Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Learning and Teaching Should Meet The Needs of The Whole Learner
Enviado por
Serkay GobsTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Learning and Teaching Should Meet The Needs of The Whole Learner
Enviado por
Serkay GobsDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
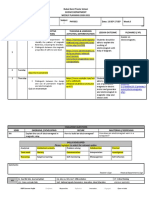
Learning and Teaching should meet the needs of the Whole Learner:
Summative Assessment
Summative Assessment is the formal testing of what has been learned in order to produce marks or grades which may be used for reports of various types. This is different from Formative Assessment, in which the emphasis is on on-going assessments of different types used to judge how best to help pupils learn further.
Points arising from Research
In formative assessment the emphasis is more on helping pupils learn. (See section on Formative Assessment Summative assessment can have a negative impact on pupils motivation Schools can work to change the culture of assessment to make more effective use of summative assessment
Key Elements of Summative Assessment
Effects on motivation (Motivation is seen as a compound of many factors) After summative assessment, low-achieving pupils had lower self-esteem than higher-achievers, whereas there had been no correlation between self-esteem and achievement before Repeated practice tests reinforce low self-esteem of low achievers Big bang tests cause anxiety in pupils, especially girls Tests do motivate some pupils. They also widen the gap between high- and low-achievers motivation Summative assessment promotes extrinsic motivation, in which pupils respond to the promise of some kind of reward rather than intrinsic motivation in which they perform because they are interested and want to do the work. When results of summative assessment are presented as primarily relating to individual pupils the negative effect on low-achievers is more pronounced than when the results are for evaluation of school or authority standards. Secondary age low-achievers may deliberately underperform in summative assessments because they are failing anyway Summative assessments can be limiting for the most able Curriculum and teaching The curriculum can be narrowed by teaching to the test. This can even mean that time is taken away from curriculum content. It can also produce distortion in terms of teaching techniques Summative test questions may not be framed in the same way as those preferred for formative assessment. Teachers can spend a lot of time on summative assessment which does not directly improve pupils learning.
Teachers sometimes adopt a more didactic transmission style of teachin g which disadvantages those who dont respond well to it. Validity and reliability Validity must be assured in terms of the following: The content of the assessment The way in which the assessment is constructed A tests linkage with the way the items have been taught Reliability must be assured in terms of the following:
Consistency across tasks Consistency in scoring/grading Positive potential Schools have little direct control over the nature of external summative assessments and must be careful to prepare pupils effectively for these. However, certain principles can inform the effective use of summative assessment of coursework. These principles are seen as ways of encouraging skills and attitudes for lifelong learning. Intrinsic interest in tasks can be encouraged (see above) Pupil awareness of learning goals rather than test performance goals can be developed A wide range of types of understanding can be included in summative assessment Some formative assessment evidence may be included in summative reports Peer- and self-assessment could be included in summative records Tests dont need to be formal written assessments The comparison of individual pupils on the basis of scores can be avoided Summative tests can be placed before the end of a teaching block so that there is some opportunity for follow-up based on the results, and even reassessment Summative judgements can be made on the basis of a variety of tests (varied both in form and content) Pupils could carry forward lessons from assessments even into the next school session (eg in the form of a copy of their school report) Feedback can be given to pupils in terms of the learning goals rather than just a test mark Tests might be devised to assess separate elements of the course separately In practising for summative assessment, pupils can make up and answer their own questions. (Research has shown this to be an effective strategy) Tests can be timed according to pupil readiness rather than leaving them to the end of the block of work Summative assessment can be presented to pupils realistically, as being limited Tests can provide evidence for evaluating courses and teaching approaches Whole-school discussion of such assessment principles can be helpful
Reflection and Discussion
Do you feel that time spent of summative assessment tasks is as profitable as it might be? Can summative assessment be exploited for formative purposes?
Some Activities Relating To the Issue Summative Assessment Key Objective Action element Some examples and suggestions Effects on Motivation
Big bang tests cause anxiety in pupils, especially girls. Summative tests can be presented as merely the culmination of the formative process. The aim would be a culture in which the pupil attempts to do well in all types of assessment, so that there is no need to give special prominence to final assessments. Take stock of your approach to preparing pupils for tests. Do you still adopt the same range of teaching approaches? Is there a tendency for pupils and teachers to become anxious and revert to less involving strategies. A pupil questionnaire can be used to sample pupil opinion after the assessment has been completed. Tests are sometimes made up by people who have taught the course in a different way or not taught it at all. Are your summative test items related to your own approach? Check, for example, that pupils understand all the language in the assessment. This is frequently not the case. Do you or can you build in items testing ability to solve new problems, think critically, make informed decisions?
Curriculum and Teaching
It can also produce distortion in terms of teaching techniques.
Validity and Reliability
A tests linkage with the way the items have been taught
Positive Potential
A wide range of types of understanding can be included in summative assessment.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Civil Law PDFDocumento54 páginasCivil Law PDFAlyssa Fabella ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Present Value Factor For Annuity: Periods 1% 2% 3% 4% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10%Documento28 páginasPresent Value Factor For Annuity: Periods 1% 2% 3% 4% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10%Serkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Magallona V Ermita Case DigestDocumento2 páginasMagallona V Ermita Case DigestSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Universal Law of GravitationDocumento3 páginasThe Universal Law of GravitationSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- United Christian Missionary Society, United Church Board ForDocumento5 páginasUnited Christian Missionary Society, United Church Board ForSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Statutory ConstructionDocumento3 páginasStatutory ConstructionSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Theories of InvestmentDocumento15 páginasTheories of InvestmentSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Effective Use of Learning ObjectivesDocumento6 páginasEffective Use of Learning ObjectivesIamKish Tipono ValenciaAinda não há avaliações
- MuyongDocumento10 páginasMuyongSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- Statutory ConstructionDocumento3 páginasStatutory ConstructionSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Macariola vs. AsuncionDocumento13 páginasMacariola vs. AsuncionSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Statutory ConstructionDocumento3 páginasStatutory ConstructionSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Philippine environmental laws and policies summaryDocumento12 páginasPhilippine environmental laws and policies summarySerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- An Essay on the Benefits of Boy ScoutsDocumento1 páginaAn Essay on the Benefits of Boy ScoutsSerkay Gobs100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Theo PT 1Documento3 páginasTheo PT 1Serkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Financial MangementDocumento11 páginasFinancial MangementSerkay GobsAinda não há avaliações
- Ten FramesDocumento5 páginasTen Framesapi-334723488Ainda não há avaliações
- Ged 110Documento4 páginasGed 110JanrayBernalAinda não há avaliações
- The Difference Between Reason and Will Reason and WillDocumento20 páginasThe Difference Between Reason and Will Reason and WillRotsen YodicoAinda não há avaliações
- Science, Technology, Society and The HumanDocumento30 páginasScience, Technology, Society and The HumanFranz goAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Theology as the Foundation of MetaphysicsDocumento20 páginasTheology as the Foundation of MetaphysicsHaris MacićAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Lesson 17Documento1 páginaLesson 17Doreen TingAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Habits For Inner PeaceDocumento94 páginas4 Habits For Inner Peacejustintime54Ainda não há avaliações
- Cognate TheoryDocumento2 páginasCognate TheoryAriel CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Persuasive Writing UbdDocumento3 páginasPersuasive Writing Ubdapi-33562418Ainda não há avaliações
- 220-320 Lecture 20Documento7 páginas220-320 Lecture 20Károly PálAinda não há avaliações
- Alisha Rasmussen - 19059378 - Inclusive Education Assignment 1Documento13 páginasAlisha Rasmussen - 19059378 - Inclusive Education Assignment 1api-466919284Ainda não há avaliações
- Helmholtz and The Psychophysiology of Time: Claude DebruDocumento23 páginasHelmholtz and The Psychophysiology of Time: Claude DebruCrystal JenningsAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Drawing Assessment CriteriaDocumento1 páginaDrawing Assessment Criteriaapi-254314751Ainda não há avaliações
- Report on Principles of Design and Artist Milton GlaserDocumento4 páginasReport on Principles of Design and Artist Milton GlaserVoltaire Von AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Indian Culture Through Various MethodologiesDocumento16 páginasUnderstanding Indian Culture Through Various MethodologiesRavi Soni100% (1)
- Nativization Model & Accommodation Theory23Documento15 páginasNativization Model & Accommodation Theory23marco_meduranda93% (15)
- Philosophical Semantics: (Oscar Wild, The Remarkable Rocket', 1888)Documento10 páginasPhilosophical Semantics: (Oscar Wild, The Remarkable Rocket', 1888)Prevoditeljski studijAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence LawDocumento29 páginasEvidence LawMukul Singh RathoreAinda não há avaliações
- Biophilia Perception of The EnvironmentDocumento37 páginasBiophilia Perception of The EnvironmentAaditaChaudhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Steam Proposal Fhps Final1Documento6 páginasSteam Proposal Fhps Final1api-288075910Ainda não há avaliações
- (Sozomena 14) David Sider, Dirk Obbink (Eds.) - Doctrine and Doxography - Studies On Heraclitus and Pythagoras-Walter de Gruyter (20Documento372 páginas(Sozomena 14) David Sider, Dirk Obbink (Eds.) - Doctrine and Doxography - Studies On Heraclitus and Pythagoras-Walter de Gruyter (20Enrique Hulsz100% (2)
- Weekly Lesson Plan WEEK 3 YEAR 11 SKDocumento2 páginasWeekly Lesson Plan WEEK 3 YEAR 11 SKSukanya VedavyasaAinda não há avaliações
- Hes6606 Assignment 1Documento10 páginasHes6606 Assignment 1Salil PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Toward A Deliberative CurriculumDocumento10 páginasToward A Deliberative CurriculumYahya AbdurrohmanAinda não há avaliações
- Co-Creating Rubrics. The Effects On Self-Regulated Learning, Self-Efficacy and Performance of Establishing Assessment Criteria With StudentsDocumento8 páginasCo-Creating Rubrics. The Effects On Self-Regulated Learning, Self-Efficacy and Performance of Establishing Assessment Criteria With StudentssantimosAinda não há avaliações
- Definitions of Open Distance LearningDocumento8 páginasDefinitions of Open Distance LearningOlanrewju LawalAinda não há avaliações
- Target Audience Research Objective IVDocumento25 páginasTarget Audience Research Objective IVMarcus RhodesAinda não há avaliações
- ENGLISH Argumentative Essay QuizDocumento1 páginaENGLISH Argumentative Essay QuizMark Joseph DelimaAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On Profile of An Effective Communicator: Presented To: Dr. Pragya AwasthiDocumento14 páginasCase Study On Profile of An Effective Communicator: Presented To: Dr. Pragya AwasthiNur Amalyna YusrinAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Research (Word Association)Documento6 páginasExperimental Research (Word Association)Christine Eunice PiguerraAinda não há avaliações
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (402)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionNo EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2475)