Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
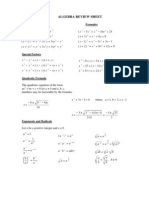
Integer INTEGRAL EXPONENTS
Enviado por
Rosenia Santiago PascualDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Integer INTEGRAL EXPONENTS
Enviado por
Rosenia Santiago PascualDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
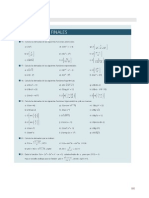
Integer Exponents
Laws of Exponents
(1) x m x n = x m + n
(2)
xm
x
= x
mn
Example: x 5 x 2 = x 7
, if m > n
x10
Examples:
= x8
1, if m = n
1
x2
, if m < n
xnm
( )n = x mn
x6
1
x4
( )3 = x 6
(3) x m
Example: x 2
(4) (xy )n = x n y n
Example: (xy )3 = x 3 y 3
x
xn
(5) =
yn
y
x
x2
Example: =
y2
y
(6) x 0 = 1 , x 0
Example: 2 x 3 y
(7) x n =
1
x
x
(8)
y
,
x
y
=
x
= xn
)0 = 1
Examples: 2 3 =
2
Example:
3
1
= ,
8
2
= x4
32 9
3
= =
=
2
22 4
Additional Examples:
(1) x 3 x 2 =
(3)
x2
x3
1
x
(2) x 3 y 2
)2 = x 6 y 4 = xy 6
(2x 2 y 3 )1 (x 3 y 4 )3 = 2 1 x 2 y 3 x 9 y 12 = y 3 x 9 y 2 = x 9 y 5 = x
22 x6 y 2
2 2 x 6 21 x 2 y12 2 3 x 8 y12 8 y 7
(2 x 3 y 1 )2
1
Practice Sheet Integer Exponents
I. Evaluate each of the following:
1
(1) 3 4 =
(4) 3 2 =
(7)
(2) ( 2) 3 =
(5) (2) 3 =
2
(8)
3
(3) (4) 4 =
3
(6) =
4
2 3
=
3
(9) (25) 0 =
II. Simplify; write answers with only positive exponents and assume that all variables are
non-zero:
( )4 =
(1) x 4 x 5 =
(9) x 3
(2) 2 3 2 7 =
(10) x 2 y 3
(3)
(4)
(5)
x8
x4
x3
x9
28
25
(12) x 2 y 3 xy 2
(13) x 2 y 2
( )5 =
(8)
)3 =
x2
=
(11)
y 3
(6) x 3
(7) x
x 4
x7
x =
(14)
(15)
(16)
)( )3 =
)3 (x 4 y 5 ) =
x 3 y 2
x4 y5
(x 2 y 3 )2
x4 y5
(2 x 2 y )2 =
(3x 1 y 4 )(xy 2 )3
2
Solution Key for Integer Exponents
I. (1) 81
(4)
1
9
(2) 8
(5)
(3) 256
(6)
II. (1) x 9
(7) 2 3 = 8
1
8
(8)
27
64
(9) 1
(9)
x12
y9
(2) 210 = 1024
(10)
(3) x 4
(11) x 4 y 6
(12) x 5 y 9
(4)
27
8
(5) 2 3 = 8
(13)
(6) x15
(14)
(7) x 2
(15)
(8) x 3
(16)
x6
x2
y11
1
x7 y3
y
x8
1
12 x 6
Você também pode gostar
- A2 Cornhole QuadraticsDocumento20 páginasA2 Cornhole QuadraticsRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Angles in Standard Position WorksheetDocumento5 páginasAngles in Standard Position WorksheetRosenia Santiago Pascual0% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of FFT Analyzer TechnologyDocumento3 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of FFT Analyzer TechnologyNarendra KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- VLAN Implementation BenefitsDocumento13 páginasVLAN Implementation Benefitsdev_panwarAinda não há avaliações
- Penyelesaian: Log (17 X +5 Y) 17 X +5 Y: MATDAS I (Hal 34) Hitung X Dan y Dari: 1. (4 X 7) 1 3 4.3 27Documento19 páginasPenyelesaian: Log (17 X +5 Y) 17 X +5 Y: MATDAS I (Hal 34) Hitung X Dan y Dari: 1. (4 X 7) 1 3 4.3 27dhanda1Ainda não há avaliações
- DERIVADASDocumento12 páginasDERIVADASJesús Los ArcosAinda não há avaliações
- The Evolution of Calculus: AnswersDocumento11 páginasThe Evolution of Calculus: AnswersAtharva DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Equations and Inequalities IDocumento4 páginasEquations and Inequalities IElvir CrncevicAinda não há avaliações
- Factorizar: Ejercicio 1 ResueltoDocumento7 páginasFactorizar: Ejercicio 1 ResueltoBenjamin Alejandro Casanova FloresAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Calculus I (SS)Documento11 páginas2013 Calculus I (SS)sholeslotAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of Absolute ValueDocumento5 páginasDefinition of Absolute ValueLae LeeAinda não há avaliações
- C D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X FDocumento0 páginaC D I 2 L E - D: X X X F X X X X Fglobaltech164768Ainda não há avaliações
- Guía Final LogDocumento4 páginasGuía Final LogJavier Cerda InfanteAinda não há avaliações
- MatematicasDocumento9 páginasMatematicasYoel Lopez MejiasAinda não há avaliações
- Limits: (EAMCET 2009)Documento6 páginasLimits: (EAMCET 2009)vipulAinda não há avaliações
- Operations On Polynomials (Revised)Documento6 páginasOperations On Polynomials (Revised)Elvin PrestoAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet: Logarithmic FunctionDocumento12 páginasWorksheet: Logarithmic FunctionKatrina ElleAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra Review 05Documento2 páginasAlgebra Review 05lmlAinda não há avaliações
- CaaaDocumento2 páginasCaaaOrigamiAinda não há avaliações
- 5.real NumbersDocumento10 páginas5.real Numbersbhariprasad_mscAinda não há avaliações
- SolutionsDocumento3 páginasSolutionskakuzakumitroshoshiAinda não há avaliações
- 2011 Maths Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsDocumento12 páginas2011 Maths Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsCisum ErupAinda não há avaliações
- Mi AH Mathematics All 2011Documento12 páginasMi AH Mathematics All 2011QwaAlmanlawiAinda não há avaliações
- Sim Cee 100 Week 1 9 Unit1Documento30 páginasSim Cee 100 Week 1 9 Unit1Lance Kristoffer Lamera LewisAinda não há avaliações
- 101 - Full Derivative ReportDocumento25 páginas101 - Full Derivative ReportAmroKashtAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering MathsDocumento8 páginasEngineering MathsSanthosh SanAinda não há avaliações
- Guia 1 Inf 11Documento4 páginasGuia 1 Inf 11Ingrid GuerraAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Quadratic FunctionsDocumento26 páginas3 Quadratic FunctionsMariAm NabiLah NaSrudinAinda não há avaliações
- Real Numbers: Key FormulaeDocumento7 páginasReal Numbers: Key FormulaeKomanduri Murali SrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- PT BPT Mu Va Logarit Phan2Documento26 páginasPT BPT Mu Va Logarit Phan2Duc NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook of Industrial Engineering Equations, Formulas and CalculationsDocumento8 páginasHandbook of Industrial Engineering Equations, Formulas and CalculationsartustAinda não há avaliações
- CEBEP Bridging Algebra 2Documento8 páginasCEBEP Bridging Algebra 2cebep math pilipinasAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra Review SheetDocumento2 páginasAlgebra Review SheetGiulio CAinda não há avaliações
- Balik Aral (Algebra)Documento17 páginasBalik Aral (Algebra)Mj DimapilisAinda não há avaliações
- Matlab Assignment 4Documento5 páginasMatlab Assignment 4Carlo KaramAinda não há avaliações
- DifferentiationDocumento35 páginasDifferentiationMariAm NabiLah NaSrudinAinda não há avaliações
- Ejercicios de Derivadas para 1º Bachiller CCSS (Y 2)Documento2 páginasEjercicios de Derivadas para 1º Bachiller CCSS (Y 2)leoncio54Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006Documento2 páginasWorksheet 7: Math3 (814013) - Group F31 - Fall 2006dennieboyAinda não há avaliações
- Derivadas: Hallar, SiDocumento6 páginasDerivadas: Hallar, SiYack Brenan Palma PilcoAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra ExerciciosDocumento3 páginasAlgebra ExerciciosEstevao DimacaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersDocumento8 páginasUnit 2 Chapter 13 AnswersashtigosineAinda não há avaliações
- Secondary III Concept Notebook 120514Documento4 páginasSecondary III Concept Notebook 120514api-272176575Ainda não há avaliações
- 2k Summary of Differentiation TechniquesDocumento7 páginas2k Summary of Differentiation Techniques13sandipAinda não há avaliações
- Finding Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsDocumento3 páginasFinding Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsRonan SibbalucaAinda não há avaliações
- Questions On EXACT and NON-EXACT Equations (Zill 8 Edition, 2005)Documento1 páginaQuestions On EXACT and NON-EXACT Equations (Zill 8 Edition, 2005)lakersem310Ainda não há avaliações
- IB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1Documento13 páginasIB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1DeeganasAinda não há avaliações
- 薛定宇 高等应用数学问题matlab求解(第三版)课后答案 PDFDocumento160 páginas薛定宇 高等应用数学问题matlab求解(第三版)课后答案 PDFAlexandra WangAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Graphs and Polynomials SolutionsDocumento24 páginasChapter 1 Graphs and Polynomials SolutionsTSebastiaanVanWagensveldAinda não há avaliações
- Soluciones A "Ejercicios y Problemas" Soluciones A "Ejercicios y Problemas"Documento6 páginasSoluciones A "Ejercicios y Problemas" Soluciones A "Ejercicios y Problemas"eveeeeeAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra of Matrices: Previous Eamcet BitsDocumento10 páginasAlgebra of Matrices: Previous Eamcet BitseamcetmaterialsAinda não há avaliações
- Functions, Limits & Continuity DifferentiationDocumento5 páginasFunctions, Limits & Continuity DifferentiationSharath Aefdsffdf FdAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersDocumento28 páginasUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineAinda não há avaliações
- Tecnicas de DerivacionDocumento5 páginasTecnicas de DerivacionBreisner CamachoAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential and Logarithmic Functions: Properties of Exponents and LogarithmsDocumento11 páginasExponential and Logarithmic Functions: Properties of Exponents and LogarithmsWidodo PurwantoAinda não há avaliações
- Quadratic Functions PDFDocumento26 páginasQuadratic Functions PDFyen 1978Ainda não há avaliações
- 2011 MAV Exam 1 SolutionsDocumento4 páginas2011 MAV Exam 1 SolutionslAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Geometry: y y M X XDocumento10 páginasAnalytical Geometry: y y M X XKomanduri Murali SrinivasAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsAinda não há avaliações
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageAinda não há avaliações
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Ainda não há avaliações
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Ninjago Bunting LloydDocumento1 páginaNinjago Bunting LloydRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Mil QaDocumento7 páginasMil QaRosenia Santiago Pascual100% (1)
- Quadrantal Angles Worksheet Answer Key Points: 0 Evaluate.: o o o oDocumento2 páginasQuadrantal Angles Worksheet Answer Key Points: 0 Evaluate.: o o o oRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Ninjago Bunting ZaneDocumento1 páginaNinjago Bunting ZaneRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture ProbabilityDocumento2 páginasLecture ProbabilityRosenia Santiago Pascual100% (1)
- Information Literacy QuizDocumento7 páginasInformation Literacy QuizRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Coterminal Angles and Reference Angles PDFDocumento4 páginasCoterminal Angles and Reference Angles PDFMark Abion ValladolidAinda não há avaliações
- Semester 2 - Test #8 - Practice: Multiple ChoiceDocumento6 páginasSemester 2 - Test #8 - Practice: Multiple ChoiceRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- First Year and Second Year MTAPDocumento8 páginasFirst Year and Second Year MTAPandroidaptoide100% (4)
- Square of BinomialDocumento7 páginasSquare of BinomialRosenia Santiago Pascual67% (6)
- Module 1 Tg-Grade 8 MathematicsDocumento62 páginasModule 1 Tg-Grade 8 MathematicsGary Nugas76% (29)
- Solving One-Step Equations: Let's PracticeDocumento5 páginasSolving One-Step Equations: Let's PracticeRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Question 2: What Is A Linear Function?: Example 2 Determine If An Equation Represents A FunctionDocumento8 páginasQuestion 2: What Is A Linear Function?: Example 2 Determine If An Equation Represents A FunctionRosenia Santiago PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Square of BinomialDocumento7 páginasSquare of BinomialRosenia Santiago Pascual67% (6)
- Apollo DevelopmentsDocumento2 páginasApollo DevelopmentscarlosAinda não há avaliações
- Synopsis On Turing MachineDocumento4 páginasSynopsis On Turing MachineVivek MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Tempo2 Examples Ver1 PDFDocumento41 páginasTempo2 Examples Ver1 PDFCassey WashingtonAinda não há avaliações
- How To Convert A Number To WordsDocumento20 páginasHow To Convert A Number To WordsdanieldotnetAinda não há avaliações
- MB Memory Ga g41m ComboDocumento2 páginasMB Memory Ga g41m Combonotsure1Ainda não há avaliações
- Iso21500 Management Products Map 130105 v1 0 HENNY PORTMANDocumento1 páginaIso21500 Management Products Map 130105 v1 0 HENNY PORTMANjrinconcolAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding AES Mix-Columns Transformation Calculation: Kit Choy Xintong University of Wollongong, Year 3 StudentDocumento4 páginasUnderstanding AES Mix-Columns Transformation Calculation: Kit Choy Xintong University of Wollongong, Year 3 StudentViet Xuan DaoAinda não há avaliações
- SRIM Setup MessageDocumento3 páginasSRIM Setup MessageRicardo Bim100% (1)
- Jitter and WanderDocumento2 páginasJitter and WanderFareed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Computers in RailwaysDocumento1.014 páginasComputers in Railwaysgokulvarmarajak100% (5)
- Using Tooltips On ControlsDocumento4 páginasUsing Tooltips On Controlsyuo2Ainda não há avaliações
- Weiss - Cryp PDFDocumento3 páginasWeiss - Cryp PDFDaniele SambenedettoAinda não há avaliações
- Passport Automation SystemDocumento140 páginasPassport Automation SystemjimAinda não há avaliações
- UGC NET Answer Key Home Science - July 2016 UGC NET JULY 2016 - CBSE-NETDocumento5 páginasUGC NET Answer Key Home Science - July 2016 UGC NET JULY 2016 - CBSE-NETsubirAinda não há avaliações
- MATLAB/SIMULINK Based Model of Single-Machine Infinite-Bus With TCSC For Stability Studies and Tuning Employing GADocumento10 páginasMATLAB/SIMULINK Based Model of Single-Machine Infinite-Bus With TCSC For Stability Studies and Tuning Employing GAsathish@gk100% (2)
- Multiple Hypothesis Tracking For Multiple Target TrackingDocumento14 páginasMultiple Hypothesis Tracking For Multiple Target TrackingMinh Long Tran0% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv - A Calabarzon City Schools Division of CabuyaoDocumento2 páginasRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Iv - A Calabarzon City Schools Division of CabuyaoMaann RubioAinda não há avaliações
- Math QuizDocumento2 páginasMath QuizAllyvic Albarico OteroAinda não há avaliações
- This Manual Is Part of The Tru-Balance Box-Type Sifter and Should Be Kept Near The Machine For Users To ReadDocumento1 páginaThis Manual Is Part of The Tru-Balance Box-Type Sifter and Should Be Kept Near The Machine For Users To ReadmiguelAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual 11 DSADocumento12 páginasLab Manual 11 DSAinft18111035 KFUEITAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Things Every System Administrator Should Know About OpensshDocumento7 páginas7 Things Every System Administrator Should Know About Opensshsumit303Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Programming: Seif Haridi KTHDocumento44 páginasIntroduction To Programming: Seif Haridi KTHengineer_khaula7035Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco UCS To Brocade Connectivity Guide: White PaperDocumento33 páginasCisco UCS To Brocade Connectivity Guide: White Paper5songAinda não há avaliações
- PLSQL 2 2Documento23 páginasPLSQL 2 2ssmileAinda não há avaliações
- Questions and Answers About Proof by InductionDocumento16 páginasQuestions and Answers About Proof by InductionJulio JoséAinda não há avaliações
- A Quick and Simple Guide To Crontab Usage - CrontabrocksDocumento3 páginasA Quick and Simple Guide To Crontab Usage - CrontabrocksbaazigarAinda não há avaliações
- RTS MID AnswersDocumento11 páginasRTS MID AnswershafeezaAinda não há avaliações
- Bible HistoryDocumento81 páginasBible Historyram ganeshAinda não há avaliações