Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Acid Base Solutions
Enviado por
Casey SangalliDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Acid Base Solutions
Enviado por
Casey SangalliDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________
ID: A
Ch 15,16,19 Practice Test
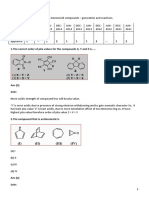
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Properties of Water ____ 1. Which atom in a water molecule has the least electronegativity? a. one of the hydrogen atoms b. both hydrogen atoms c. the oxygen atom d. There is no difference in the electronegativities of the atoms in a water molecule. 2. After dissoving a salt, what part of a water molecule will be closest to the cation (positive ion)? a. oxygen c. all parts will have equal distances b. either of the hydrogens d. Water does not dissolve cations 3. After dissoving a salt, what part of a water molecule will be closest to the anion (negative ion)? a. oxygen c. all parts will have equal distances b. either of the hydrogens d. Water does not dissolve anions Solutions ____ 4. If the solubility of a particular solute is
____
____
20g at 20C, which of the following solution concentrations 100g H 2 O
would represent a supersaturated aqueous solution of that solute? 19g 29g at 20C c. at 20C a. 100g H 2 O 100g H 2 O b. ____
10g at 20C 100g H 2 O
d.
11g at 20C 100g H 2 O
____
____
5. What is the term for the dissolving medium in a solution? a. solvent c. solvator b. solute d. emulsifier 6. What type of compound is always ionic? a. polar covalent c. electrolyte b. nonpolar covalent d. network solid 7. What mass of Na 2 SO 4 is needed to make 2.0 L of 2.0 M solution? (Na = 23 g; S = 32 g; O = 16 g) a. 284 g c. 142 g b. 568 g d. 710 g 8. What is the molarity of a solution containing 36.0 grams of solute in 0.50 liters of solution? (molar mass of solute = 18 g) a. 0.67M c. 1.67M b. 4M d. 0.17M 9. Which of the following operations yields the number of moles of solute? c. molarity mass of solution a. molarity moles of solution b. molarity liters of solution d. moles of solution volume of solution
____
____
Name: ________________________ ____ 10. A solution is a mixture ____. a. from which the solute can be not be filtered b. that has the same properties throughout c. that is homogeneous d. all of the above ____ 11. What is the molarity of 100 mL of solution in which 2.0 moles of sodium bromide is dissolved? a. 20.0M c. 0.20 M b. 100 M d. 200 M ____ 12. Which of the following pairs of factors affects the solubility of a particular substance? a. temperature and the nature of solute and solvent b. temperature and degree of mixing c. particle size and degree of mixing d. particle size and temperature ____ 13. Which of these statements is correct? a. Particles can be filtered from a suspension. b. A solution is heterogeneous. c. A colloidal system does not exhibit the Tyndall effect. d. The particles in a colloidal system are affected by gravity. ____ 14. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 6 moles of solute in 0.5 liters of solution? a. 6M c. 7M b. 12M d. 3M ____ 15. What does NOT change when a solution is diluted by the addition of solvent? a. volume of solvent c. number of moles of solute b. mass of solvent d. molarity of solution ____ 16. Which of the following mixture types is characterized by the settling of particles? a. solution c. colloid b. suspension d. hydrate
ID: A
Name: ________________________
ID: A
____ 17. Which of the following molecules is least soluble at 0 C? (refer to above graph) a. KNO3 c. KClO3 b. NaCl d. NaNO3 ____ 18. Which of the following molecules is most soluble at 70 C? (refer to above graph) a. KNO3 c. NaCl b. NaNO3 d. KCl ____ 19. How many grams of KNO3 does it take to saturate 100 g of H2O at 60C? (refer to above graph) a. 92 g c. 60 g b. 125 g d. 110g ____ 20. Which of the following, as it heats up, decreases its solubility in water? (refer to above graph) a. NH4Cl c. HCl b. NaCl d. NaNO3 ____ 21. How many grams of KCl does it take to saturate 300 g of H2O at 90C? (refer to above graph) a. 55 g c. 110 g b. 165 g d. 220 g 3
Name: ________________________
ID: A
____ 22. How many grams of NaCl does it take to saturate 25 g of H2O at 100C? (refer to above graph) a. 40 g c. 79 g b. 20 g d. 10 g ____ 23. A saturated solution of 100C 100 g of KCl is made then allowed to cool to room temperature
(22C), how much KCl should precipitate out of solution? (refer to above graph) a. 32 g c. 15 g b. 57 g d. 25 g
____ 24.
Which word best describes why water dissolves salts?
a. clear c. tasteless b. polar d. non-polar ____ 25. Which of the following occurs as temperature increases? a. Solubility of salts decreases. c. Solubility remains the same. b. Solubility of salts increases. d. Molarity doubles. ____ 26. Which of the following substances is less soluble in hot water than in cold water? a. LiBr (ionic solid) c. CuNO 3 (ionic solid) b. CaCl2 (ionic solid) d. NO 2 (semipolar gas) ____ 27. Which of the following substances is the most soluble in water? a. carbon (nonpolar solid) c. Chlorine (nonpolar gas) b. ethane (nonpolar gas) d. Lithium bromide (ionic solid) ____ 28. Predict which one of the following compounds would be insoluble in water. c. Sugar C6H12O6 (polar solid) a. Methane CH4 (nonpolar gas) b. HBr (polar gas) d. AgNO3 (ionic solid) ____ 29. Which of the following expressions is generally used for solubility? a. grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent b. grams of solute per 100 milliliters of solvent c. grams of solute per 100 grams of solution d. grams of solute per 100 milliliters of solution Acids and Bases ____ 30. Which of the following is not a property of acids? a. taste sour c. b. dissolve some metals d.
can dissolve marble produce a pH greater than 7 when added to water
____ 31. Which of the following is a property of an acid? a. sour taste c. strong color b. nonelectrolyte d. unreactive ____ 32. What is a property of a base? a. bitter taste c. strong color b. watery feel d. unreactive ____ 33. When an acid reacts with a base, what compounds are formed? a. a salt only c. metal oxides only b. water only d. a salt and water
Name: ________________________ ____ 34. What is the charge on the hydroxide ion? a. 1 c. 0 b. 2 d. 1+ ____ 35. What is the charge on the hydronium ion? a. 1 c. 0 b. 2 d. 1+ ____ 36. Which of the following reactions illustrates amphoterism? H 3 O + + OH c. HCl + H 2 O a. H 2 O + H 2 O
ID: A
H 3 O + + Cl
b. NaCl Na + + OH d. NaOH Na + + OH ____ 37. Which compound can act as both a Brnsted-Lowry acid and a Brnsted-Lowry base? a. water c. sodium hydroxide b. ammonia d. hydrochloric acid ____ 38. What is pH? a. the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration b. the positive logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration c. the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration d. the positive logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration ____ 39. In a neutral solution, the [H + ] is ____. c. 1 10 +7 M a. 10 14 M b. zero d. equal to [OH ] ____ 40. Which type of solution is one with a pH of 6? a. acidic b. basic c. neutral d. The type varies, depending on the solution. ____ 41. If the pH is 6, what is the pOH a. 6 b. 8 c. 14 d. 10 ____ 42. If the pH is 10, what is the pOH a. 3 b. 6 c. 10 d. 4 ____ 43. If the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 10 -4M, is the solution acidic, alkaline (basic), or neutral? a. acidic c. neutral b. alkaline d. The answer cannot be determined. ____ 44. If the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 10 -7M, is the solution acidic, alkaline (basic), or neutral? a. acidic c. neutral b. alkaline d. The answer cannot be determined. ____ 45. If the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 10 -8M, is the solution acidic, alkaline (basic), or neutral? a. acidic c. neutral b. alkaline d. The answer cannot be determined.
Name: ________________________ ____ 46. If the [H+] goes up what happens to the [OH-]? a. it goes down c. it goes up b. it stays the same d. it is directly proportional ____ 47. If a solution goes from a pH of 4 to a pH of 8, which of the following is true about the [H+]? a. It increases by a factor of 4 c. It decreases by a factor of 4 b. It increases by a factor of 10000 d. It decreases by a factor of 10000 ____ 48. If a solution goes from a pH of 7 to a pH of 5, which of the following is true about the [H+]? a. It increases by a factor of 2 c. It decreases by a factor of 2 b. It increases by a factor of 100 d. It decreases by a factor of 100 ____ 49. Which of these solutions is the most basic? c. [H + ] = 1 10-9M a. [H + ] = 1 10 2 M d. [OH ] = 1 10 13 M b. [OH ] = 1 10 4 M ____ 50. Which of the following things will not affect the reading of an indicator? a. color of the liquid c. volume of the liquid b. temperature of the liquid d. salt concentration of the liquid ____ 51. What characterizes a strong acid or base? a. polar covalent bonding b. complete ionization in water c. ionic bonding d. presence of a hydroxide or hydrogen ion ____ 52. What type of acid is hydrochloric (HCl) acid? a. monoprotic c. triprotic b. diprotic d. none of the above ____ 53. Acetic acid ionizes in water as follows: CH 3 COO + H 3 O + CH 3 COOH + H 2 O
ID: A
Fewer than 1% of ethanoic acid molecules are ionized at any instant. The acetate ion (CH 3 COO ) is therefore ____. a. a poor hydrogen-ion acceptor c. a poor hydrogen-ion donor b. a good hydrogen-ion acceptor d. a good hydrogen-ion donor ____ 54. A 0.12M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would be termed ____. a. concentrated and weak c. dilute and weak b. strong and dilute d. concentrated and strong ____ 55. What is another name for the acid dissociation constant? a. equilibrium constant c. rate constant b. ionization constant d. mole fraction ____ 56. A substance with a K a of 1 10-1 would be classified as a ____. a. strong acid c. strong base b. weak acid d. weak base ____ 57. The K a of carbonic acid is 4.3 10 7 . H + + HCO 3 H 2 CO 3 This means that H 2 CO 3 is a ____. a. good hydrogen-ion acceptor b. poor hydrogen-ion acceptor
c. d.
good hydrogen-ion donor poor hydrogen-ion donor
Name: ________________________ ____ 58. A base has a K b of 2.5 10 11 . Which of the following statements is true? a. This is a concentrated base. b. This base ionizes slightly in aqueous solution. c. This is a strong base. d. An aqueous solution of this base would be acidic. ____ 59. Which of the following will not produce an acid when mixed with water c. SO2 a. NO2 b. CO2 d. NaCl Titrations: Molarity of acid x Volume Acid = Molarity of Base x Volume Base
ID: A
____ 60. If 10.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH are needed to neutralize an unknown volume of 0.05 M HCl, what is volume of the
HCl?
a. 10 ml c. 30 ml b. 15 ml d. 20 ml ____ 61. In a titration, when the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide ions, what is said to have happened? a. The equivalence point has been reached. b. The end point has been reached. c. The point of neutralization has been reached. d. The titration has failed. ____ 62. The process of adding a known amount of solution of known concentration to determine the concentration of another solution is called ____. a. neutralization c. titration b. hydrolysis d. buffer capacity ____ 63. If 30.0 mL of 0.500 M KOH are needed to neutralize 10.0 mL of HCl of unknown concentration, what is
molarity of the HCl?
a. b.
150 M 0.17 M
c. d.
20.5 M 1.5 M
ID: A
Ch 15,16,19 Practice Test Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: OBJ: 2. ANS: 3. ANS: 4. ANS: OBJ: 5. ANS: OBJ: 6. ANS: OBJ: 7. ANS: OBJ: 8. ANS: OBJ: 9. ANS: OBJ: 10. ANS: OBJ: 11. ANS: OBJ: 12. ANS: OBJ: 13. ANS: OBJ: 14. ANS: OBJ: 15. ANS: OBJ: 16. ANS: OBJ: 17. ANS: 18. ANS: 19. ANS: 20. ANS: 21. ANS: 22. ANS: 23. ANS: 24. ANS: 25. ANS: OBJ: B 15.1.1 A B C 16.1.3 A 15.2.1 C 15.2.3 B 16.2.1 B 16.4.1 B 16.2.1 D 15.2.2 A 16.2.1 A 16.1.3 A 15.3.1 | 15.3.2 B 16.2.1 C 16.2.2 B 15.3.1 C A D C B D D B B 16.1.3 PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: STA: 1 DIF: Ch.1.c | Ch.2.g 1 1 1 DIF: Ch.6 1 DIF: Ch.6.a 1 DIF: Ch.5.a 1 DIF: Ch.6.d 1 DIF: Ch.6.d 1 DIF: Ch.6.d 1 DIF: Ch.6.a 1 DIF: Ch.6.d 1 DIF: Ch.6.c 1 DIF: 1 Ch.6.d 1 Ch.6.d 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Ch.6.c L2 REF: p. 446
L3 L1 L1 L3 L2 L2 L3 L2 L2 L2
REF: p. 474 REF: p. 450 REF: p. 452 REF: p. 481 | p. 482 REF: p. 491 REF: p. 480 REF: p. 450 REF: p. 481 REF: p. 473 | p. 474 REF: p. 450 | p. 459 | p. 460 | p. 461 REF: p. 481 REF: p. 483 REF: p. 459
DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1
DIF: L2
REF: p. 474
ID: A 26. ANS: OBJ: 27. ANS: OBJ: 28. ANS: OBJ: 29. ANS: OBJ: 30. ANS: 31. ANS: OBJ: 32. ANS: OBJ: 33. ANS: OBJ: 34. ANS: OBJ: 35. ANS: OBJ: 36. ANS: OBJ: 37. ANS: OBJ: 38. ANS: OBJ: 39. ANS: OBJ: 40. ANS: OBJ: 41. ANS: OBJ: 42. ANS: OBJ: 43. ANS: OBJ: 44. ANS: OBJ: 45. ANS: OBJ: 46. ANS: 47. ANS: 48. ANS: 49. ANS: OBJ: 50. ANS: 51. ANS: OBJ: D 16.1.3 D 15.2.2 A 15.2.2 A 16.1.2 D A 19.1.1 A 19.1.1 D 19.1.1 A 19.2.1 D 19.2.1 A 19.1.2 A 19.1.2 A 19.2.2 D 19.2.1 A 19.2.2 B 19.2.2 D 19.2.2 A 19.2.1 C 19.2.1 B 19.2.1 A D B B 19.2.2 C B 19.3.1 PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: STA: 1 Ch.6.c 1 Ch.6.b 1 Ch.6.b 1 Ch.6.d 1 1 Ch.5.a 1 Ch.5.a 1 Ch.5 1 Ch.5.b 1 Ch.5.b 1 Ch.5.e 1 Ch.5.e 1 Ch.5.f 1 Ch.5.d 1 Ch.5.d 1 Ch.5.d 1 Ch.5.d 1 Ch.5.f 1 Ch.5.f 1 Ch.5.f 1 1 1 1 Ch.5.d 1 1 Ch.5.c DIF: L2 DIF: L2 DIF: L3 DIF: L2 REF: p. 475 REF: p. 451 REF: p. 451 REF: p. 473
DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L2 DIF: L2 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1 DIF: L1
REF: p. 587 REF: p. 588 REF: p. 587 REF: p. 594 REF: p. 594 REF: p. 592 REF: p. 591 REF: p. 596 REF: p. 595 REF: p. 597 REF: p. 597 REF: p. 597 REF: p. 595 REF: p. 595 REF: p. 595
DIF: L2
REF: p. 597 | p. 598
DIF: L1
REF: p. 605
ID: A 52. ANS: OBJ: 53. ANS: OBJ: 54. ANS: OBJ: 55. ANS: OBJ: 56. ANS: OBJ: 57. ANS: OBJ: 58. ANS: OBJ: 59. ANS: 60. ANS: 61. ANS: OBJ: 62. ANS: OBJ: 63. ANS: A 19.1.2 B 19.3.2 C 19.3.2 B 19.3.1 A 19.3.3 D 19.3.3 B 19.3.4 D D A 19.4.2 C 19.4.1 D PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: PTS: PTS: STA: PTS: STA: PTS: 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 Ch.5.c 1 1 1 Ch.5 1 Ch.5 1 DIF: L2 DIF: L3 DIF: L3 DIF: L2 DIF: L2 DIF: L3 DIF: L3 REF: p. 588 REF: p. 609 REF: p. 609 REF: p. 607 REF: p. 607 REF: p. 607 REF: p. 608
DIF: L1 DIF: L1
REF: p. 613 | p. 614 | p. 615 REF: p. 613 | p. 614 | p. 615
Você também pode gostar
- Experiments in Physical Chemistry: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionNo EverandExperiments in Physical Chemistry: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical ChemistryDocumento19 páginasAnalytical ChemistryEshetie YenehunAinda não há avaliações
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisNo EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Modern Boiler Design 2012Documento28 páginasModern Boiler Design 2012Nguyễn Thanh TùngAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Converting Concentrations To Different UnitsDocumento2 páginas5 Converting Concentrations To Different UnitsJacob DaughertyAinda não há avaliações
- MCQS of Inorganic BS6THDocumento12 páginasMCQS of Inorganic BS6THPhoton Online Science AcademyAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ For Test Final 26-11-15Documento4 páginasMCQ For Test Final 26-11-15Aamir NaweedAinda não há avaliações
- Chem MCQ FinalDocumento258 páginasChem MCQ FinalDare DevilAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Chem Q&ADocumento8 páginasAnalytical Chem Q&AFritzhelle GernaleAinda não há avaliações
- Mcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarDocumento5 páginasMcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarPhoton Online Science Academy0% (1)
- Unit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment 0Documento5 páginasUnit 1 - How To Access The Portal: Assignment 0Fatma MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4rth Liquids and Solids McqsDocumento6 páginasChapter 4rth Liquids and Solids McqsHaider JalalAinda não há avaliações
- Aromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Documento14 páginasAromatic Hydrocarbon (Q.B.) (MSC)Raj ModiAinda não há avaliações
- 11c PDFDocumento44 páginas11c PDFHunnyAinda não há avaliações
- Mcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanDocumento29 páginasMcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanMalikXufyanAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 4-Day 4Documento6 páginasExam 4-Day 4Anabel AbulenciaAinda não há avaliações
- APEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFDocumento2 páginasAPEF Electrochem MC Ans PDFMuhammad UsmanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Equilibrium MCQDocumento13 páginasChemical Equilibrium MCQNidhi SisodiaAinda não há avaliações
- B 65 B 8075Documento13 páginasB 65 B 8075Bla NkAinda não há avaliações
- Harris QCA 8e Chapter 17 NewDocumento2 páginasHarris QCA 8e Chapter 17 NewClarisse WongAinda não há avaliações
- MFT Samp Questions ChemistryDocumento13 páginasMFT Samp Questions ChemistryМаријана КрговићAinda não há avaliações
- All Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFDocumento37 páginasAll Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFAGAH LUCKYAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM108 GuideDocumento18 páginasCHEM108 GuidenadyahginiceAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDocumento27 páginasMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 7 17 MC PracticeDocumento13 páginasTopic 7 17 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan Yadav100% (1)
- Acids and Bases StudentDocumento24 páginasAcids and Bases StudentVictor BritoAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsDocumento5 páginasAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونةAinda não há avaliações
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Documento12 páginasQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Mcqs For Ssc-IDocumento5 páginasChemistry Mcqs For Ssc-IAbdul QayyumAinda não há avaliações
- APEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2Documento2 páginasAPEF - Electrochemistry - Multiple Choice Questions - Page 1 of 2alyaa sheirAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 As Chemistry Chapter 11 Review - GASESDocumento11 páginas2013 As Chemistry Chapter 11 Review - GASESbiancae697Ainda não há avaliações
- Distribution CoefficientDocumento5 páginasDistribution CoefficientPrem Mohan SinghAinda não há avaliações
- اسئلة MCQ reactorDocumento5 páginasاسئلة MCQ reactorSalah Farhan NoriAinda não há avaliações
- Class Test 1: Section A (Multiple-Choice Questions)Documento10 páginasClass Test 1: Section A (Multiple-Choice Questions)Kgaugelo TraciaAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrochemDocumento75 páginasElectrochemMhyl HitsuyagamikaelsonAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Documento7 páginasMCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Sanjeev Chaudhary100% (1)
- Solved Multiple Choice Questions Chemical EquilibriumDocumento16 páginasSolved Multiple Choice Questions Chemical EquilibriumAliLakhoAinda não há avaliações
- XII Physics MCQS With KeyDocumento38 páginasXII Physics MCQS With KeyfateenAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFDocumento9 páginasICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFPrajakta DigheAinda não há avaliações
- T.Y.B.Sc .-V Analytical-ChemistryDocumento9 páginasT.Y.B.Sc .-V Analytical-ChemistryVaibhav GadeAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 9 (MCQs-Other Boards)Documento85 páginasChemistry 9 (MCQs-Other Boards)Zaheer AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry McqsDocumento51 páginasChemistry McqsEngr Muhammad MubeenAinda não há avaliações
- Test - D18 Dec 2022Documento9 páginasTest - D18 Dec 2022PrinceAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Chemistry - MCQsDocumento11 páginasSurface Chemistry - MCQsHumaira RazzaqAinda não há avaliações
- Question BankDocumento39 páginasQuestion Bankamany mohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Chemistry Book2Documento272 páginasInorganic Chemistry Book2bhaks1976Ainda não há avaliações
- R A e R A K X X R: InstructionsDocumento2 páginasR A e R A K X X R: InstructionsAdrian NavarraAinda não há avaliações
- Aromaticity: Aromaticity: Benzenoid and Non-Benzenoid Compounds - Generation and ReactionsDocumento7 páginasAromaticity: Aromaticity: Benzenoid and Non-Benzenoid Compounds - Generation and ReactionsSankar AdhikariAinda não há avaliações
- Radiolysis of Water MCQ: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 MSC I-Organic ChemistryDocumento2 páginasRadiolysis of Water MCQ: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 MSC I-Organic ChemistrySarita YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Exam 4 2007 PDFDocumento12 páginasExam 4 2007 PDFanon_281065744Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 151Documento5 páginasAssignment 151Hai Xuan DoAinda não há avaliações
- High Pressure Liquid Chromatography - Analytical Instrumentation Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocumento4 páginasHigh Pressure Liquid Chromatography - Analytical Instrumentation Questions and Answers - SanfoundryVarsha Bankar Dhodre0% (1)
- Moving Charges FinalDocumento41 páginasMoving Charges FinalVinothAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Base - Q - MSDocumento41 páginasAcid Base - Q - MSAnonymous AAinda não há avaliações
- KSP MCQDocumento5 páginasKSP MCQalvin2282Ainda não há avaliações
- A) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionDocumento5 páginasA) Iron's Molar Mass Must Be Known To Calculate The Moles of Iron in SolutionBla NkAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Renewal TheoryDocumento3 páginasSurface Renewal TheoryMonty Jack-Sparrow DavisAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ On Mass Spectroscopy: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 Msc-I Organic ChemistryDocumento3 páginasMCQ On Mass Spectroscopy: Sarita Lalji Yadav Roll No-26 Msc-I Organic ChemistrySarita YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Energy: Thermodynamics & Statistical PhysicsDocumento4 páginasEnergy: Thermodynamics & Statistical PhysicsM. BalakrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- 10.true False (D and F Block Elements)Documento11 páginas10.true False (D and F Block Elements)rajeshwariAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsDocumento3 páginasChem 132 2019 Tutorial QuestionsYusuf Zaynab100% (1)
- Organic reactive intermediatesNo EverandOrganic reactive intermediatesSamuel McManusAinda não há avaliações
- Uops4 Exp ScreeningDocumento6 páginasUops4 Exp ScreeningCasey SangalliAinda não há avaliações
- Propiedades Termodinámicas R134ADocumento4 páginasPropiedades Termodinámicas R134AedhcoAinda não há avaliações
- B400 Physical ChemistryDocumento56 páginasB400 Physical ChemistryCasey SangalliAinda não há avaliações
- ALMA ElectronicsDocumento2 páginasALMA ElectronicsCasey Sangalli100% (2)
- Chapter 13Documento8 páginasChapter 13Casey SangalliAinda não há avaliações
- Probs UmDocumento13 páginasProbs UmCasey SangalliAinda não há avaliações
- CHPT 22 TestDocumento5 páginasCHPT 22 TestCasey SangalliAinda não há avaliações
- 3.AcidBases FinalDocumento35 páginas3.AcidBases FinalSoham RaneAinda não há avaliações
- MasterSpec Consolidated TOCDocumento39 páginasMasterSpec Consolidated TOCsheevesAinda não há avaliações
- Chromatography PharmacyDocumento41 páginasChromatography PharmacyfarisaAinda não há avaliações
- Installation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyDocumento28 páginasInstallation and Operating Instructions: Busch Produktions GMBH Schauinslandstr. 1 79689 Maulburg GermanyRenārs BērtiņšAinda não há avaliações
- The 7 TH International Conference On Unsaturated Soils (UNSAT2018)Documento7 páginasThe 7 TH International Conference On Unsaturated Soils (UNSAT2018)pooAinda não há avaliações
- Scale-Up of Protein Purification Downstream Processing Issues PDFDocumento13 páginasScale-Up of Protein Purification Downstream Processing Issues PDFCapAinda não há avaliações
- (2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewDocumento16 páginas(2017) Toxicological Effects of Glycyrrhiza Glabra (Licorice) A ReviewicaAinda não há avaliações
- Indian Regulations On Food PackgingDocumento20 páginasIndian Regulations On Food PackgingchoudhurykisanAinda não há avaliações
- HINO Cableado ElectricoDocumento11 páginasHINO Cableado ElectricoWalter Eduard100% (1)
- Dissolution TestDocumento5 páginasDissolution TestAlecza Mae SavellaAinda não há avaliações
- Cut Diet Lean MassDocumento62 páginasCut Diet Lean Masspakzeeshan167% (3)
- Sarcosine MsdsDocumento41 páginasSarcosine MsdsAnonymous ZVvGjtUGAinda não há avaliações
- Poster Carica PDFDocumento1 páginaPoster Carica PDFBimo A.SAinda não há avaliações
- Phyton 27 MSDSDocumento2 páginasPhyton 27 MSDSBernardo UenoAinda não há avaliações
- Gravimetric Analysis Laboratory ReportDocumento9 páginasGravimetric Analysis Laboratory ReportShawn RizalAinda não há avaliações
- AIChE Journal Volume 23 Issue 6 1977 (Doi 10.1002/aic.690230602) Karl Gardner Jerry Taborek - Mean Temperature Difference - A ReappraisalDocumento10 páginasAIChE Journal Volume 23 Issue 6 1977 (Doi 10.1002/aic.690230602) Karl Gardner Jerry Taborek - Mean Temperature Difference - A Reappraisalneozero2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Alcohols (The Production Of)Documento15 páginasAlcohols (The Production Of)verity glenAinda não há avaliações
- IB-DU1000 Metal-Enclosed Bus PDFDocumento12 páginasIB-DU1000 Metal-Enclosed Bus PDFdestro57Ainda não há avaliações
- Agricultural Control Chemicals (1950)Documento277 páginasAgricultural Control Chemicals (1950)Sveti JeronimAinda não há avaliações
- Specifications: Customer Item Model Name Part No DateDocumento11 páginasSpecifications: Customer Item Model Name Part No Datejoroma58Ainda não há avaliações
- 4th Health2 For Demo Explicit TeachingDocumento4 páginas4th Health2 For Demo Explicit TeachingLeony Cipriano100% (2)
- DS335 - E - Earthing ImprovementDocumento2 páginasDS335 - E - Earthing ImprovementCarlos PintoAinda não há avaliações
- Wear Debris AnalysisDocumento2 páginasWear Debris Analysisthoma111sAinda não há avaliações
- "Promotional Activity of RCF Fertilizers Through Print Media (RCF Sheti PatrikaDocumento26 páginas"Promotional Activity of RCF Fertilizers Through Print Media (RCF Sheti PatrikagirishtorawaneAinda não há avaliações
- Dehydrated Culture MediaDocumento92 páginasDehydrated Culture MediaTitan Biotech Ltd.0% (1)
- Ipa18 202 SeDocumento15 páginasIpa18 202 SeDimas Suryo WicaksonoAinda não há avaliações
- Fick Second LawDocumento9 páginasFick Second LawJohnny WoodsAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Management AustriaDocumento34 páginasWaste Management AustriaregiapursofAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo Scientific Taq Dna Polymerase With KCL Buffer: DescriptionDocumento3 páginasThermo Scientific Taq Dna Polymerase With KCL Buffer: DescriptionCHIRANJEEVIAinda não há avaliações