Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Enviado por
डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Enviado por
डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Determine the design angle FAB = 321 lb, FAB = 383 lb, FAB = 171.1 lb, FAB = 215 lb,
<90) bretween the two struts so that the 500-lb horizontal force has a
component of 600lb directed from A toward C. That is the component of force acting along member AB? A. B. C. D. = 40.0 = 36.9 = 20.0 = 52.7
Workspace
2.
If F1 = F2 = 30lb, determine the angles
and
so that the resultant force is directed along the
positive x axis and has a magnitude of FR = 20 lb. A. B. C. D. = = = = = 70.5 = 41.4 = 19.47 = 18.43
Workspace
3.
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
1/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Force F acts on peg A such that one of its components, lying in the x-y plane, has a magnitude of 50 lb. Express F as a Cartesian vector. A. B. C. D. F = (43.3 i + 25.0 j + 25.0 k) lb F = (43.3 i + 25.0 j + 28.9 k) lb F = (43.3 i - 25.0 j + 25.0 k) lb F = (43.3 i - 25.0 j + 28.9 k) lb
Workspace
4.
Determine the force in members GF, CF, CD of the symmetric roof truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression. A. B. C. D. CD = 1.783 kN C, CF = 0, GF = 1.427 kN T CD = 3.48 kN C, CF = 00904 kN T, GF = 1.783 kN T CD = 2.79 kN C, CF = 0.723 kN T, GF = 1.427 kN T CD = 2.23 kN C, CF = 0, GF = 1.783 kN T
Workspace
5.
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
2/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Determine the force in members FF, FB, and BC of the Fink truss and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression. A. B. C. D. BF = 693 lb T, FG = 1800 lb C, BC = 1212 lb T BF = 8660 lb C, FG = 3600 lb C, BC = 1212 lb T BF = 3810 lb T, FG = 3600 lb C, BC = 1212 lb T BF = 1732 lb T, FG = 2400 lb C, BC = 1212 lb T
Workspace
6.
A uniform beam has a mass of 18 kg and rests on two surfaces at points A and B. Determine the maximum distance x to which the girl can slowly walk up the beam before it begins to slip. The girl has a mass of 50 kg and walks up the beam with a constant velocity. A. B. C. D. x = 0.678 m x = 0.508 m x = 1.005 m x = 0.712 m
Workspace
7.
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
3/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
The dragster has a mass of 1.3 Mg and a center of mass at G. If a braking parachute is attached at C and provides a horizontal braking force FD, determine the maximum deceleration the dragster can have upon releasing the parachute without tipping the dragster over backwards (i.e., the normal force under the wheels and assume that the engine is disengaged so that the wheels are freely rolling. A. B. C. D. a = 16.35 m/s 2 a = 8.46 m/s 2 a = 2.75 m/s 2 a = 35.0 m/s 2
Workspace
8.
Determine the moment of force F2 about point A on the beam. A. B. C. D. M2 = 800 ft-lb M2 = 50 ft-lb M2 = 600 ft-lb M2 = 37.5 ft-lb
Workspace
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
4/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
9.
Determine the moment of the force at A about point P. Use a vector analysis and express the result in Cartesian vector form. A. B. C. D. MP = (160 i+240 j+40 k) N-m MP = (380 i+160 j+400 k) N-m MP = (280 i+200 j+400 k) N-m MP = (40 i+80 k) N-m
Workspace
10.
Determine the magnitude and direction of the couple shown. A. B. M = 1200 N-m CW M = 400 N-m CCW
5/10
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
C. D.
M = 400 N-m CW M = 1200 N-m CCW
Workspace
11.
The composite cross section for the column consists of two cover plates riveted to two channels. Determine the radius of gyration k with respect to the centroidal axis. Each channel has a crosssectional area of Ac = 11.8 in.2 and moment of inertia (I A. B. C. D. k = 7.74 in. k = 6.29 in. k = 5.44 in. k = 4.25 in.
Workspace
)c = 349 in.4 .
12.
Determine the tension in the supporting cables BC and BD and the components of reaction at the balland-socket joint A of the boom. The boom supports a drum having a weight of 200 lb. at F. Points C and D lie in the xy plane. A. B. Ax = 0, Ay = 150 lb, Az = 562 lb, TBC = 300 lb, TBD = 212 lb Ax = 0, Ay = 150 lb, Az = 456 lb, TBC = 150 lb, TBD = 212 lb
6/10
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
C. D.
Ax = 0, Ay = 267 lb, Az = 843 lb, TBC = 533 lb, TBD = lb Ax = 0, Ay = 150 lb, Az = 500 lb, TBC = 212 lb, TBD = 212 lb
Workspace
13.
A stunt driver in car A travels in free flight off the edge of a ramp at C. At the point of maximum height he strikes car B. If the direct collision is perfectly plastic (e = 0), determine the required ramp speed vC at the end of the ramp C, and the approximate distance s where both cars strike the ground. Each car has a mass of 3.5 Mg. Neglect the size of the cars in the calculation. A. B. C. D. vC = 25.9 m/s, s = 10.99 m vC = 22.4 m/s, s = 9.52 m vC = 25.9 m/s, s = 10.99 m vC = 25.9 m/s, s = 10.99 m
Workspace
14.
The projectile having a mass of m = 3 kg is fired from a cannon with a muzzle velocity of vO= 500 m/s. Determine the projectile's angular momentum about point O at the instant it is at the maximum height of its trajectory. A. B. C. D. H0 = 15.11(10 6 ) kg- m2 /s CCW H0 = 6.76(10 6 ) kg- m2 /s CCW H0 = 15.11(10 6 ) kg- m2 /s CW H0 = 6.76(10 6 ) kg- m2 /s CW
Workspace
15.
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
7/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
Arm ABCD is printed at B and undergoes reciprocating motion such that
= (0.3 sin 4 t) rad, where t is
measured in seconds and the argument for the sine is in radiaus. Determine the largest speed of point A during the motion and the magnitude of the acceleration of point Dat this instant. A. B. C. D. vAmax = 0.0600 m/s, a D = 1.002 m/s 2 vAmax = 0.300 m/s, a D = 0.960 m/s 2 vAmax = 0.0600 m/s, a D = 0.916 m/s 2 vAmax = 0.300 m/s, a D = 0.288 m/s 2
Workspace
16.
If the rim of the wheel and its hub maintain contact with the three stationary tracks as the wheel rolls, it is neccessary that slipping occurs at the hub A if no slipping occurs at B. Under these conditions, what is the speed at A if the wheel has an angular velocity ? A. B. C. vA = (r2 -r1 ) vA = r1 vA = (r2 -r1 )
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
8/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
D.
vA = r1
Workspace
17.
A ball having a mass of 2 kg slides without friction within a vertical circular slot. If it is released from rest when = 10, determine the force it exerts on the slot when it arrives at points A and B. A. B. C. D. NA = 38.6 N, NB = 96.6 N NA = 30.9 N, NB = 61.8 N NA = 30.9 N, NB = 81.2 N NA = 38.6 N, NB = 77.3 N
Workspace
18.
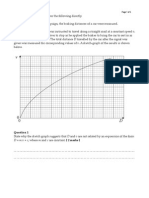
A car travels up a hill with the speed shown in the graph. Compute the total distance the car moves until it stops at t = 60 s. What is the acceleration at t = 45 s? A. B. C. D. s = 400 m, a 45 = -3.00 m/s 2 s = 450 m, a 45 = -0.333 m/s 2 s = 400 m, a 45 = -3.00 m/s 2 s = 450 m, a 45 = 0.333 m/s 2
Workspace
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random 9/10
11/26/13
Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Random
19.
A car is traveling along the circular curve of radius r = 300 ft. At the instant shown, its angular rate of rotation is = 0.4 rad / s , which is increasing at the rate of = 0.2 rad / s 2 . Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car at this instant. A. B. C. D. a = 108.0 ft/s 2 a = 60.0 ft/s 2 a = 48.0 ft/s 2 a = 76.8 ft/s 2
Workspace
20. A particle is moving along a straight line through a fluid medium such that its speed is measured as v = (2 t) m/s, where t is in seconds. If it is released from rest at s = 0, determine its positions and acceleration when t = 3 s. A. B. C. D. s = 9 m, a = 2 m/s 2 s = 2 m, a = 18 m/s 2 s = 18 m, a = 2 m/s 2 s = 2 m, a = 9 m/s 2
Workspace
www.indiabix.com/online-test/engineering-mechanics-test/random
10/10
Você também pode gostar
- Engg Mechanics Assign MentsDocumento11 páginasEngg Mechanics Assign Mentsdayanand moreAinda não há avaliações
- AM SPDocumento7 páginasAM SPJacobAinda não há avaliações
- Preboard Examination 1 (SDC)Documento13 páginasPreboard Examination 1 (SDC)LopiyAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam (Sec)Documento15 páginasFinal Exam (Sec)Sherwin ConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Five PointsDocumento16 páginasPhysics Five PointsMary Grace VelitarioAinda não há avaliações
- EVALUATION EXAM #2: FORCES AND FLUID MECHANICSDocumento9 páginasEVALUATION EXAM #2: FORCES AND FLUID MECHANICSShu RubioAinda não há avaliações
- CE - Structural EngineeringDocumento17 páginasCE - Structural EngineeringMara100% (2)
- GNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Documento3 páginasGNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Stefano MazzaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Exam Multiple ChoiceDocumento10 páginasDiagnostic Exam Multiple ChoiceYedda M IlaganAinda não há avaliações
- STRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETDocumento6 páginasSTRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETLa BeamAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocumento11 páginasMCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamJi KanAinda não há avaliações
- Design Preboard PracticeDocumento13 páginasDesign Preboard PracticeKyle MarfsAinda não há avaliações
- MECHANICSDocumento6 páginasMECHANICSNicole RodilAinda não há avaliações
- Nov2022 Coaching JGBDocumento51 páginasNov2022 Coaching JGBNadzAinda não há avaliações
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Documento5 páginasUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- CE Pre-Board Structural Engineering and ConstructionDocumento13 páginasCE Pre-Board Structural Engineering and ConstructionpppppAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 3Documento3 páginasTutorial 3Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- BEAM DESIGNDocumento55 páginasBEAM DESIGNMhel CenidozaAinda não há avaliações
- 2010 Physics Model YekaDocumento9 páginas2010 Physics Model YekaTizita EmanaAinda não há avaliações
- Preboard 2 SECDocumento14 páginasPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- BISRATE GEBREAL INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET FOR GRADE TWELVEDocumento7 páginasBISRATE GEBREAL INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET FOR GRADE TWELVEBeza EnyAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics TutorialDocumento23 páginasMechanics TutorialDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Model-EM-29 5 13Documento2 páginasModel-EM-29 5 13rkumaravelanAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics Summer 2016Documento9 páginasDynamics Summer 2016islamatta91Ainda não há avaliações
- Steel column design and analysis problemsDocumento12 páginasSteel column design and analysis problemsDan Casurao100% (1)
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDocumento11 páginasOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDiego Naspud UrgilesAinda não há avaliações
- Set BDocumento12 páginasSet BDan CasuraoAinda não há avaliações
- Equivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsDocumento14 páginasEquivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsYun RamAinda não há avaliações
- Struc Const 1 1Documento23 páginasStruc Const 1 1Marichu Davillo Garbiles100% (1)
- PSAD-PreBoardExam02 ManilaRoundDocumento10 páginasPSAD-PreBoardExam02 ManilaRoundSharmaine FajutaganaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment QuizDocumento6 páginasAssessment QuizHeiro KeystrifeAinda não há avaliações
- Refresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Documento14 páginasRefresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Steven Valerio100% (1)
- JC2 Physics Prelim Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento17 páginasJC2 Physics Prelim Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsMohd Syukri KausAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorials 1 5Documento7 páginasTutorials 1 5faizankhan260690Ainda não há avaliações
- 82 - Engineering Mechanics Refresher SetDocumento6 páginas82 - Engineering Mechanics Refresher Setdevilene nayazakoAinda não há avaliações
- Examples - Stress Analysis 1Documento4 páginasExamples - Stress Analysis 1hippokgAinda não há avaliações
- RC Pier TabaDocumento20 páginasRC Pier TabaAbera MamoAinda não há avaliações
- CEN 301 Structural TheoryDocumento5 páginasCEN 301 Structural TheorySJ MananquilAinda não há avaliações
- Assignmnet 2 EMDocumento29 páginasAssignmnet 2 EMRakhmeen GulAinda não há avaliações
- ENGN 36 HomeworkDocumento50 páginasENGN 36 Homework082292fer67% (3)
- Engineering Mechanics 1Documento11 páginasEngineering Mechanics 1george290Ainda não há avaliações
- Review in Design and Construction Compre FinalDocumento6 páginasReview in Design and Construction Compre FinalJohn Paul Niño OrdenizaAinda não há avaliações
- Axially Loaded RC Column DesignDocumento17 páginasAxially Loaded RC Column DesignBert EngAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Choice MechDocumento17 páginasMultiple Choice MechMary Joy Rosales0% (1)
- Structural Theory Refresher Set PDFDocumento6 páginasStructural Theory Refresher Set PDFezer joseph bacoAinda não há avaliações
- The tutorial problems have been highlightedDocumento14 páginasThe tutorial problems have been highlighteddarkknightoneAinda não há avaliações
- Strut and tie modeling, yield line analysis, and plastic analysis of concrete and steel structuresDocumento9 páginasStrut and tie modeling, yield line analysis, and plastic analysis of concrete and steel structuresmalumius100% (2)
- PHYSICS I PROBLEMS KINETICS OF A PARTICLEDocumento3 páginasPHYSICS I PROBLEMS KINETICS OF A PARTICLEPablo AlejandroAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Outcome 3Documento4 páginasLearning Outcome 3kyar paukAinda não há avaliações
- Problemas Cinetica PDFDocumento7 páginasProblemas Cinetica PDFMoisés DuranAinda não há avaliações
- ETABS Software Verifies Reinforced Concrete Beam DesignDocumento5 páginasETABS Software Verifies Reinforced Concrete Beam DesignVILCAAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 12Documento6 páginasQuiz 12John Taylor BernasAinda não há avaliações
- 2007 JC2 Preliminary Exams Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento16 páginas2007 JC2 Preliminary Exams Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsMohd Syukri KausAinda não há avaliações
- November 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review InnovationsDocumento4 páginasNovember 2022 Civil Engineering Board Exam: Review Innovationsggomo15100% (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNo EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersAinda não há avaliações
- ShellDocumento1 páginaShellडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Fea L7Documento8 páginasFea L7डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- List of Industries in Mechanical EngineeringDocumento3 páginasList of Industries in Mechanical Engineeringडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Jecrc University, Jaipur B.TECH III SEMESTER (END Semester Examination-2017) Mechanical EngineeringDocumento9 páginasJecrc University, Jaipur B.TECH III SEMESTER (END Semester Examination-2017) Mechanical Engineeringडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Final Response SheetDocumento14 páginasFinal Response Sheetडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Give The Main Group of Foundry SandDocumento2 páginasGive The Main Group of Foundry Sandडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Characterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded MaterialsDocumento4 páginasCharacterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded Materialsडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- JECRC M.Tech I Sem Timetable for Mechanical EngineeringDocumento1 páginaJECRC M.Tech I Sem Timetable for Mechanical Engineeringडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Characterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded MaterialsDocumento4 páginasCharacterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded Materialsडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Elastic Bending Analysis of FGM Plate Under Mechanical LoadingDocumento10 páginasElastic Bending Analysis of FGM Plate Under Mechanical Loadingडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Database Prefinal ME TPODocumento4 páginasDatabase Prefinal ME TPOडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Characterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded MaterialsDocumento4 páginasCharacterizing Stress-Strain Transfer in Functionally Graded Materialsडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Mid-Term Question Paper MCQ Ps 5Documento2 páginas1st Mid-Term Question Paper MCQ Ps 5डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Jecrc University, Jaipur B.TECH III SEMESTER (END Semester Examination-2017) Mechanical EngineeringDocumento9 páginasJecrc University, Jaipur B.TECH III SEMESTER (END Semester Examination-2017) Mechanical Engineeringडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Solution Mm1 End TermDocumento5 páginasSolution Mm1 End Termडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Small Wind TurbineDocumento11 páginasAn Introduction To Small Wind TurbineAmlan DasAinda não há avaliações
- Elastic Bending Analysis of FGM Plate Under Mechanical LoadingDocumento10 páginasElastic Bending Analysis of FGM Plate Under Mechanical Loadingडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- MM-II END SemDocumento4 páginasMM-II END Semडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Project Initial FileDocumento4 páginasProject Initial Fileडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- OBE-Assessment Formats MS-XL WorksheetsDocumento12 páginasOBE-Assessment Formats MS-XL WorksheetsArun Pratap Singh0% (1)
- Volume 2 Issue 5 (May - 2015)Documento1 páginaVolume 2 Issue 5 (May - 2015)डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- OBE-Assessment Formats MS-XL WorksheetsDocumento10 páginasOBE-Assessment Formats MS-XL Worksheetsडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Matlab Programme To Study Nonlinear Vibration of A Cantilever BeamDocumento8 páginasDevelopment of Matlab Programme To Study Nonlinear Vibration of A Cantilever BeamIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- 1st in Sem MM-1 (Odd Sem) 2018Documento2 páginas1st in Sem MM-1 (Odd Sem) 2018डॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Inverting Matrices: Determinants and Matrix MultiplicationDocumento4 páginasInverting Matrices: Determinants and Matrix Multiplicationडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus M.tech MechanicalDocumento23 páginasSyllabus M.tech Mechanicalडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Jaipur National University, JaipurDocumento11 páginasJaipur National University, Jaipurडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- IEEE PCS Series Book Proposal Template 4 17updateDocumento3 páginasIEEE PCS Series Book Proposal Template 4 17updateडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Nmgiifemintro PDFDocumento23 páginasNmgiifemintro PDFडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माAinda não há avaliações
- Robot Structural Analysis API Code Samples & MacrosDocumento9 páginasRobot Structural Analysis API Code Samples & Macrosrahulgehlot2008100% (1)
- Studying The Airflow Over A Car Using An Ahmed Body - COMSOL BlogDocumento11 páginasStudying The Airflow Over A Car Using An Ahmed Body - COMSOL BlogSOURAVAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulic jump analysis and energy dissipationDocumento11 páginasHydraulic jump analysis and energy dissipationAhmed Al-IraqiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To TurbomachineryDocumento1 páginaIntroduction To TurbomachineryRAJENDRA PADAMATAAinda não há avaliações
- The Working SubstanceDocumento10 páginasThe Working SubstanceBryan YuAinda não há avaliações
- Important Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 7Documento61 páginasImportant Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 7MugdhaAinda não há avaliações
- Civflum Quiz 1Documento4 páginasCivflum Quiz 1Jhun CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Acoustic Fatigue Assessment of Piping System Components by FeaDocumento13 páginasAcoustic Fatigue Assessment of Piping System Components by FeaTeknologi TermutakhirAinda não há avaliações
- Beam and Column Design in Reinforced ConcreteDocumento21 páginasBeam and Column Design in Reinforced ConcreteSambhav PoddarAinda não há avaliações
- FMM Cia 2 2019Documento2 páginasFMM Cia 2 2019Vinay KorekarAinda não há avaliações
- Mech3410 ExamsDocumento117 páginasMech3410 ExamsekampreetAinda não há avaliações
- Key information on motor dataDocumento8 páginasKey information on motor dataRadj90Ainda não há avaliações
- Soalan Pre TestDocumento9 páginasSoalan Pre TestZa Liza MNorAinda não há avaliações
- Bolted Connection ModuleDocumento5 páginasBolted Connection ModuleMakolAinda não há avaliações
- LeaP-Science-G5-Week 1-Q3Documento7 páginasLeaP-Science-G5-Week 1-Q3Marie Grace Eguia MagsinoAinda não há avaliações
- FlexuralCapacity-FRP - CNR-DT200-2013 - WIPDocumento55 páginasFlexuralCapacity-FRP - CNR-DT200-2013 - WIPAlberto AraújoAinda não há avaliações
- Friction Laws of Dry Friction-Pivot and CollarDocumento25 páginasFriction Laws of Dry Friction-Pivot and CollarNavya ChinniAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Choice Questions: D. A Is False But R Is TrueDocumento11 páginasMultiple Choice Questions: D. A Is False But R Is Truepriya dharshiniAinda não há avaliações
- General Instructions: Answer The Following Directly.: Phy13Hl Page 1 of 5Documento5 páginasGeneral Instructions: Answer The Following Directly.: Phy13Hl Page 1 of 5bananacrunchAinda não há avaliações
- Schofield1998 - The Mohr-Coulomb Error CorrectionDocumento3 páginasSchofield1998 - The Mohr-Coulomb Error CorrectionandresmelodAinda não há avaliações
- Homework-1 Fall 2021Documento1 páginaHomework-1 Fall 2021Elif HalıcıAinda não há avaliações
- 20 MTR GA DRAWING, TDS, STR. CALCULATION - CleanedDocumento20 páginas20 MTR GA DRAWING, TDS, STR. CALCULATION - CleanedLeroyAinda não há avaliações
- Monday 13 January 2020: PhysicsDocumento28 páginasMonday 13 January 2020: Physicskholod SheikhAinda não há avaliações
- CE 323/ BES 222 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Chapter 2 - StrainDocumento6 páginasCE 323/ BES 222 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Chapter 2 - StrainNadlor Gasco OzausAinda não há avaliações
- Diagrid Mono Column Structures With Different Geometry in Plan A ReviewDocumento6 páginasDiagrid Mono Column Structures With Different Geometry in Plan A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Dynamics of Cricket Ball SwingDocumento13 páginasFluid Dynamics of Cricket Ball SwingIosef HayalaAinda não há avaliações
- General Wave Properties IGCSE Physics MSDocumento2 páginasGeneral Wave Properties IGCSE Physics MSeren parkAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Method in Structure Ass-ALEDocumento19 páginasFinite Element Method in Structure Ass-ALENatinael WoldeAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Chemistry of InterfacesDocumento20 páginasPhysical Chemistry of InterfacesTeka KamAinda não há avaliações