Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Grade7 Curriculum Questions
Enviado por
Jeanalmira0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
36 visualizações8 páginasMathematics Grade 7
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoMathematics Grade 7
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
36 visualizações8 páginasGrade7 Curriculum Questions
Enviado por
JeanalmiraMathematics Grade 7
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 8
Grade 7 - Patterning & Algebra
Number patterns. Sample questions
1. Describe each pattern, write the next 3 terms, find the 50
th
term for the following
a. 4, 7, 10, 13, ...
b. 1, 4, 9, 16, ...
2. Look at patterns:
a. Explain how they are the same.
b. Explain how they are different.
c. Write the next three terms.
d. Write the 20
th
term in each pattern.
3. Given a picture pattern and assuming the pattern continues:
a. How many squares would be in the 10
th
figure?
b. What are the perimeters of the 4
th
figure and the 5
th
figure?
c. What is the perimeter of the 10
th
figure?
d. How many square are there in the figure with perimeter 72?
e. Could you make one of the figures using exactly 27 small squares? Explain.
4. Create two different number patterns that contain the numbers 16, 20, 25. Write the first 5 terms in each pattern.
Graphing patterns
1. Copy and complete this table for each pattern.
a. Multiply each Input number by 3.
b. Add 2 to each Input number.
c. Multiply each Input number by 3, then add 2.
d. Add 2 to each Input number, then multiply by 3.
Input Output
1
2
3
4
5
2. For each table:
a. Describe the pattern in the Output column.
b. How can you find an Output number when you know an Input number?
c. Write the next 3 rows in each table.
INPUT OUTPUT
2 6
4 8
6 10
8 12
10 14
Input Output
2 6
4 12
6 18
8 24
10 30
3. Variables
1. A car travels at an average speed of 50 km/h How far will the car travel in:
a. 3 hours
b. t hours
2. A pizza with cheese and tomato toppings costs $8.00. There is a cost of $1.00 for each extra topping. Write
an algebraic expression for the cost of a pizza with e extra toppings.
2
Evaluating algebraic expressions
1) Write an algebraic expression for each statement.
a) Six more than a number
b) A number multiplied by eight
c) A number decreased by six
d) A number divided by four
2) A person earns $4/h baby-sitting. Find the money earned for each time.
a) 5h
b) 8h
c) t hours
Reading and writing equations
1) Write an equation for each sentence.
a) Eight more than a number is 12.
b) Three times a number is 12.
c) an a number is 12. Eight less th
ence
a) 9
2) Writ for each equation. e a sent
b) 8
12 +n = 1
n
c) = S
S = 1
12 -n
d)
n
2
= 6
Solving equations
a)
1) Solve each equation.
x + S = 12
y + 9 = 9
c) 1u + 2z = 2u
b)
2) Shenker has 45 CDs.
a) Write an equation you can solve to find how many CDs
b) Solve the equation
Grade 7 - Data Management & Probability
Collecting data & Recording data
1. Survey 20 people about their favourite sport.
a. Make up a tally chart to show the data.
b. Make a frequency table for the data.
c. Display the data using a bar graph.
d. What is the most popular flavour?
e. What is the least popular flavour?
Stem-and-Leaf plots
1. A group of students wrote a test. Their scores, out of 50, are shown below.
10 21 32 47 12 22
34 47 14 25 36 18
a. What will the stem values represent?
b. What will the leaf values represent?
c. Create the stem-and-leaf plot.
d. How many students scored in the 30s?
e. How many students scored in the 10s?
3
Line graphs
Average monthly rainfall (cm)
Month Vancouver Ottawa
January 14.0 1.5
February 12.0 1.6
March 9.6 3.2
April 5.8 5.8
May 4.9 7.5
June 4.7 7.7
July 2.6 8.8
August 3.5 9.2
September 5.4 8.3
October 11.7 7.0
November 13.8 6.3
December 16.4 3.3
1.
(a) What does this table show?
(b) Draw a line graph for each city on the same grid.
(c) Describe the trends in rainfall for the two cities. How do the line graphs illustrate these trends?
(d) In which month(s) do the line graphs cross? What does this mean?
(e) What is the average annual rainfall for each city?
Applying mean, median, and mode
1. Use these data: 28, 30, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41
a. Find the mean, median and mode.
b. What happens to the mean, median, and mode in each case?
i. Each number is increased by 10.
ii. Each number is doubled.
Explain the results you observe.
Data analysis
1. Draw a graph to display the data if we have a situation where the directors want the expenses to look,
a. High.
b. Low.
Board of Directors Expenses
Quarter Amount ($)
1
st
85,000
2
nd
104,000
3
rd
125,000
4
th
155,000
Probability (listing outcomes)
1. When 2 coins are tossed, the outcomes for each coin are heads (H) or (T).
a. List the outcomes of the first coin toss.
b. For each outcome in part a, list the outcomes of the second coin toss.
c. List the outcomes for the coins tossed together.
2. List the possible outcomes when rolling a 6 sided dice.
Probability (experimental)
1. A paper cup is tossed. The cup lands with the top up 27 times, the top down 32 times, and on its side 41 times.
a. What are the possible outcomes of tossing a paper cup?
b. Are the outcomes equally likely? Explain.
c. State the relative frequency of each outcome.
2. Try the paper cup experiment from the previous question. Decide how to hold the cup to drop it.
a. Repeat the experiment until you have 100 results.
b. Compare your results with those from the previous question. Are the numbers different, explain.
4
Probability (theoretical)
1. A bag contains these granola bars: 12 apple, 14 banana, 18 raisin, and 10 regular. You pick one bar at random.
Find the probability of choosing:
a. A banana granola bar
b. An apple granola bar
c. A regular granola bar
2. Construct a spinner with red, yellow, blue and green sectors, so the following probabilities are true. (red = , yellow =
, blue = 1/6 , green = 1/12).
a. In 200 trials, about how many times would the pointer land on each colour.
Probability (applications)
1. a. Three coins are tossed. Find the chance of tossing:
i. One heads and two tails
ii. Exactly two heads
iii. At least two tails
iv. No heads
b. Why do we need the words at least in part a, iii? What if these words were left out? How would the answer
change?
c. Why do we need the word exactly in part a, ii? What if this word was left out? How would the answer
change?
Grade 7 - Geometry & Spatial Sense
Classifying polygons
1) Identify the polygons in the signs
2) If a regular pentagon has the same perimeter as a regular decagon, which figure has the longer sides? Explain.
Congruent figures
1) The triangles are congruent. Match the equal parts. (insert labels G,H,K for first triangle, and R, S,T for the second)
a) GH = ?
G
R
b) HK = ?
c) GK = ?
d) G = ?
e) H = ?
f) K = ?
H K
S T
2) Name the corresponding parts of each pair of congruent figures (put labels: A,B,C,D for one and W,X,Y,Z for the
other)
Y
X
B
W
A
D C Z
5
Transformations
1) Copy each figure onto dot paper. Draw the rotation image for each rotation about A
a. 90 counterclockwise
b. 180 clockwise
c. 270 counterclockwise
A
2) For the figure above (problem one above), find
a. The reflection image of the figure (Hint: red line)
b. Draw the translation image for a translation of 3 units up and 4 units to the right
Transformations involve a lot of plotting using graph paper/dot paper. This deals with symmetry, reflections,
rotations, rotational symmetry
Tiling Patterns
1) Start with a figure that till the plane like a square, plotted on graph/dot paper
a. Then have the students remove triangles from one side and move them to the bottom
b. Then play with these new figures and combine them to make patterns
Problems are more geared towards coloured shapes, flips, slides or turns, using basic shapes.
Rectangular prisms
1) Present three different cubes:
a. Solid Cube (plasticine)
b. Shell of a cube (bristol board)
c. Skeleton of a cube (sticks and plasticine)
- Have students work in groups and decide the reasoning for each cube being considered as a solid, shell or skeleton
- Go through with the class definitions for each particular shape
- Have the students brainstorm/develop a new list of objects that are considered skeletons, shape and solid
Grade 7 - Measurement
Area of parallelogram & triangle
1. Calculate the Area of the Parallelogram
6
2. Find the area of the triangle.
Area & perimeter of trapezoid
1. Find the area and perimeter of each trapezoid.
Irregular figures:
1. Find the dimensions in this shape that are marked with a question mark (?).
7
2. Find two different ways to calculate the area of this shape.
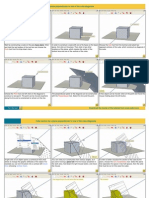
Rectangular prism (surface area & volume)
1. Find the surface area and volume (with proper units) of this rectangular prism.
2. The city wants to build childrens pool in the park. The pool floor and sides of the swimming pool must be lined with
tiles. The swimming pool is rectangular in shape and is 10 metres long, 5 metres wide and 1 metre deep. Calculate
the surface area of the swimming pool that must be covered with tiles, and calculate the amount of water the
swimming pool can hold.
Grade 7 - Number Sense and Numeration
Exponents
1. Write the base & exponent of each power:
a. 2
4
b. 3
2
c. 7
3
d. 10
5
2. Write in exponent form & solve
a. 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2
b. 9 x 9 x 9
c. 6 x 6
When numbers are repeated in multiplication we can write them in exponent form
Factors & multiples
1. Analyse the numbers in the circles
Abundant Deficient Perfect
18 15
12 8 6
20 7
2. Is each number prime or composite? How do you know?
a. 18
8
b. 13
c. 9
d. 19
e. 61
f. 2
Emphasize the 100 chart.
Square & square roots
1. (Square): Find the square of each number
a. 4
b. 17
c. 13
d. 52
2. (Square Roots): Calculate the side length of a square with each area
a. 100 m
2
b. 64 m
2
c. 81 m
2
Emphasize the importance of grid paper.
Ratios
1. Write three ratios equivalent to each ratio
a. 3:4
b. 14:4
2. The official Canadian flag has a length to width ratio of 2:1. Doreen has a sheet of paper that measures 30cm by 20cm. What are the length and width
of the largest Canadian flag Foreen can draw? Sketch a picture of the flag.
Fractions ( ) +, -
1. (add):
1
2
+
1
3
2. Subtract):
2
5
-
1
3
Decimals (multiplying & dividing)
1. (Multiplying): 5 x 0.1
2. (Dividing): 7.44 2
Emphasize the place-value chart to assist in above
Decimals (order of operations)
1. Evaluate: 7.4 3 + 2.3 x 4
2. Evaluate & Show all Steps: 0.38+ 16.2 x (2.1 + 4) + 21 3.5
Emphasize when & why brackets are necessary
Integers (define)
Positive and negative whole numbers are called integers
The set of numbers ... -3, -2. -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, ...
Integers (comparing & ordering)
1. Order the integers in each set from greatest to least OR least to greatest
2. Place < or > between the integers (use a number line if it helps).
Integers (adding)
1. Copy & complete: (+5) + = +8
2. Add: (+12) + (-3) + (-2)
Integers (subtracting)
1. Copy & complete: (+5) - = +8
2. Subtract: (+12) - (-3) - (-2)
Integers (algebra tiles)
1. Correspond algebra tiles on the number line
2. Reflect on the subtraction & addition rules (have them choose the integers):
a. Negative Negative
b. Negative Positive
c. Positive Positive
d. ...
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Archemidian SolidsDocumento22 páginasArchemidian Solidspositron999100% (1)
- Could King Kong Exist?: Teacher's Guide - Getting StartedDocumento10 páginasCould King Kong Exist?: Teacher's Guide - Getting StartedBOB100% (1)
- H Angles StudentDocumento36 páginasH Angles StudentJeanalmira100% (2)
- ST Albans School 12+ Mathematics SpecimenDocumento9 páginasST Albans School 12+ Mathematics SpecimenJeanalmira100% (1)
- Factoring PracticeDocumento6 páginasFactoring PracticeJeanalmiraAinda não há avaliações
- 2013-04-04 Gilat Showcases Its Lightweight Compact Satellite Communications Solution For UAVs at LAAD 2013Documento3 páginas2013-04-04 Gilat Showcases Its Lightweight Compact Satellite Communications Solution For UAVs at LAAD 2013JeanalmiraAinda não há avaliações
- ET01Documento25 páginasET01JeanalmiraAinda não há avaliações
- Mesh Modeling AutoCAD 2010Documento6 páginasMesh Modeling AutoCAD 2010arutapub100% (1)
- Reading 7 Part 2 VolumesDocumento20 páginasReading 7 Part 2 VolumesHassan FarhatAinda não há avaliações
- Q4 Lesson 87 Name The Unit of Measure For Measuring The Volume of Cube and Rectangular Prism.Documento27 páginasQ4 Lesson 87 Name The Unit of Measure For Measuring The Volume of Cube and Rectangular Prism.Patrick ErozaAinda não há avaliações
- Cube SectionDocumento2 páginasCube SectionKARLOSNUNAinda não há avaliações
- Euclidean GeometryDocumento11 páginasEuclidean GeometryNomar Bontigao DayatanAinda não há avaliações
- Www.estudentzone.com Www.estudentzone.comDocumento8 páginasWww.estudentzone.com Www.estudentzone.comchinnihardwareAinda não há avaliações
- Parent Guide: Identifying and Describe The Properties of 2D and 3D ShapesDocumento19 páginasParent Guide: Identifying and Describe The Properties of 2D and 3D Shapesjennifer sayongAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Design Essentials of The StructureDocumento65 páginas2 - Design Essentials of The StructureJaelaurence DiosanaAinda não há avaliações
- Volume and Surface Area of Prisms Chapter - 12Documento44 páginasVolume and Surface Area of Prisms Chapter - 12smaniya5707100% (2)
- Plans Elevations WorksheetDocumento4 páginasPlans Elevations WorksheetAbdallah ElmenawyAinda não há avaliações
- THEORY of Architecture TransesDocumento27 páginasTHEORY of Architecture TransesREYES, JAN MERCK M.Ainda não há avaliações
- WC - Cubes and DiceDocumento36 páginasWC - Cubes and DiceAnishAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Stage5 SOW v1 July11 Tcm142-353884Documento69 páginasMaths Stage5 SOW v1 July11 Tcm142-353884Samer Khattab-Teaching FacultyAinda não há avaliações
- MC Maths - Lesson Plans - Stage 6 - C03Documento13 páginasMC Maths - Lesson Plans - Stage 6 - C03syasmiitaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Wrinkles For Teachers and Private Learners by SI Jones (1912)Documento344 páginasMathematical Wrinkles For Teachers and Private Learners by SI Jones (1912)morefaya2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Answers - : ApplicationsDocumento7 páginasAnswers - : ApplicationsNahir Cabrera100% (2)
- Mensuration: Area of A TrapeziumDocumento61 páginasMensuration: Area of A TrapeziumSahil EduAinda não há avaliações
- Prim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit 11 TestDocumento3 páginasPrim Maths 6 2ed TR Unit 11 TestKabagambe HamimAinda não há avaliações
- Visualize The Volume of Cube and Rectangular PrismDocumento17 páginasVisualize The Volume of Cube and Rectangular PrismasdwasdwaAinda não há avaliações
- Mineralogy 1Documento50 páginasMineralogy 1Karla Fermil SayenAinda não há avaliações
- LS3 Modules With Worksheets Solid FiguresDocumento13 páginasLS3 Modules With Worksheets Solid Figureskathleenjane100% (1)
- Application - of - Derivatives MCQ-12Documento6 páginasApplication - of - Derivatives MCQ-12Sudhir DixitAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Without Borders Age Group 7 SPRING 2019: PermissionDocumento3 páginasMathematics Without Borders Age Group 7 SPRING 2019: PermissionElevenPlus ParentsAinda não há avaliações
- Nets PDFDocumento10 páginasNets PDFDrcreeperPhdAinda não há avaliações
- Polyhedral & Tessellation PISMP Semester 2 - LNDocumento81 páginasPolyhedral & Tessellation PISMP Semester 2 - LNkaloi07Ainda não há avaliações
- DLL Math Q4 W2Documento8 páginasDLL Math Q4 W2CHARMAINE MONTESAinda não há avaliações
- IKMC-2015 Grade5&6Documento7 páginasIKMC-2015 Grade5&6Akash50% (2)
- Amc12 2020Documento11 páginasAmc12 2020Jingxuan SeanAinda não há avaliações