With its alumni placed in
the best oI organizations in India and some abroad, Jetking vocational training and
placement promises has helped build the career prospects oI many young boys and girls.
Jetking has partnered with some oI the worlds most renowed names in networking
to provide you with cutting edge courses and technologies. With academic partnerships
with MicrosoIt, Comp TIA,LINUX, NOVELL, and person VUE .
Jetking Chandigarh is a division oI Hi-Tech point. Hi-Tech point is an ISO 9001-
2000 IT company. It was established in year 1993 and run by a company oI IT
proIessionals. Jetking Chandigarh branch is considered to be the best centre among all
centers. It has bagged number 1 center award consecutively Ior last 7 years. Here training
on various Iields is going on like Basic Electronic, Hardware, Networking, JCHNP
Analog and Digital electronics and Hardware, RHCE, RHCSS, MNA, MCSE (MicrosoIt
System Engineers), MCITP, MNA, CCNA (CISCO CertiIied Network Associate),
CCNP(CISCO CertiIied Network ProIessional).
Partnership with industry leaders like MicrosoIt and Red Hat Jetking ensure its
students authentic courseware and technology.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
2. LITERATURE RIEVIEW
Computer Networking is a very vast project in the present developing era oI electronics
and communication. Now a days, computers are used in a wider range. All the
organizations are using multiple computers within their departments to perIorm their day
to day work. Computer network allows the user to share data , share Iolders and Iiles with
other users connected in a network. Computer Networking has bound the world in a very
small area with it wide networking processes like LAN, MAN, WAN.
The courses in jetking comprises lecture and theory session, with a great Iocus on active
participation through smart lab plus ,that Iocuses on audio visual and learning with
hands-on training and equips students with an in depth domain knowledge that is
technical; it also equips students with soIt skills ,to Iace the multi-Iaceted challenges oI
corporate world.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3. NETWORKING
3.1 Introduction to networking
Networking is a practice oI linking oI two or more computing devices such as
PCs, printers, Iaxes etc., with each other Connection between two devices is through
physical media or logical media to share inIormation, data and resources. Networks are
made with the hardware and soItware.
Cable/media
Fig 1: computer network
3.1.1 Models of Networking
Model means the connectivity oI two computers. We have many types oI
networking models.
(i) Client Server Model
(ii) Peer to Peer Model (Workgroup Model)
(iii) Domain Model
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(i) Client -Server Model
In a Client server model we have one server and many clients. A Client can share
the resources oI server, but a server cannot share the resources on clients.
On the point oI view oI administrator it`s very easy to control the network
because we combine with the server also at security point oI view. It is very useIul
because it uses user level security in which users have to remember only one password to
share the resources.
(ii) Peer to Peer Model (Workgroup Model)
In Peer to Peer networking model all computers are in equal status, that is we
cannot manage centralization, administration secutity. In Peer to Perr networking client
use operating system like Window 98, Window XP, Window 2000, Window Vista.
(iii) Domain Model
It is a mixture oI client server and peer-to-peer model. In this clients can share
their resources as peer-to-peer but with the permission oI the server as in client server
model thereIore it is commonly used model because in this security is more as we can put
restriction on both server and clients.
Difference between Workgroup & Domain
Table 1
Workgroup Domain
1. It is a peer to peer networking model.
2. There is no client and no server. All the
computers are in equal status.
1. It is a server based networking model.
2. There is a centralized dedicated server
computer called domain controller which
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3. This model is recommended Ior small
networks, upto 10 computers.
4. There is no centralized administrated
separately.
5. In this model, low grade OS like
2000/XP proIessional, WIN 98 etc. can be
used.
6. Users accounts are created in each PC
and are called as Local Users.
controls all other computers called clients.
3. This model is recommended Ior large
networks.
4. There is centralized administration and
each PC can be administrated and managed
Irom the server.
5. in this model high grade OS like WIN
2000/2003 Server can be used.
6. Users accounts are created on the server
side and are called Domain Users.
3.1.2 Categories of network
Networks can be categorized as per geographical area to be covered by the
network. Computer network are divided into Iour categories includes: Local Area
Network (LAN), Campus Area Network (CAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) and
Wide Area Network (WAN).
3.1.2.1 Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is a computer network that is used to connect computers and work station to
share data and resources such as printers or Iaxes. LAN is restricted to a small
area such as home, oIIice or college. Devices used in LAN are : HUB and switch.
Media Ior LAN is UTP cables. Figure 1.2 shows how all work stations, server and
printer are interconnected with the help oI the network device.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 2: Local Area Network
Types of LAN
In LANs, data can be transIerred using techniques like token passing. As per
techniques used Ior data sharing, LANS are classiIied into Ethernet, Token Bus, Token
Ring and Fiber Distributed Data InterIace (FDDI).Figure 3.3 shows LAN classiIication.
Fig 3: LAN classification
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Advantages of LAN
a). Provides communication in smaller networks, easy to install and conIigure.
b). many users can share data or network elements at the same time which results
in Iast work.
Disadvantages of LAN
a). limited number oI computers are connected in a LAN.
b). LAN cannot cover large area.
c). Network perIormance degrades as the number oI users exceeds.
3.1.2.2 Campus Area Network (CAN)
Campus Area Network is a computer network made up oI two or more LANs
within a limited area. It can cover many buildings in an area. The main Ieature oI
CAN is that all oI the computers which are connected together have some
relationship to each other e.g. diIIerent buildings in a campus can be connected
using diIIerent CAN. It will help to interconnect academic departments, library
and computer laboratories. CAN is larger than LAN but smaller than WAN.
Figure 3.4 shows a CAN network.
Fig 4: Campus Area Network
Devices used in CAN are : HUB, Switch, Layer-3 switch, Access Point .And the media
used Ior CAN is Unshielded twisted pair oI cables and Fiber Optics Cable.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.1.2.3 Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN is the interconnection oI networks in a city. MAN is not owned by a single
organization. It act as a high speed network to allow sharing resources with in a
city. MAN can also be Iormed by connecting remote LANs through telephone
lines or radio links. MAN supports data and voice transmission. The best example
oI MAN is cable T.V network in a city.
Fig 5 : Metropolitan Area Network
3.1.2.4 Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN covers a wide geographical area which include multiple computers or
LANs. It connects computer networks through public networks like, telephone system,
microwave, satellite link or leased line.
Most oI the WANs use leased lines Ior internet access as they provide Iaster data transIer.
WAN helps an organization to establish network between all its departments and oIIices
located in the same or diIIerent cities. It also enables communication between the
organization and rest world.
Devices used in WAN is only Router
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.2 IP ADDRESSES and MAC Addresses
It is also called as logical addresses. IP is a 32 bit long and it is divided into 4
octets and dot (.) is used to separate one octet Irom another. It is represented in the
Iorm oI decimals. There are two versions oI IP addresses:
- IPv4
- IPv6
Table 2 Comparison between IPv4 and IPv6
3.2.1 IP Address Classes
IP address is a 32 bit address. It is divided into various classes namely Class A, Class
B, Class C, Class D and Class E. TCP/IP deIines Class D Ior experimental purpose.
TCP /IP address contains two addresses embedded within one IP address; Network
address and host address as shown in Iigure 3.1
NETWORK
ADDRESS
HOST ADDRESS
0 bits 31 bits
IPv4 IPv6
- It is 32 bit long.
- It is divided into 4 octets.
- Ipv4 perIorms broadcasting,
multicasting and unicasting.
- IPv4 is divided into 5 classes:
A to E.
IPv4 is in decimal Iorm.
- It is 128 bit long.
- It is divided into 16 octets.
- IPv6 doesn`t support
broadcasting, it perIorms
multicasting and unicasting.
- Ipv6 doesn`t support classes.
- IPv6 is in hexadecimal Iorm.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Class A consists oI 8-bit network ID and 24-bit host ID. Class B consists oI 16-
bit network ID and 16-bit oI host ID. And Class C consists oI 24-bit oI network
ID and 8-bit oI host ID.
Address Classes
Table 3: Address Classes
`
Addres
s
Class
Starting
Bits
(Iirst-byte)
Range oI First
Octet
Mask Value Valid Hosts
Class A 0 1to 127 255.0.0.0 256*256*256-2
16,777,214
Class B 10 128 to 191 255.255.0.0 256*256-265,534
Class C 110 192 to 223 255.255.255.0 256-2
Class D 1110 224 to 239 Reserved Ior multicasting
Class E 1111 240 to 255 Reserved Ior research and
development
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.2.1.1 How to Assign IP Address to Computer
An IP address assigned to a computer may either be permanent address or address
that is assigned to a computer on a time lease or Ior temporary basis. Hence, the address
granted to computers is divided into two categories Dynamic IP addresses and Static
addresses.
Dynamic IP Addresses
Dynamic IP addresses are assigned to the devices that require temporary
connectivity to the network or non-permanent devices such as portable computer. The
most common protocol used Ior assigning Dynamic IP address is DHCP also called
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Dynamic Host ConIiguration Protocol. The DHCP grants IP address to the computer on
lease basis.
Static IP Addresses
Static IP addresses are assigned to the device on the network whose existence in
the network remains Ior a longer duration. These static IP addresses are semi-permanent
IP addresses which remain allocated to a speciIic device Ior longer time e.g. Server.
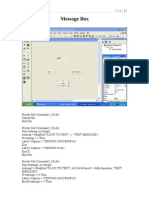
3.2.1.2 How to Configure IP Address in window 2003
Right click on My Network Places- properties
right click on working LAN card- properties
select internet protocol (TCP/IP) -properties
Tick on- Use the following IP addresses - now Iill the IP address e.g
10.0.0.1
Tick on Use the following DNS server address
Fill the preferred DNS server 10.0.0.1
Ok
Close
Now check the connectivity oI computer with itselI with command
Start-run-cmd-ping 10.0.0.1
3.2.2 MAC Addressing
MAC address is a hardware address that is embedded in the NIC card. It is also known
as hardware address or physical address. Every NIC card has a unique MAC address
assigned by IEEE. MAC address is used to identiIy the nodes at lower levels oI OSI
model. The MAC address operates at the data link layer oI the OSI model.
MAC address is a 12 digit hexadecimal number (48 bit address). It is made up oI
numbers Irom 0-9 or a letter Irom A-F. MAC address can be written in any one oI the
Iormats:
> MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
> MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS
T o identiIy the MAC address in window:
Click Start Run
Enter cmd in the Open text book
Type ipconfig /all
Press Enter
The 12 digit MAC address will be shown as say 00:11:11:EA:8D:F6
3.3 NETWORKING MEDIA
To do networking we need to use some type oI media. There are many types oI media.
(i) Coaxial Cable
(ii) Fiber optic cable
(iii) Twisted Pair oI Cables
(iv) Micro- wave
(iv) Satellite
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable consists oI an insulated copper conductor surrounded by a tube
shaped copper braid outer copper tune and the inner conductor have the same axis oI
curvature hence it called coaxial cable. It is basically oI two types:
(i) Base Band Cable (RG 59)
(ii) Broad Band Cable (RG 58)
We used Base Band signal cable in Networking oI Computers, It is so called because
it carries single Irequency. Its speed is 10 Mbps and impedance is 50 O. Where as Broad
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Band Cables carries multiple Irequencies. Connector used Ior Coaxial cable is
BNC(British Novel Connector) connector. ARCnet uses RG-62 coaxial cable. It has an
impedance oI 93 O and has a comparatively lesser attenuation, hence yield greater
distances. These cables are expensive and provide high propagation Iactor.
Fiber Optical Cable
Fiber optic cable consists oI a very Iine Iiber made Irom two types oI glass, one Ior the
inner core and the other Ior the outer layer. Here signal is transmitted in the Iorm oI light.
DiIIerent varieties oI Iiber optics is used depending on the size oI the network. Single
mode Iiber optics is used Ior networks spanning longer distance. Fiber Optics has lower
propagation Iactor than coaxial cable. It is a costly but more secure transmission media.
Twisted Pair Cable
There are two wires, which are twisted with each other to avoid EMI (Electro
Magnetic Induction).these cables are easy to terminate. However they have a slightly
higher value oI attenuation value and hence have limited distance covering capacity.
Connector used Ior Twisted Pair oI Cable is (Registered Jack) RJ-45 and RJ-11. There
are two types oI twisted pair oI cables:
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair):
In this an extra wire which is called shielded wire is wrapped over the inner
cover which holds copper in pairs. This protection is used to protect signal Irom
external noise.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
In this type oI wire no shielded cover is there Ior extra protection Irom noise.
There are diIIerent categories oI UTP cables:
Categories of UTP Cables
Table 4: Category and Speed of UTP cables
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Category Speed
CAT-1
CAT-2
CAT-3
CAT-4
CAT-5
CAT-6
CAT-7
56 Kbps
4 Mbps
10 Mbps
16-20 Mbps
100 Mbps
1Gbps
1Gbps
3.3.1 Ethernet Cabling
There are three types oI Ethernet cables:
Straight cable
Crossover cable
Rolled cable
3.3.1.1 Straight cable
It is used when we have to connect
PC TO Switch
PC to Hub
Hub to Router
Switch to Router
Colour Coding for straight Cable
TABLE 5
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
568A
(one end) (other end)
568B
(one end) (other end)
Green/white
Green
Orange/white
Blue
Blue/white
Orange
Brown/white
Brown
Green/white
Green
Orange/white
Blue
Blue/white
Orange
Brown/white
Brown
Orange/white
Orange
Green/white
Blue
Blue/white
Green
Brown/white
Brown
Orange/white
Orange
Green/white
Blue
Blue/white
Green
Brown/white
Brown
3.3.1.2 Crossover Cable
It is used when we have to connect:
PC to PC
Hub to Hub
Switch to switch
Router to Router
PC to Router
Hub to Switch
Colour Coding for Crossover cable
Table 6 Colour Coding for Crossover cable
(one end) (other end)
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Orange/white
Orange
Green/white
Blue
Blue/white
Green
Brown/white
Brown
Green/white
Green
Orange/white
Blue
Blue/white
Green
Brown/white
Brown
3.3.1.3 Rollover Cable
Rollover cable isn`t used to connect any Ethernet connections together, but
Rollover cable can be used to connect a host to a router console serial communication
(com) port.
NOTE: Straight cable and Cross cables are used Ior data transIer but Rollover
cables are not used Ior data transIer.
There are two methods Ior manuIacturing Rollover cables:
Table 7 Colour Coding for Rollover Cable
568A
(one end) (other end)
568B
(one end) (other end)
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Green/white
Green
Orange/white
Blue
Blue/white
Orange
Brown/white
Brown
Brown
Brown/white
Orange
Blue/white
Blue
Orange/white
Green
Green/white
Orange/white
Orange
Green/white
Blue
Blue/white
Green
Brown/white
Brown
Brown
Brown/white
Green
Blue/white
Blue
Green/white
Orange
Orange/white
3.4 OPERATING SYSTEM
3.4.1 Types of Operating Systems
(i) DOS (Desktop Operating System) (ii) NOS (Network Operating System)
Table 8: Operating Systems
DOS
1. It is a desktop operating system.
2. It is used in small networks.
3. In this OS, there is less security.
4. In this OS, all computers are clients.
5. In this OS, MS-DOS, GUI package
Win
3.1, Win 95, Win 98, Win ME comes.
NOS
1. It is a network operating system.
2. It is used Ior large networks.
3. In this OS, there is more security.
4. In this OS, there are servers and
clients.
5. In this OS Win NT, Win 2000, Win
2003, LINUX, UNIX, Novell and
MAC comes.
3.4.1.1 Introduction to Window 2003 Server
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Window server 2003 (also reIerred to as WIN 2k3) is a server operating system produced
by MicrosoIt. Introduced in 24
th
April 2003 as the successor to window 2000 server, it is
considered by MicrosoIt to be the corner stone oI its window server system line oI
business server products. An update version Window Server 2003 R2 was released
manuIacturing on 6
th
dec, 2005. its successor window 2008 was released on 4
th
Ieb, 2008.
According to MicrosoIt, window server 2003 is more scalable and deliver better
perIormance than its predecessor window 2000.
Features of Window 2003
(i) A signiIicant improved version oI Internet InIormation Service (IIS)
(ii) Increased deIault security over previous version due to the built in Iirewall
and having most services disabled by deIault.
(iii) Manage your server-a role management administrative tools that allow an
administrator to choose what Iunctionality the server should provide.
(iv) Improvement to Active Directory.
(v) Improvement to Group Policy handling and Administration.
(vi) Provides a Backup system to restore lost Iiles.
(vii) Improved disk management, including the ability to Backup Irom shadows oI
Iiles, allowing the Backup oI open Iiles.
(viii) Improved security and command line tools which are part oI MicrosoIt
initiative to bring a complete command shell to the next version oI window.
(ix) Support Ior a hard based 'Watch Dog Timer, which can restart the server iI
the operating system does not suspend with in a certain amount oI time.
Removed Features
The ability oI creating server disk automated system recovery (ASR) is used
instead .
Edition of Window 2003
Window server 2003 comes in a number oI editions, each targeted towards a
particular size and type oI business. In general, all variant oI window server 2003
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
have the ability to share Iiles and printers, act as application server and host
message queue, provide email services, authenticate users, act as an X.509
certiIicate server, provide LDAP (Light Weight Directory Access Protocol)
services, serve streaming media, and to perIorm other server-oriented Iunctions.
3.5 DNS SERVER
DNS stands Ior domain name system. DNS system is a standard technology
Ior managing the names oI websites and other internet domains. DNS techniques allows
you to type names into your web browser like computer networking, about computer and
allow your computer to automatically Iind that address on internet. DNS is the resolution
mechanism used by Window Server 2003 clients to Iind other computers and services
running on those computers Ior computers in a window 2003 network inIrastructure to
talk to one another, one oI the key ingredients is the DNS server .Host name alone do not
communicate globally but communicate locally, but iI domain name is added along with
it then the host name can communicate globally. DNS is use Ior name reservation i.e. to
convert IP address to host name and host name to IP address or the Iunction oI DNS is to
resolve host name such as www.yahoo.com to an IP address. User identiIy only user
Iriendly name and all computers and technologies identiIy IP address and MAC address
DNS is use to solve this problem because DNS is used to convert host name FQDN (Iully
qualiIied domain name) to IP address and IP address to host name .
3.5.1 PARTS OF DNS SYSTEM
(i) Host name
(ii) Domain name
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(iii) FQDN
(iv) Namespace
(v) DNS server
3.5.1.1 HOST NAME
Host name is a computer name and is also called is NetBIOS (network basic
Input/ output system) name. NetBIOS is actually an application layer protocol that can
use the transport services oI TCP/ IP when used in routed network. A NetBIOS name is
16- byte addresses that identiIy a NetBIOS resource on the network.
3.5.1.2 DOMAIN NAME
Domain name is used to identiIies the internet site one can identiIies the location
without having to remember the IP address oI every location e.g. yahoo.com or
gmail.com
3.5.1.3 FQD
FQDN means Iully qualiIied domain name which represents a hostname appended to the
parent name space in hierarchy. Also in Iully qualiIied domain name diIIerent levels oI
namespace are visualize as in Iig below this hierarchy is visualized- the root level
namespace, top- level domain, and so on, in use throughout the internet today. LeIt most
portion oI the FQDN is the host portion oI the name. A host name is alias we give to an
IP address.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 6:To find location of a computer using FQDN
FQDN is a unique name in the computer on the network. We can identiIy host id and
location oI a computer as in Iig above. Suppose we want to Iind location oI pc1 with
IP address 20.0.0.1, which is in lab2, 2
nd
Iloor in the organization center. The FQDN
Ior this is
Pc1.row3.lab2.floor2.center.com
But this address is very lengthy to locate pc1 so to simpliIy this we use 'c name
technique as:
Pc1.center.com20.0.0.1
3.5.1.4 Domain Namespace
DNS operates in what is known as DNS namespace. The DNS namespace is an
organized, hierarchical division oI DNS names. Domain namespace enable users to easily
locate the network services and resources. The domain namespace include the root
domain, the top level domain oI the organization and organize these domain in a
hierarchical tree structure. Namespace works on the hierarchical tree structure oI root
domain. There are total 13 root domain working in the internet, they are A, B, C, D, E, F,
G, H, I, J, K, L and M. There is one root domain, which acts as the starting point oI the
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Iully qualiIied domain names. This root domain is designated with a dot (.). Fig 6.2
shows the tree structure or domain namespace.
Fig 7: Tree structure or Domain Namespace
3.5.1.5 DNS server
Any computer providing domain namespace is a DNS server. DNS server is used to
convert host name FQDN into IP address and IP address into host name FQDN. To store
the name-to-IP-addresses mappings so crucial to network communication, name server
uses zone Iiles.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.5.2 DNS Zone
Zone is the part oI DNS database that contain record oI domain or multiple domain.
II the domains represents logical division oI the DNS namespace, zones represents the
physical separation oI the DNS namespace. In other words inIormation about records oI
the resources within DNS domain is stored in a zone Iiles, and this zone Iiles exist on
hard drive oI server. Zone Iiles are divided into one oI two basic types:
Forward lookup zone: Provides host-name-to-IP-address resolution
Reverse lookup zone: Provides IP-address-to-host-name resolution
3.5.2.1 Resource record stored in a zone file
Each record stored in a zone Iile has a speciIic purpose. Some oI the records set the
behavior oI the name server, others have the job oI resolving a host name or service into
an IP table.
(i) NS (Name Server):
These speciIy the name servers that are authoritative Ior a given portion
oI DNS namespace. These records are essential when DNS servers are perIorming
iterative queries to perIorm name resolution.
(ii) SOA (Start of Authority):
This resource record indicates the name oI origin Ior the zone contains the name
oI the server that is the primary source Ior inIormation about the zone. The inIormation in
an SOA record aIIect how oIten transIer oI the zone are done between servers
authoritative Ior the zone. It is also used to store other properties such as version
inIormation and timings that aIIect zone renewal or expiration.
(iii) CNAME (Canonical Name):
CNAME can be used to assign multiple names oI a single IP address.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
For example, the server hosting the site www.abc.com is probably not named www, but a
CNAME record exist resolution oI www to an IP address all the same. The CNAME
record actually points not to an IP address, but to an existing A record in the zone.
3.5.2.2 Steps to Install and configure DNS server
Start control panel add and remove program
Add remove window components
Select networking services and click on detail button
Check box oI DNS server
Ok and finish
3.5.2.3 Creating a Forward Lookup Zone
Statically Iill the IP address
Start administrator tools
DNS right click on forward lookup zone
New zone next
Select primary zone next
Enter zone name (abc.com) next
Tick Allow both secure and non secure updates and secure dynamic
updated
next next
now click on created zone (abc.com)
new host enter host name Ior global level (i.e by entering www) Iill IP
address oI the web server , click on add button
enter another host name, a blank host with same IP i.e do not Iill its host name
steps to change SOA and NS records
Right click on SOA records properties
Fill primary server e.g (www.abc.com) responsible person
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
host master.abc.com apply ok
right click on NS records
click on add button enter FQDN www.abc.com
resolve ok apply ok
Now go to start menu ping abc.com
On Client Side To access DNS server Iill IP address oI server then use ping command
e.g ping www.abc.com
3.5.2.3 Creating a Reverse Lookup Zone
Right click on reverse lookup zone
New zone next select primary zone next
Iill Network ID next next
Select allow both non secure and non secure dynamic updates
Finish
Right click on created reverse zone new pointer
enter host IP number e.g (50.0.0.50)
enter FQDN (www.chd.com)
3.5.2.4 Some DNS Commands
(i) c:~tracert www.yahoo.com
command is used to check the path , a data packet Iollow Irom one router
to another router.
(ii) c:>nslookup
command display the domain name with IP (works only when reverse lookup
zone is set up).
(iv) c:>ipconfig /all
This command display FQDN, IP address, MAC address.
(iv) c:>ipconfig /flushdns
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
This command Ilush or clear all the inIormation in the cache that is retrieved
Irom DNS server.
(v) c:>ipconfig /displaydns
Display the current contents or entries in the cache.
(vi) c:>ip config /register
register any DNS name
3.6 DHCP SERVER
DHCP (Dynamic Host ConIiguration Protocol) is a protocol that allocates IP address to
computer on a network. DHCP centralized the management oI IP address allocation and
reduces human error associated with manual IP conIiguration. DHCP server supplies all
the necessary networking param-eters. Two things are always handed out as a part oI
DHCP conIiguration: IP address and subnet mask. Further DHCP will Irequently
conIigure clients with optional values, such as a deIault gateway, DNS server address,
and the address oI a Window Internet Naming Server, iI one is present. Scenario showing
DHCP server IP address allocation.
3.6.1 Working of DHCP Server
(i) DHCP Scope
(ii) DHCP Super Scope
(iii) Exclusion IP Range
(iv) DHCP Lease Time
(v) IP Reservation
DHCP Scope
Scope having the range oI IP address Ior providing dynamic IP address to other
computer. A group oI IP address within a scope is called as DHCP scope.
DHCP Super Scope
A super scope is used to combine two or more scopes each serving diIIerent subnets, and
can make the administration oI several scopes on window 2003 DHCP server more
manageable. Using super scope you can group multiple scopes as a single administrative
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
entity that allows the client to lease Irom either one. With this Ieature, a DHCP server
can:
Support DHCP clients on a single physical network segment where multiple
logical IP networks are used. When more than one logical IP network is used on
each physical subnet or network, such conIiguration is called multinets.
Support DHCP clients located on the Iar side oI DHCP and BOOTP relay agent.
In multinet conIiguration, DHCP superscope can be used to group and activate
individual scope ranges oI IP addresses used on your network. In this way , a
DHCP server computer can activate and provide leases Irom more than one scope
to clients on a single physical network.
Exclusion IP range
II you want to reserve some IP Ior any computer i.e iI we want that Irom the series oI
192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.100 iI we want that a series oI IP addresses must not be
assigned automatically then at can be done using exclusive IP range.
DHCP Leased Time
DHCP lease time is validity oI IP address. By deIault DHCP lease time is 8 days
minimum,1 day maximum 999 days, 23 hours to53 day.
With in 8 days:-
AIter 80 oI day clients demand new IP some times server reIuse the client request.
AIter 87.5 oI days it will retry, and iI the server did not give the new IP address then
the client will receive APIPA address (Automatic Private IP Address).
When a DHCP client is unable to locate a DHCP server, the client picks out a random IP
address Irom the private APIPA address range oI 169.254.*.*, with a subnet mask oI
255.255.0.0. The 169.254.*.* IP range is private because that network number is not in
use on the internet, it is random because the client generates an arbitrary host number Ior
that network.
The signiIicance oI APIPA is that DHCP client computers that cannot Iind a
DHCP server can still be assigned an IP address and communicate with other computers
on the same subnet mask that also cannot Iind DHCP server. It allows communication
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
when DHCP server is down or just plain not there. Note that APIPA does not assign a
deIault gateway, and thereIore it cannot communicate with any computer that lives on the
other side oI a router.
IP Reservation
There are some DHCP clients that you want to be the DHCP clients, but you will also
want to make sure that they get same IP address every time. This can be done by
statically Iilling the IP address. We can reserve IP address with the help oI MAC address
Ior a particular computer.
3.6.2 Installation Steps of DHCP Server
start control panel
add and remove program add and remove window components
select networking services and click on detail button
check box oI DHCP server
ok finish
3.6.2.1 Steps To Configure DHCP Server
start program administrative tool
select DHCP
create new scope in action menu new scope next
give scope name next
give IP address range next
add exclusion name next
check lease duration next finish
AIter DHCP server is conIigured, it is required to be authorized and DHCP scope
should be active. For that select DHCP server and click on authorize in action menu.
Then right click on scope name and click on active.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.6.2.2 On Client Side
Go to LAN card properties select TCP/IP protocol properties
Select obtain IP address automatically
Go to command prompt (cmd)
Give command
3.6.2.3 Backup of DHCP Server
We can take backup oI all the conIiguration in DHCP server with the help oI
administrator. Backup means to export the DHCP database to another system, as it is
helpIul in case due to any reason our data is corrupted or deleted, we can take our
database Irom the place where it is stored. Steps oI taking backup :
Stop the DHCP server and disable the DHCP server services
Copy the DHCP server directory to a temporary location, say pen drive or
on a new DHCP server.
3.6.3 DHCP Relay Agent
The DHCP relay agent is a soItware that listen DHCP discover packet and Iorward to
DHCP server. In window 2003 server system the DHCP relay agent can be enabled as a
part oI Routing and Remote Access (RRAS).
3.6.3.1 Steps To Configure DHCP Relay Agent
Set the network, Iill the IP address and select two LAN cards
Open Routing and Remote Access enable Routing and Remote Access
Right click on general new routing protocols
Select DHCP relay agent
New interface
Select LAN card which is to be connected to the cross cable i.e L1
Ok
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Right click on relay agent properties
Enter IP address of DHCP server
add apply ok
3.7 ACTIVE DIRECTORY
With the release oI Windows 2000, MicrosoIt introduced Active Directory, a scalable,
robust directory service. Active Directory is used to create server based networking.
Active Directory`s job is to store and make available a Directory database i.e inIormation
about the user, its class, name, address, mails, phone numbers, location.
Active Directory is a technology created by MicrosoIt that provides a variety oI
network services like Directory Services, DNS based naming and other network
inIormation. Active Directory also allows administrator to assign policies, deploy
soItware and apply critical updates to an organizations. Active Directory was previewed
in 1999, released Iirst with window 2000 server edition and revised to extend Iunctionally
and improve administration in Window 2003. Additional improvements were made in
Window server 2003 and Window server 2008.
The Iundamental building block oI MicrosoIt`s Directory services continues to be a
domain. A domain is logically grouping oI network resources, including shares, printers,
groups and users accounts. The user account represents the individual to domain, and
allows Ior diIIerent type oI access and diIIerent types oI tasks. Every users account is
unique. It has uniqueness oI the user account that allows administrator to control access
Ior every member oI domain.
There are two types oI users accounts: local account and domain account. Local
accounts are maintained in the local database oI a computer and cannot be used to grant
access to network resources. Local users are primarily used to administer a computer or
to allow several people to share a single computer that is not a member oI a domain.
Whereas domain users accounts are much more widely used in organizations that local
user accounts because they allow Ior central administration and user can log onto any
computer in the domain. Domain users accounts are stored in Active Directory.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.7.1 Active Directory Services
A computer network can be divided logically into two networking models.
Workgroup
Domain
Difference Between Workgroup and Domain
Table 9
Workgroup Domain
1. It is a peer-to-peer networking
model.
2. There is no client and no server.
All computers are in equal status.
3.This model is recommended Ior
small networks (upto 10 pcs).
4. There is no centralized Admin-
istration and each PC is
administrated separately.
5.In this model, low grade operating
system like 2000/xp proIessional,
win 98 etc can be used.
6. Workgroup can be given names
like sales, HR, accounts etc.
1. It is a server based networking model.
2.there is a centralized dedicated server
computer called domain controller
(DC)which controls all other computers
called clients.
3. This model is recommended Ior large
networks.
4. There is centralized administration
and each PC can be administrated and
managed Irom the server.
5.In this model high grade operating
system ,like win2000/2003 server are
used.
6. Domain can also given names like
abc.com, xyz.com etc.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
7 Users accounts are created in each
PC and are called as 'Local Users. 7.Users accounts are created on sever
side DC and are called as Domain
Users.
Active Directory uses domain to hold objects, each domain has security boundary.
Users must authenticates to the domain in which their users account resides beIore they
can access resources, such as a shared Iolders. Active Directory also links related
domains in a hierarchical structure and users can access resources in any oI the domain in
which their user account resides. The hierarchical structures oI related domain is called a
tree, and all domains in the tree share the same Domain Name System (DNS) namespace.
All the domains and the trees in a single organization are called a Iorest. All domains in
the Iorest share same schema.
3.7.1.1 Types of Domain
Domain Forest
Domain Tree
Organization unit
Domain Forest
A Iorest is created when window 2k3 server computer is conIigured as a domain
controller. A Iorest is a collection oI multiple domain link together and relationship
between the domains.
Domain Tree
A domain tree is made up when there is a parent child relationship between the domain
in the Iorest. The child domain includes the complete parent domain name. a tree is a set
oI two or more domains sharing common namespace e.g we can create a parent domain
and then child domain like mail.yahoo.com; where mail- child domain, yahoo- parent
domain.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 8: Structure of domain forest and domain tree
Organization Unit (OU)
Organization unit is the smallest unit in a domain network that can contain users,
computer groups, shared Iolders, printers and group policy object in simple words. OU
means department like sale department, accounts department like sales, accounts in a
company OU can be used to apply diIIerent security policies to computer and users in
diIIerent department. OU also helps in dividing administration among diIIerent
administrator oI managing only computer and users oI sales department.
3.7.1.2 Types of Domain Controller
(i) PDC : Primary domain controller
(ii) ADC : Additional domain controller
(iii) BDC : Backup domain controller
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Primary Domain Controller (PDC)
This is the Iirst domain controller, in this domain all entries are created in it like
users account, group policy, Organization unit etc. All FSMO role are done in PDC.
Additional Domain Controller (ADC)
It is a domain network, it is important to have more than one DC so that iI one
DC Iails, the other DC will continue serving the client. There is also load balancing oI
Active Directory Service iI we have more than one DC.
The Iirst DC we create is simply called PDC and iI we create an extra DC then
that DC is known as ADC. ADC has same conIiguration oI AD as primary domain
controller.
All domain controllers in a domain networking are masters. We can make a
change in the active directory oI any domain controller and that change is replicated to all
other domain controllers. Replication takes place among all the domain controllers and it
is controlled automatically. II we create a user in the Iirst domain controller, it is
automatically created in the ADC because oI replication.
All the domain controllers in the domain networking are peers and this model is
called as multi- master model .
Fig 9: Multi-Master Model
3.7.1.3 Requirements of Active Directory
(i) Window 2000/2003 server computer.
(ii) Atleast one NTFS partition.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(iii) Static IP address
(iv) Atleast 1GB Iree hard disk space
(v) LAN card enabled and connected to the network
(vi) Install DNS, iI not installed oI Active Directory and conIigure it.
It should be noted that active directory cannot work without DNS.DNS is
automatically installed and conIigured during the Active Directory installation.
3.7.1.4 Installation of Active Directory
First oI all Iill the static IP address, then install DNS service into it and aIter that
install the Active Directory
start run dcpromo
Ok
Welcome to active directory next next
Select domain controller Ior a new domain e.g (gmail.com)
Next
Domain NETBIOS name (gmail.com)
Next
Data Iolder, Iolder new tech directory service next (SYS VOL)
Next
Click on install and conIigure the DNS server on this computer to use this
DNS server as its preIerred DNS server.
Tick on permission compatible only with window server
Next
Enter the restore mode and the password
next next finish
now restart computer
Command used Ior the removal oI Active Directory
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
start run dcpromo
This command is also used to remove active directory, iI aIter this command the
active directory is not removed then type
startrun
cmddcpromo /forceremoval
Ok
How to identify Active Directory installation
Start administrator tool
AIter that iI three options speciIied iI come, it means that Active Directory
has been installed
- Active Directory domain and trusts
- Active Directory sites and services
- Active Directory users and computer
Open DNS console by
Administrator toolsDNS
Forward lookup zone
- msdcs.exam.edu
- start oI authority (SOA)
- name server (NS)
Now ping active directory with domain name like
start run ping gmail.com
Backup of Active Director
Active Directory backup come in use when there is some problem in active directory. II
there is any problem in active directory then remove it and restore the backup.
Start runntbackupok
Select advance mode and untick that is already ticked
Select backup
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Selsct system state
Change backup path browse keep in your hardware and then send it to the
pen drive
D:\adbackup
3.7.2 CHILD DOMAIN
A domain is created say 'xyz.com. this domain is known as parent domain or the
root domain. Now 'chd.xyz.com will be the child domain or the sub domain oI xyz.com.
Fig 10 : parent-child relationship model
A child domain is created to ease administration in a very large domain network. We can
create the parent domain in the head oIIice oI the company and the child domain in the
branch oIIices.
Each branch oIIice will have its own administrator to manage the users oI the
child domain present in the branch oIIice.
A true relationship is automatically created between the parent domain and the
child domain. This means users in the child domain can access the Iile server oI the
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
parent domain. Moreover users oI either domain can use clients oI either domain Ior
logging in the domain but a user can always logon only in the domain in which his
account resides, though he physically can use client pc oI parent or client domain. Users
oI either domain can logon its own domain Irom either side but only when it use its own
domain name. users oI parent domain can communicate with child domain but he has to
use its domain name Ior that.
3.7.2.1 Steps to create child domain
First oI all install the active directory on pc1 i.e on the parent domain. Now make Tom
user on it. On pc2 create the child domain, then make users on it, user- Ram
Below are the steps to cerate child domain.
Fill the IP address in the child domain
Now ping to the parent domain with the domain name (xyz.com)
Run dcpromo ok
next select domain controller Ior a new domain
next select child domain and existing domain name (mcse.com)
next
enter username, password and domain name
enter user parent domain name also enter child domain name
enter complete DNS name i.e xyz.mcse.com
next next next next
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
it should be noted that parent domain can logon into child domain but on the other
hand child domain cannot logon to the parent domain. Also parent domain can apply
policies or security on the child domain.
Make the client member by entering particular user with its domain name.
First right click on My Computer
Properties
Computer name
Change
Write domain name ok
Now logoII start and then write user name - Tom
Domain name - mcse.com
Again logoII and check the other user
Start-user name- abc
Domain name mail.mcse.com
3.8 INTERNET SHAREING
We can share a single internet connection to multiple computers with the help oI
networking or internet sharing. There are Iour ways to share internet.
(i) Direct sharing
(ii) ICS Internet connection sharing
(iii) Win Proxy
(iv) NAT Network Address Translation
3.8.1 Direct Sharing
Internet sharing can be done between computers directly, just by taking internet
connection directly Irom ISP (Internet Server provider), then it is provided to ADSL
model, ADSL modem is connected to the ISP through RJ-11 connector. Then it is
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
connected to the switch with RJ-45 connector. Switch, Iurther connects computers those
have to be provided with internet connection. The scenario Ior direct sharing is as shown
in Iigure:
Fig: 11: Direct Sharing Scenario
ADSL modem has IP address 192.168.1.1. All the PCs are assigned with a DNS
(Domain Name Server) and GW (gateway) -192.168.1.1. Also DHCP (Dynamic Host
Communication Protocol) is enabled which will provide IP addresses to the PCs
automatically.
3.8.2 ICS (Internet Connection Sharing)
Internet Connection sharing provides an alternate way to provide Internet Sharing.
ICS requires a server with two network interIaces, one Ior the private internal network
conIigured with IP 192.168.0.1 address and an adapter Ior public connection. ICS
requires two connections in order to work: one public and one private i.e. ICS server
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
requires two LAN cards, Internal (Private) and External (Public). Internal LAN card uses
Local LAN card (L2) and External LAN card (L1) is used by Internet. ICS is designed to
be as simple as possible. ICS works on Iollowing windows: XP, Vista, 2K3 Server, 2k3
Server SP1.it doesn`t work on the server in which ADSP1 is present. The scenario Ior
ICS is shown below:
Fig 12: ICS scenario
Note:- When we conIigure ICS then the local card detect 192.168.0.1 address
automatically.
How to configure ICS
Open network and sharing center
Network- Properties
Click on Manage network connections
Right click on LAN Card which is used Ior internet- Properties
Click on sharing
Enable ICS
Ok
yes
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.8.3 Win Proxy Server
Win Proxy is a third party soItware which is used Ior sharing internet and we can
also block the web site with the help oI win proxy. WIN Proxy supports all the three
classes A, B, C also it is supported by all operating systems. The scenario Ior WIN proxy
is shown below:
Fig 13: scenario of win proxy server
In win proxy as shown in the scenario above we can share internet. First oI all a ADSL
modem is connected to the ISP (Internet Service Provider) by a RJ-11 connector and
other end oI ADSL modem is connected to the PC1 through RJ-45. Assign IP address
192.168.1.1 to the ADSL modem also enable the DHCP server and set the start IP
address oI 192.168.1.2 and end IP address oI 192.168.1.254. Then aIter ADSL modem
connect PC1, assign GW 192.168.1.1 and
3.8.4 NAT (Network Address Translation)
II we have to connect many computers with a single IP address then we will use NAT.
NAT exchange IP packet between local network and internet. The routing and remote
access server oI window 2K3 server provide us with a component known as NAT. By
enabling NAT on a Server 2003 system, you allow connected users on a private system to
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
share a single connection to access a public network such as the internet i.e. NAT enable
multiple client computer to connect the internet through a single publicly registered IP
address. A NAT server translate private IP address to public addresses. NAT eliminates
the need Ior large number oI IP addresses by mapping externally assigned IP addresses.
Fig 14: NAT server
When deploying NAT, it is needed to conIigure setting on both the client side
and the server side. On the server side oI NAT Iill the IP address statically.
3.8.4.1 Steps to enable NAT server
Open internet Tools Internet options
connections LAN settings
untick the IP and port address
ok ok give site name
. On the client side oI NAT, client side is conIigured to obtain IP addresses
automatically and then restart the client system. Assuming NAT is used Ior address
assignment, the client system will receive TCP/IP inIormation Irom the NAT server. The
client inIormation includes:
IP address Irom 192.168.0.0 private addressing range
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
DNS server address, which would be the address oI the NAT interIace
on the server.
With the client side conIigured, there are Iew things to do on NAT server:
The Iirst step to conIigure NAT server is to actually install the Routing and Remote
Access Services. To do this, start the Routing and Remote Access Service Setup Wizard.
Start administrator tools Routing & Remote Access
Right click on My Computer right click on computer name
Select option Configure and enable routing & remote access
Welcome to routing next next
Select NAT next
Select LAN card which is to be connected to internet
next next
From any oI the Iour methods oI internet sharing only method is used at a
time to remove the other method
go to start setting
add & remove
change/ remove, tick on remove.
3.9 VIRTUAL PRIVATE NETWORK (VPN)
A virtual private network is used to convert public network address to private
network. All the clients oI VPN dial to public IP address oI VPN server and receive
private IP Irom virtual VPN dynamic host protocol (DHCP).in VPN one can have
multiple virtual connections to a single IP address. This way ,one network card can host
several inbound connections, rather than require a modem and telephone line Ior each
simultaneous remote user.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 15 : scenario of VPN server
Using VPN server we can connect many private networks to internet services i.e the
remote connection. We can create a private network through public network, we can use
Iirewall Ior security and data encryption in VPN server.
3.9.1 VPN components
(i) VPN server
(ii) VPN Clients
(iii) WAN Option
(iv) Security Options
VPN Server
VPN server, serve as the end points oI a VPN connection. When conIiguring a
VPN server, you can allow access to just that server, or pass traIIic through VPN server
so that the remote user gain access the resources oI the entire network.
VPN Client
VPN clients establish connection to VPN server. They can also be routers that
obtain the router-to-router secure connection. VPN client soItware is included in all the
modern window operating systems, including Window 2003 server. Router-to router
VPN connection can be made Irom computers running server2003 and Windows 2000
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
running Routing and Remote Access. Additionally, any client that support PPTP or
L2TP connections can be VPN clients oI a window server 2003 system.
WAN Options
These provide the physical mechanism Ior passing data back and Iorth. These
connections typically include such similar network technologies such as T1or Irame
relay. In order Ior VPN connections to be successIul, the VPN client and VPN server
must be connected to each other using either permanent WAN connection or by dialing
into an internet server provider (ISP).
Security Options
Since a VPN uses a network that is generally open to the public, it is important
that the data passed over the connection remain secure. To aid with secure
communication routing and remote access supports such security measure as logon and
domain security, data encryption, smart cards, IP packet Iiltering and caller ID.
3.9.2 Types of VPN
(i) PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol )
(ii) L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) according to CCNA.
Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is MicrosoIt`s legacy protocol Ior supporting VPN. It was developed in
conjunction with other communications companies such as Robotics as an extension to
the PPP protocol. PPTP encapsulates IP or IPX packets inside oI PPP datagram`s. This
means that you can remotely run programs that are dependent upon particular network
protocols. One oI the keys to remember about PPTP is that the protocol provides
encryption capabilities, making it much saIer to send inIormation over nonsecure
networks.
Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
L2TP is a standard based encapsulation protocol with roughly the same
Iunctionality as a Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). One oI the key diIIerences
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
between Window`s server 2003 implementation oI L2TPand it cousin PPTP is that
L2TPis designed to run natively over IP networks only. This implementation oI L2TP
does not support native tunneling over X.25, Irame relay, or ATM networks. Like PPTP,
L2TPencapsulates Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) Irames, which then encapsulate IP or
IPX protocols, allowing users to remotely run programs that are dependent on speciIic
network protocols . But unlike the PPTP protocol, L2TP does not provide encryption oI
the data. For data security L2TPrelies on the services oI another standards- based
protocol, IPSec.
3.9.3 How to configure VPN
startadministrative tools
Routing and Remote access
Right click on computer name configure and enable Routing and Remote
access
next select remote access (dial up or VPN)
next VPN next
select LAN card which is connected to internet (172.15.15.50) public IP
disable enable security next
Irom a speciIic range oI address nextnew
enter the required range
oknext no radius
next finish
3.9.4 Create users in VPN server
open user properties dial in allow access
apply ok
3.9.5 Working on Client Side
Right click on My Network Places properties
Double click on New Network Wizard next
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Connect to network at my work place next
Virtual private network connection next
Enter company name (abc) next
Enter public IP address oI VPN server next
Any one use next
finish
3.10 ROUTING
It is a process oI transIerring inIormation through an inter network i.e Irom one
network to another. Routing connect diIIerent networks having ID help in process oI
routing. The dial-in properties also allow Ior speciIic IP address to be assigned to a user.
This is the only way in Window Server 2003 that you can assign a speciIic IP to a user.
To assign a speciIic IP to a user, check the box next to assign A Static IP Address and
enter a valid IP in the space provided. Static routing can also be speciIied as per user. By
deIining static routes, users can be limited to only speciIic parts oI networks.
In an internetwork a router must then about all the networks present in the Ior
eIIort websites, there are hardware routers like CISCO. Even win 2003 server computer
conIigured as router. In simple words Router is a computer with two network cards.
These two network cards, then, are attached to two diIIerent logical IP networks. The
routing table helps direct traIIic that is passed through the router.
Now when there is a router, also there is a routing table, there is a need to
conIigure the router in order Ior that router to pass along traIIic to the proper network.
There are two ways the routing table can be built and modiIied: either manually or
automatically.
3.10.1 Types of Routing
(i) Static Routing
(ii) Dynamic Routing
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.10.1.1 Static Routing
In this routing inIormation required Ior routing is manually entered into the router
by administrator.
How to configure LAN routing
Enter the static IP in the router
Administrator tools
Routing and Remote access
Right click on computer name (pcc1)
Configure and enable routing and remote access
next custom configuration
select LAN routingnext finish
yes and logon to see IP table route
Enable LAN routing enable LAN routing
InterIace WAN InterIace WAN 10.0.0.0
IP 172.15.0.0 IP 10.0.0.0
SNM 255.255.0.0 SNM 255.0.0.0
GW 20.0.0.2 GW 20.0.0.1
Fig 16 : scenario for LAN routing
How to configure static routing
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
At Router R1:
enable LAN routing
right click on static route
interface WAN
destination 172.15.0.0
mask 255.255.0.0
GW 20.0.0.2
At Router R2:
Enable LAN routing
Right click on static route
Interface WAN
Destination 10.0.0.0
Mask 255.0.0.0
GW 20.0.0.1
Fig 17 : static routing
3.10.1.2 Dynamic Routing
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
The other way to manage a router routing tables is to let the computer do it
Ior you. Just like DHCP allocate IP addresses, conIiguring the dynamic routing
protocol usually means less errors due to human error, and less administrative
overhead.
In dynamic routing, routing inIormation is automatically entered in the
router using protocols like RIP AND OSPF. These routing protocols used by
Window Server 2003 use one oI two kinds oI algorithms to determine the best
possible path Ior a packet to get to its destination, either distance vector or link
state. RIP is used Ior small networks where as OSPF is used Ior large networks.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
The distance vector protocol in use on Window 2003 is called Routing
InIormation Protocol (RIP) Ior IP. This protocol was designed Ior the exchange oI
the routing inIormation within a small to medium size IP network.
When Router is enabled on Window 2003 machine, the routing table includes
entries only Ior the networks that are physically connected. When RIP is enabled
Ior an interIace, the router will periodically send an announcement oI its routing
table to inIorm other RIP routers oI the networks it can reach. RIP version1 uses
broadcast packets Ior its announcement. RIP version2 oIIers an improvement and
can be conIigured to use either multicast or broadcast packets when
communicating with other routers. Also, RIP version2 oIIers more Ilexibility in
subnetted and classless inter domain routing (CIDR) environments.
The biggest advantage oI RIPis its simplicity. With a Iew clicks in the Routing
and Remote Access Server and MMC console, you can deploy RIP. With the RIP
dynamic routing protocol installed on Window`s Server 2003, you get the
Iollowing Ieatures:
(i) RIP version1 and version2, with the ability to conIigure individual
network cards with separate versions.
(ii) Calculations used to avoid routing loops and speed recovery oI the
network whenever topology changes occur.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(iii) Route Iilters; you can conIigure RIP to except inIormation Irom
only certain networks, and also choose which routes will be shared
with RIP routers.
(iv) Peer Iilters, which allow control over which router announcements
are accepted.
(v) Simple password authentication support.
But there are signiIicant drawbacks, which makes RIP a poor, iI not unusable
solution Ior large networks. For example, the maximum hop count used Ior RIP routers
is15, making network 16 hops away (or more) unreachable where RIP is concerned.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
Where RIP is built to work to work in smaller networks, the Open Shortest Path
First (OSPF) routing protocol is designed Ior large or very large networks. The goal is the
same: inIormation about connection to other networks is shared Irom one router to
another. It oIIers several advantages over RIP, especially signiIicant in large networks:
(i) Routes calculated with OSPF are always loop Iree.
(ii) OSPF can scale much more easily than RIP.
(iii) ReconIiguration Ior network topology changes is Iaster.
The biggest reason OSPF is the choice in large networks is its eIIiciency; instead
oI changing routing table via broadcast the way RIP does, OSPF conIigured routers
maintain a map oI the network. The mapping is called the link state database, OSPF
routers keep the link state database up to date. Once changes have been made to link state
database, an OSPF router`s link state database is recalculated.
As the networks start to multiply, the size oI the link state database increases, and
a corresponding hit on router perIormance results. To combat this, OSPF sub divide the
network into smaller sections, called areas. Areas are connected to each other through a
backbone area, with each router only responsible Ior the link state database Ior those
areas connected to the routers. Area Border Routers (ABRs) then connect one backbone
area to another.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
The biggest drawback oI OSPF is its complexity; OSPF requires proper planning
and is more diIIicult to conIigure and administer.
3.11 EXCHANGE SERVER
Exchange server is a mail server, we can send and receive mail Irom one user to another
user. Exchange server is the mail server oI MicrosoIt.
3.11.1 Elements of Exchange Server
Mail Server
A server which helps to the users to send and receive mail is called mail server.
Mail Box
A storage place where senders and receivers mails are stored.
3.11.2 Exchange Version
Table 10: Exchange Server with diIIerent operating systems
Exchange Version Operating System
Exchange Server 5.5
Exchange Server 2000
Exchange Server 2003
Exchange server 2007
WIN NT or 2000 server (without SP).
WIN NT or 2000 server (SP3,SP4)
without (SP).
WIN 2000 Server or WIN2003 server
(SP4) without SP.
WIN2003 server or R2/WIN 2008
server with SP1.
Where SP stands Ior Service Pack. Service Pack are the services which are loaded
externally to remove some bugs that come during installation oI server CD.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.11.3 Requirements for Exchange Server
Protocols Required
POP3 (Post Office Protocol)
This protocol is used Ior receiving e- mails.
IMAE4 (Internet Messaging Access Protocol)
This protocol is advance version oI POP, this is also used to receive mail.
LMTP (Local Mail Transfer Protocol)/SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
This protocol is used to send mails.
NNTP (Network News Transfer protocol)
This protocol is used Ior transIerring messages on internet.
Hardware Requirements
Processor: min. 133MHz Rec. 733MHz
RAM: min. 256MB Rec. 512MB
Other Requirements
OS: 2k or 2k3 Server
NTFS partition
Static IP address
Active Directory
DNS installation with AD zone
IIS installed with ASP.net, SMTP, NNTP and www service
3.12 Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model
OSI model is the layer approach to design, develop and implement network. OSI
provides Iollowing advantages: -
(i) Development oI new technology will be Iaster.
(ii) Devices Irom multiple vendors can communicate with each other.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(iii) Implementation and troubleshooting oI network will be easy.
3.12.1 Description of Different Layers
Application Layer
Application layer accepts data and Iorward into the protocol stack. It creates user
interIace between application soItware and protocol stack.
Presentation Layer
This layer decides presentation Iormat oI the data. It also able to perIorms other
Iunction like compression/decompression and encryption/decryption.
Session Layer
This layer initiate, maintain and terminate sessions between diIIerent applications.
Due to this layer multiple application soItware can be executed at the same time.
Transport Layer
Transport layer is responsible Ior connection oriented and connection less
communication. Transport layer also perIorms other Iunctions like
(i) Error checking
(ii) Flow Control
BuIIering
Windowing
Multiplexing
(iii) Sequencing
(iv) Positive Acknowledgement
(v) Response
(vi)
Network Layer
This layer perIorms Iunction like logical addressing and path
determination. Each networking device has a physical address that is MAC
address. But logical addressing is easier to communicate on large size network.
Logical addressing deIines network address and host address. This type oI
addressing is used to simpliIy implementation oI large network. Some
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
examples oI logical addressing are: - IP addresses, IPX addresses etc.
Network layer has diIIerent routing protocols like RIP, EIGRP, BGP, and
ARP etc. to perIorm the path determination Ior diIIerent routing protocol.
Network layer also perIorm other responsibilities like deIining quality oI service,
Iragmentation and protocol identiIication.
Data Link Layer
The Iunctions oI Data Link layer are divided into two sub layers
Logical Link Control
Media Access Control
(i) Logical Link Control deIines the encapsulation that will be used by the
NIC to delivered data to destination. Some examples oI Logical Link
Control are ARPA (Ethernet), 802.11 wi-Ii.
(ii) Media Access Control deIines methods to access the shared media and
establish the identity with the help oI MAC address. Some examples oI
Media Access Control are CSMA/CD, Token Passing.
Physical Layer
Physical Layer is responsible to communicate bits over the media this
layer deals with the standard deIined Ior media and signals. This layer may also perIorm
modulation and demodulation as required.
3.13 ROUTERS
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
13.13.1 Router Architecture and its Key Component
Incomplete
IOS
IOS
Startup ConIiguration
Fig 18 : Architecture of router
Processor
Speed: - 20 MHz to 1GHz
Architecture: - RISC
Reduce Instruction set computer
ManuIacturers: - Motorola, IBM, Power PC, Texas, Orion, Intel.
Flash RAM
Flash memory is just like a hard copy oI the computer. Flash RAM is the
permanent read/write memory. This memory is used to store one or more copies
oI router O/S. Router O/S is also called IOS (Internetwork Operating System).The
size oI Flash RAM in the router is 4MB to 256MB. This memory is Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM).
NVRAM
NVRAM is a 'Non Volatile Random Access Memory. It is used to store
the startup conIiguration oI the Router. It is on chip RAM, its size is 32kb.
Processor
Memory
Controller
BIOS
ROM
NVRAM
RAM
Flash
RAM
O/S
I/O
Controller
LAN
WAN
Ports
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is a volatile memory. All the activities we do are stored in RAM,this means that
it holds the running conIiguration. RAM oI the router is divided into two logical
parts.
Primary RAM
Shared RAM
Primary RAM
Primary RAM is used Ior: -
(i) Running copy oI IOS.
(ii) Running conIiguration
(iii) Routing table
(iv) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table (IP address to MAC
address)
(v) Processor & other data structure
Shared RAM
Shared RAM is used as a buIIer memory to shared the data received Irom
diIIerent interIaces. Size oI RAM in a router may vary Irom 2 MB to 512 MB.
The types oI memory that may be present in a RAM are:
(i) DRAM -~ Dynamic RAM
(ii) EDORAM -~ Extended Data Out RAM
(iii) SDRAM -~ Synchronous Dynamic RAM
ROM (Random Access Memory)
It has Iour components:
POST (Power on SelI Test)
It perIorms hardware testing.
BOOT Strap
Boot strap speciIies Irom where and which inter operating system is to be
loaded.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Mini IOS
Cisco 2500, 1600
ROM MOW
333333 Router Inter!ces " #orts
InterIace is used to connect LAN networks or wan networks to the router.
InterIace will use protocol stacks to send/receive data. Ports are used Ior the
conIiguration oI routers. Ports are not used to connect diIIerent networks. The primary
purpose oI port is the management oI router.
33333333 Router Interface
Table 11: Router interfaces and connectors
AUI Attachment Unit InterIace
EPABX Electronic Private Automatic Branch
PSTN Public Services Telephone Network
3.13.2.2 Router Ports
Table 12: Router Ports
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
333333 Modes o Router
When we access router command prompt the router will display diIIerent modes.
According to the modes, privileges and rights are assigned to the user.
User mode
Router>
In this mode, we can display basic parameter and status oI the router we can test
connectivity and perIorm telnet to other devices. In this mode we are not able to change
and save router conIiguration.
Privileged mode
Router#
In this mode, we can display all inIormation, conIiguration, perIorm administration task,
debugging, testing and connectivity with other devices. We are not able to perIorm here
conIiguration editing oI the router.
The command to enter in this mode is enable`. We have to enter enable
password or enable secret password to enter in this mode. Enable secret has more priority
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
than enable password. II both passwords are conIigured then only enable secret will
work.
Global configuration
Route(config)#
This mode is used Ior the conIiguration oI global parameters in the router. Global
parameters applied to the entire router. All the changes are perIormed in this mode. But
here we cannot see and save the changes.
For e.g: - router hostname or access list oI router, password, Banner, Routing, Security.
The command to enter in this mode is conIigure terminal`
Line configuration mode
In this mode we can set the password oI the user mode, i.e to set user mode
password .This mode is used to conIigure lines like console, vty and auxiliary. There are
main types oI line that are conIigured.
(i) Console
Router(config)#line console 0
(ii) Auxiliary
Router(config)#line aux 0
(iii) Telnet or vty
Router(config)#line vty 0 4
Interface configuration mode
In this mode we can set ip addresses oI the interIaces. This mode is used to
conIigure router interIaces. For e.g:- Ethernet, Serial, BRI etc.
Router(config)#interIace type~ number~
Router(config)#interIace serial 1
Routing configuration mode
This mode is used to conIigure routing protocol like RIP, EIGRP, OSPF etc.
Router(config)#router protocol~ |option~|
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config)#router eigrp 10
333333 Coni$urin$ #!ss%ord
There are Iive types oI password available in a router
Console Password
router#conIigure terminal
router(conIig)#line console 0
router(conIig-line)#password word~
router(conIig-line)#login
router(conIig-line)#exit
To erase password do all steps with no command.
Vty Password
router~enable
router#conIigure terminal
router(conIig)#line vty 0 4
router(conIig-line)#password word~
router(conIig-line)#login
router(conIig-line)#exit
Auxiliary Password
router#conIigure terminal
router(conIig)#line Aux 0
router(conIig-line)#password word~
router(conIig-line)#login
router(conIig-line)#exit
Enable Password
router~enable
router#conIigure terminal
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
router(conIig)#enable password word~
router(conIig)#exit
Enable Secret Password
Enable Password is the clear text password. It is stored as clear text in
conIiguration where as enable secret password is the encrypted password.
Router~enable
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#enable secret word~
Router(conIig)#exit
Encryption all passwords
All passwords other than enable secret password are clear text password. The
command to encrypt all password are
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#service password-encryption
3.13.& M!n!$in$ Coni$ur!tion
There are two types oI conIiguration present in a router
(i) Startup ConIiguration
(ii) Running ConIiguration
Startup conIiguration is stored in the NVRAM. Startup conIiguration is used to
save settings in a router. Startup conIiguration is loaded at the time oI booting in to the
Primary RAM.
Running ConIiguration is present in the Primary RAM wherever we run a
command Ior conIiguration, this command is written in the running conIiguration.
To save configuration
Router#copy running-conIiguration startup-conIiguration
Or
Router#write
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
To abort configuration
Router#copy startup-conIiguration running-conIiguration
To display running-configuration
Router#show running-conIiguration
To display startup configuration
Router#show startup-conIiguration
Coni$urin$ 'ost N!me
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#hostname name~
name~#exit or end or /\z
Router#conIig terminal
Router(conIig)#hostname r1
R1(conIig)#
Coni$ur!tion Inter!ces
InterIaces conIiguration is one oI the most important part oI the router
conIiguration. By deIault, all interIaces oI Cisco router are in disabled mode. We have to
use diIIerent commands as our requirement to enable and conIigure the interIace.
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace type~ no~
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address ip~ mask~
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router(conIig-iI)#exit
To display interface status
Router#show interIaces (to show all interIaces)
Router#show interIace type~ no~
This command will display Iollowing parameters about an interIace
(1) Status
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
(2) Mac address
(3) IP address
(4) Subnet mask
(5) Hardware type / manuIacturer
(6) Bandwidth
(7) Reliability
(8) Delay
(9) Load ( Tx load Rx load)
(10) Encapsulation
(11) ARP type (iI applicable)
(12) Keep alive
Configuring optional parameter on WAN interface
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIac type~ no~
Router(conIig-iI)#encapsulation protocol~
Router(conIig-iI)#clock rate value~
Router(conIig-iI)#end
Command displaying history of Router
To display commands present in history
Router#show history
To display history size
Router#show terminal
To change history size
Router#conIig terminal
Router(conIig)#line console 0
Router(conIig-iI)#history size value(0-256)~
Router(conIig-iI)#exit
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Coni$urin$ (!nners
Banners are just a message that can appear at diIIerent prompts according to the type.
DiIIerent banners are: -
Message oI the day (motd)
This banner appear at every access method
Login
Appear beIore login prompt
Exec
Appear aIter we enter to the execution mode
Incoming
Appear Ior incoming connections
Syntax:-
Router#conIig terminal
Router(conIig)#banner type~ delimation char~Text Massage
delimation char~
Router(conIig)#
Example
Router#conIig terminal
Router(conIig)#banner motd $ This router is distribution 3600 router
connected to Reliance $
Router(conIig)#
To set time in router
We can conIigure router clock with the help oI two methods:
(i) ConIigure clock locally
(ii) ConIigure clock on NTP server (Network Time Protocol)
Router does not have battery to save the clock setting. So that clock will reset to the
deIault on reboot.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
To display clock
Router#show clock
To configure clock
Router#clock set hh:mm:ss day month year
Router#clock set 7:15:10 9 June 2009
To configure clock from NTP server
Router#conIig terminal
Router(conIig)#ntp server IP address~
Router(conIig)#exit
C:\~ping pool.ntp.org
To get ntp server ip Irom internet
C:\~route print
3.14 SUBNETTING
Subnetting is a process or a technique to divide large and complex networks into
smaller parts or smaller networks and each network is called as subnet. Subnetting is
done to reduce the wastage oI IP addresses ie instead oI having a single huge network Ior
an organization smaller networks are created within a given huge network. Subnetting
allows the user to create multiple logical networks within a single Class A, B or C based
networks.
In subnetting, the IPv4 address is broken into two parts; network id and host id.
This process borrows bits Irom the host id Iield. In this process, the network size does not
shrink but the size oI hosts per network shrinks in order to include sub-networks within
the network.
333333 Advantages of subnetting
Size oI the physical networks is reduced and hence easy to manage.
Reduce network traIIic.
Easy to troubleshoot.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Reduce the wastage oI IP address.
Subnet Mask
A subnet mask speciIies the part oI IP address that is to be used Ior identiIying a
sub network. A subnet mask when logically ANDed with IPaddress provides a 32- bit
network address. This binary address gives the Iirst address in the subnet block speciIied
in the large network.
Default Mask
ClassIull addresses consists oI three classes; Class A, Class B, Class C used Ior
subnet.Each class has a deIault subnet mask C lass A consists oI eight 1s in the network
address Iield and 24 0s in remaining Iield, Class B consists oI 16 1s in network address
Iield and 16 0s in remaining Iield, and Class C cointains 24 1s in the network address
Iield and remaining 8 bytes as 0s. the deIault address mask in binary and dotted-decimal
is shown in the table
To Calculate the Subnet Mask
1. IdentiIy the class oI address assigned. For this example the class oI IP address
is Class B.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
2. check the deIault address mask Ior the appropriate class and convert it to
binary Iormat .Ior this example the deIault address mask is 255.255.0.0 and
the equivalent binary Iormat is; 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
3. check the no. oI 1s in the deIault mask. E.g this address contains 16 1s in class
B, 16 bits 2 octat are Ior net id and the last 16 bits 2 octates are Ior host id.
4. now iI we need 9 subnets. This no. 9 is not a power oI 2. the next no. that is
power oI 2 and greater than 2 is 16. So, we require 4 extra 4 extra 1s in the
network Iield which has to be borrowed Irom the host id Iield.
5. the total no. oI 1s is 16420, as 16 1s are Irom network id and 4 1s are oI
additional bits required Ior subnetwork. The no. oI 0s in the n/w is 32-2012.
which deIines whole address.
6. hence address is given as 11111111.11111111.11110000.00000000 and in
decimal Iormat can be given as 255.255.240.0
Table 14: decimal and binary values of subnet mask
Decimal
Binary
0
128
192
224
240
248
252
254
255
00000000
10000000
11000000
11100000
11110000
11111000
11111100
11111110
11111111
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
333333 Types of Subnetting
Fixed Length Subnet Mask (FLSM)
Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM)
Steps of Subnetting for FLSM
For IP address 192.168.10.0 (Class C)
Step 1:
IdentiIy the total no. oI subnets 2`n no.oI subnets
Where n are the no.s and borrowed bytes Irom host ID portion. Let we are given
that we have to make 4 subnets. ThereIore 2`n 4 i.e n2
Step 2:
To idettiIy the total no. oI the valid hosts Ior each subnet.
2`m-2 no.oI valid hosts. Where m are the remaining no. oI bits in host ID 2`6-
262
Step 3:
Calculate the subnet mask and range
Subnet mask Ior n/w 192.168.10.0/26 is
11111111.11111111.11111111.1100000000 ie 255.255.255.192
range~ 256-19264
step 4:
IdentiIy the total no oI subnets, no. oI valid hosts and the broadcast address.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Table 15: showing subnet mask, valid hosts, broadcast address
Subnetwork Valid Host Broadcast Address
192.168.10.0
192.168.10.64
192.168.10.12
8
192.168.10.19
2
192.168.10.1 to
192.168.10.63
192.168.10.65 to
192.168.10.126
192.168.10.129 to
192.168.10.190
192.168.10.193 to
192.168.10.254
192.168.10.63
192.168.10.127
192.168.10.191
192.168.10.255
VLSM
In VLSM to allocate IP addresses to subnets depending upon the no. oI hosts. The
network having more no oI hosts is given priority and the one having least no oI host
comes at last and Ior each network the subnet is assigned separately. As in the scenario
given:
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
)i$ 1*+ ,!ri!-le su-net m!s.
3.15 TELNET
Telnet stands Ior terminal network, telephone network, terminal encapsulation on
the network. Purpose oI Telnet is to access the remote device in order to conIigure it. It
provides textual access oI the remote device. It uses the services oI TCP. Telnet service is
used where small bandwidth is low. It provides textual access oI the remote device. Port
number oI Telnet is 23.
3.15.1 To Access the Device Remotely
For this purpose we have to assign the IP addresses to the PCs and the interIaces.
For Telnet the Routers are to be conIigured with RIP version1 , so that the device can
ping each other. Also DCE cable is used to connect the Routers. The serial link should
have the speed oI 64K also apply vty password and enable secret password. Set up the
Routers so that they can manage via Telnet.
First oI all select the PCs and the routers connect the ports to the router, double
click on router, switch oII the router iI it is on. Then select the serial port according to the
routers, switch on the router. Select the cable to connect the Routers. Router to Router
connections are made by the serial cable, so go on Iirst Router select the serial port as
s0/1/0 in the scenario, then go to the other Router and connect the serial cable at interIace
s1/0. Accordingly connect the third Router with interIaces s1/1 and s1/2.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Now connect the PCs to the routers, to do this Iirst select the console cable, click on the
PC select RS232 option, then connect it on the Router and select console cable. Now
select cross- over cable on the PC select Fast Ethernet option and on the Router select
I0/0 option now as the PCs and Routers are connected to each other assign IP addresses
to the PCs and the Routers. According to the Iig set the IP addresses oI the PCs double
click on the PC choose the option oI desktop IP conIiguration. Now set the IP
address, subnet mask, and the deIault gateway. Like wise set the IP address oI all the
PCs. Now set the IP address oI the interIaces oI router.
3.15.2 Commands to assign IP addresses to the interfaces:
At Router1:
Router~
Router~enable
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace I0/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Fig 20: scenario of Telnet
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Router#
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace s0/1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 40.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router(conIig)#interIace s0/1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#clock rate 64000
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Now to check the assigned IPaddresses to the interIaces the command used is
Router#show ip interIace brieI
At router 2:
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace I0/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router#
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 40.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/1
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 50.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/1
Router(conIig-iI)#clock rate 64000
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
At router 3:
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace I0/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 30.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
Router#
Router#conIigure terminal
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#ip address 50.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
Router(conIig-iI)#no shutdown
To Telnet a device from Router
At all the Routers use these commands
Router(conIig)#line vty 0 4
Router(conIig-line)#password cobra
Router(conIig-line)#login
Router(conIig)#enable password cobra
Router(conIig)#enable secret cobra1
To telnet a device from router
Router#telnet IP~
Or
Router~telnet IP~
To exit from telnet session
Router#exit
To exit from a hanged telnet session
CtrlshIt6
Or
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Router#disconnect
To display connected session
Router#show sessions
This command shows those sessions, which are created or connected by us.
II we want anyone can telnet our router without password then on the line vty type
command 'No Login.
3.16 ROUTING
Routing is a process or technique to identiIy the path Irom one network to
another. Routers don`t really care about hoststhey only care about networks and the
best path to each network.
To route the packet the router must know the Iollowing things:
Destination network
Neighbour device Irom witch it can learn about remote Networking.
Possible number oI routers to reach the destination.
Best route to reach the destination.
How to maintain & veriIy the routing inIormation.
3.16.1 TYPES OF ROUTING
Static routing.
DeIault routing.
Dynamic routing.
3.16.1.1 STATIC ROUTING
In static routing an administrator speciIies all the routes to reach the destination.
Static routing occurs when you manually add routes in each router`s routing table.By deIault,
Static routes have an Administrative Distance (AD) oI 1
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Features
There is no overhead on the router CPU.
There is no bandwidth usage between routers.
It adds security, because the administrator can choose to allow routing access to certain
networks only.
Advantages of static routing
(1) Fast and eIIicient.
(2) More control over selected path.
(3) Less overhead Ior router.
(4) Bandwidth oI interIaces is not consumed in routing updates.
Dis!d,!nt!$es o st!tic routin$
(1) More overheads on administrator.
(2) Load balancing is not easily possible.
(3) In case oI topology change routing table has to be change manually.
Syntax for Static Routing
Router (conIig)# ip route destination N/w~ Subnet mask~ Next
Hope- address or exit interIace~ |administrative distance~Permanent|.
To c/ec. t/e routin$ t!-le o router
Router # show ip route
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 21: scenario of static routing
Static routing oI router (R1)
Router(conIig)#ip route 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.2
Router(conIig)#ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.2
Router(conIig)#ip route 50.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.2
Router(conIig)#interIace so/1/0
Router(conIig)# clock rate 64000
Router # show ip route
Static routing oI router (R2)
Router(conIig)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 40.0.0.1
Router(conIig)#ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.2
Router#show ip route
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/0
Router(conIig)# clock rate 64000
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/1
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Router(conIig)#clock rate 64000
Router#show ip route
Static routing oI router (R3)
Router(conIig)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.1
Router(conIig)#ip route 20.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.1
Router(conIig)#ip route 40.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 50.0.0.1
Router(conIig)#interIace s1/0
Router(conIig)# clock rate 64000
Router#show ip route
3.16.1.2 DEFAULT ROUTING
DeIault routing is used to send packets with a remote destination network
not in the routing table to the next-hop route.
DeIault routing is also a type oI static routing which reduces the routing
overhead & deIault routing is also used with stub networks. Stub networks are those
having a single exit interIace. DeIault routing is also used Ior unknown destination.
A special address is used to perIorm the deIault routing ie 0.0.0.0
The scenario Ior deIault routing is same and but the commands used at the routers
having single exit interIace like R1 and R3 have diIIerent commands.
At Router (R1)
Router(conIig)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 40.0.0.2
Router#show ip route
At Router (R3)
Router(conIig)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 50.0.0.1
Router#show ip route
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.16.1.3 DYNAMIC ROUTING
Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to Iind networks and update
routing table on routers.
A routing protocol deIines the set oI rules used by router when it communicates
routing inIormation between neighbor routers. In dynamic routing, we will enable a
routing protocol on router. This protocol will send its routing inIormation to the neighbor
router. The neighbors will analyze the inIormation and write new routes to the routing
table.
The routers will pass routing inIormation receive Irom one router to other
router also. II there are more than one path available then routes are compared and best
path is selected. Some examples oI dynamic protocol are: -
RIP, IGRP, EIGRP, OSPF
There are two type oI routing protocols used in internetwors:
Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs)
IGPs are used to exchange routing inIormation with routers in the same
Autonomous System(AS) number. Routing which is perIormed within a single
autonomous system is known as interior routing. The protocol that are used to perIorm
this type oI routing are known as IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol).
These protocols are:-
(i) RIPv1 (Routing InIormation Protocol Version 1)
(ii) RIPv2 (Routing InIormation Protocol Version 2)
(iii) EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
(iv) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
(v) IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System)
Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs)
EGPs are used to communicate between diIIerent Autonomous System.
Protocol that used to do this type oI routing are called exterior gateway protocols.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Autonomous System:- An autonomous system is a collection oI networks under a
common administrative domain, which basically means that all routers sharing the same
routing table inIormation are in the same AS.
3.16.2 Routing Protocol Basics
(i) Administrative Distances
(ii) Routing protocol
(iii) Routing Loops
Administrative Distances
The Administrative Distance (AD) is used to rate the trustworthiness oI routing
inIormation received on a router Irom a neighbor router. An Administrative Distance is
an integer Irom 0 to 255, where 0 is the most trusted and 255 means no traIIic will be
passed via this route.
II a router receives two updates listing he sane remote network, the Iirst thing the router
checks is the AD. II one oI the advertised routes has lower AD than the other, then the
route with the lowest AD will be placed in the routing table.II both advertised routes to
the same network have the same AD, then routing protocol metrics (such as hop count or
bandwidth oI the lines) will be used to Iind the best path to the remote network. The
advertised route with the lowest metric will be placed in the routing table.
But iI both advertised routes have the same AD as well as the same metrics, then the
routing protocol will load-balance in the remote network.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.16.2.1 Classes of Routing Protocols
There are three classes oI Routing Protocol
(i) Distance vector protocol
(ii) Link state protocol
(iii) Hybrid protocol.
Distance vector protocol
The Distance-vector protocols Iind the best path to remote network by
judging distance. Each time a packet goes through a router, that`s called a hop. The route
with the least number oI hops to the network is determined to be the best route. The
vector indicates the direction to the remote network. They send the entire routing table to
directly connected neighbors.
Ex: RIP, IGRP.
The distance-vector routing algorithm passes complete routing table contents to
neighboring routers.
A router receiving an update Irom a neighbor router believes the inIormation
about remote networks without actually Iinding out Ior itselI.
It`s possible to have network that has multiple links to the same remote network,
and iI that`s the case, the administrative distance is checked Iirst. II the AD is the
Route Source Default AD
Connected interIace 0
Static Route 1
EIGRP 90
IGRP 100
OSPF 110
RIP 120
External EIGRP 170
Unknown 255 This route will never be used
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
same, the protocol will have to use other metrics to determine the best path to use
to that remote network.
Fig 16: Routing table
Converged Network
Fig 23 : Routing table of covered networks
Routing Loops
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Distance-vector routing protocols keep track oI any changes to the internet work
by broadcasting periodic routing updates out all active interIaces. This broadcast includes
the complete routing table.
Routing loops can occur because a every router isn`t updated simultaneously.
Routing Loops Example
Router 0
Router (
Router D
Router C Router 1
Net%or. 3 Net%or. 2 Net%or. &
Fig 24: Routing loops
The interIace to Network 5 Iails. All routers know about Network 5 Irom Router
E. Router A, in its tables, has a path to Network 5 through Router B.
When Network 5 Iails, Router E tells Router C. This causes Router C to stop
routing to Network 5 through Router E. But Routers A, B, and D don`t know about
Network 5 yet, so they keep sending out update inIormation. Router C will eventually
send out its update and cause B to stop routing to Network 5, but Routers A and D are
still not updated. To them, it appears that Network 5 is still available through Router B
with a metric oI 3.The problem occurs when Router A sends out its regular 30-second
'Hello, I`m still herethese are the links I know about message, which includes the
ability to reach Network 5 and now Routers B and D receive the wonderIul news that
Network 5 can be reached Irom Router A, so Routers B and D then send out the
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
inIormation that Network 5 is available. Any packet destined Ior Network 5 will go to
Router A, to Router B, and then back to Router A. This is a routing loop.
Link state protocol
Also called shortest-path-Iirst protocols, the routers each create three
separate tables. One keeps track oI directly attached neighbors, one determines the
topology oI the entire internet work, and one is used as the routing tables. Link state
routers know more about the internet work than any distance-vector routing protocol.
Link state protocols send updates containing the state oI their own links to all other
routers on the network
Ex: OSPF
Hybrid protocol
Hybrid protocol use aspects oI both distance-vector and link state protocol.
Ex: EIGRP
3.16.3 RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Routing InIormation Protocol is a true distance-vector routing protocol. It
is an IGB (Inter Gateway Protocol). It sends the complete routing table out to all active
interIaces every 30 seconds to its immediate neighbour. This is slow convergence means
that one router sends a request to other about its route or network get networks which are
not assigned to it aIter all thee three routers have same networks, this process is repeated
to send and receive request so it is called slow convergence
RIP only uses hop count to determine the best way to remote network, but
it has a maximum allowable hop count oI 0-15 by deIault, meaning that 16 is deemed
unreachable.
RIP version 1 uses only class Iull routing, which means that all devices in
the network must use the same subnet mask.
RIP version 2 provides something called preIix routing, and does send
subnet mask inIormation with the route updates. This is called classless routing.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Hop Count
It is a way oI measurement. Hop count limit is15.This routing supports only 15
routers, iI there is one more router in the network then this routing will Iails.
Default administrative distance (120)
Timers of RIP
(i) Update timers.
(ii) Hold timers.
(iii) Invalid timers.
(iv) Flush out timers.
Route update timer
Router update timer sets the interval 30 seconds between periodic routing
updates, in which the router sends a complete copy oI its routing table out to all
neighbors.
Router invalid timers
A router invalid timer determines the length oI time that must elapse 180 seconds
beIore a router determines that a route has become invalid. It will come to this conclusion
iI it hasn`t heard any updates about a particular route Ior that period. When that happens,
thee router will send out updates to all its neighbors letting them know that the route is
invalid.
Hold-down timer
This sets the amount oI time during which routing inIormation is suppressed.
Routers will enter into the hold-down state when an update packet is received that
indicated the route is unreachable. This continues until entire an update packet is received
with a better metric or until the hold-down timer expires. The deIault is 180 seconds.
Route flush timer
Route Ilush timers` sets the time between a route becoming invalid and its interval
Irom the routing table 240 seconds. BeIore it`s removed Irom the table, the router notiIies
its neighbors oI that route`s impending demise. The value oI the route invalid timer must
be less than that oI the route Ilush timers.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Difference between RIPV1 & RIPV2
Steps to do routing (version 1)
At router 1
Router(conIig)# router rip
Router(conIig-router)#network 10.0.0.0
Router(conIig-router)#network 40.0.0.0
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Router#show ip route
At router 2
Router(conIig)# router rip
Router(conIig-router)#network 20.0.0.0
Router(conIig-router)# network 40.0.0.0
Router(conIig-router)# network 50.0.0.0
Router#show ip route
At router 3
Router(conIig)# router rip
Router(conIig-router)#network 30.0.0.0
Router(conIig-router)# network 50.0.0.0
Router#show ip route
3.16.4 IGRP ( Interior Gateway Protocol)
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) is a Cisco-proprietary distance-vector
routing protocol. To use IGRP, all your routers must be Cisco routers. IGRP has a
maximum hop count oI 255 with a deIault oI 100. IGRP uses bandwidth and delay oI the
line by deIault as a metric Ior determining the best route to an internetwork. Reliability,
load, and maximum transmission unit (MTU) can also be used, although they are not
used by deIault.
Table 18 : Difference between IGRP and RIP
IGRP RIP
Can be used in large internetworks Works best in smaller networks
Uses an autonomous system number Ior
activation
Does not yse aytibiniys system numbers
Gives a Iull route table update every 90
seconds
Gives Iull route table update every 30
seconds
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Has an administrative distance oI 100 Has an administrative distance oI 120
Uses bandwidth and delay oI the line as
metric (lowest composite metric),with a
maximum hop count oI 255
Uses only hop count to determine the best
path to a remote network, with 15 hops
being the maximum
IGRP Timers
To control perIormance, IGRP includes the Iollowing timers with deIault settings:
Update timers
These speciIy how Irequently routing-update messages should be sent. The
deIault is 90 seconds.
Invalid timers
These speciIy how long a router should wait beIore declaring a route invalid iI it
doesn`t receive a speciIic update about it. The deIault is three times the update period.
Hold down timers
These speciIy the hold down period. The deIault is three times the update timer
period plus 10 seconds.
Flush timers
These indicate how much time should pass beIore a route should be Ilushed Irom
the routing table. The deIault is seven times the routing update period. II the update timer
is 90 seconds by deIault, then 7 90 630 seconds elapse beIore a route will be Ilushed
Irom the route table.
At Router 1
R1(conIig)#router igrp 10
R1(conIig-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R1(conIig-router)#network 40.0.0.0
R1#show ip route
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
At Router 2
R2(conIig)#router igrp 10
R2(conIig-router)#network 40.0.0.0
R2(conIig-router)#network 20.0.0.0
R2(conIig-router)#network 50.0.0.0
R2#show ip route
At Router 3
R1(conIig)#router igrp 10
R1(conIig-router)#network 30.0.0.0
R1(conIig-router)#network 50.0.0.0
R1#show ip route
3.16.5 EIGRP(Enhanced Interior Routing Protocol)
Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol
that gives us a real edge over IGRP. Like IGRP, EIGRP uses the concept oI an
autonomous system to describe the set oI contiguous routers that run the same routing
protocol and share routing inIormation. But unlike IGRP, EIGRP includes the subnet
mask in its route updates. The advertisement oI subnet inIormation allows us to use
VLSM and summarization when designing our networks.
EIGRP is sometimes reIerred to as a hybrid routing protocol because it has
characteristics oI both distance-vector and link-state protocols. It sends traditional
distance-vector updates containing inIormation about networks plus the cost oI
reaching them Irom the perspective oI the adverting router. EIGRP has a maximum
hop count oI 255.
Powerful features that make EIGRP a real standout from IGRP
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Support Ior IP, IPX, and AppleTalk via protocol-dependent modules Considered
classless (same as RIPv2 and OSP
Support Ior VLSM/CIDR
Support Ior summaries and discontiguous networks
EIIicient neighbor discovery
Communication via Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP)
Best path selection via DiIIusing Update Algorithm (DUAL)
Cisco calls EIGRP a distance vector routing protocol, or sometimes an
advanced distance vector or even a hybrid routing protocol. EIGRP supports diIIerent
Network layer protocols through the use oI protocol-dependent modules (PDMs). Each
EIGRP PDM will maintain a separate series oI tables containing the routing inIormation
that applies to a speciIic protocol. It means that there will be IP/EIGRP tables,
IPX/EIGRP tables, and AppleTalk/EIGRP tables.
Neighbor Discovery
BeIore EIGRP routers are willing to exchange routes with each other, they must
become neighbors. There are three conditions that must be met Ior neighborship
establishment:
Hello or ACK received
AS numbers match
Identical metrics (K values)
To maintain the neighborship relationship, EIGRP routers must also continue
receiving Hellos Irom their neighbors. EIGRP routers that belong to diIIerent
autonomous systems (ASes) don`t automatically share routing inIormation and they don`t
become neighbors.
The only time EIGRP advertises its entire routing table is when it discovers a new
neighbor and Iorms an adjacency with it through the exchange oI Hello packets. When
this happens, both neighbors advertise their entire routing tables to one another. AIter
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
each has learned its neighbor`s routes, only changes to the routing table are propagated
Irom then on.
EIGRP maintains three tables containing inIormation about the internetworks.
(i) Neighbor Table
Records inIormation about routers with whom neighborship relationships
have been Iormed.
(ii) Topology Table
Stores the route advertisements about every route in the internetwork received
Irom each neighbor.
EIGRP Metrics
Another really sweet thing about EIGRP is that unlike many other protocols that
use a single Iactor to compare routes and select the best possible path, EIGRP can use a
combination oI Iour:
Bandwidth
Delay
Load
Reliability
3.16.6 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is an open standards routing protocol that`s been
implemented by a wide variety oI network vendors, including Cisco. This works by using
the Dijkstra algorithm. First, a shortest path tree is constructed, and then the routing table
is populated with the resulting best paths. OSPF converges quickly, although perhaps not
as quickly as EIGRP, and it supports multiple, equal-cost routes to the same destination.
But unlike EIGRP, it only supports IP routing.
OSPF is an IGP protocol. It is a link state routing protocol. It is supported by
many operating systems. Its deIault AD is 110, hop count limit is unlimited.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
It is classless routing protocol, supports VLSM/CIDR. By deIault the highest IP address
oI interIace will be elected as Router id.
OSPF provides the following features
Consists oI areas and autonomous systems
Minimizes routing update traIIic
Allows scalability
Supports VLSM/CIDR
Has unlimited hop count
Allows multi-vendor deployment (open standard)
OSPF is supposed to be designed in a hierarchical Iashion, which basically means
that you can separate the larger internetwork into smaller internetworks called areas. This
is the best design Ior OSPF.
The reasons Ior creating OSPF in a hierarchical design include:
To decrease routing overhead
To speed up convergence
To conIine network instability to single areas oI the network
Each router in the network connects to the backbone called area 0, or the
backbone area. OSPF must have an area 0, and all routers should connect to this area iI
at all possible. But routers that connect other areas to the backbone within an AS are
called Area Border Routers (ABRs). Still, at least one interIace must be in area 0.
OSPF runs inside an autonomous system, but can also connect multiple
autonomous systems together. The router that connects these ASes together is called an
Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR).
OSPF Terminology
Link
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
A link is a network or router interIace assigned to any given network. When an
interIace is added to the OSPF process, it`s considered by OSPF to be a link.
Router ID
The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identiIy the router. Cisco chooses
the Router ID by using the highest IP address oI all conIigured loopback interIaces. II no
loopback interIaces are conIigured with addresses, OSPF will choose the highest IP
address oI all active physical interIaces.
Neighbors
Neighbors are two or more routers that have an interIace on a common
network,such as two routers connected on a point-to-point serial link.
Adjacency
An adjacency is a relationship between two OSPF routers that permits the direct
exchange oI route updates. OSPF is really picky about sharing routing inIormation
unlike EIGRP, which directly shares routes with all oI its neighbors. Instead, OSPF
directly shares routes only with neighbors that have also established adjacencies. And not
all neighbors will become adjacentthis depends upon both the type oI network and the
conIiguration oI the routers.
OSPF Topologies database
The topology database contains inIormation Irom all oI the Link State
Advertisement packets that have been received Ior an area. The router uses the
inIormation Irom the topology database as input into the Dijkstra algorithm that computes
the shortest path to every network. LSA packets are used to update and maintain the
topology database.
A Link State Advertisement (LSA) is an OSPF data packet containing link-state
and routing inIormation that`s shared among OSPF routers. There are diIIerent types oI
LSA packets. An OSPF router will exchange LSA packets only with routers to which it
has established adjacencies.
A designated router (DR) is elected whenever OSPF routers are connected to the
same multi-access network. A prime example is an Ethernet LAN.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
A backup designated router (BDR) is a hot standby Ior the DR on multi-access
links The BDR receives all routing updates Irom OSPF adjacent routers, but doesn`t
Ilood LSA updates.
OSPF areas
An OSPF area is a grouping oI contiguous networks and routers. All routers in the
same area share a common Area ID.
Broadcast (multi-access)
Broadcast (multi-access) networks such as Ethernet allow multiple devices to
connect to (or access) the same network, as well as provide a broadcast ability in which a
single packet is delivered to all nodes on the network. In OSPF, a DR and a BDR must be
elected Ior each broadcast multi-access network.
Non-broadcast multi-access
Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) networks are types such as Frame Relay,
X.25, and Asynchronous TransIer Mode (ATM). These networks allow Ior multi-access,
but have no broadcast ability like Ethernet. So, NBMA networks require special OSPF
conIiguration to Iunction properly and neighbor relationships must be deIined.
Point-to-point
Point-to-point reIers to a type oI network topology consisting oI a direct
connection between two routers that provides a single communication path. The point-to-
point connection can be physical, as in a serial cable directly connecting two routers, or it
can be logical.
Point-to-multipoint
Point-to-multipoint reIers to a type oI network topology consisting oI a series oI
connections between a single interIace on one router and multiple destination routers. All
oI the interIaces on all oI the routers sharing the point-to-multipoint connection belong to
the same network. As with point-to-point, no DRs or BDRs are needed.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
SPF Tree Calculation
Within an area, each router calculates the best/shortest path to every network in
that same area. This calculation is based upon the inIormation collected in the topology
database and an algorithm called shortest path Iirst (SPF)
OSPF uses a metric reIerred to as cost. A cost is associated with every outgoing
interIace included in an SPF tree. The cost oI the entire path is the sum oI costs oI the
outgoing interIaces along the path.
Cisco uses a simple equation oI 10
8
/ bandwidth.The bandwidth is the conIigured
bandwidth Ior the interIace. Using this rule, a 100Mbps Fast Ethernet interIace would
have a deIault OSPF cost oI 1 and a 10Mbps Ethernet interIace would have a cost oI 10.
An interIace set with a bandwidth oI 64,000 would have a deIault cost oI 1563.
Benefits of OSPF
(i) Minimum routing updates.
(ii) Priorities on all the CISCO routers the priority is 1.
(iii) The routers having highest IP address become BRD(Border Destination
Router)
Steps to apply OSPF
Syntax:
Router(conIig)#router ospI ospI process id~
Router(conIig-router)#network network address~ wild card mask~ area
area number~
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 25: OSPF Scenario
At Router r1
Router(conIig)#router ospI 1
Router(conIig-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig)#interIace s0/1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#clock rate 64000
Router#show ip route
At Router r1
Router(conIig)#router ospI 2
Router(conIig-router)#network 20.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig-router)#network 40.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig-router)#network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig)#interIace s0/1/0
Router(conIig-iI)#clock rate 64000
Router#show ip route
At Router r3
Router(conIig)#router ospI 1
Router(conIig-router)#network 30.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router(conIig-router)#network 50.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router#show ip route
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
3.13 40N S5ITC'IN6
3.17.1 SWITCH
Switches are generally used to segment a large LAN smaller segments. Smaller
switches such as the Cisco Catalyst 2924XL have 24 ports capable oI oI creating 24
diIIerent network segment Ior the LAN. Larger switches such as the Cisco Catalyst 6500
can have hundreds oI ports. Switches can also be used to connect LANs with diIIerent
media, Ior example, a 10 Mbps Ethernet LAN and 100 Mbps Ethernet LAN can be
connected using a switch. Some switches support cut through switching, witch reduces
latency and delays in the network, while bridges support only store-and-Iorward traIIic
switching. Finally switches reduce collision on network segment . A switch is a
networking device which Iilters and Iorward packets through the network. It is a layer 2
device. It is more advanced then hub but not as advanced as router.The basic Iunction oI
a switch is to manage the signal Ilow. When the switch is open, it allows the signal to
Ilow through it and when it is closed, it stopes the signal to Ilow. Switch connects
separate LAN segment. It allows multiple system to transmit simultaneously. A switch is
a hardware device that Iilters and Iorward data packets between network segments.
Ethernet switches are used in LAN to create Ethernet networks. Switches Iorward the
traIIic on the basis oI MAC address. Switches maintain a switching table in which MAC
addresses and port numbers are used to perIorm switching decision.
WORKING OF SWITCH
When switches receives data Irom one oI connected devices, it Iorward data only
to the port on witch the destinated system is connected.It use the media access Control
(MAC) address oI the device to determine the correct port.The MAC address is a uniqe
number that is programed in to every Network InterIace Card(NIC). Concider, device A
wants to send data to device B.When device A passes the data, switch receives it. Switch
than cecks the MAC address oI the destination system. It then transIer data to device B
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
only instead oI brodcasting to all the devices. By Iorwarding data only to the system to
witch the data is addressed, switch decreases the amount oI traIIic on each network link.
SWITCHING METHODS
There are three types oI switching method:
Store-and-forward switching
The entire Irame is received and the CRC is computed and veriIied beIore
Iorwarding the Irame. II the Irame is too short (i.e. less than 64 bytes including the
CRC), too long (i.e. more than 1518 bytes including the CRC), or has CRC error, it
will be discarded.
It has the lowest error rate but the longest latency Ior switching. However, Ior
high-speed network (e.g. Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet network), the latency is
not signiIicant. It is the most commonly used switching method, and is supported by
most switches.
Cut-through switching
It is also known as Fast Forward switching. A Irame is Iorwarded as soon as
the destination MAC address in the header has been received (the 1st 6 bytes
Iollowing the preamble). It has the highest error rate (because a Irame is
Iorwarded without veriIying the CRC and conIirming there is no collision) but
the shortest latency Ior switching
Fragment-free switching ( Modified Cut-through switching )
A Irame is Iorwarded aIter the Iirst 64 bytes oI the Irame have been
received. Since a collision can be detected within the Iirst 64 bytes oI a Irame,
Iragment-Iree switching can detect a Irame corrupted by a collision and drop
it.ThereIore, Iragment-Iree switching provides better error checking than cut-
through switching.
The error rate oI Iragment-Iree switching is above store-and-Iorward
switching and below cut-through switching. The latency oI Iragment-Iree
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
switching is shorter than store-and- Iorward switching and longer than cut-
through switching.
NOTE:
Bridges only support store-and-Iorward switching. Most new switch models also
use store-and-Iorward switching. However, it should be noted that Cisco 1900 switches
use Iragment-Iree switching by deIault.
Types of switch based on OSI model
(i) Layer-2 switch
(ii) Layer-3 switch
Layer-2 Switching
Layer-2 switching is hardware based, which means it uses the MAC
address Irom the host NIC card to Iilter the network traIIic. Layer-2 switch can be
considered as multi- port bridge.
Layer 2 switches are Iast because they do not look at the network layer
header inIormation, instead it looks at the Irames hardware address beIore deciding to
either Iorward the Irame or drop it.
Limitations of Layer 2 Switching
With bridge the connected networks are still one large broadcast domain.
Layer 2 switch cannot break the broadcast domain, this cause perIormance issue which
limits the size oI your network. For this one reason the switch cannot completely replace
routers in the internetwork.
3.17.1.1 VLAN (Virtual LAN)
VLAN provides Virtual Segmentation oI Broadcast Domain in the network. The
devices, which are member oI same Vlan, are able to communicate with each other. The
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
devices oI diIIerent Vlan may communicate with each other with routing. So that
diIIerent Vlan devices will use diIIerent n/w addresses.
Vlan provides Iollowing advantages: -
Logical Segmentation oI network
Enhance network security
Creating port based Vlan
In port based Vlan, Iirst we have to create a Vlan on manageable switch then we
have to add ports to the Vlan. A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a broadcast domain created
based on the Iunctional, security, or other requirements, instead oI the physical locations
oI the devices, on a switch or across switches. With VLANs, a switch can group diIIerent
interIaces into diIIerent broadcast domains. Without VLANs, all interIaces oI a switch
are in the same broadcast domain; switches connected with each other are also in the
same broadcast domain, unless there is a router in between. DiIIerent ports oI a switch
can be assigned to diIIerent VLANs. A VLAN can also span multiple switches.
The advantages of implementing VLAN are
It can group devices based on the requirements other than their physical
locations.
It breaks broadcast domains and increases network throughput.
It provides better security by separating devices into diIIerent VLANs.
Since each VLAN is a separate broadcast domain, devices in diIIerent VLANs
cannot listen or respond to the broadcast traIIic oI each other.
Inter-VLAN communication can be controlled by conIiguring access control
lists on the router or Layer 3 switch connecting the VLANs.
Types of VLAN
Static VLAN
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Assigning VLANs to switch ports based on the port numbers. It is easier to set
up and manage.
Dynamic VLAN
Assigning VLANs to switch ports based on the MAC addresses oI the
devices connected to the ports.
A VLAN management application is used to set up a database oI MAC addresses, and
conIigure the switches to assign VLANs to the switch ports dynamically based on the
MAC addresses oI the connected devices. The application used by Cisco switches is
called VLAN Management Policy Server (VMPS).
Cisco switches support a separate instance oI spanning tree and a separate bridge
table Ior each VLAN.
A VLAN A Broadcast Domain Logical Network (Subnet)
VLAN Operation
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 26: VLAN Operation
Each logical VLAN is like a separate physical bridge.
VLANs can span across multiple switches.
Trunks carry traIIic Ior multiple VLANs.
Trunks use special encapsulation to distinguish between diIIerent VLANs.
VLAN links
There are two diIIerent types oI links in a switched network:
Access link
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
A link Irom Pc to switch is called as access link or A link that is part oI only one
VLAN. ThereIore, a port connecting to an access link can be a member oI only one
VLAN. And the mode oI port is called as access mode.
Trunk link
A link Irom switch to switch or switch to router is called as trunk link. A 100
Mbps or 1000 Mbps point-to-point link that connects switches or routers, and carries
Irames oI diIIerent VLANs . ThereIore, a port connecting to a trunk link can be a member
oI multiple VLANs. All VLANs are conIigured on a trunk link by deIault. VLAN
Trunking, by making use oI Irame tagging, allows traIIic Irom diIIerent VLANs to
transmit through the same Ethernet link (trunk link) across switches.
VLAN Trunking identiIies the VLAN Irom which a Irame is sent by tagging the
Irame with the source VLAN ID (12-bit long). This Ieature is known as Irame tagging or
Irame identiIication. When there are multiple switches then we have to use trunk links to
connect one switch with other. II we are not using trunk links then we have to connect
one cable Irom each vlan to the corresponding vlan oI the other switch.
With Irame tagging, a switch knows which ports it should Iorward a broadcast
Irame (Iorward out the ports which have the same VLAN ID as the source VLAN ID). It
also knows which bridge table it should use Ior Iorwarding an unicast Irame (since a
separate bridge table is used Ior each VLAN).
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
A Irame tag is added when a Irame is Iorwarded out to a trunk link, and is
removed when the Irame is Iorwarded out to an access link. ThereIore, any device
attached to an access link is unaware oI its VLAN membership.
Commands to create Vlan
Switch#vlan database
Switch(vlan)#vlan no.~ |name name oI vlan~|
Switch(vlan)#exit
Commands to configure ports for a Vlan
By deIault, all ports are member oI single vlan that is Vlan1. we can change vlan
membership according to our requirement.
Switch(conIig)#interIace type~ no.~
Switch(conIig-iI)#switchport access vlan no.~
Switch(conIig-iI)#exit
Commands to configure multiple ports in a vlan
Switch(conIig)#interIace range type~ slot/port no. (space)(space) port no.~
Switch(conIig-iI)#switchport access vlan no.~
Switch(conIig-iI)#exit
Example: - Suppose we want to add interIace Iast Ethernet 0/10 to 0/18 in vlan5
Switch(conIig)#interIace range Iastethernet 0/10 18
Switch(conIig-iI)#switchport access vlan 5
Switch(conIig-iI)#exit
To display mac address table
Switch#show mac-address-table
Vlan Mac address type ports
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
20 00-08-a16-ab-6a-7b dynamic Ia0/7
To Display Vlan and port membership
Switch#show vlan brieI
Command to make Trunk link
Switch(conIig)#interIace type~ type number~
Note :- Trunk mode should not be a member oI any vlan port.
3.17.1.2 Vlan Trunking Protocol (VTP)
With the help oI VTP, we can simpliIy the process oI creating Vlan. In multiple
switches, we can conIigure one switch as VTP server and all other switches will be
conIigured as VTP client. We will create Vlans on VTP server switch. The server will
send periodic updates to VTP client switches. The clients will create Vlans Irom the
update received Irom the VTP server.
VTP Operation
VTP advertisements are sent as multicast Irames.
VTP servers and clients are synchronized to the latest revision number.
VTP advertisements are sent every 5 minutes or when there is a change.
VTP Modes
VTP server mode
By deIault all the switches in this mode are in server mode. VTP server is a
switch in which we can create, delete or modiIy Vlans.yhe switch in this mode
Iorwords the vlans to next switch. The server will send periodic updates Ior VTP
clients.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
VTP client mode
On VTP client, we are not able to create, modiIy or delete Vlans. The switch
in this mode creates the vlans that are received Irom server mode switch.The client
will receive and Iorward vtp updates. The client will create same Vlans as deIined in
vtp update.
VTP Transparent mode
Transparent is a switch, which will receive and Iorward VTP update. It is able
to create, delete and modiIy Vlans locally. A vlan created in this mode cannot be
Iorworded into next switch. A transparent will not send its own VTP updates and will
not learn any inIormation Irom received vtp update.
VTP configuration
At Switch 1:
Creat vlan
Port assignment
Trunk port
Switch vtp
Switch(conIig)#vtp mode server
Switch(conIig)#vtp domain cisco
Switch(conIig)#vtp password sun
At switch 2:
Switch(conIig)#vtp mode server
Switch(conIig)#vtp domain cisco
Switch(conIig)#vtp password sun
At switch 3:
Switch(conIig)#vtp mode server
Switch(conIig)#vtp domain cisco
Switch(conIig)#vtp password sun
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 27 : VTP Configuration
To see all the configurations
Switch#show vtp password
Switch#show vlan brieI
Switch#show vtp status
Vtp version
Vtp domain
Vtp mode
Vtp pruning
Vtp reusion number
Maximum vlan supporting
Total no. oI vlans
VTP Pruning
Pruning is the VTP Ieature through which a trunk link can be automatically
disable, Ior a particular Vlan iI neighbor switch does not contain ports in that Vlan. Vlan1
is not prun eligible.
Increases available bandwidth by reducing unnecessary Ilooded traIIic
Example: Station A sends broadcast, and broadcast is Ilooded only toward
any switch with ports assigned to the red VLAN
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Command to configure VTP Pruning
We have to use only one command on VTP server Ior VTP Pruning.
Switch#conIigure terminal
Switch(conIig)#vtp pruning
Switch(conIig)#exit
Fig 28 : VTP Pruning
Spanning Tree Protocol
When we connect multiple switches with each other and multiple path exist Irom
one switch to another switch then it may lead to the switching loop in the network.
Multiple paths are used to create redundancy in the network. STP is only required when
multiple path exist then there is possibility oI loop in n/w.
Problems that occur with redundancy path
(i) Multiple copies oI the Irame will be received by destination.
(ii) Frequent changes in the mac address table oI switch.
(iii) A mac address may appear at multiple ports in a switch.
(iv) Packets may enter in the endless loop.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Spanning Tree Protocol will solve this problem by blocking the redundancy
interIace. So that only one path will remain active in the switches. II the primary path
goes down then disabled link will become enable and data will be transIerred through that
path.
Spanning Tree Protocol Basics
Spanning Tree Protocol or STP (IEEE 802.1d) is used to solve the looping
problem.It runs on bridges and switches in a network. It implements a Spanning
Tree Algorithm (STA), which calculates a loop-Iree topology Ior the network.
STP ensures that there is only one active path between any two network segments
by blocking the redundant paths. A redundant path is used only when the
corresponding active path Iailed. It is not used Ior load-balancing.
Because STP solves the looping problem by blocking one or more links in a
network, the Irames traveling between some source / destination devices may not
be able to use the shortest physical path.
Bridges exchange STP inIormation using messages called Bridge Protocol Data
Units (BPDUs) through Layer 2 multicast.
3.18 Wi-Fi (WIRELESS FIDELITY)
The term "Wi-Fi" suggests "Wireless Fidelity", compared with the long-
established audio recording term "High Fidelity" or "Hi-Fi". The term "Wi-Fi", Iirst used
commercially in August 1999. Wi-Fi is an IEEE standard 802.11.
3.18.1 Wireless LAN
Wi-Fi is also known as wireless LAN. The name oI a popular wireless
networking technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless high-speed Internet and
network connections. "Wi-Fi works with no physical wired connection between sender
and receiver by using radio Irequency (RF) technology, a Irequency within the
electromagnetic spectrum associated with radio wave propagation. When an RF current is
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
supplied to an antenna, an electromagnetic Iield is created that then is able to propagate
through space.
The Typical Range of a Wi-Fi LAN
The range oI a home Wi-Fi LAN depends on the wireless access point (WAP) or
wireless router being used. Factors that determine a particular WAP or wireless router's
range are:
the speciIic 802.11 protocol employed
the overall strength oI the device transmitter
the nature oI obstructions and interIerence in the surrounding area
A general rule oI thumb in home networking says that 802.11b and 802.11g
WAPs and routers support a range oI up to 150 Ieet (46 m) indoors and 300 Ieet (92 m)
outdoors. Another rule oI thumb holds that the eIIective range oI 802.11a is
approximately one-third that oI 802.11b/g.
Obstructions in home such as brick walls and metal Irames or siding greatly can
reduce the range oI a Wi-Fi LAN by 25 or more. Because 802.11a employs a higher
signalling Irequency than 802.11b/g, 802.11a is most susceptible to obstructions.
InterIerence Irom microwave ovens and other equipment also aIIects range. 802.11b and
802.11g are both susceptible to these.
3.18.2 Wireless Standards
The diIIerent wireless standards that are used Ior IEEE 802.11 standard are
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Fig 29: IEEE 802.11 Standards
802.11
It was released in year 1997. The standard was original oI 802.11. the max. data
rate oI this is 2Mbps and Irequency oI this is 2.4GHz and can cover upto 46m.
802.11a
It was modiIied in year 1999. this is improved version oI original standard.
Operates at the Irequency oI 5GHz, which is less crowded than 2.4GHz where telephones
and microwaves may cause interIerence. Although the speed is up to 54Mbps, the range
is only up to 75 Ieet or distance covered is 46m. 802.11a standard is incompatible with
both 802.11b and g because it operates at a diIIerent Irequency.
802.11b
This standard was released in 1999. Operates on the 2.4GHz Irequency band and
can transmit data at speeds oI up to 11Mbps within a range oI up to 100-150 Ieet or a
distance oI 90m.Wireless range can be aIIected by reIlective or signal-blocking obstacles,
such as mirrors, walls, devices and location, whether indoors or outdoors.
802.11g
This standard was released in 2003. The max. data rate Ior the standard is 54Mbps.
It supports a Irequency range oI 2.4GHz, covers a distance oI 90m.
802.11n
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
The latest version oI IEEE 802.11 standard that is still in progress oI
development. The next generation oI high-speed wireless networking, capable oI
delivering the range and capacity to support today's most bandwidth-hungry applications
like streaming high deIinition video, voice, and music. Wireless-n is based on MIMO
(Multiple Input, Multiple Output) technology, which uses multiple radios to transmit
multiple streams oI data over multiple channnels.
Operates in two modes oI Irequency 2.4GHz and 5.6GHz Irequency band and
can transmit data at speeds oI up to 11Mbps within a range oI up to 100-150 Ieet .
Wireless range can be aIIected by reIlective or signal-blocking obstacles, such as mirrors,
walls, devices and location, whether indoors or outdoors.
Wi-Fi is supported by many applications and devices
video game consoles
home networks
PDAs
mobile phones
major operating systems
other types oI consumer electronics
3.18.3 Wireless Security
A common but unproductive measure to deter unauthorized users is to suppress the
AP's SSID broadcast, "hiding" it. This is ineIIective as a security method because the
SSID is broadcast in the clear in response to a client SSID query. Another unproductive
method is to only allow computers with known MAC addresses to join the network.
MAC address are easily spooIed. II the eavesdropper has the ability to change his MAC
address, then he may join the network by spooIing an authorized address.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption was designed to protect against casual
snooping, but is now considered completely broken. Tools such as AirSnort or aircrack
can quickly recover WEP encryption keys.
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
To counteract this in 2002, the Wi-Fi Alliance blessed Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
Ior wireless security. Though more secure than WEP, it has outlived its designed liIetime,
has known attack vectors and is no longer recommended.
In 2004 the Iull IEEE 802.11i (WPA2) encryption standards were released. II used with a
802.1X server or in pre-shared key mode with a strong and uncommon passphrase WPA2
is still considered secure, as oI 2009.
4. CONCLUSION
General Conclusion
Computer Networking is a very vast project in the present developing era oI
electronics and communication. Now a days, computers are used in a wider range. All the
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
organizations are using multiple computers within their departments to perIorm their day
to day work. Computer network allows the user to share data , share Iolders and Iiles with
other users connected in a network. Computer Networking has bound the world in a very
small area with it wide networking processes like LAN, MAN, WAN.
Applications
Communication Field
Industries
Medical Field
Rearch Field
Organisations
School
Colleges
REFRENCES
www.goole.com
www.jetkinginIotrain.com
www.microsoIt.com
www.nythimes.com
www.digitech-engineers.com
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Network Essentials module
4-in-1 MCSE study material
Introduction to Window Server2003
CISCO CretiIied Network Associate
Faruk Husain
www.final-yearprojects.co.cc | www.troubleshoot4free.com/fyp/
Você também pode gostar
- Understanding Route Redistribution: Franck Le Geoffrey G. Xie Hui ZhangDocumento13 páginasUnderstanding Route Redistribution: Franck Le Geoffrey G. Xie Hui ZhangAjit SangwanAinda não há avaliações
- Final Year ProjectsDocumento1 páginaFinal Year ProjectsSaitejaTallapellyAinda não há avaliações
- VPN PresentationDocumento15 páginasVPN PresentationNishtha SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Visual BasicDocumento51 páginasVisual BasicdipanshuhandooAinda não há avaliações
- CAN Campus Network Feasibility StudyDocumento65 páginasCAN Campus Network Feasibility StudyAjit SangwanAinda não há avaliações
- Computer System Architecture Chapt 4. Register Transfer & MicrooperationsDocumento35 páginasComputer System Architecture Chapt 4. Register Transfer & MicrooperationsWaqas AnjumAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 DBMSDocumento33 páginasUnit 4 DBMSankit47100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Adapter Configuration Guide: Ibm Security Qradar Risk ManagerDocumento49 páginasAdapter Configuration Guide: Ibm Security Qradar Risk Managersecua369Ainda não há avaliações
- A10 Training 08 High - AvailabilityDocumento17 páginasA10 Training 08 High - AvailabilityMario AlcazabaAinda não há avaliações
- Motorola DSR-6100 ManualDocumento98 páginasMotorola DSR-6100 Manualburrows00Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Communication & Networks: Network Layer: Logical AddressingDocumento46 páginasComputer Communication & Networks: Network Layer: Logical AddressingAli AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Fill in The Blanks:: ACTS National Resource Center, Pune Question Bank - DCN (Solved)Documento15 páginasFill in The Blanks:: ACTS National Resource Center, Pune Question Bank - DCN (Solved)blackpanther00Ainda não há avaliações
- Airspan ASN-700 As - Net Flexnet ReviewDocumento7 páginasAirspan ASN-700 As - Net Flexnet ReviewSynworks Development GroupAinda não há avaliações
- ZXHN+F670+V1 0+PON+ONT+Maintenance+Management PDFDocumento186 páginasZXHN+F670+V1 0+PON+ONT+Maintenance+Management PDFAnonymous u8XKgo878% (9)
- EventoDocumento52 páginasEventoj.franco0483Ainda não há avaliações
- Elements of Computer Networking: An Integrated Approach (Concepts, Problems and Interview Questions)Documento58 páginasElements of Computer Networking: An Integrated Approach (Concepts, Problems and Interview Questions)CareerMonk Publications80% (10)
- ATOSNTUserManual 6.1.12Documento603 páginasATOSNTUserManual 6.1.12alessandroAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Profile Profibus DP MPCDocumento34 páginasFunctional Profile Profibus DP MPCIldar NasAinda não há avaliações
- FGT1 05 SSL VPNDocumento32 páginasFGT1 05 SSL VPNpbougoinAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Communication and Newtworks: Introduction To Wi-Fi Mesh NetworksDocumento14 páginasWireless Communication and Newtworks: Introduction To Wi-Fi Mesh NetworksSwapna RaaviAinda não há avaliações
- How To Login To The Huawei B315s-22Documento3 páginasHow To Login To The Huawei B315s-22abebaAinda não há avaliações
- SNF 8010 Manual PDFDocumento140 páginasSNF 8010 Manual PDFsatriya bendoAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To VLANs and VLAN TrunkingDocumento21 páginasAn Introduction To VLANs and VLAN TrunkingShyam SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 70 640Documento175 páginas70 640KARTHIKRAJDGAinda não há avaliações
- Integrating Routing With Content Delivery Networks: Brian Field PH.DDocumento6 páginasIntegrating Routing With Content Delivery Networks: Brian Field PH.DmisbahuddinaflahAinda não há avaliações
- Basic of NetworkingDocumento46 páginasBasic of Networkingapi-281601506Ainda não há avaliações
- Configure A Professional Firewall Using PfsenseDocumento7 páginasConfigure A Professional Firewall Using PfsensenoahkrpgAinda não há avaliações
- PSI 300 Particle Size Analyzers Maintenance Manual: Code 10000004258e Revision A Page 1Documento22 páginasPSI 300 Particle Size Analyzers Maintenance Manual: Code 10000004258e Revision A Page 1Juan Miguel RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- BR 6324NL Manual BookDocumento161 páginasBR 6324NL Manual BookAshutosh PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Ec2 WGDocumento844 páginasEc2 WGRamarolahy Dadan'i Elia100% (1)
- Sun Storagetek 2530 CamDocumento201 páginasSun Storagetek 2530 CamCriis Britez MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- S.No Topics Lec: Advanced Computer Network ETCS-401Documento4 páginasS.No Topics Lec: Advanced Computer Network ETCS-401Anshul MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Manual SwitcherDocumento80 páginasManual SwitcherDAN ROSALES FILMSAinda não há avaliações
- DATAKOM D500 Ethernet ConfigurationDocumento14 páginasDATAKOM D500 Ethernet ConfigurationOrion PeresvitAinda não há avaliações
- MS-DOS Basics - A TutorialDocumento56 páginasMS-DOS Basics - A TutorialSALEEMAinda não há avaliações
- MSS OverviewDocumento38 páginasMSS OverviewNoman Saeed100% (1)
- Net CommandsDocumento11 páginasNet CommandsCalidaz VbAinda não há avaliações