Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Light
Enviado por
lilysuhany0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações4 páginasDiagram 9. Shows a ray of light directed perpendicularly at a side of the semi circular glass block. The ray passes through the glass block to a point O before leaving the glass block. The angle of incidence in the glass block is 30deg. Distance to the size of image that formed on the screen.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDiagram 9. Shows a ray of light directed perpendicularly at a side of the semi circular glass block. The ray passes through the glass block to a point O before leaving the glass block. The angle of incidence in the glass block is 30deg. Distance to the size of image that formed on the screen.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações4 páginasLight
Enviado por
lilysuhanyDiagram 9. Shows a ray of light directed perpendicularly at a side of the semi circular glass block. The ray passes through the glass block to a point O before leaving the glass block. The angle of incidence in the glass block is 30deg. Distance to the size of image that formed on the screen.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
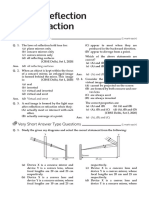
CHAPTER 5:LIGHT distance to the size of image that formed on the
1.(a). Diagram 9.1 shows a ray of light screen. [ 5 marks ]
directed perpendicularly at a side of the
semi circular glass block. The ray passes
through the glass block to a point O
before leaving the glass block. The angle
of incidence in the glass block is 30°.
You are required to give suggestions to
design a fibre optics which can works Diagram 9.4
efficiently. Using your knowledge on (c) While driving a car on a hot day, you may see a
light, and the properties of material, mirage on the road. Explain how mirage occurred.
explain [ 4 marks ]
the suggestion based on the following
Diagram 9.1 aspects; (d) Diagram 9.5 shows a simple astronomical
(i) What is meant by angle of incidence? (i) the refractive index of outer and telescope.
(ii) Explain how total internal reflection inner layer
occurs in (ii) flexibility
Diagram 9.1 above? (iii) strength
[4 marks] (iv) thickness
(v) density of the glass Diagram 9.5
(b) Diagram 9.2 and Diagram 9.3 show two By using two prism and a telescope in Diagram 9.5,
rectangular glass blocks with different suggest modification that can be done to make a
optical density and refractive index. Ray 2.A slide projector is used to view an image from
a slide. The power of the lens used by the binocular.
of light is directed toward the glass In your explanation,
blocks with the same angle of incidence projector slide is + 5D.
(a) What is meant by power of lens?. [ 1 mark ] (i) draw the arrangement of the prisms and lenses
30°. (ii) draw ray diagram to explain how the image form
Density = 2600 kgm-3 Density = 2670 kgm-3 (b) A student used a slide projector to view the
image from the slide. When the slide is place (iii) state two advantages using binocular compared
nearer to the lens the sharp image form on the to telescope when observing far object on the
screen as shown in Diagram 9.1. ground. [ 10 marks ]
When the slide is place further from the lens the
sharp image form on the screen as shown in
3.(a) Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2 show a transparent
block made of a material with a different
refractive index. A light ray travel in both
Diagram 9.2 Diagram 9.3 blocks with the same incident angle, i.
Based on Diagram 9.2 and Diagram 9.3,
(i) compare the densities of the glass
blocks.
(ii) compare the refractive index of the
glass blocks
(iii) compare the angle of refraction of the
glass blocks
(iv) relate the angle of refraction, r and the Based on Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2, compare (i) What is meant by a refractive index? [1 mark]
density of the glass blocks. the object distance, the image distance and size of (ii) Using Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2, compare the
(v) relate the angle of refraction, r and the image that formed on the screen. Relate the object refractive index, refraction angle and critical
refractive index of the glass blocks distance to the image distance and the object angle between the two blocks. Base on Diagram
[5 marks] 9.1 and Diagram 9.2, relate the refractive index
(c) Diagram 9. 4 shows a fibre optic. with critical angle. [5 marks]
1
(b) (i) State two conditions under which light ray
would undergo total internal reflection. [2 marks]
(ii) Diagram 9.3 shows a light ray is incident on a piece
of Crown Glass of critical angle 42°.Draw the light
ray to show how a ray emerging from the Crown
Glass
DIAGRAM 9.1
(c) Diagram 9.4 shows the structure of an optical fibre
used in telecommunications.
(a) (i) What is meant by real image? [1 mark] DIAGRAM 9.2
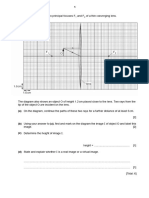
(i) Based on Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2,
compare the object distance, the image (a) (i) What is meant by focal length? [1 mark]
distance and the size of image. Relate the size (ii) With reference to Diagram 9.1 and Diagram
of the image with the image distance to make 9.2, compare the thickness of the lenses and
a deduction regarding the relationship the effects it has on the refracted rays to
Optical fibres are made of fine strands of glass. Each between the object distance and the size of the make a deduction regarding the relationship
single glass fibre (inner core) is coated with a thin layer image. [5 marks] between the thickness of the lenses and their
of another type of glass (outer cladding).You are (b) Describe how you estimate the focal length of focal length. [5 marks]
required to give some suggestions in designing an a convex lens. [4 marks] (b) Diagram 9.3 shows the ray diagram of a
optical fibre which can carry more information. (c) You are given two convex lenses, R and S, simple microscope.
Explain your suggestions base on the following aspects: with focal lengths of 40 cm and 10 cm
(i) refractive index of the inner and outer glass respectively. Both the lenses are used to build
(ii) the properties of material used for optical fibre a compound microscope.
(iii) the thickness of the glass [10 marks] (i) Using the two lenses, explain how you would
build a compound microscope. [6 marks]
4. Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2 show light rays from (ii) Suggest a suitable optical device to modify
two identical objects passing through a convex the microscope you built in (c)(i) to produce
lens.Both situations produce real images. F is the brighter image.
focal point for the convex lens (c)(i) supaya menghasilkan imej yang lebih jelas.
[2 marks]
(iii) Suggest and explain a method to produce a
bigger image in the compound microscope.
[2 marks] Fe : Focal point of eyepiece.
Fo : Focal point of objective lens.
5.Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2 show the parallel
rays of light directed towards the convex lenses
J and K. Both the lenses produce real images. F
is the focal point for each lens. DIAGRAM 9.3
(i) State the function of the eyepiece. [1 mark]
2
(ii) State the characteristics of the image formed by a
microscope. [3 marks] (d) Figure 9(d) shows a man who is standing in a
(c) You are given two convex lenses S and Q of swimming pool.
different focal length. Lens S has a longer
focal length than lens Q.
(i) Using the two lenses above explain how are
you would make a simple astronomical
telescope. [4 marks]
(ii) Suggest modification that need to be done
on the telescope to produce clearer and
bigger images. [6
marks]
(i) State your observation on the length of
On a hot and sunny day, a driver sees a pool of his feet and explain your observation.
water on the road in front of him. The position of [3 marks]
driver and the pool of water are as shown in (ii) The depth of water is 0.4 m. calculate
Figure 9(b). the distance of the image of the foot at
(a)(i) Explain the meaning of refractive index [1 point P from the surface of the water.
mark] [Refractive index of water = 1.33]
6.Diagram 9.1 and 9.2 show light rays passing through
(ii) Based on your observations in the above
a convex and a concave lenses.
figures, state the common characteristics.
Relate the above common characteristics to
deduce a relevant physics concept. [5
marks]
(b) Which mirror is used as the rear mirror of 8. Figure 4 shows two ways of making a fire
vehicles? Explain your answer. [3 marks]
(c) Figure 9(c) below shows a spear which was
thrown by a fisherman towards a fish in a
(a)(i) Define reflective index of a medium [1 mark] pool.
(ii) With reference to Diagram 9.1 and 9.2, compare
the light ray before and after passing through both
lenses. And then deduce a physics concept. [5 marks]
(b) Explain why a fish in a pond able to see objects
around although there are obstacles. [4 marks] Figure 4
(c) You are given two right angles prisms to build a
periscope (a) i. What are the energy changes
(i) Explain how you are going to build a periscope. involved? [1m]
[6 marks]
(i) Given that the spear did not hit the
(ii) Suggest modification to be made to convert the ii. Based on your observations of the
fish, explain the observation.
periscope to binoculars [4 marks] first and second situations, describe the
[3 marks]
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show how the characteristics that differ in the
image of the fish is formed. situations. Then correlate the
7. Figure 9(a) shows a submarine which uses a characteristics to develop a physics
[2 marks]
periscope to see objects above the water surface. concept [5m]
(iii) Suggest a way which can be used by
(b) At the beginning of the century, a
the fisherman so that the spear hit the
scientist by the name of Archimedes
target. [ 1 mark]
successfully drove off enemy ships with
3
the help of women and children using
only mirrors. How did the women and
children help Archimedes? [4m]
(c) Periscope using prisms are better than
those using mirrors
i. How does the prismatic Explain what happens to the image if
periscope function? [4m] (i) the girl moves backwards 2 m (the
ii. How can a prismatic periscope focal length is 0.8 m)
be modified to see distant object (ii) the concave mirror replaced with
[6m] convex mirror
You may use the diagram to illustrate your
answers. [4 marks]
(d) You are given two pieces of plane mirrors
measuring 4 cm x 5 cm and a long cardboard tube
to make a periscope.
(i) Using the plane mirrors and other materials,
describe how you would make the periscope.
(ii) Explain why the images observed through the
periscope using plane mirrors are not very clear.
(iii) Suggest modification that can be made to the
periscope to produce clearer and bigger images.
[10 marks]
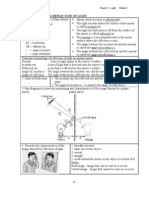
9.(a) Diagram 7.1 shows the parallel rays of light
directed towards the concave mirrors P and Q. In
each diagram, C is the centre of curvature, CM is
the radius of curvature of the mirror and F is the
focal point of the lens.
(a) What is meant by centre of curvature? [1 mark]
(b) Using Diagram 7.1 and Diagram 7.2, compare the
curvature of mirrors P and Q and the effects on
reflected rays. State the relationship between the
curvature of the mirrors and their focal lengths.
[5 marks]
(c) Diagram 7.3 shows a girl standing in front of a
concave mirror. The image formed in the mirror is
virtual image and bigger than original size.
Você também pode gostar
- Bab 6 Cahaya (K2-Skema)Documento28 páginasBab 6 Cahaya (K2-Skema)Shaavitaa naaidu MurugaiahAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan 5 & 9Documento6 páginasSoalan 5 & 9magisperanAinda não há avaliações
- Light - Reflection and Refraction - 2022-23 PYQDocumento9 páginasLight - Reflection and Refraction - 2022-23 PYQnithishwarann097Ainda não há avaliações
- Light 4 QPDocumento9 páginasLight 4 QPahmedAinda não há avaliações
- Light 4 QPDocumento9 páginasLight 4 QPHabibullah AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Light 4 QP - 240314 - 053608Documento10 páginasLight 4 QP - 240314 - 053608diyanooooooorAinda não há avaliações
- Mac Test F5 2009Documento6 páginasMac Test F5 2009NURUL AIN TAY BT ABDULLAH100% (1)
- 1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1Documento3 páginas1822-12 Phy P15 Ray Optics B 30Q (1) - 1JeevanAinda não há avaliações
- S5 Paper Ii Physics End of Term-YearDocumento5 páginasS5 Paper Ii Physics End of Term-Yearlubangakene.francisAinda não há avaliações
- General Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)Documento2 páginasGeneral Instructions: Section (A) : (1 Marks)exploreharyanaAinda não há avaliações
- S.6 Phy p2 Lubiri Test22Documento7 páginasS.6 Phy p2 Lubiri Test22kayiwaabdulrahman1Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Reflection at Curved Surfaces - New Aug 2022Documento18 páginas6 Reflection at Curved Surfaces - New Aug 2022WaleedAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Form FourDocumento143 páginasPhysics Form FourCarol SoiAinda não há avaliações
- Section B Paper 2 Chapter 2:forces and MotionDocumento12 páginasSection B Paper 2 Chapter 2:forces and Motionlilysuhany100% (4)
- Chapter 5 P2 AnswerDocumento13 páginasChapter 5 P2 AnswerSiti Hajar Johari100% (1)
- Kings College Budo (Physics) PDFDocumento3 páginasKings College Budo (Physics) PDFVictor Lusiba100% (1)
- Physics IRP - 3Documento11 páginasPhysics IRP - 3Cart KartikaAinda não há avaliações
- A With A Line in Column B.: Worksheet Light Grade 9Documento8 páginasA With A Line in Column B.: Worksheet Light Grade 9Marilyn Castro LaquindanumAinda não há avaliações
- Light Part 1 AssignmentDocumento6 páginasLight Part 1 AssignmentSumit WAinda não há avaliações
- 32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2Documento10 páginas32.4-Light-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qp 2LiliAinda não há avaliações
- Sainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XDocumento4 páginasSainik School Goalpara: Extra Homework Subject: Science (Physics) Class: XBornil Bikash BhuyanAinda não há avaliações
- Kings College Budo (Physics 2)Documento3 páginasKings College Budo (Physics 2)Victor Lusiba100% (1)
- XII Q Group 3Documento3 páginasXII Q Group 3Sanskriti VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Questions I: Plane Mirror Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Shape Effect On Parallel Rays Type of FocusDocumento1 páginaQuestions I: Plane Mirror Concave Mirror Convex Mirror Shape Effect On Parallel Rays Type of FocusGodfrey MuchaiAinda não há avaliações
- Homework 1: Chinese New Years BreakDocumento11 páginasHomework 1: Chinese New Years BreakgamahimeAinda não há avaliações
- 32.5 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPDocumento9 páginas32.5 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPLiliAinda não há avaliações
- Ncert 0Documento6 páginasNcert 0ritamnath337Ainda não há avaliações
- Light 3 QPDocumento10 páginasLight 3 QPMuhammad KalimAinda não há avaliações
- Light 2 QPDocumento11 páginasLight 2 QPgambixo3005Ainda não há avaliações
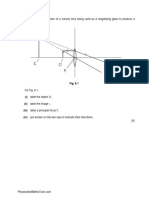
- Virtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce ADocumento11 páginasVirtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce AahmedAinda não há avaliações
- SET 4 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B5 2018 SkemaDocumento41 páginasSET 4 MODUL CEMERLANG FIZIK F4B5 2018 SkemaJeemion JealiAinda não há avaliações
- Problems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETDocumento19 páginasProblems On Ray Optics and Optical Instruments For NEETRohit Gupta100% (1)
- View Synthesis Using Convex and Visual HullsDocumento10 páginasView Synthesis Using Convex and Visual HullsCyrille LamasséAinda não há avaliações
- Waves WorksheetDocumento28 páginasWaves WorksheetShepherd W NgwenyaAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Worksheet - Reflection Refraction of LightDocumento3 páginasCBSE Class 10 Physics Worksheet - Reflection Refraction of LightDarshuram DudheAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Optics QBDocumento2 páginasWave Optics QBshivya aroraAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Optics MCQDocumento8 páginasRay Optics MCQVamsi Vangara100% (1)
- Light: CORE QuestionsDocumento10 páginasLight: CORE QuestionsBlahAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)Documento4 páginasPHYSICS-test Electric Potential, Current Electricity-A, Ray Optics-A 1mark Questions: (ANSWER ALL)shylaAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection at Curved SurfacesDocumento6 páginasReflection at Curved SurfacesTitus KaselaAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection & Refraction PDFDocumento5 páginasReflection & Refraction PDFSushri Sangeeta MohantyAinda não há avaliações
- Classroom Practice Assignment Cbse Class-X: PhysicsDocumento4 páginasClassroom Practice Assignment Cbse Class-X: PhysicsAditya MondalAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Optics TestDocumento4 páginasRay Optics TestPaarth GulatiAinda não há avaliações
- S.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past PapersDocumento3 páginasS.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past Paperskinene richardAinda não há avaliações
- Light PDFDocumento3 páginasLight PDFVasu GargAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5, Form 4Documento9 páginasChapter 5, Form 4Teoh MilayAinda não há avaliações
- 32.1 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPDocumento12 páginas32.1 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPnppxftgcdvAinda não há avaliações
- A Level Physics 2 QuestionsDocumento43 páginasA Level Physics 2 QuestionsTRIPPLE KAYZ UGAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Yr Phy-7CDocumento48 páginas2nd Yr Phy-7CRakshitha BSAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Kelas Bimbingan Fasa 2 Chapter 5: Light SPM 2003, Section A, No. 4 (7Documento9 páginasModul Kelas Bimbingan Fasa 2 Chapter 5: Light SPM 2003, Section A, No. 4 (7Teoh MilayAinda não há avaliações
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Objective SectionDocumento31 páginasLight - Reflection and Refraction: Objective SectionAnshul BagoriaAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection of Light TestDocumento2 páginasReflection of Light TestVaishnavi RajgopalAinda não há avaliações
- Hkcee Physics - Section 3 Waves - P.1Documento34 páginasHkcee Physics - Section 3 Waves - P.1Y AdaAinda não há avaliações
- Class 10 (Light)Documento31 páginasClass 10 (Light)Himanshu KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Igcse Phy 07Documento2 páginasIgcse Phy 07Kamrul Hasan SagarAinda não há avaliações
- Class X Light Q BANKDocumento1 páginaClass X Light Q BANKISHAAN GOYALAinda não há avaliações
- Light 1 QP PDFDocumento11 páginasLight 1 QP PDFalishaluthfiyaAinda não há avaliações
- LightDocumento8 páginasLightcxsdvAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To PhysicsDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To PhysicsChrise RajAinda não há avaliações
- Ohm's Law Peka 4pd3Documento2 páginasOhm's Law Peka 4pd3lilysuhany100% (4)
- Force and MotionDocumento29 páginasForce and MotionChrise RajAinda não há avaliações
- PrecautionaryDocumento2 páginasPrecautionarylilysuhany0% (1)
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Documento16 páginasTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- The Apparatus Is Set Up As Shown in The Diagram.: 1/u (CM) 1/v (CM)Documento3 páginasThe Apparatus Is Set Up As Shown in The Diagram.: 1/u (CM) 1/v (CM)lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- Skema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1Documento14 páginasSkema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- Bab 5Documento8 páginasBab 5lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- Rumus FizikDocumento2 páginasRumus Fiziklilysuhany80% (5)
- Bab 9Documento10 páginasBab 9Chrise RajAinda não há avaliações
- Latihan FpressureDocumento4 páginasLatihan FpressureMohamad Rizal MukhtarAinda não há avaliações
- Section B Paper 2 Chapter 2:forces and MotionDocumento12 páginasSection B Paper 2 Chapter 2:forces and Motionlilysuhany100% (4)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics: Diagram 2.1 Diagram 2.2Documento3 páginasChapter 1: Introduction To Physics: Diagram 2.1 Diagram 2.2lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Percubaan 2007 MRSM Physics Paper 2Documento28 páginasSPM Percubaan 2007 MRSM Physics Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (1)
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 WavesDocumento28 páginasNota Padat Fizik F5 Wavesslokkro98% (102)
- Chapter 5: LightDocumento21 páginasChapter 5: Lightlilysuhany100% (1)
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 RadioactivityDocumento23 páginasNota Padat Fizik F5 Radioactivityslokkro97% (33)
- SPM Trial Examination 2007Documento40 páginasSPM Trial Examination 2007lilysuhanyAinda não há avaliações
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectromagnetDocumento36 páginasNota Padat Fizik F5 Electromagnetslokkro100% (40)
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectronicDocumento21 páginasNota Padat Fizik F5 Electronicslokkro100% (24)
- Luminarios Lista09052011Documento116 páginasLuminarios Lista09052011NelvaAinda não há avaliações
- Tir Lens Guide-Web PDFDocumento8 páginasTir Lens Guide-Web PDFFilozófus ÖnjelöltAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable EnergiesDocumento4 páginasRenewable EnergiesGiampaolo SpiragliaAinda não há avaliações
- MANKO Low-E Cross Reference GlassDocumento2 páginasMANKO Low-E Cross Reference GlassbatteekhAinda não há avaliações
- 01.introduction To Lighting SystemsDocumento23 páginas01.introduction To Lighting SystemsInnovtech Solutions LankaAinda não há avaliações
- Dpi RequestDocumento4 páginasDpi RequestMuhammad Irwan MuhamadAinda não há avaliações
- Biotech q1w2Documento12 páginasBiotech q1w2Heena Grace PresidenteAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento8 páginasPDFDocAinda não há avaliações
- HW 1 WDocumento3 páginasHW 1 WAnni bannAinda não há avaliações
- Onyx Solar Asi Solutions Brochure SQMDocumento4 páginasOnyx Solar Asi Solutions Brochure SQMvarsha2795Ainda não há avaliações
- LONGi LR5 72HBD 545M RETC 211 210525 PV6-79.PANDocumento1 páginaLONGi LR5 72HBD 545M RETC 211 210525 PV6-79.PANsamc12Ainda não há avaliações
- Functions of The Parts of The MicroscopeDocumento2 páginasFunctions of The Parts of The MicroscopeNdawula IsaacAinda não há avaliações
- You See With Your EyesDocumento16 páginasYou See With Your EyesBiblioteca ContaderoAinda não há avaliações
- GE Photographic Lamp Guide 1990Documento92 páginasGE Photographic Lamp Guide 1990Alan Masters100% (1)
- Parts and Function of A MicroscopeDocumento1 páginaParts and Function of A Microscopevanessa81% (16)
- Sylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Documento12 páginasSylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Alan Masters100% (1)
- DG-10-98 IESNA Guide To Choosing Light Sources For General LightingDocumento20 páginasDG-10-98 IESNA Guide To Choosing Light Sources For General LightingfmtzvargasAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 01 The Microscope and MicrosDocumento3 páginasActivity 01 The Microscope and MicrosRacquel BanaoAinda não há avaliações
- Kromatix Glass DatasheetDocumento4 páginasKromatix Glass Datasheetvarsha2795Ainda não há avaliações
- Mirrors and Lenses NotesDocumento19 páginasMirrors and Lenses NotesBenard OchangoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ProjectDocumento9 páginasPhysics ProjectsamAinda não há avaliações
- Light Formula SheetDocumento1 páginaLight Formula SheetManoj KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Wall Light WL11Documento1 páginaWall Light WL11EliasAinda não há avaliações
- Zeiss Microscopy From The Very BeginningDocumento66 páginasZeiss Microscopy From The Very BeginningCarmen KetAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Photovoltaic System PT-SPS-N10 2Documento1 páginaSolar Photovoltaic System PT-SPS-N10 2efendi susantoAinda não há avaliações
- Lenses: Lesson 5 (3 Hours)Documento19 páginasLenses: Lesson 5 (3 Hours)DonnaAinda não há avaliações
- Solar Roof Top Roi Calculation TemplateDocumento5 páginasSolar Roof Top Roi Calculation TemplateSarath Chandra VAinda não há avaliações
- Mcqs For ReflectionDocumento5 páginasMcqs For ReflectionHariprasanthAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet-1.2: To Study Different Parts of MicroscopeDocumento5 páginasWorksheet-1.2: To Study Different Parts of MicroscopeTej pattaAinda não há avaliações